目录
二叉树的三种遍历其实都可以借助栈来做,因为递归过程就像是入栈出栈过程
一、二叉树前序遍历
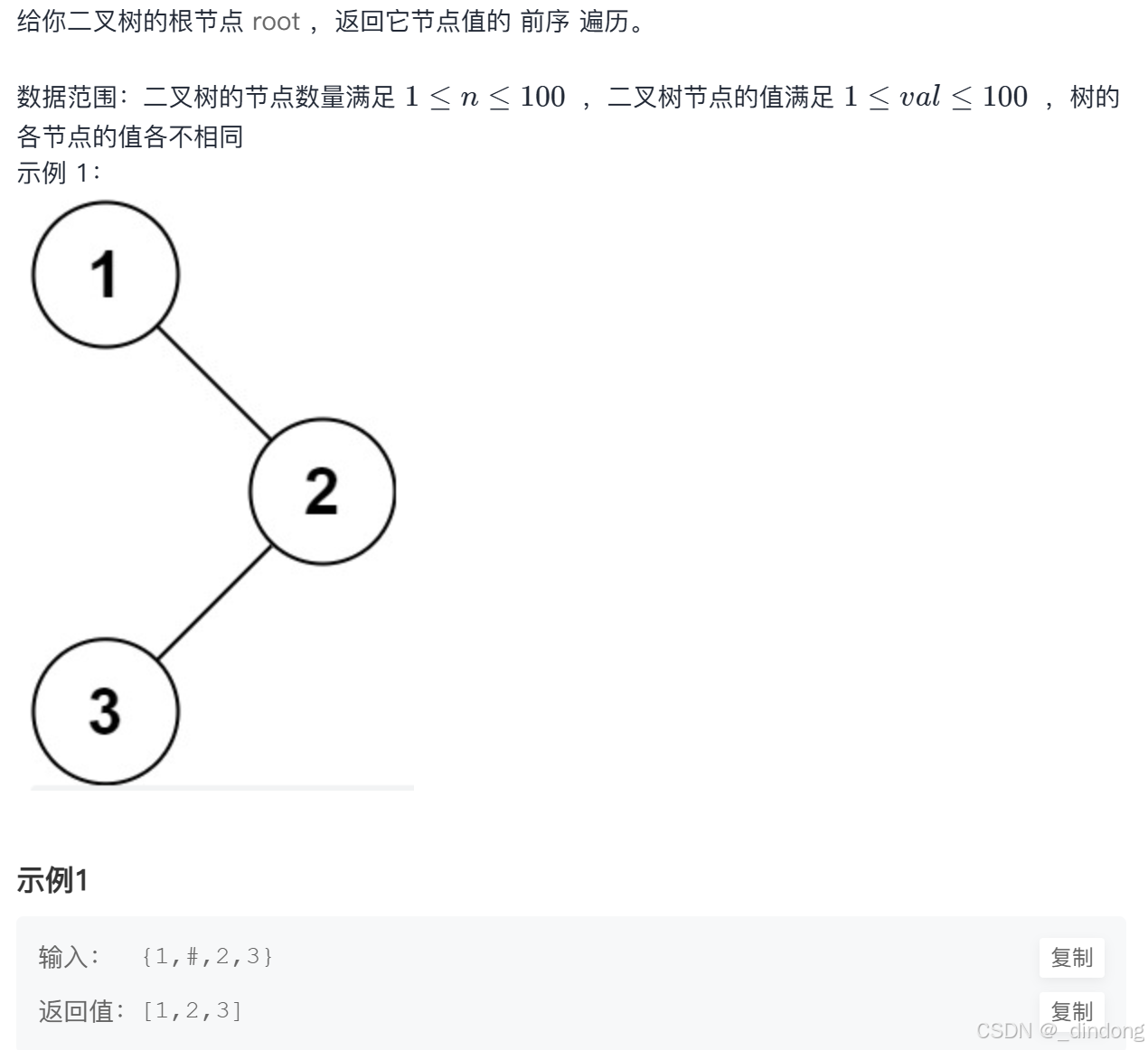
cpp
void preorder(vector<int>&res,TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)return;
res.push_back(root->val);
preorder(res, root->left);
preorder(res, root->right);
}
vector<int> preorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ret;
preorder(ret,root);
return ret;
}二、二叉树中序遍历
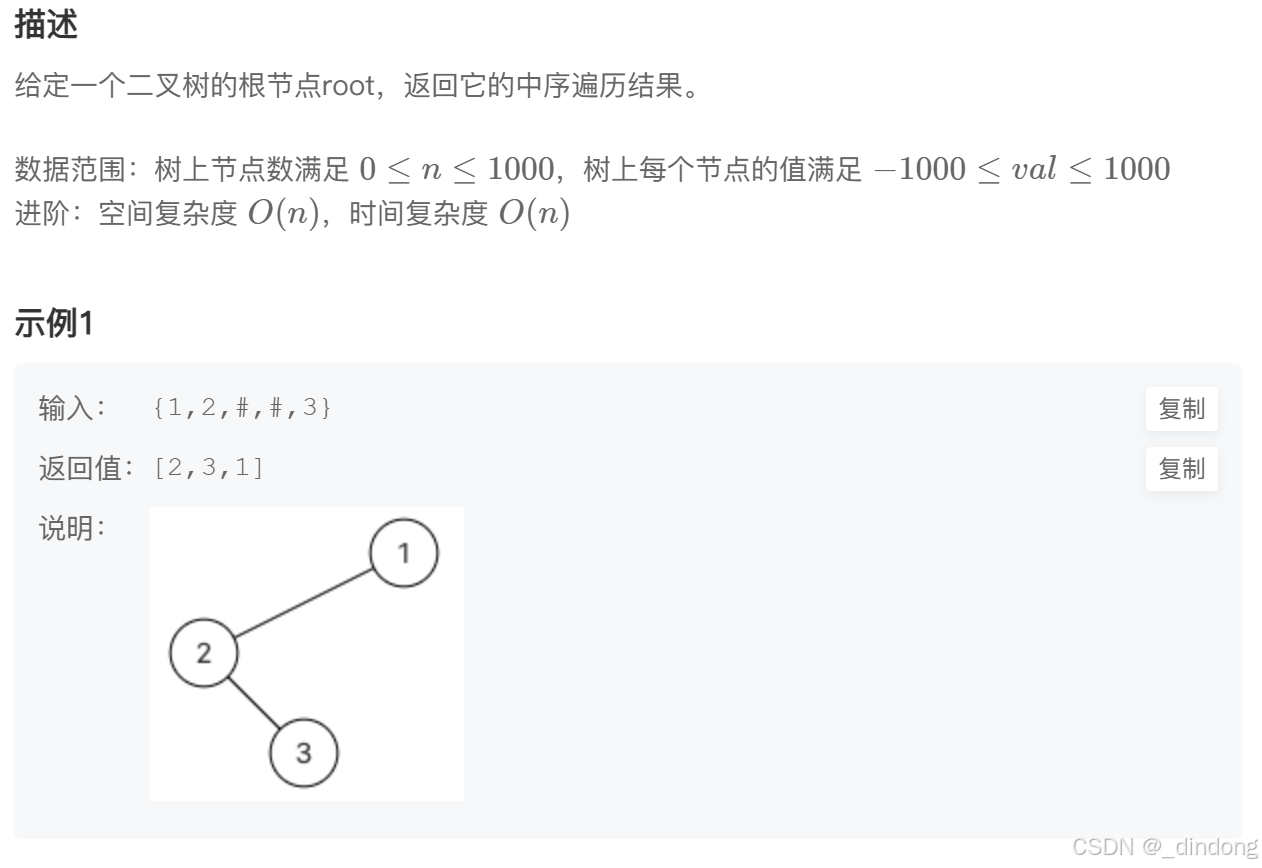
cpp
void inorder(vector<int>& ret,TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)return;
inorder(ret, root->left);
ret.push_back(root->val);
inorder(ret, root->right);
}
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ret;
inorder(ret,root);
return ret;
}三、二叉树后序遍历
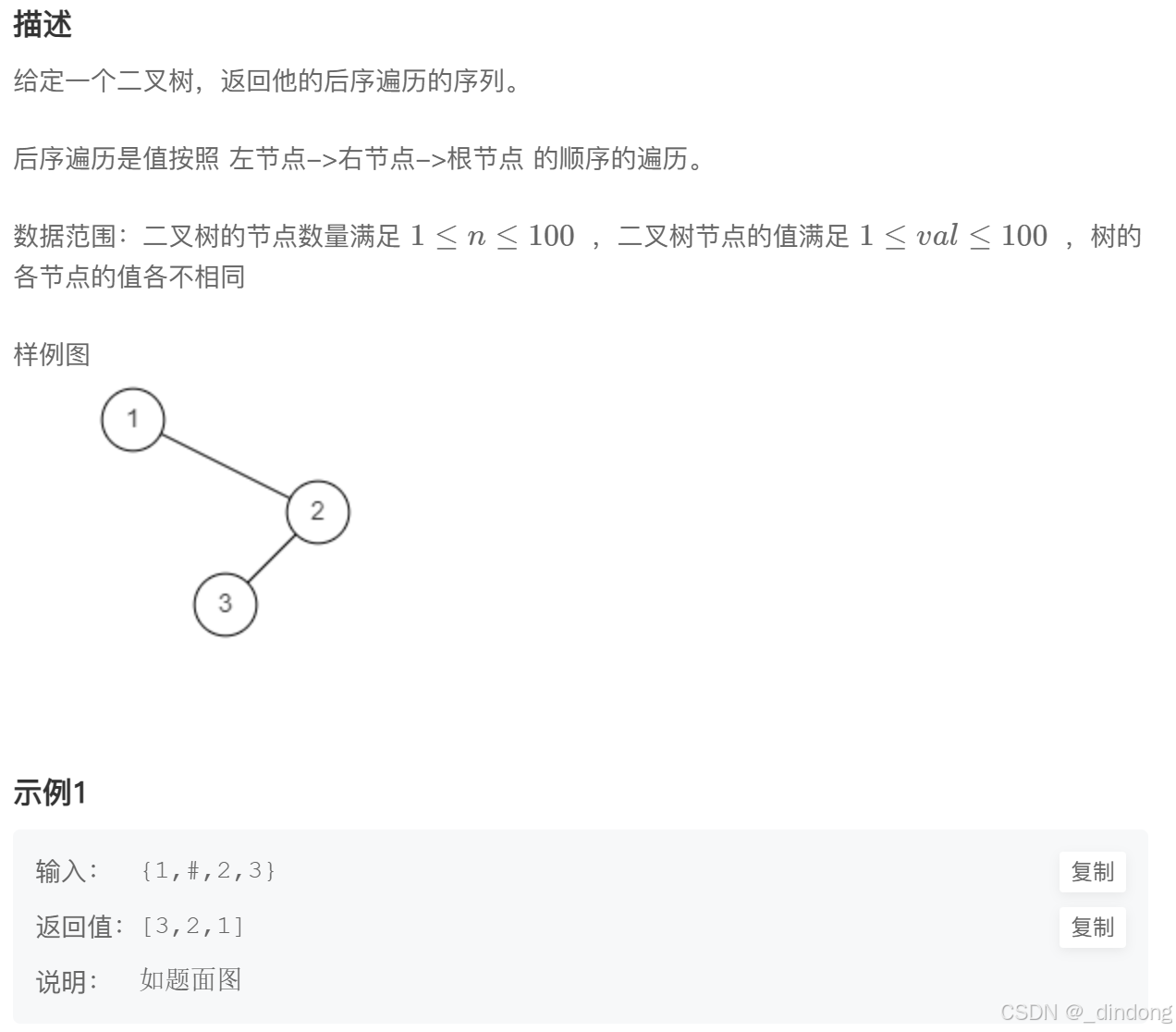
cpp
void postorder(vector<int>& ret,TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)return;
postorder(ret, root->left);
postorder(ret, root->right);
ret.push_back(root->val);
}
vector<int> postorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> ret;
postorder(ret,root);
return ret;
}四、二叉树层序遍历
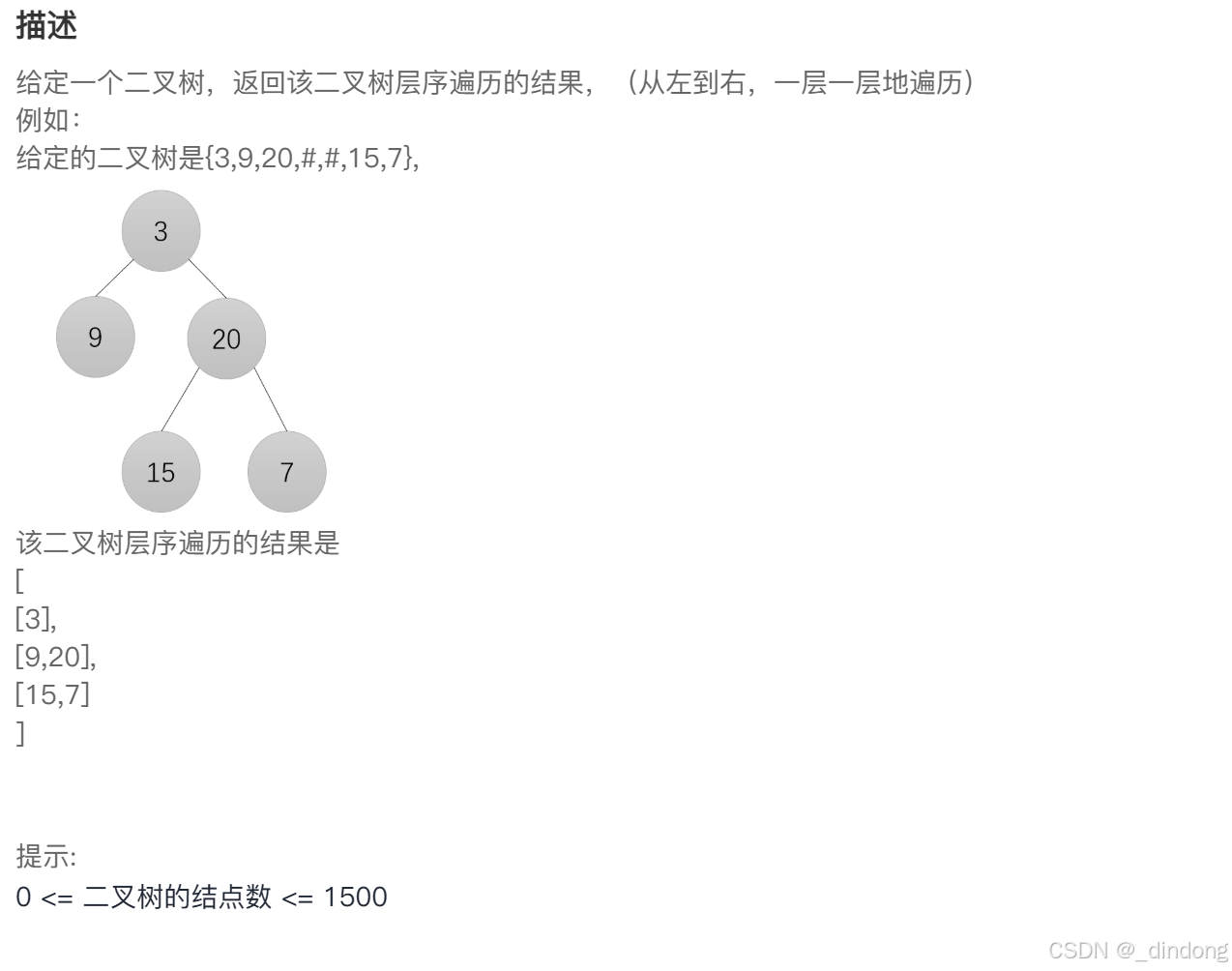
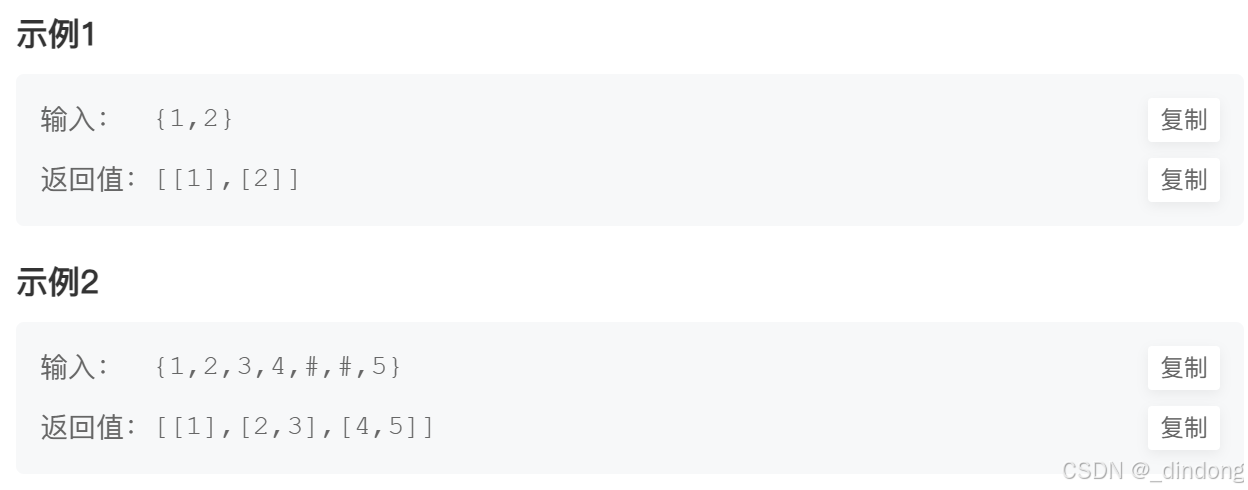
队列+BFS
cpp
vector<vector<int> > levelOrder(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> ret;
if(!root)return ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int> tmp;
int sz=q.size();
while(sz--)
{
TreeNode* t=q.front();
q.pop();
tmp.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left)q.push(t->left);
if(t->right)q.push(t->right);
}
ret.push_back(tmp);
}
return ret;
}五、按之字形顺序打印二叉树
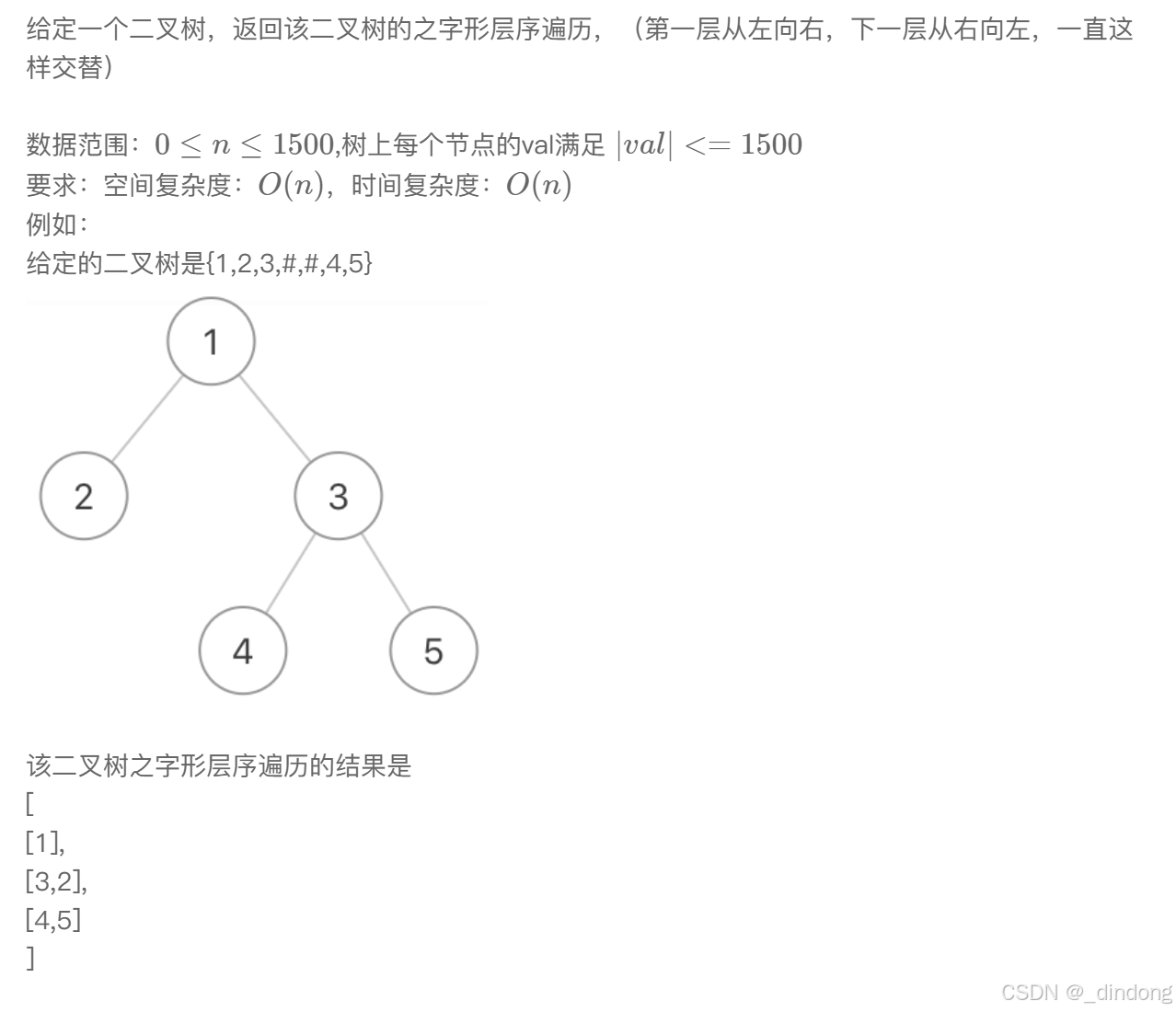
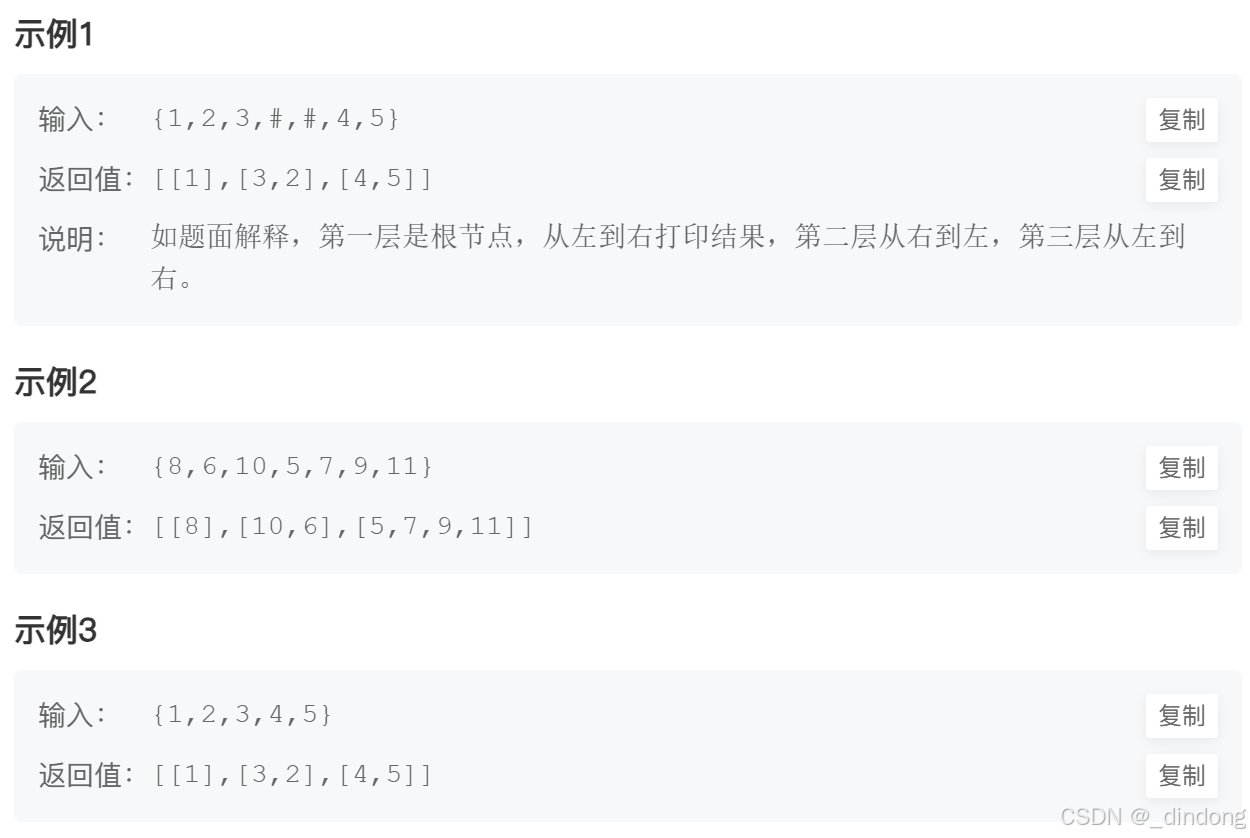
在前一题的基础上将偶数行数组逆序即可,添加一个标记位就能实现
cpp
vector<vector<int> > Print(TreeNode* pRoot) {
vector<vector<int>> ret;
if(!pRoot)return ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(pRoot);
//标记位
int flag=1;
while(!q.empty())
{
vector<int> tmp;
int sz=q.size();
while(sz--)
{
TreeNode* t=q.front();
q.pop();
tmp.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left)q.push(t->left);
if(t->right)q.push(t->right);
}
//偶数行逆序即可,别忘了更新flag
if(flag%2==0)reverse(tmp.begin(),tmp.end());
++flag;
ret.push_back(tmp);
}
return ret;
}六、二叉树最大深度

请输入文本
cpp
int maxDepth(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return 0;
return 1+max(maxDepth(root->left),maxDepth(root->right));
}七、二叉树中和为某一值的路径(一)
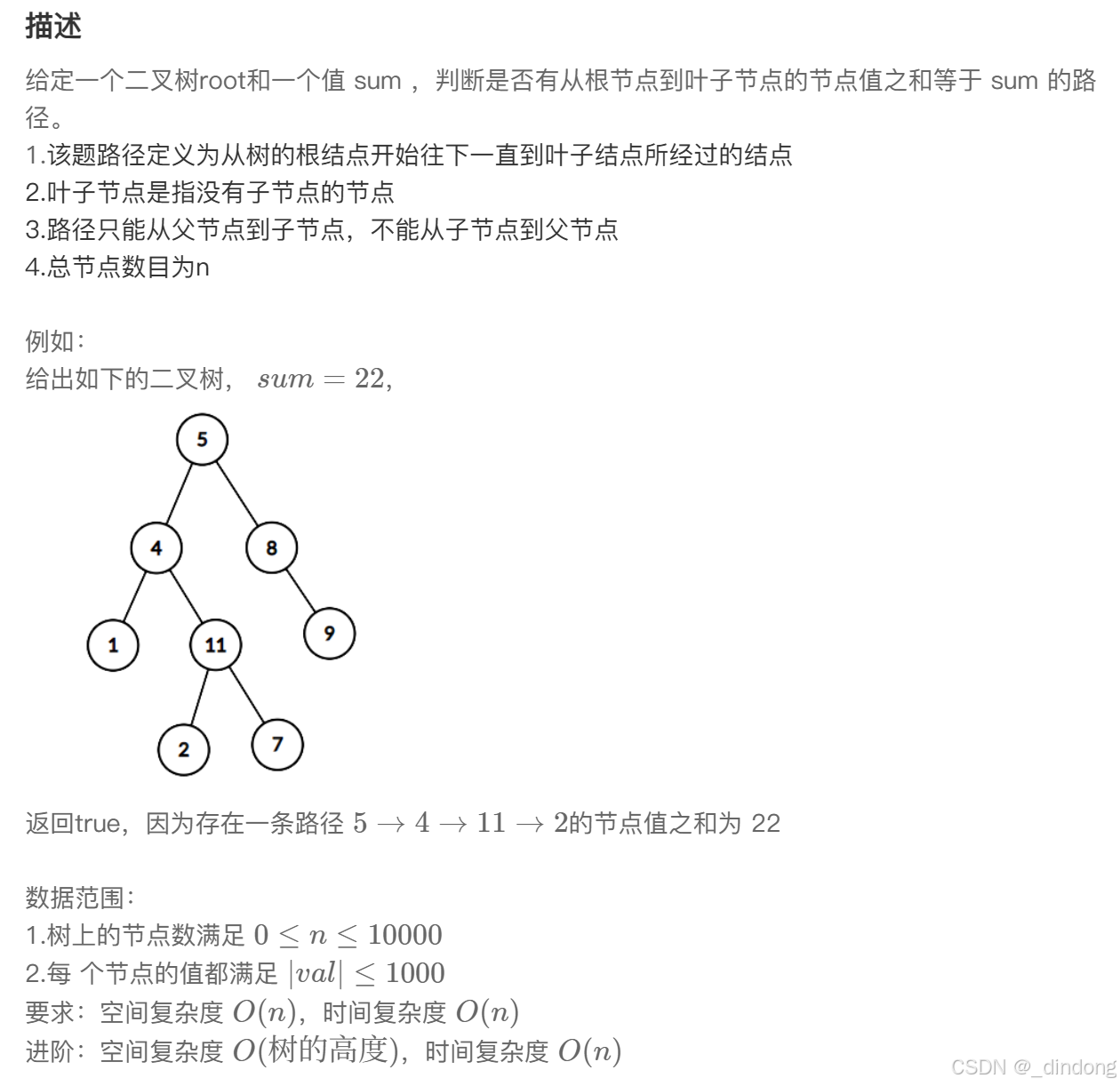
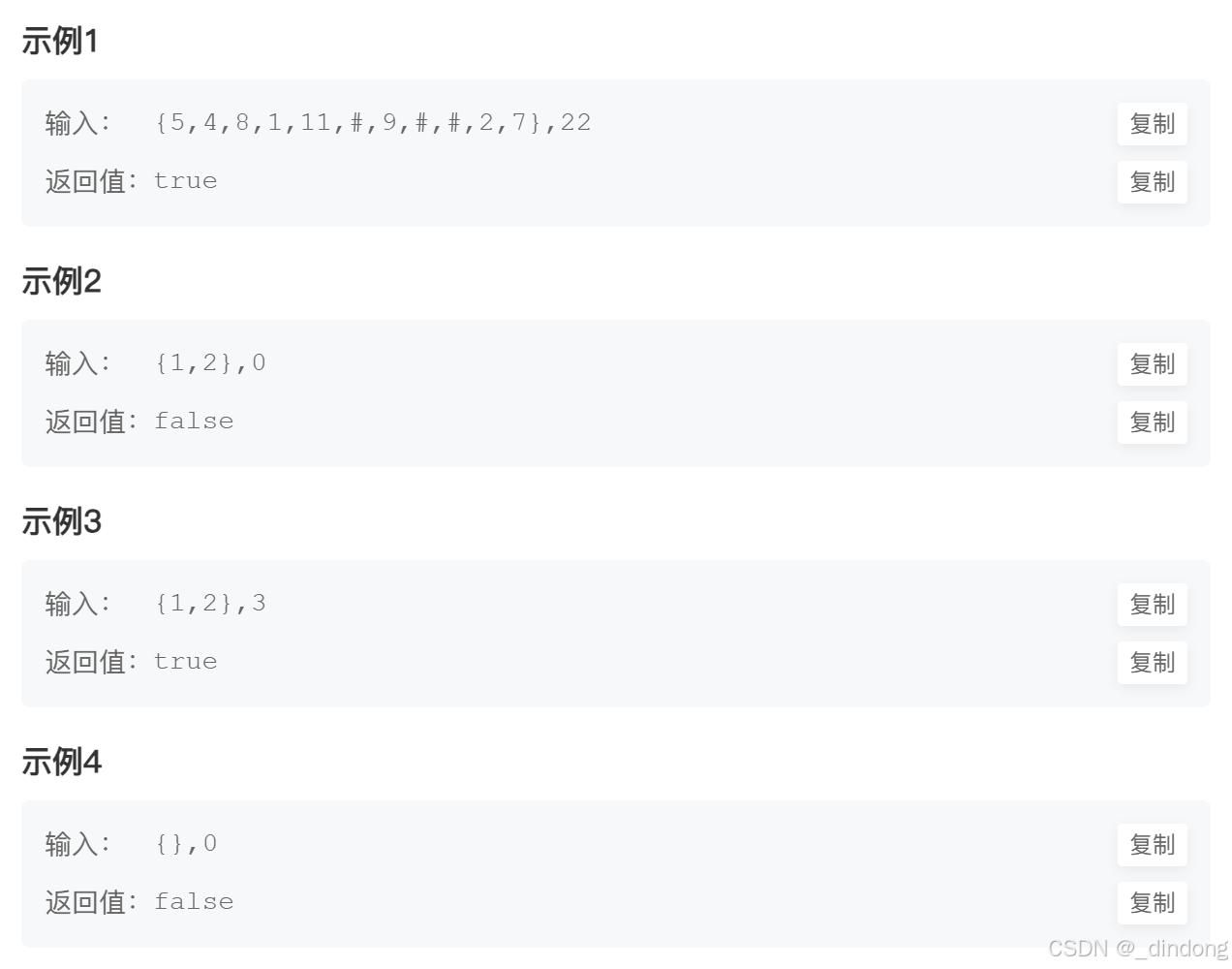
当结点为叶子结点的时候才判断,不是在root为空判断,不然比如根结点1,左节点空,右节点2的情况,sum=1,也会输出true,但这不是合法路径
cpp
class Solution {
int _sum;
public:
bool dfs(TreeNode* root, int TmpSum)
{
if(!root)return false;
if(!root->left&&!root->right)
{
if(TmpSum+root->val==_sum)return true;
return false;
}
return dfs(root->left,TmpSum+root->val)||dfs(root->right,TmpSum+root->val);
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
_sum=sum;
return dfs(root,0);
}
};八、二叉搜索树与双向链表
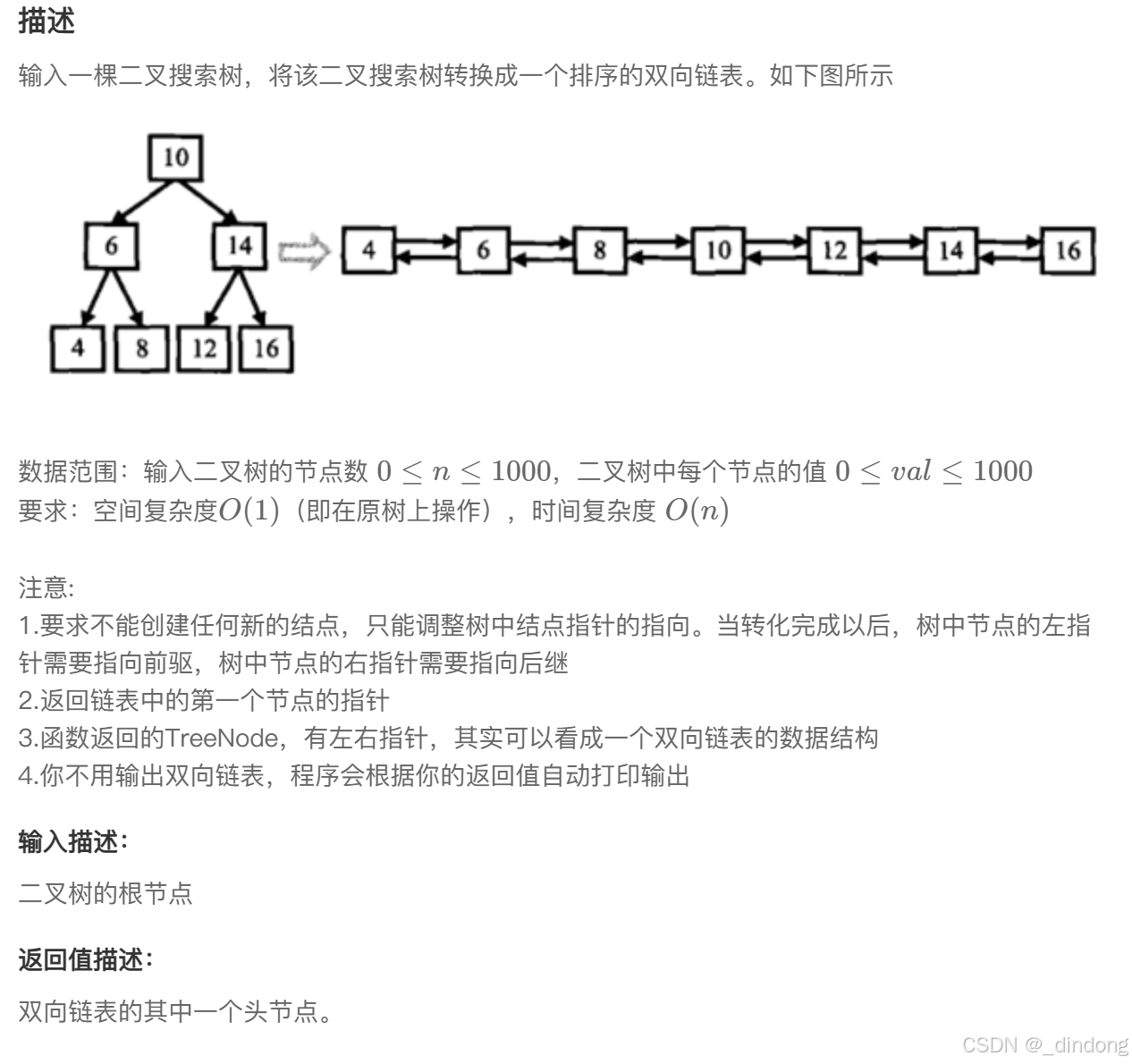

突然发现题目给的就是二叉搜索树,那中序遍历把结点存起来就行了
cpp
#include <vector>
class Solution {
vector<TreeNode*> ans;
public:
//中序遍历将结点存进数组
void InOrder(TreeNode*root)
{
if(!root)return;
InOrder(root->left);
ans.push_back(root);
InOrder(root->right);
}
TreeNode* Convert(TreeNode* pRootOfTree) {
if(!pRootOfTree)return nullptr;
InOrder(pRootOfTree);
for(int i=0;i<ans.size()-1;++i)
{
ans[i]->right=ans[i+1];
ans[i+1]->left=ans[i];
}
return ans[0];
}
};九、对称的二叉树
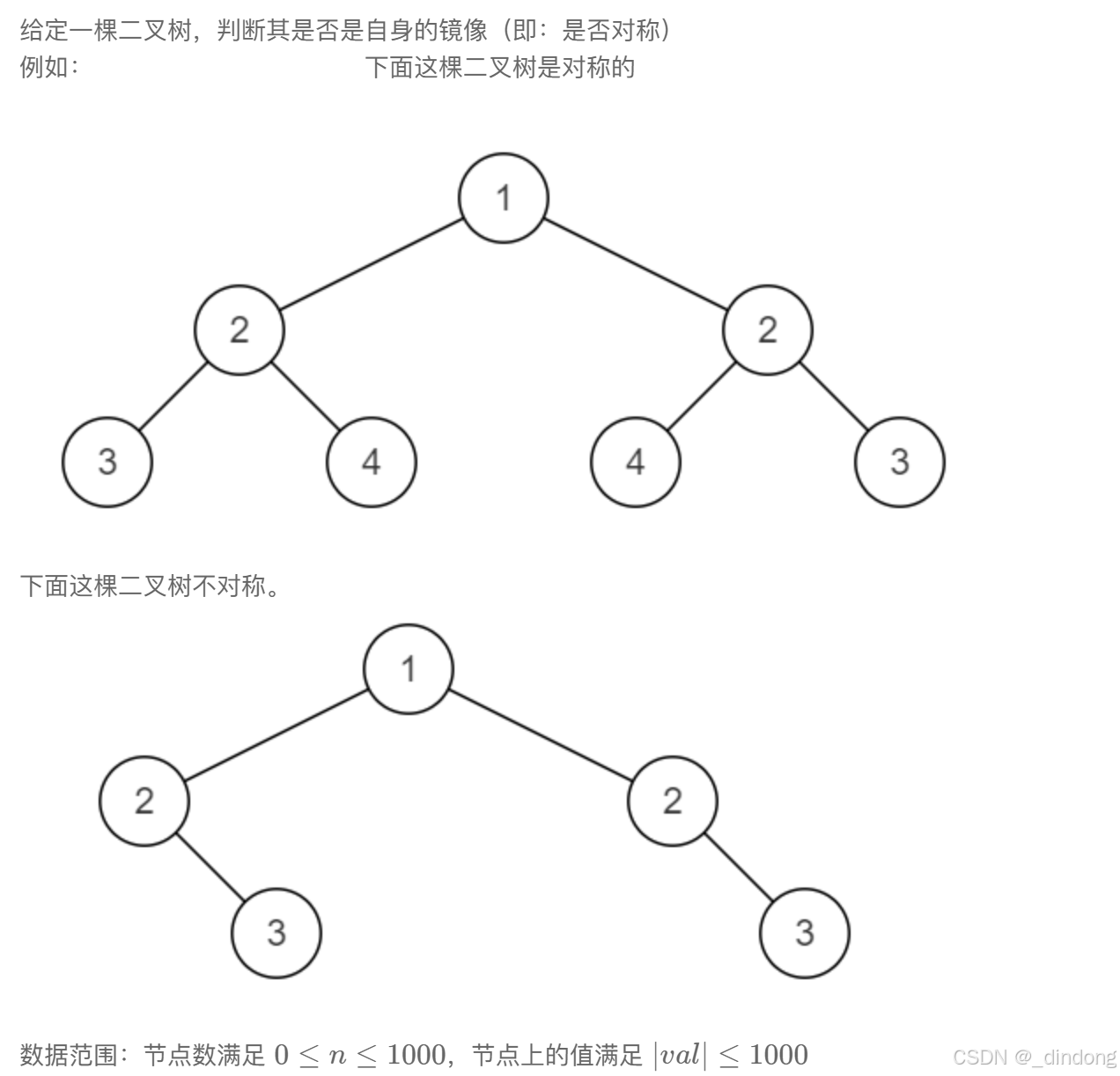

因为我们需要同时访问两颗子树的数据,仅仅使用一个结点是不够的,我们构造另一个函数。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool recursion(TreeNode* root1,TreeNode*root2)
{
if(!root1&&!root2)return true;
//注意判断顺序,能运行到判断不等的代码就说明两个结点都存在
if(!root1||!root2||root1->val!=root2->val)return false;
return recursion(root1->left,root2->right)&&recursion(root1->right, root2->left);
}
bool isSymmetrical(TreeNode* pRoot) {
return recursion(pRoot, pRoot);
}
};十、合并二叉树
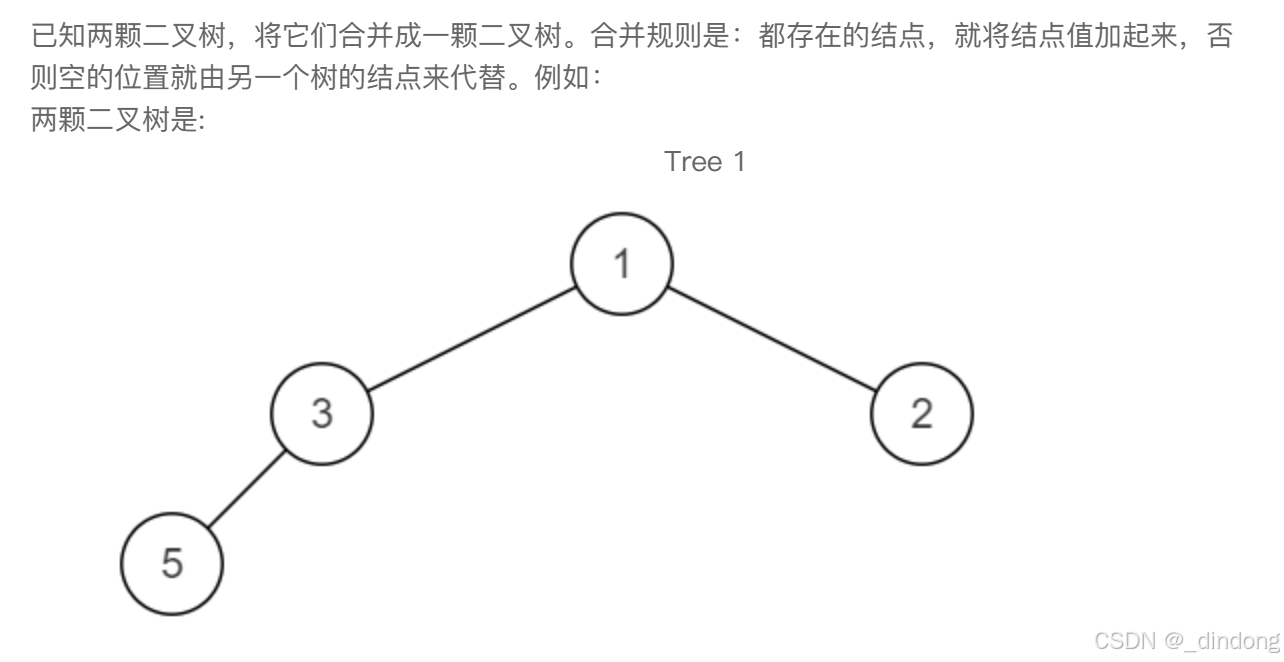
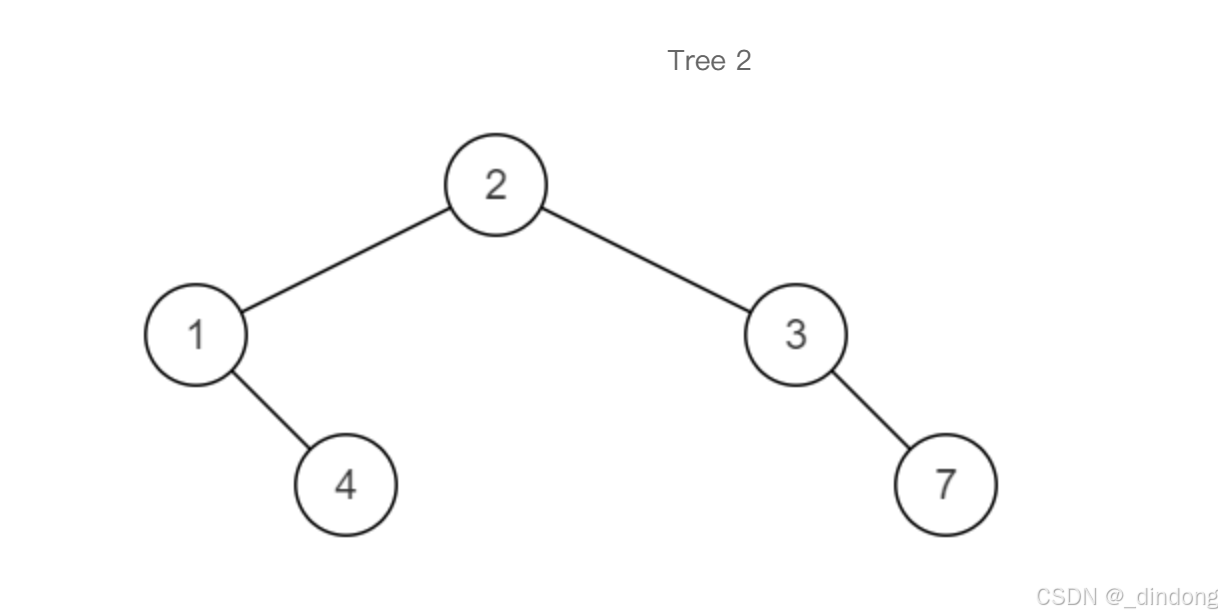
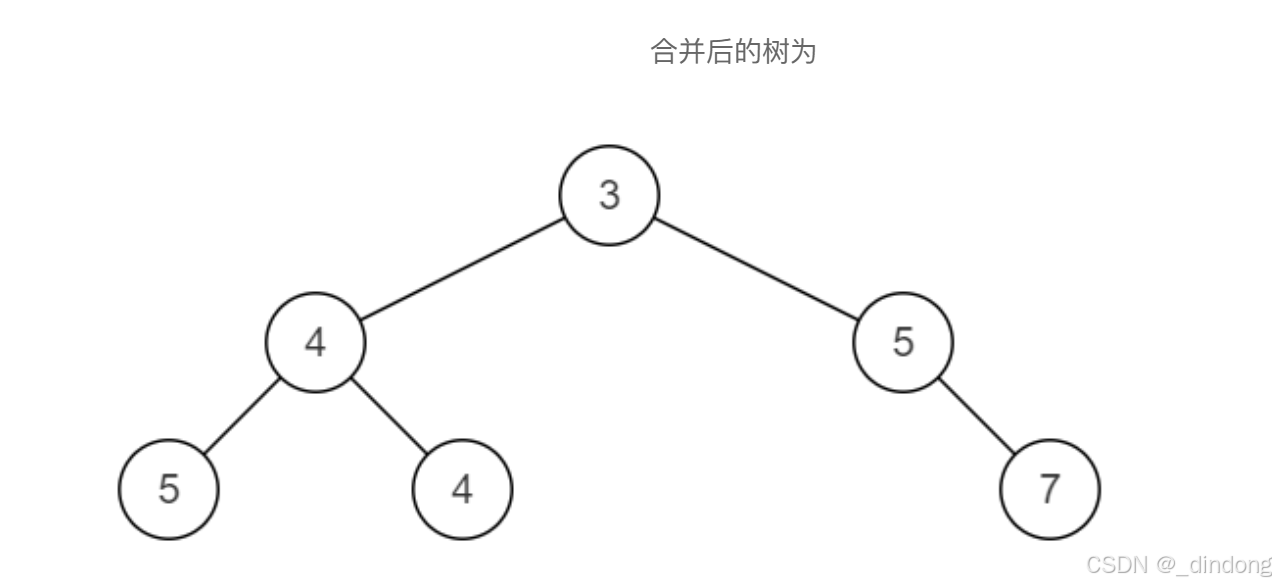

递归做即可
cpp
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* mergeTrees(TreeNode* t1, TreeNode* t2) {
if(!t1)return t2;
if(!t2)return t1;
TreeNode* head=new TreeNode(t1->val+t2->val);
head->left=mergeTrees(t1->left,t2->left);
head->right=mergeTrees(t1->right, t2->right);
return head;
}
};十一、二叉树的镜像
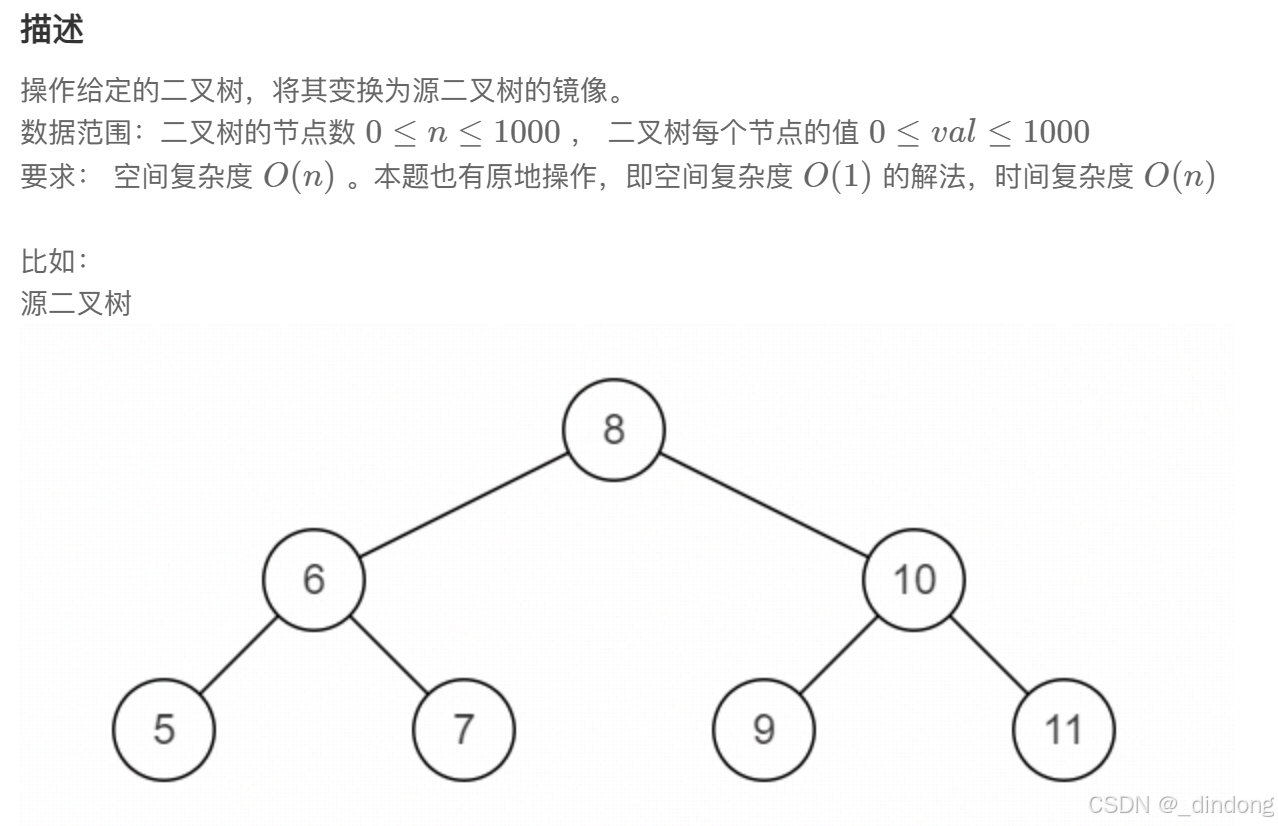
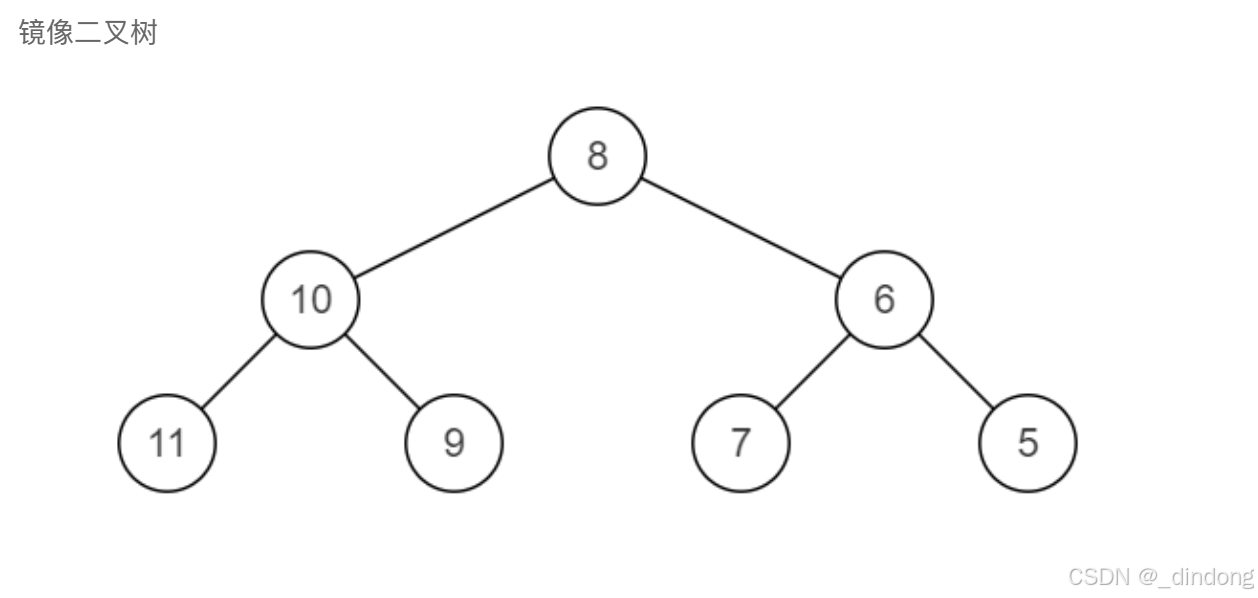

看懂后其实就是每个根节点的左节点变成右节点,右节点变成左节点,左右节点都交换位置,就达成了镜像,做二叉树递归,一定得有从局部到整体的思想。
递归往下,每层递归交换左右子树
cpp
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* Mirror(TreeNode* pRoot) {
if(pRoot==nullptr)return nullptr;
//递归子树
TreeNode*left=Mirror(pRoot->left);
TreeNode*right=Mirror(pRoot->right);
//交换,局部->整体
pRoot->left=right;
pRoot->right=left;
return pRoot;
}
};十二、判断是不是二叉搜索树
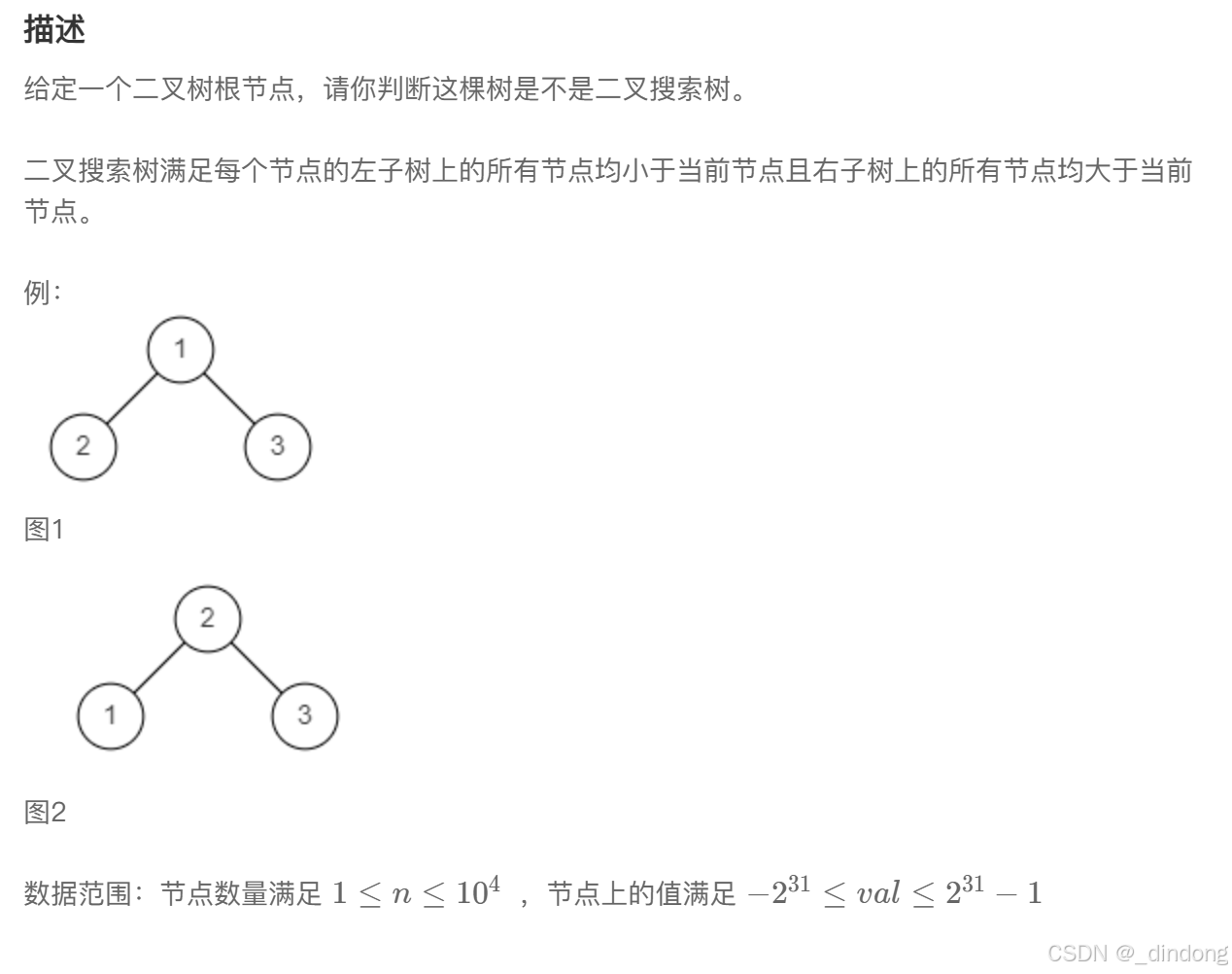

利用二叉搜索树的中序遍历是递增的这一特性判断
cpp
#include <climits>
class Solution {
public:
int prev=INT_MIN;
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return true;
if(!isValidBST(root->left))return false;
if(root->val<=prev)return false;
prev=root->val;
if(!isValidBST(root->right))return false;
return true;
}
};十三、判断是不是完全二叉树
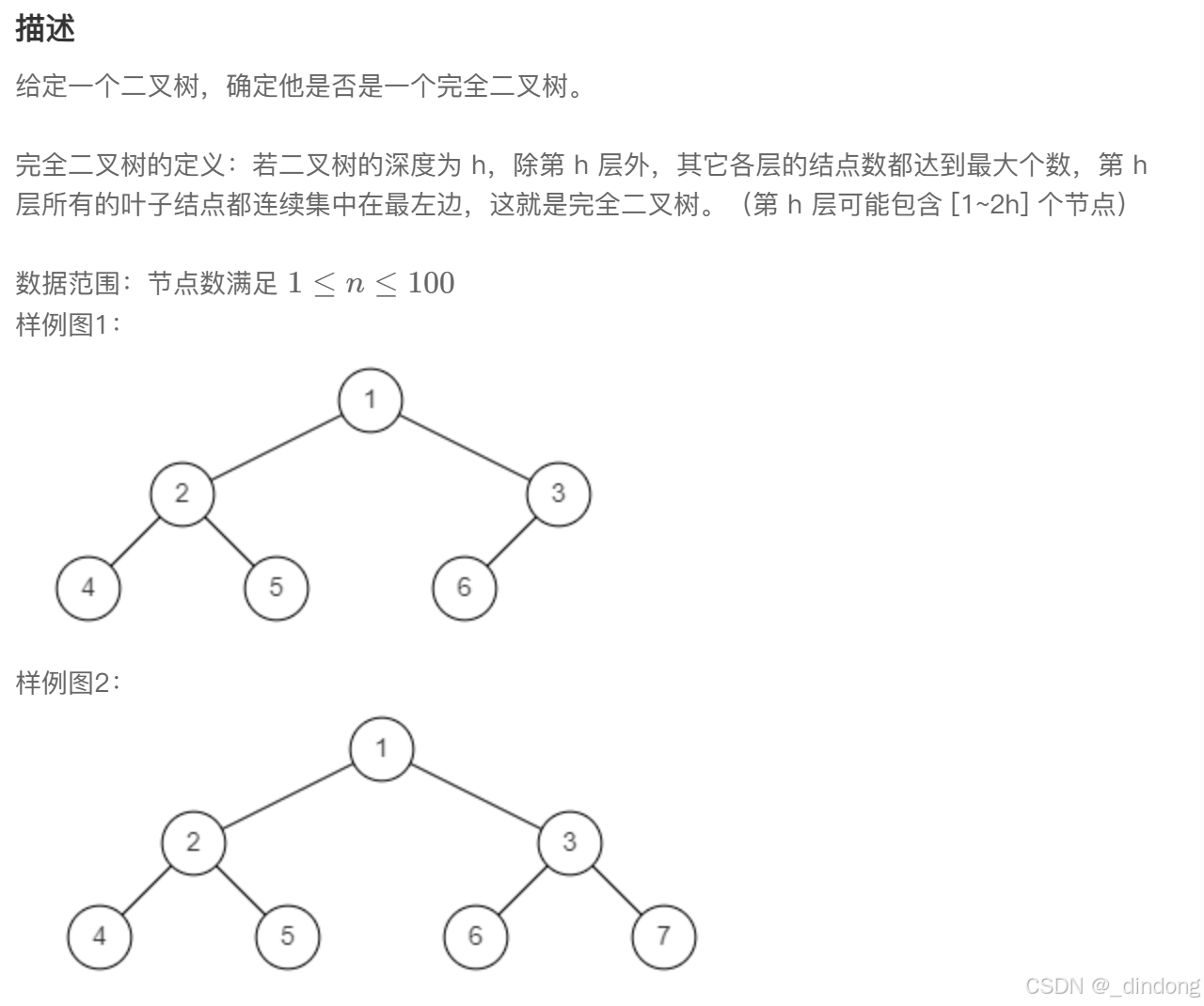
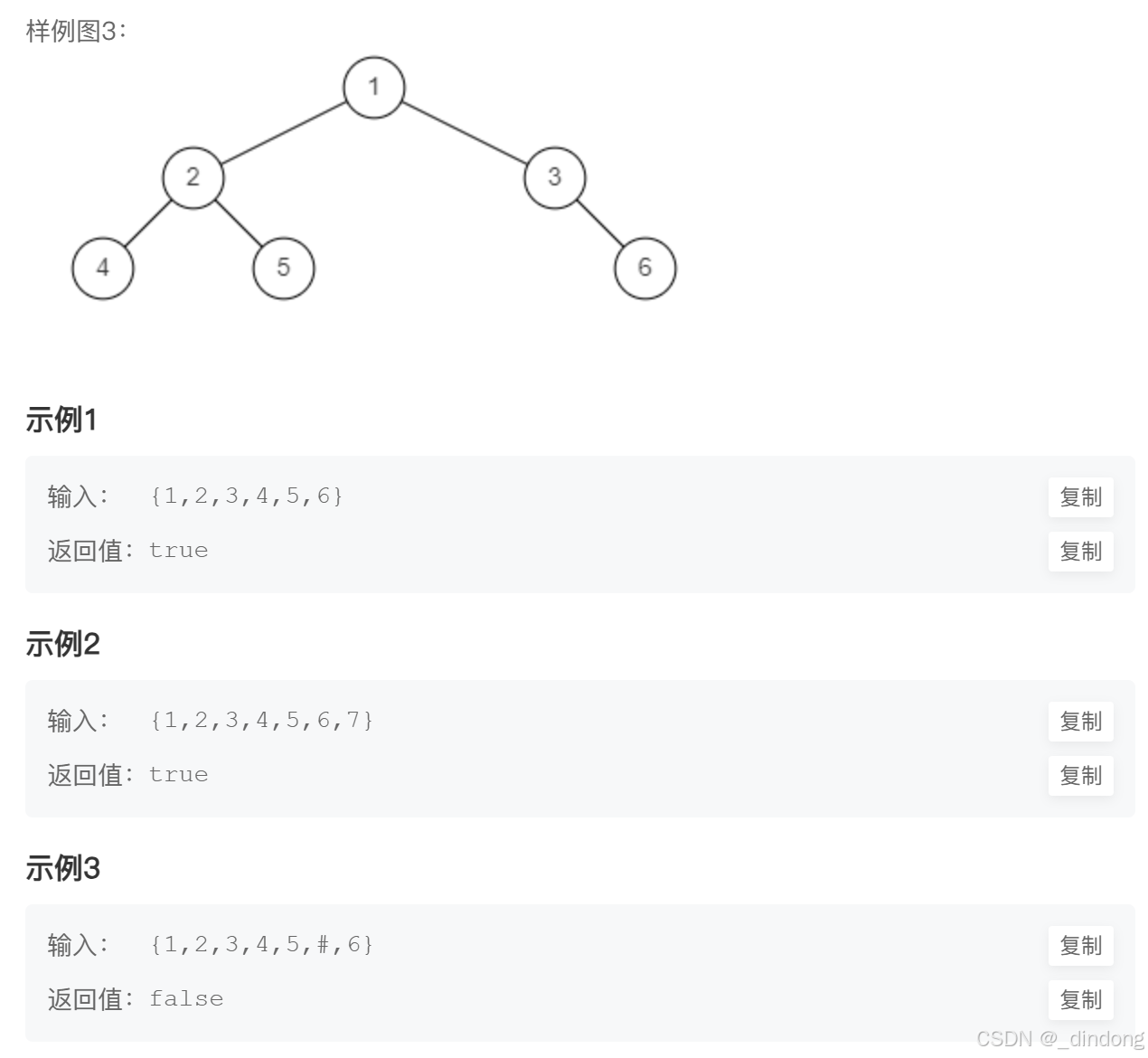
借助队列实现层序遍历
cpp
class Solution {
public:
bool isCompleteTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return true;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
bool flag=false;
while(!q.empty())
{
int sz=q.size();
while(sz--)
{
TreeNode* t=q.front();
q.pop();
//该层遇到空节点
if(!t)flag=true;
//不是空,把left和right传进来,不过得提前判断该层前面有没有出现空
else
{
if(flag)return false;
q.push(t->left);
q.push(t->right);
}
}
}
return true;
}
};十四、判断是不是平衡二叉树
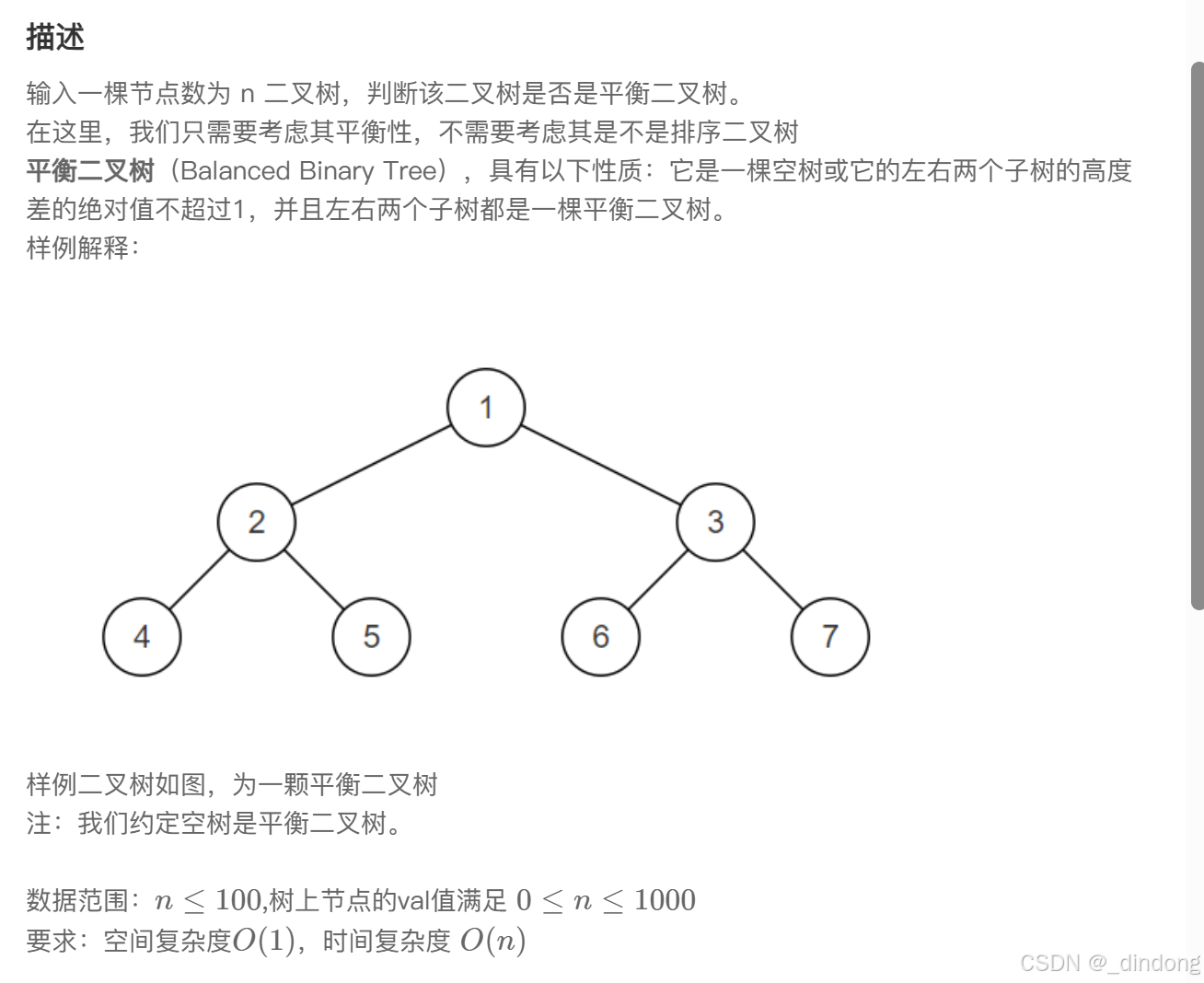

平衡二叉树判断标准:任何左右子树层数相差不超过1
解法一:自顶向下
cpp
class Solution {
public:
//计算树的最大深度
int MaxDepth(TreeNode* root)
{
if(!root)return 0;
return 1+max(MaxDepth(root->left),MaxDepth(root->right));
}
bool IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode* pRoot)
{
if(!pRoot)return true;
//处理该层
int LeftDepth=MaxDepth(pRoot->left);
int RightDepth=MaxDepth(pRoot->right);
if(LeftDepth-RightDepth>1||LeftDepth-RightDepth<-1)return false;
//同时左右子树也得平衡
return IsBalanced_Solution(pRoot->left)&&IsBalanced_Solution(pRoot->right);
}
};解法二:自底向上
cpp
class Solution {
public:
//计算该子树深度
//注意depth是引用传参!!!
bool judge(TreeNode* root, int& depth){
//空节点深度为0
if(root == NULL){
depth = 0;
return true;
}
//递归检查左右子树
int left = 0, right = 0;
if(judge(root->left, left) == false) // 检查左子树是否平衡
return false; // 左子树不平衡,整棵树直接完蛋
if(judge(root->right, right) == false) // 同理检查右子树
return false;
//检查左右子树高度差
if(left - right > 1 || left - right < -1)
return false;
//更新当前节点的深度
depth = max(left,right)+1;
//运行到这表示平衡
return true;
}
bool IsBalanced_Solution(TreeNode* pRoot) {
int depth = 0;
return judge(pRoot, depth);
}
};十五、二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
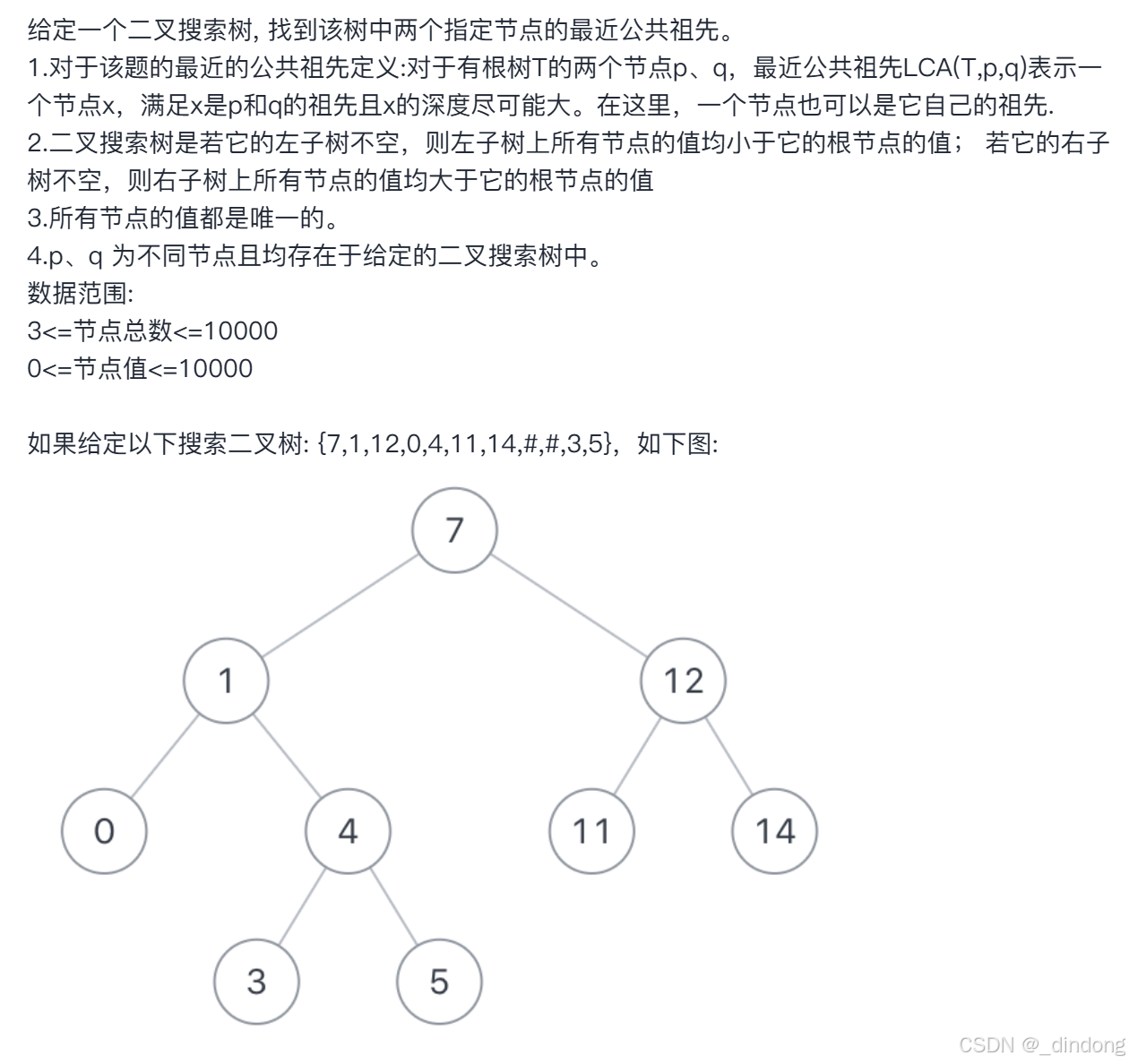
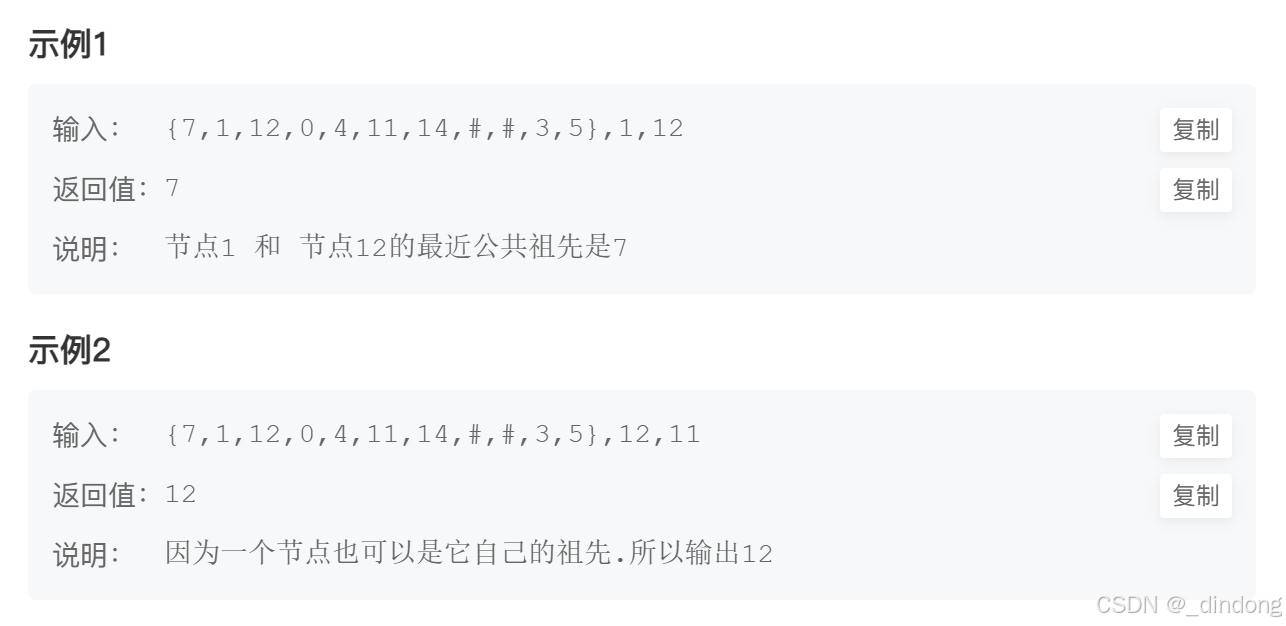
cpp
class Solution {
public:
int lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, int p, int q) {
if(!root)return -1;
int MinNum=min(p,q),MaxNum=max(p,q);
//=也在要求内
if(root->val>=MinNum&&root->val<=MaxNum)return root->val;
else if(root->val>=MaxNum)return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
else return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
}
};十六、在二叉树中找到两个节点的最近公共祖先
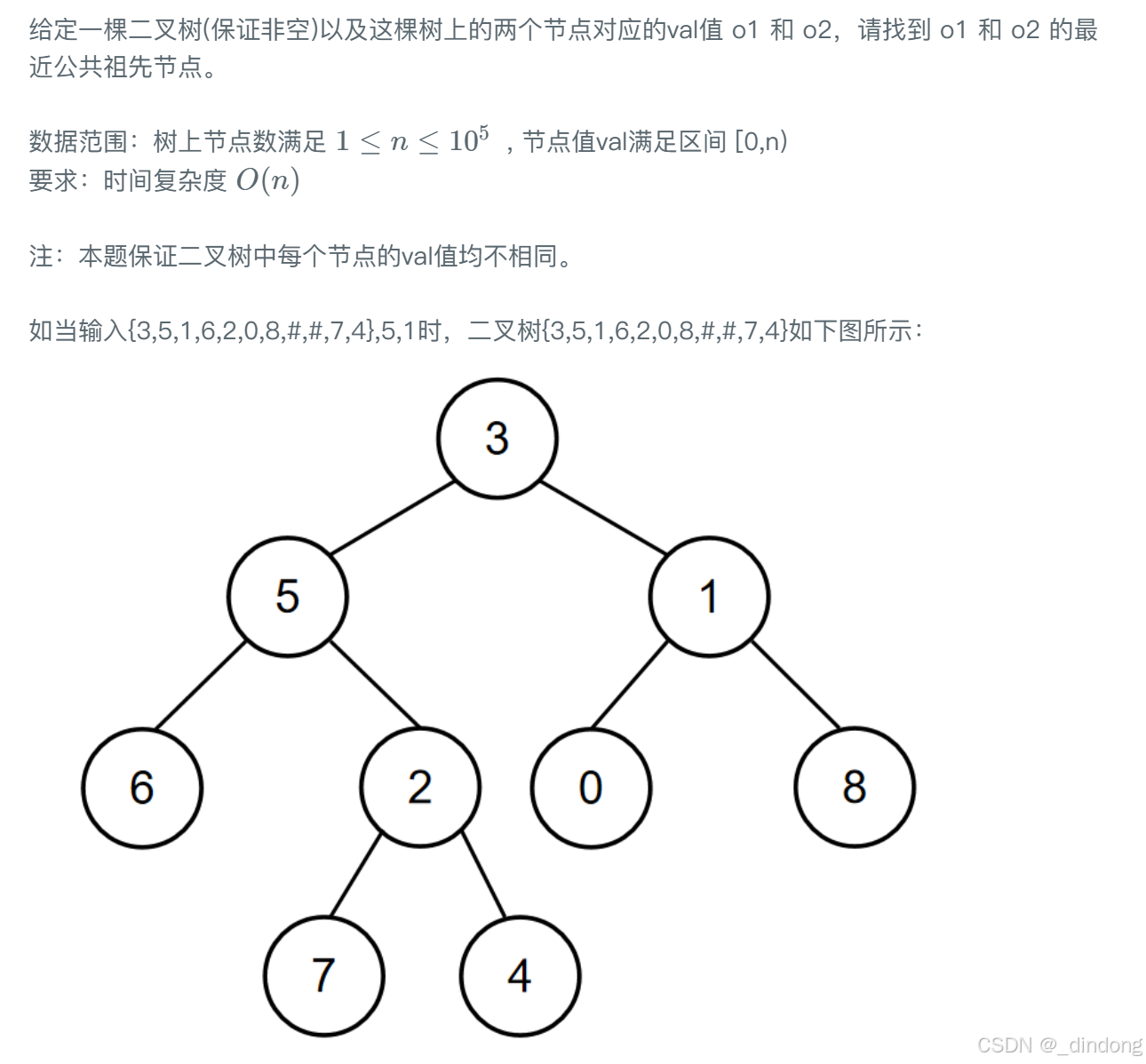
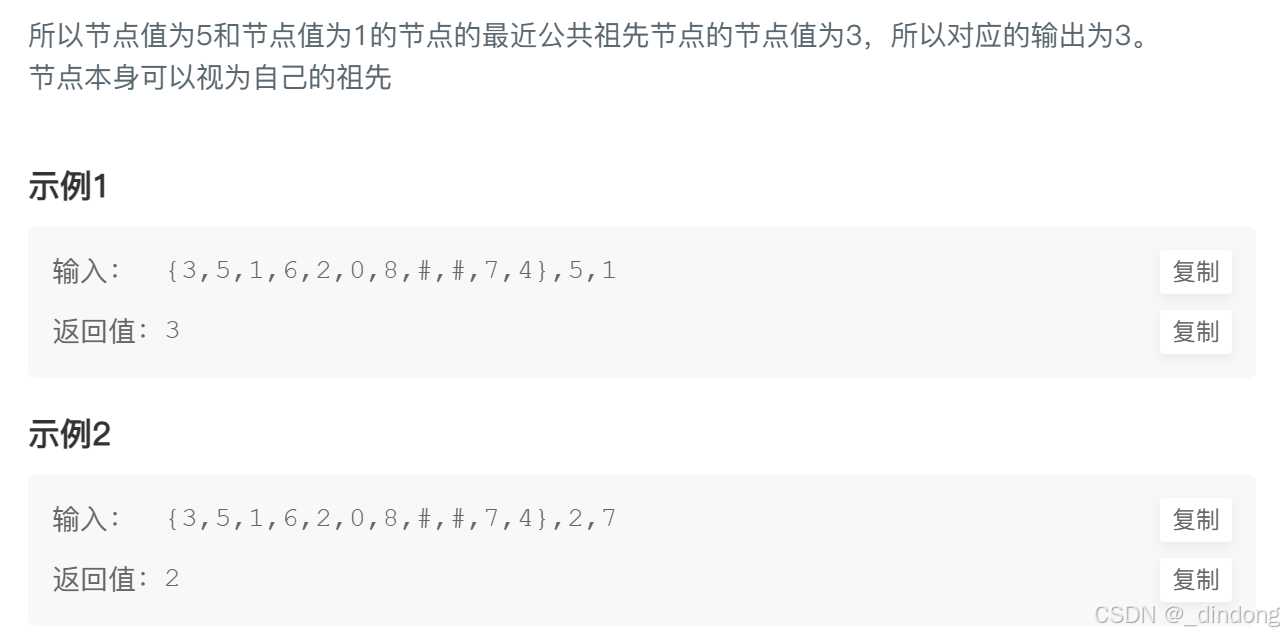
这次不再是二叉搜索树了
既然题目肯定是可以找到公共节点的,所以我们自顶向下遍历即可,遇到相等情况直接返回该局部根,否则就去左右找,左边没有那一定在右边,右边反之。如果左右都有,那么该层root恰好就是我们要的节点。
cpp
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode*dfs(TreeNode*root,int o1,int o2)
{
if(!root)return nullptr;
//此时存在一个节点是局部根的情况
//既然我们是自顶向下找的,那么我们是第一次碰到直接返回
if(root->val==o1||root->val==o2)return root;
//查看左右子树有没有目标节点
TreeNode* IfLeftTree=dfs(root->left,o1,o2);
TreeNode* IfRightTree=dfs(root->right,o1,o2);
//左子树没有,那肯定在右子树
if(!IfLeftTree)return IfRightTree;
//右子树没有,那一定在左子树
if(!IfRightTree)return IfLeftTree;
//左右子树都有,那么该root就是目标返回节点
return root;
}
int lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, int o1, int o2) {
return dfs(root,o1,o2)->val;
}
};十七、序列化二叉树
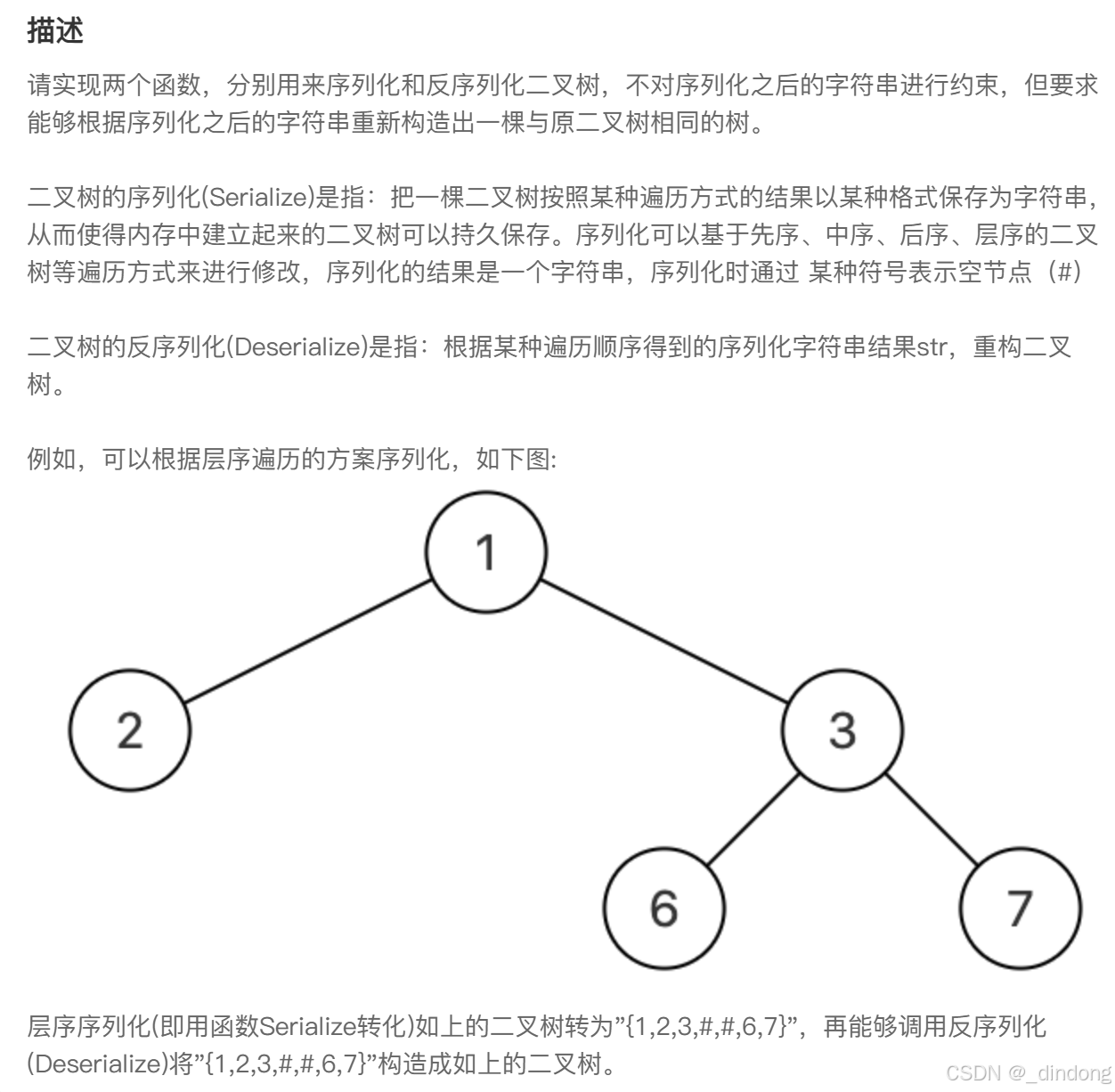
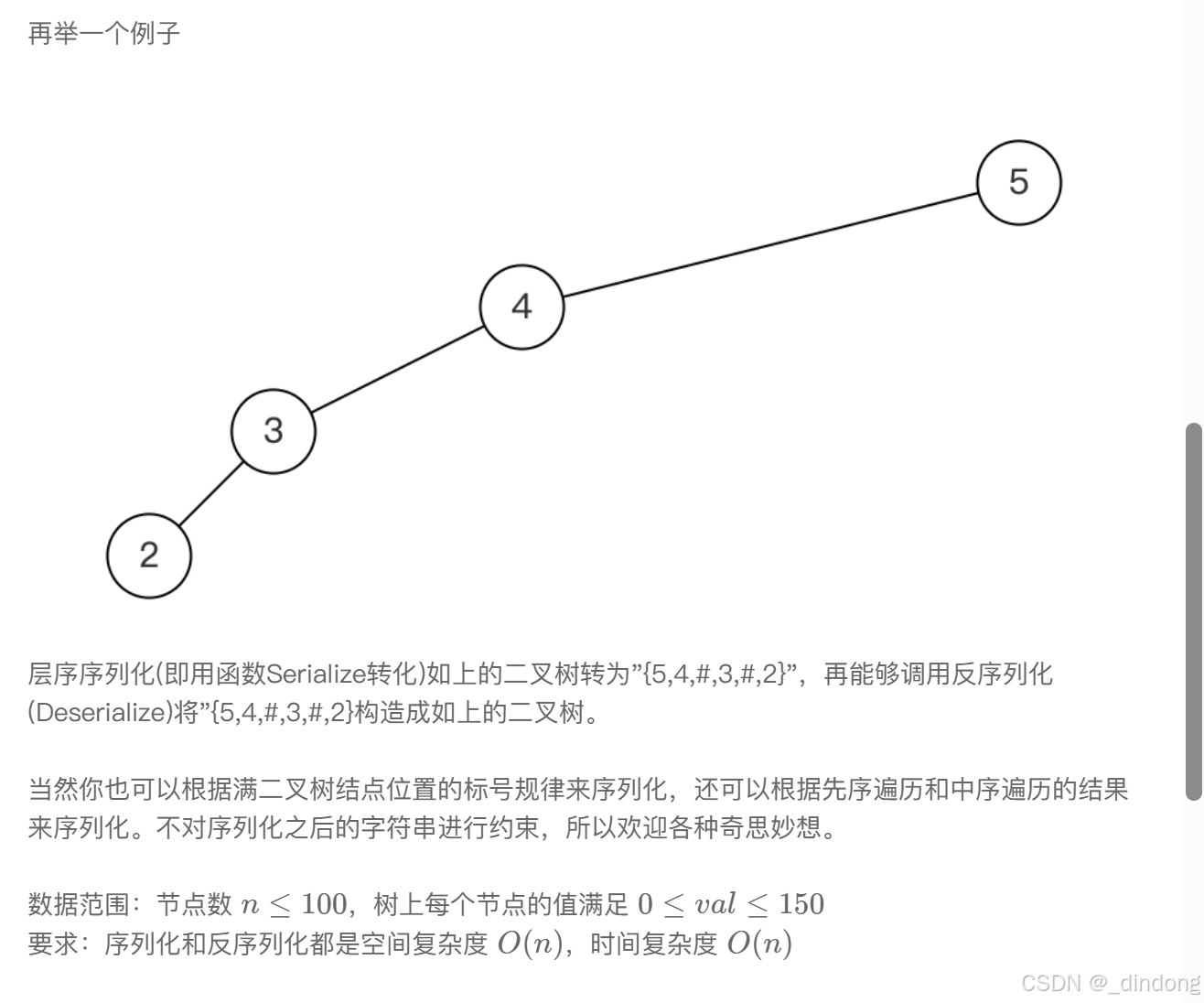
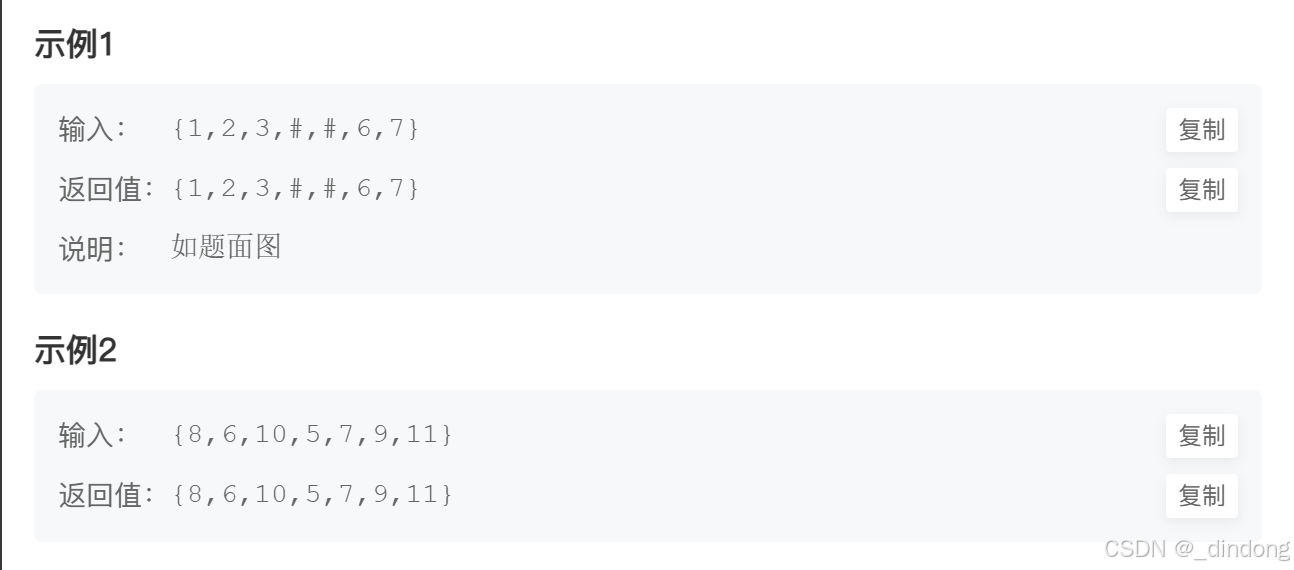
直接看官方题解吧,这里我们序列化都采用前序遍历

cpp
#include <cstring>
#include <string>
class Solution {
public:
void SerializeFunction(TreeNode*root,string &str)
{
if(!root)
{
str+='#';
return;
}
//!当作分割
// str+=(root->val+'0')+'!'; +'0'只适用于0~9
str+=to_string(root->val)+'!';
//前序遍历
SerializeFunction(root->left, str);
SerializeFunction(root->right, str);
}
char* Serialize(TreeNode *root) {
if(!root)return "#";
string str;
SerializeFunction(root, str);
//动态开辟成char*类型,不能直接return c_str
//因为c_str返回指向常量字符串的指针,存在string缓冲区函数结束会被销毁
char* newstr=new char[str.size()+1];
strcpy(newstr, str.c_str());
newstr[str.size()]='\0';
return newstr;
}
//传地址,整个函数共享一个str位置
TreeNode* DeserializeFunction(char**str)
{
if(**str=='#')
{
(*str)++;
return nullptr;
}
//数字字符串->数字
int val=0;
while(**str!='!'&&**str!='\0')
{
val=val*10+**str-'0';
//别忘记更新str位置,关于优先级问题能打括号尽量打括号吧
(*str)++;
}
TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(val);
//注意判断是否达到末尾,以防越界
if(**str=='\0')return root;
else (*str)++;
//自顶向下构建二叉树
root->left=DeserializeFunction(str);
root->right=DeserializeFunction(str);
return root;
}
TreeNode* Deserialize(char *str) {
if(*str=='#')return nullptr;
return DeserializeFunction(&str);
}
};十八、重建二叉树
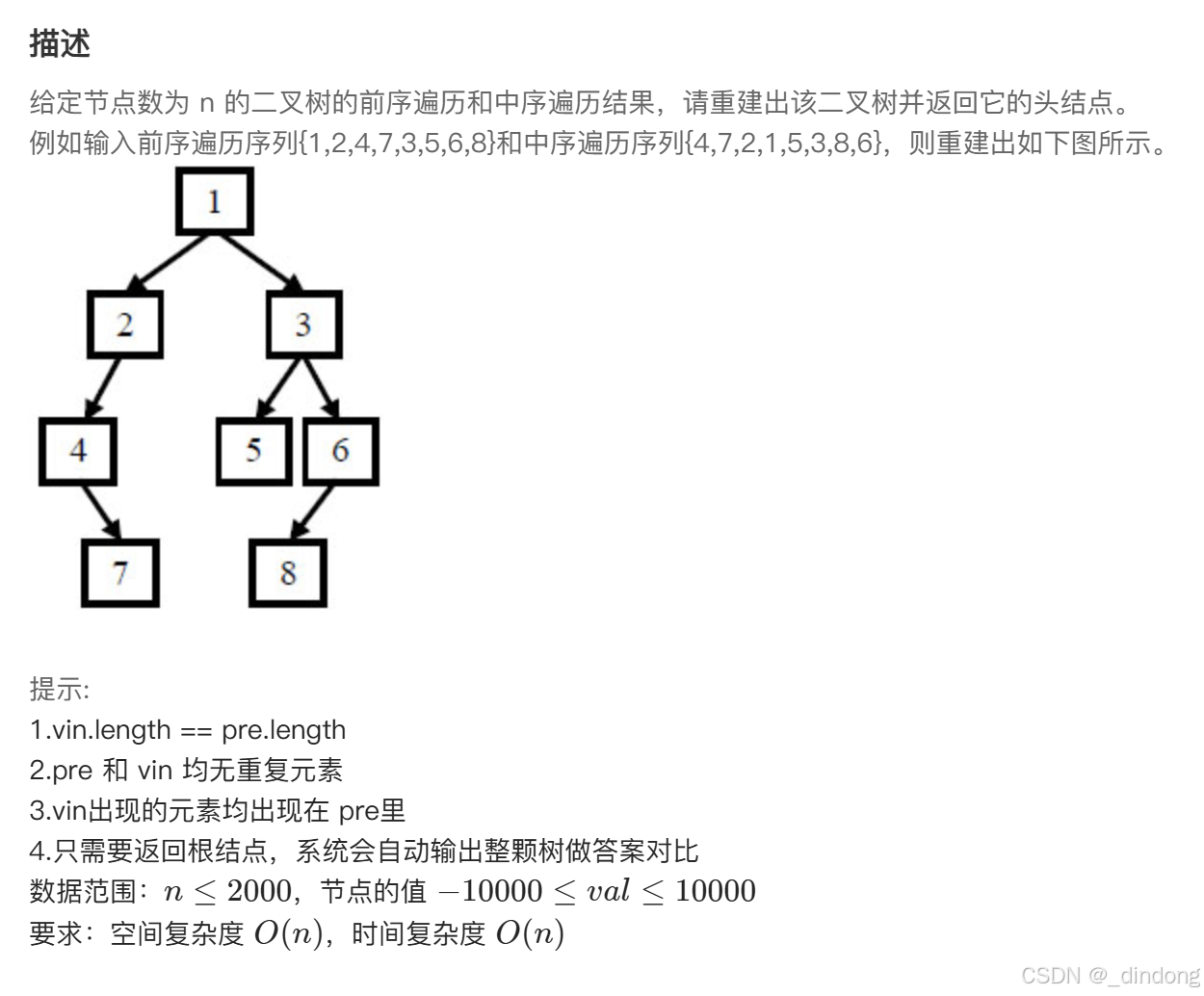

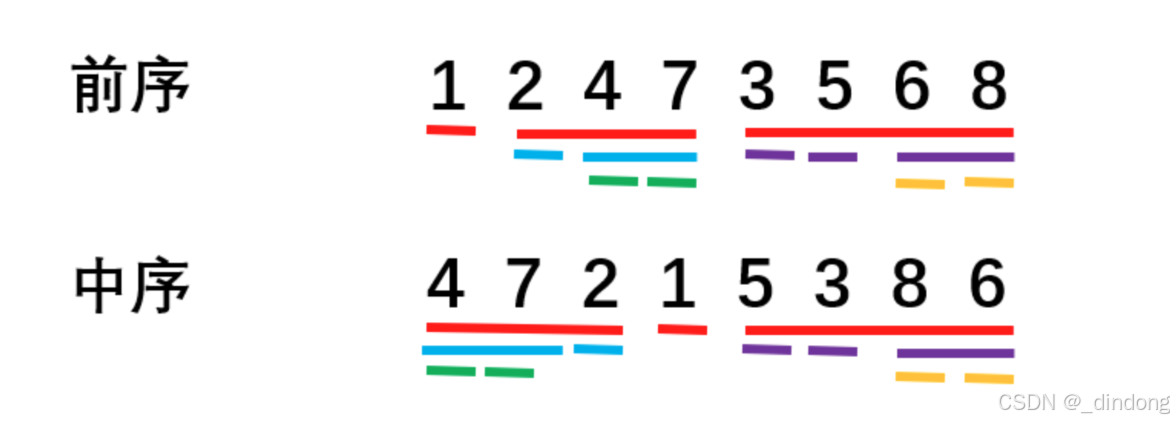
找到目标点不断递归细分pre数组和vin数组(构建左右子树前序中序遍历,依据这个顺序构建左右子树->递归)
cpp
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* reConstructBinaryTree(vector<int>& preOrder, vector<int>& vinOrder) {
int n=preOrder.size(),m=vinOrder.size();
if(n==0||m==0)return nullptr;
TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(preOrder[0]);
for(int i=0;i<m;++i)
{
if(preOrder[0]==vinOrder[i])
{
//构建左子树前序遍历
vector<int> LTreePre(preOrder.begin()+1,preOrder.begin()+1+i);
//左子树中序遍历
vector<int> LTreeVin(vinOrder.begin(),vinOrder.begin()+i);
//构建左子树
root->left=reConstructBinaryTree(LTreePre,LTreeVin);
//右子树也是一样
vector<int> RTreePre(preOrder.begin()+i+1,preOrder.end());
vector<int> RTreeVin(vinOrder.begin()+i+1,vinOrder.end());
root->right=reConstructBinaryTree(RTreePre, RTreeVin);
break;
}
}
return root;
}
};十九、输出二叉树的右视图
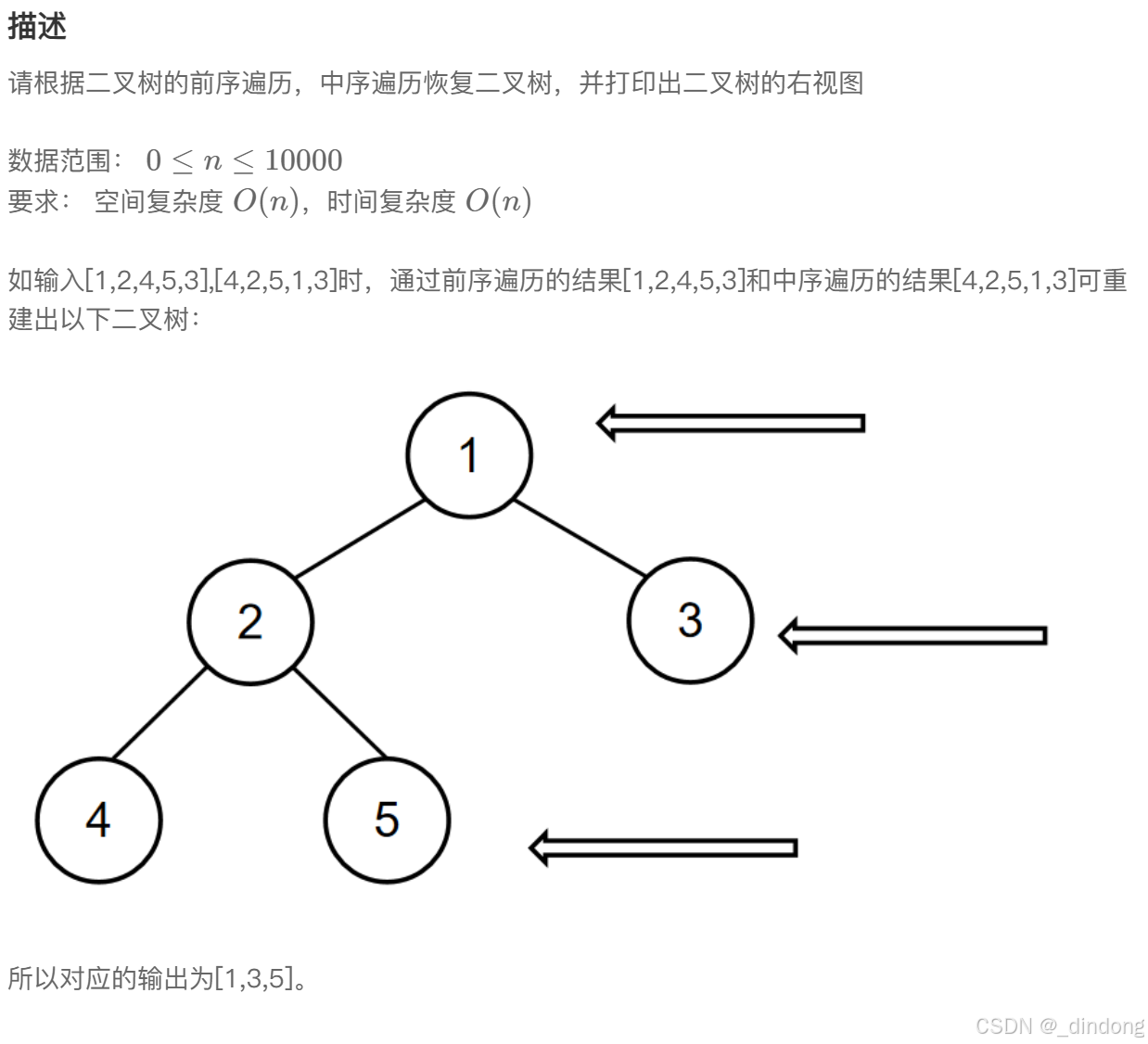

重建二叉树然后输出每层最右边那个
重建二叉树+层序遍历
cpp
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* reConstructBinaryTree(vector<int>& preOrder, vector<int>& vinOrder) {
int n=preOrder.size(),m=vinOrder.size();
if(n==0||m==0)return nullptr;
TreeNode*root=new TreeNode(preOrder[0]);
for(int i=0;i<m;++i)
{
if(preOrder[0]==vinOrder[i])
{
//构建左子树前序遍历
vector<int> LTreePre(preOrder.begin()+1,preOrder.begin()+1+i);
//左子树中序遍历
vector<int> LTreeVin(vinOrder.begin(),vinOrder.begin()+i);
//构建左子树
root->left=reConstructBinaryTree(LTreePre,LTreeVin);
//右子树也是一样
vector<int> RTreePre(preOrder.begin()+i+1,preOrder.end());
vector<int> RTreeVin(vinOrder.begin()+i+1,vinOrder.end());
root->right=reConstructBinaryTree(RTreePre, RTreeVin);
break;
}
}
return root;
}
vector<int> solve(vector<int>& preOrder, vector<int>& inOrder) {
TreeNode* root=reConstructBinaryTree(preOrder,inOrder);
vector<int> ret;
if(!root)return ret;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty())
{
int sz=q.size();
while(sz)
{
TreeNode* t=q.front();
q.pop();
if(sz==1)ret.push_back(t->val);
if(t->left)q.push(t->left);
if(t->right)q.push(t->right);
--sz;
}
}
return ret;
}
};此篇完。