98.可达路径
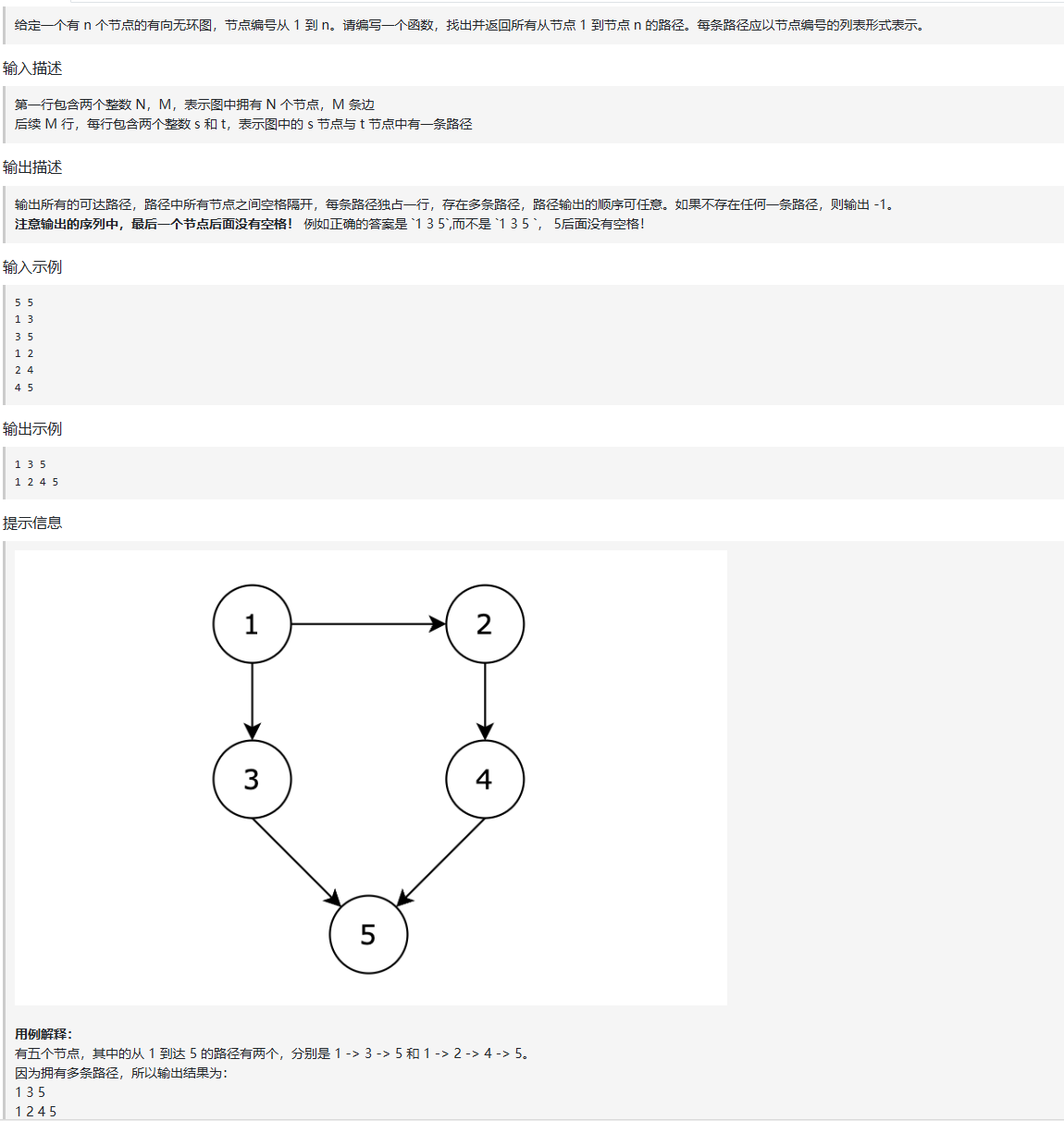
使用深度优先遍历进行递归
邻接矩阵存储,进行深度优先遍历
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
static List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
static List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
public static void dfs(int[][] graph, int cur, int target){
if(cur==target){ //如果当前遍历的就是目标节点,则说明找到了一条路径
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i=1;i<=target;i++){ //遍历当前节点对应的邻接矩阵的一行,与当前节点相连的节点可以加入路径
if(graph[cur][i]==1){
path.add(i);
dfs(graph, i, target);
path.remove(path.size()-1);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] graph = new int[n+1][n+1]; //定义邻接矩阵
while(m--!=0){
int s = sc.nextInt();
int t = sc.nextInt();
graph[s][t] = 1; //对应边的位置
}
path.add(1); ////题目要求从1开始,所以path第一个元素必须是
dfs(graph, 1, n);
if(res.isEmpty()) System.out.println(-1); //处理输出
for(List<Integer> list : res){
for(int i=0;i<list.size()-1;i++){
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println(list.get(list.size()-1));
}
}
}邻接表存储,进行深度优先遍历
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
static List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
static void dfs(List<LinkedList<Integer>> graph, int cur, int target) {
if (cur == target) {
res.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for (int i : graph.get(cur)) { //遍历当前节点对应的链表,链表上的节点可以加入路径
path.add(i);
dfs(graph, i, target);
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
List<LinkedList<Integer>> graph = new ArrayList<>(n + 1);//定义邻接表
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){ //初始化邻接表的边表(链表)
graph.add(new LinkedList<Integer>());
}
while (m-- > 0) {
int s = sc.nextInt();
int t = sc.nextInt();
graph.get(s).add(t); //将边的信息加入邻接表
}
path.add(1); //题目要求从1开始,所以path第一个元素必须是1
dfs(graph, 1, n);
if (res.isEmpty()) System.out.println(-1); //处理输出
for (List<Integer> list : res) {
for (int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; i++) {
System.out.print(list.get(i) + " ");
}
System.out.println(list.get(list.size() - 1));
}
}
}要熟悉邻接矩阵和邻接表存储图的过程,熟悉dfs遍历的写法
99.计数孤岛
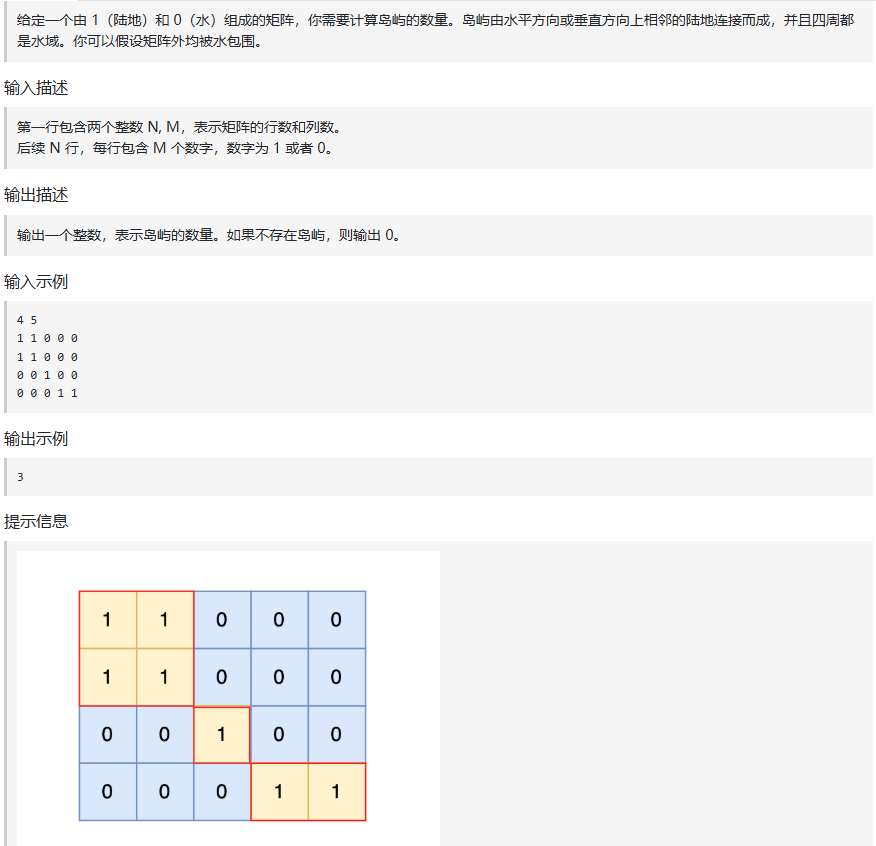
本题思路是用遇到一个没有遍历过的节点陆地,计数器就加一,然后把该节点陆地所能遍历到的陆地都标记上。
在遇到标记过的陆地节点 和海洋节点的时候直接跳过。 这样计数器就是最终岛屿的数量
深度优先遍历的写法:
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static int[][] dir = {{0,-1}, {0,1}, {-1,0}, {1,0}}; //四个方向
public static void dfs(boolean[][] visited, int[][] graph, int x, int y){
//获取四个方向的坐标
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nextX = x+dir[i][0];
int nextY = y+dir[i][1];
if(nextX<0 || nextY<0 || nextX>=graph.length || nextY>=graph[0].length) continue;
if(!visited[nextX][nextY] && graph[nextX][nextY]==1){
//该位置未被访问过,且为陆地
visited[nextX][nextY] = true;
dfs(visited, graph, nextX, nextY);
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] graph = new int[n][m];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
graph[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int res = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(!visited[i][j] && graph[i][j]==1){
visited[i][j]=true;
res++;
dfs(visited, graph, i, j);
}
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}广度优先遍历需要定义一个队列,注意每把一个Pair加入队列时,都要立马让visited标记为true,避免重复遍历
java
import java.util.*;
public class Main{
public static int[][] dir = {{0,-1}, {0,1}, {-1,0}, {1,0}};
public static class Pair{ //定义一个Pair类
int first;
int second;
public Pair(int x, int y){
this.first = x;
this.second = y;
}
}
public static void bfs(boolean[][] visited, int[][] graph, int x, int y){
Queue<Pair> que = new LinkedList<>();
que.offer(new Pair(x,y));
visited[x][y] = true;//入队就直接标记为访问过
while(!que.isEmpty()){
int curX = que.peek().first;
int curY = que.poll().second; //出队
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
int nextX = curX+dir[i][0];
int nextY = curY+dir[i][1];
if(nextX<0 || nextY<0 || nextX>=graph.length || nextY>=graph[0].length) continue; //超出图的部分直接跳出循环
if(!visited[nextX][nextY] && graph[nextX][nextY]==1){
que.offer(new Pair(nextX, nextY));
visited[nextX][nextY] = true;
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int m = sc.nextInt();
int[][] graph = new int[n][m];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
graph[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
}
}
boolean[][] visited = new boolean[n][m];
int res = 0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<m;j++){
if(!visited[i][j] && graph[i][j]==1){
res++;
bfs(visited, graph, i, j);
}
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}