博主介绍:✌全网粉丝10W+,前互联网大厂软件研发、集结硕博英豪成立软件开发工作室,专注于计算机相关专业项目实战6年之久,累计开发项目作品上万套。凭借丰富的经验与专业实力,已帮助成千上万的学生顺利毕业,选择我们,就是选择放心、选择安心毕业✌
> 🍅想要获取完整文章或者源码,或者代做,拉到文章底部即可与我联系了。🍅🍅**感兴趣的可以先收藏起来,点赞、关注不迷路,大家在毕设选题,项目以及论文编写等相关问题都可以给我留言咨询,希望帮助同学们顺利毕业 。**🍅
1、毕业设计:2026年计算机专业毕业设计选题汇总(建议收藏)✅
1、项目介绍
技术栈:
Python语言、YOLO模型、SORT算法、PyQt5界面、目标检测、目标跟踪
2、项目界面
(1)车辆识别检测跟踪
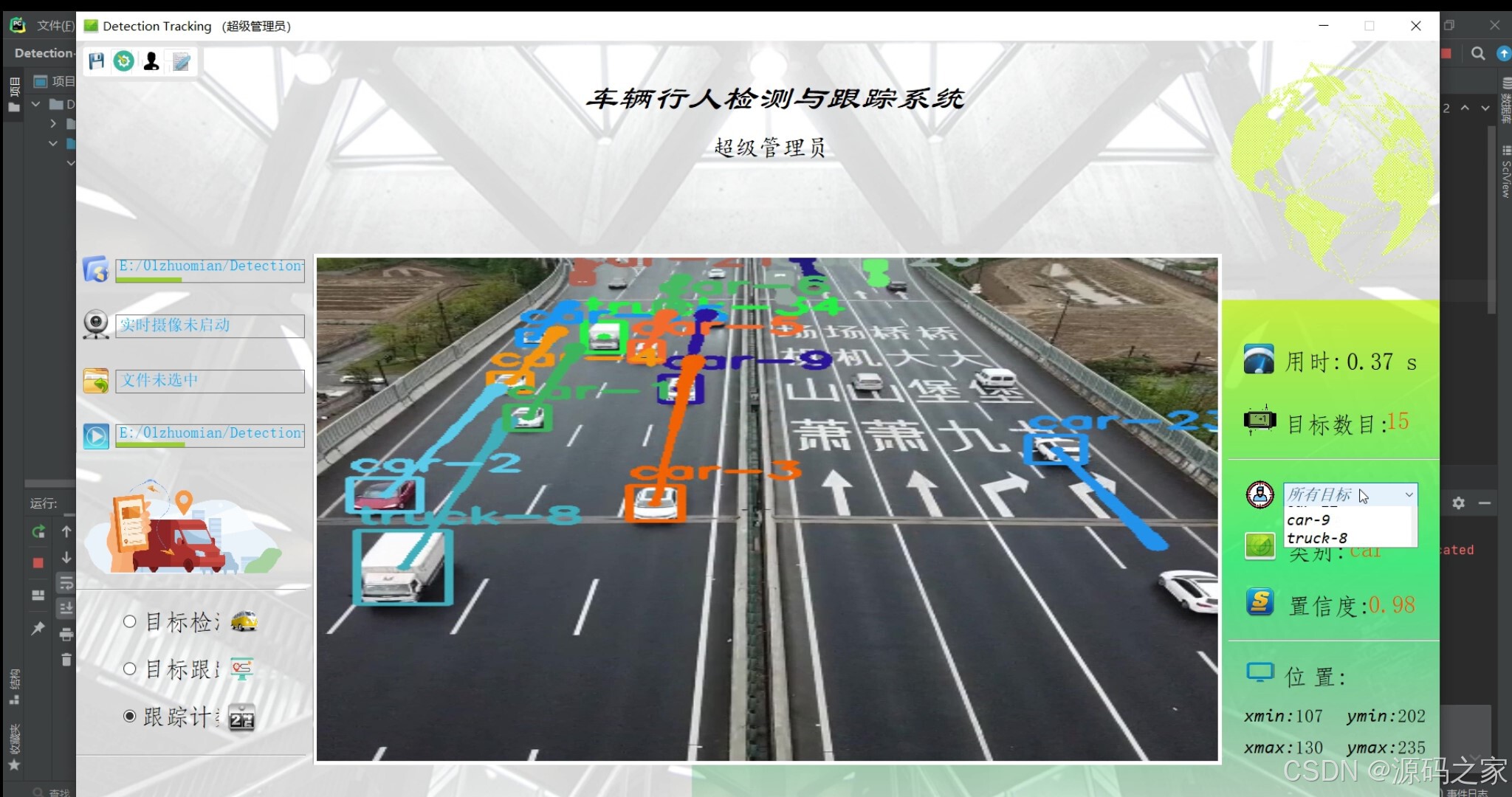
(2)车辆+行人识别检测跟踪

(3)车辆识别检测跟踪
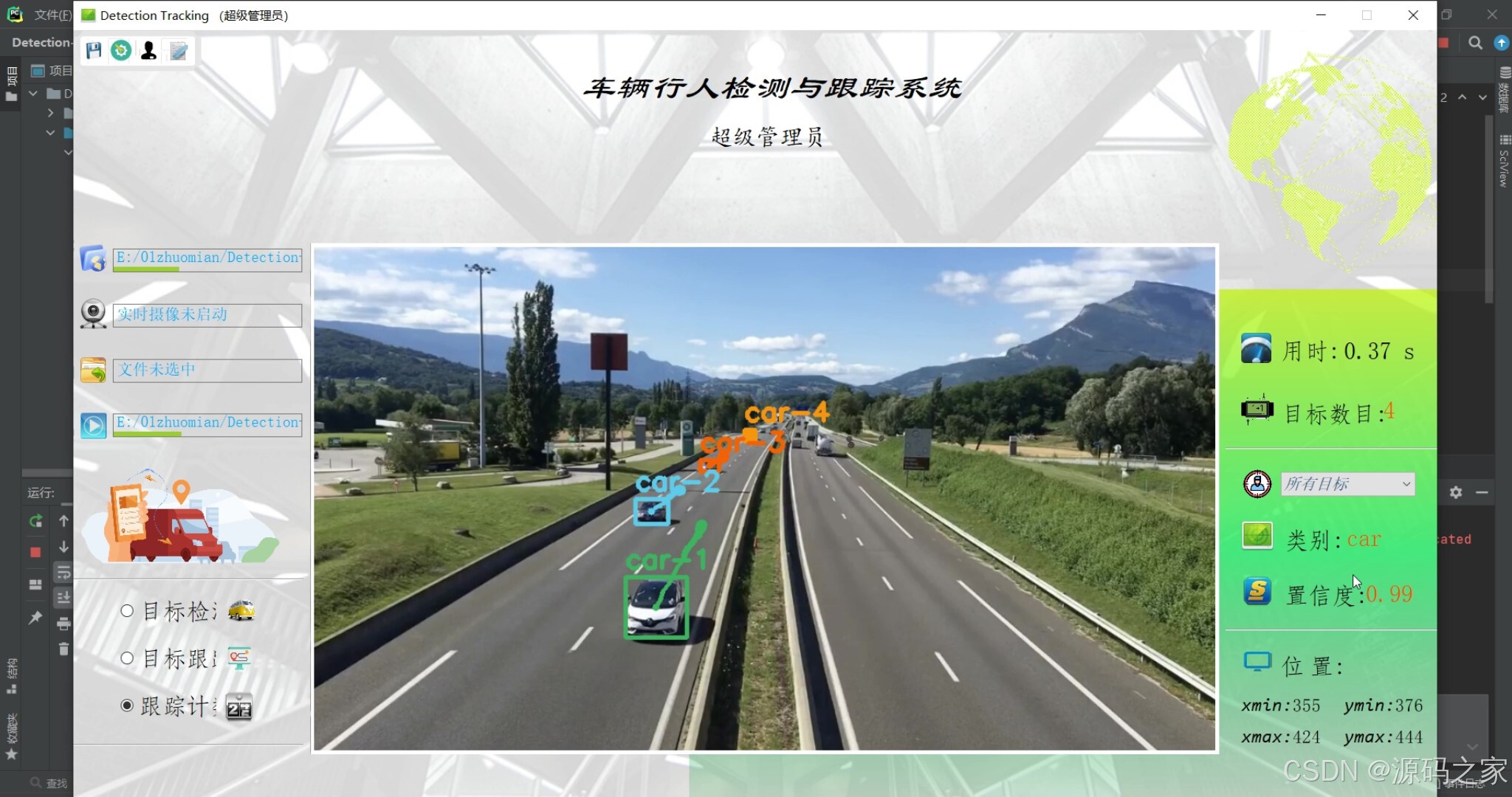
(4)摄像头---识别检测跟踪

(5)行人识别检测跟踪

(6)系统界面

3、项目说明
摘要:
本文详细介绍如何利用深度学习中的YOLO及SORT算法实现车辆、行人等多目标的实时检测和跟踪,并利用PyQt5设计了清新简约的系统UI界面,在界面中既可选择自己的视频、图片文件进行检测跟踪,也可以通过电脑自带的摄像头进行实时处理,可选择训练好的YOLO v3/v4等模型参数。该系统界面优美、检测精度高,功能强大,设计有多目标实时检测、跟踪、计数功能,可自由选择感兴趣的跟踪目标。
4、核心代码
python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# 本程序用于调用摄像头进行车辆行人等多目标检测跟踪
import warnings
import os
import time
from collections import deque
import cv2
import numpy as np
from sort import Sort
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
if __name__ == '__main__':
CAM_NUM = 0 # 摄像头序号
if_save = 1 # 是否需要保存录制的视频,1表示保存
filter_confidence = 0.5 # 用于筛除置信度过低的识别结果
threshold_prob = 0.3 # 用于NMS去除重复的锚框
model_path = "./yolo-obj" # 模型文件的目录
# 载入数据集标签
labelsPath = os.path.sep.join([model_path, "coco.names"])
LABELS = open(labelsPath).read().strip().split("\n")
# 载入模型参数文件及配置文件
weightsPath = os.path.sep.join([model_path, "yolov4-tiny.weights"])
configPath = os.path.sep.join([model_path, "yolov4-tiny.cfg"])
# 初始化用于标记框的颜色
np.random.seed(42)
COLORS = np.random.randint(0, 255, size=(200, 3), dtype="uint8")
# 用于展示目标移动路径
pts = [deque(maxlen=30) for _ in range(9999)]
# 从配置和参数文件中载入模型
print("[INFO] 正在载入模型...")
net = cv2.dnn.readNetFromDarknet(configPath, weightsPath)
ln = net.getLayerNames()
ln = [ln[i[0] - 1] for i in net.getUnconnectedOutLayers()]
# 初始化视频流
vs = cv2.VideoCapture(CAM_NUM)
(W, H) = (None, None)
frameIndex = 0
ret, frame = vs.read()
vw = frame.shape[1]
vh = frame.shape[0]
print("[INFO] 视频尺寸:{} * {}".format(vw, vh))
if if_save:
fourcc = cv2.VideoWriter_fourcc(*'XVID')
output_video = cv2.VideoWriter("./output/captured.avi", fourcc, 20.0, (vw, vh)) # 处理后的视频对象
else:
output_video = None
tracker = Sort() # 实例化追踪器对象
# 遍历视频帧进行检测
while True:
# 逐帧读取画面
(grabbed, frame) = vs.read()
# 获取画面长宽
if W is None or H is None:
(H, W) = frame.shape[:2]
# 将一帧画面读入网络
blob = cv2.dnn.blobFromImage(frame, 1 / 255.0, (416, 416), swapRB=True, crop=False)
net.setInput(blob)
start = time.time()
layerOutputs = net.forward(ln)
end = time.time()
boxes = [] # 用于检测框坐标
confidences = [] # 用于存放置信度值
classIDs = [] # 用于识别的类别序号
# 逐层遍历网络获取输出
for output in layerOutputs:
# loop over each of the detections
for detection in output:
# extract the class ID and confidence (i.e., probability)
# of the current object detection
scores = detection[5:]
classID = np.argmax(scores)
confidence = scores[classID]
# 过滤低置信度值的检测结果
if confidence > filter_confidence:
box = detection[0:4] * np.array([W, H, W, H])
(centerX, centerY, width, height) = box.astype("int")
# 转换标记框
x = int(centerX - (width / 2))
y = int(centerY - (height / 2))
# 更新标记框、置信度值、类别列表
boxes.append([x, y, int(width), int(height)])
confidences.append(float(confidence))
classIDs.append(classID)
# 使用NMS去除重复的标记框
idxs = cv2.dnn.NMSBoxes(boxes, confidences, filter_confidence, threshold_prob)
dets = []
if len(idxs) > 0:
# 遍历索引得到检测结果
for i in idxs.flatten():
(x, y) = (boxes[i][0], boxes[i][1])
(w, h) = (boxes[i][2], boxes[i][3])
dets.append([x, y, x + w, y + h, confidences[i], classIDs[i]])
np.set_printoptions(formatter={'float': lambda x: "{0:0.3f}".format(x)})
dets = np.asarray(dets)
# 使用sort算法,开始进行追踪
tracks = tracker.update(dets)
boxes = [] # 存放追踪到的标记框
indexIDs = []
cls_IDs = []
c = []
for track in tracks:
boxes.append([track[0], track[1], track[2], track[3]])
indexIDs.append(int(track[4]))
cls_IDs.append(int(track[5]))
if len(boxes) > 0:
i = int(0)
for box in boxes: # 遍历所有标记框
(x, y) = (int(box[0]), int(box[1]))
(w, h) = (int(box[2]), int(box[3]))
# 在图像上标记目标框
color = [int(c) for c in COLORS[indexIDs[i] % len(COLORS)]]
cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (w, h), color, 4)
center = (int(((box[0]) + (box[2])) / 2), int(((box[1]) + (box[3])) / 2))
pts[indexIDs[i]].append(center)
thickness = 5
# 显示某个对象标记框的中心
cv2.circle(frame, center, 1, color, thickness)
for j in range(1, len(pts[indexIDs[i]])):
if pts[indexIDs[i]][j - 1] is None or pts[indexIDs[i]][j] is None:
continue
thickness = int(np.sqrt(64 / float(j + 1)) * 2)
cv2.line(frame, (pts[indexIDs[i]][j - 1]), (pts[indexIDs[i]][j]), color, thickness)
# 标记跟踪到的目标和数目
text = "{}-{}".format(LABELS[int(cls_IDs[i])], indexIDs[i])
cv2.putText(frame, text, (x, y - 10), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, color, 3)
i += 1
# 实时显示检测画面
cv2.imshow('Stream', frame)
if if_save:
output_video.write(frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
print("FPS:{}".format(int(0.6/(end-start))))
frameIndex += 1
print("[INFO] 运行结束...")
if if_save:
output_video.release()
vs.release()
exit()🍅✌**感兴趣的可以先收藏起来,点赞关注不迷路,想学习更多项目可以查看主页,大家在毕设选题,项目编程以及论文编写等相关问题都可以给我留言咨询,希望可以帮助同学们顺利毕业!**🍅✌
5、源码获取方式
🍅**由于篇幅限制,获取完整文章或源码、代做项目的,拉到文章底部即可看到个人联系方式。**🍅
点赞、收藏、关注,不迷路,下方查看 👇🏻获取联系方式👇🏻