一.OPENCV图形面积、弧长计算的API介绍
在之前的章节中,我们已经讲解了图形轮廓检测和画框功能。本章节我们将重点介绍如何利用轮廓检测API来计算图形面积,包括矩形、圆形等多种形状的面积计算。这些面积和弧长计算方法在车辆识别、桥梁识别等实际应用中起着重要作用。课程将涉及contourArea、arcLength、minAreaRect、boundingRect、rectangle、line等常用API的使用。
1.1.contourArea的API讲解

**contourArea**函数主要用于计算轮廓曲线包围的区域面积,即图像中目标物体的实际面积。如上图所示,该函数会计算白色区域的面积,其内部实现通常采用微积分等数学方法进行面积计算。
函数原型:
cpp
CV_EXPORTS_W double contourArea(InputArray contour, bool oriented = false);参数说明:
contour:输入轮廓的点集数据oriented:可选参数,用于指定是否返回带方向的面积值(当设为true时,返回值可能为负数)
返回值: 返回计算得到的轮廓面积值(单位:像素)
1.2. arcLength的API讲解

arcLength 函数主要用于计算轮廓的周长,即图形边缘的曲线总长度。如下图所示,该函数通过计算轮廓点之间的连线长度来获取轮廓周长。
函数定义:
cpp
CV_EXPORTS_W double arcLength(InputArray curve, bool closed);参数说明:
curve:输入轮廓的2D像素点集closed:布尔值,表示轮廓是否闭合(true表示闭合)
返回值: 计算得到的轮廓周长数值
1.3. minAreaRect的API讲解
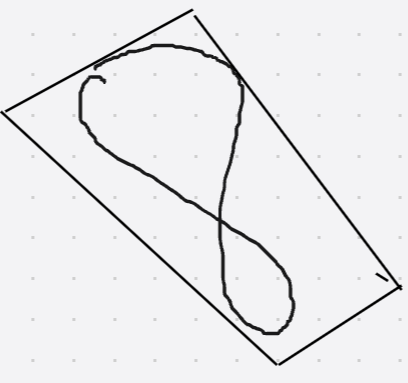
minAreaRect的核心功能是计算最小外接矩形,即能够完全包含所有给定点的最小面积矩形。如图所示,数字"8"的形状被minAreaRect生成的矩形完美包围。这个矩形不仅能完整覆盖整个形状的所有点,还具有旋转特性 - 即使"8"存在倾斜角度,最小矩形也能准确贴合包裹。
cpp
CV_EXPORTS_W RotatedRect minAreaRect( InputArray points );第一个参数:points输入的二维点数,可以Mat类型也可以是std::vector的向量类型
返回值:RotatedRect 的矩形对象,它表示的是一个轮廓的最小外接矩形,我们来看看RotatedRect结构体成员变量
cpp
template<typename _Tp> class Point_
{
public:
typedef _Tp value_type;
//! default constructor
Point_();
Point_(_Tp _x, _Tp _y);
Point_(const Point_& pt);
Point_(const Size_<_Tp>& sz);
Point_(const Vec<_Tp, 2>& v);
Point_& operator = (const Point_& pt);
//! conversion to another data type
template<typename _Tp2> operator Point_<_Tp2>() const;
//! conversion to the old-style C structures
operator Vec<_Tp, 2>() const;
//! dot product
_Tp dot(const Point_& pt) const;
//! dot product computed in double-precision arithmetics
double ddot(const Point_& pt) const;
//! cross-product
double cross(const Point_& pt) const;
//! checks whether the point is inside the specified rectangle
bool inside(const Rect_<_Tp>& r) const;
_Tp x; //!< x coordinate of the point
_Tp y; //!< y coordinate of the point
};center: 旋转矩形的质心
****size:****旋转矩形的宽度和高度
****angle:****顺时针的旋转角度。
RotatedRect 矩形四个点的确定
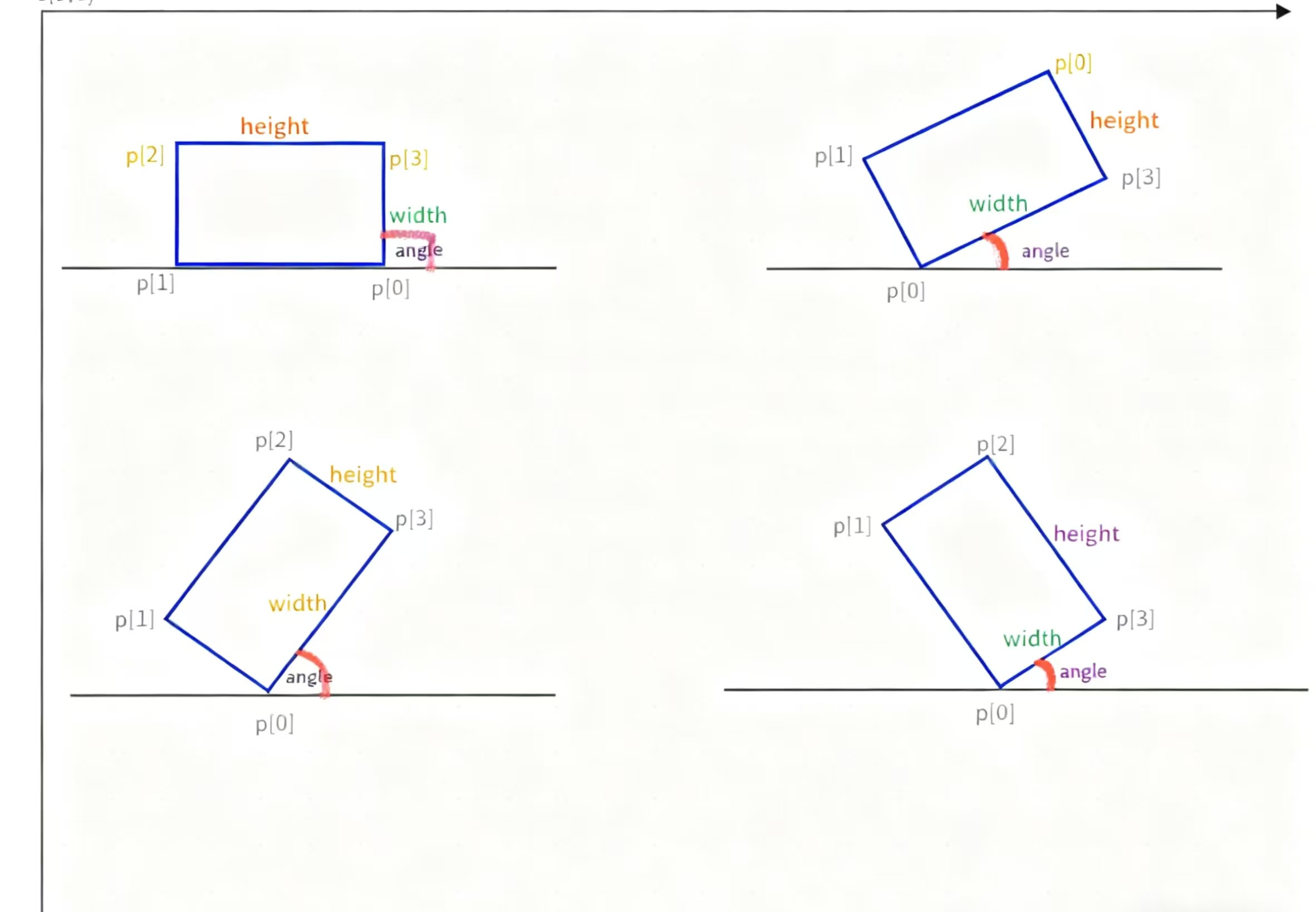
在RotatedRect中,矩形的四个顶点通常用Point2f表示,其中p[0]点的确定尤为重要。p[0]的位置主要分为两种情况:
- 当最小外接矩形不与坐标轴平行时,Y坐标最大的点即为p[0],如图2、3、4所示
- 当最小外接矩形与坐标轴平行时,会有两个Y坐标最大的点,如图1所示
1.4. boundingRect的API讲解
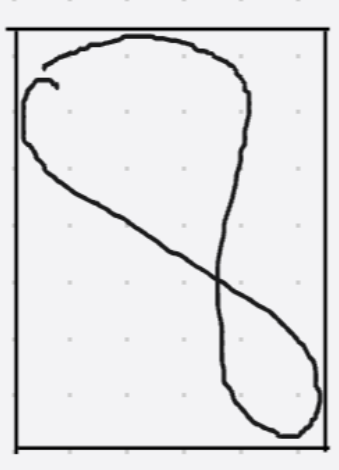
boundingRect的核心功能是计算图形轮廓的最小垂直边界矩形,该矩形必须与图像的上下边界平行。如上图所示:我们仍以数字8的形状为例,它保持在原先的位置。boundingRect生成的矩形能够完整包围数字8的垂直边界。
cpp
CV_EXPORTS_W Rect boundingRect( InputArray array );第一个参数: array输入的灰度图像或者2D点集,数据类型为vector或者Mat矩阵数据
返回值:Rect的矩形对象,它表示的是物体轮廓的最大外接矩形。我们来看看Rect主要的成员变量
cpp
template<typename _Tp> class Point_
{
public:
typedef _Tp value_type;
//! default constructor
Point_();
Point_(_Tp _x, _Tp _y);
Point_(const Point_& pt);
Point_(const Size_<_Tp>& sz);
Point_(const Vec<_Tp, 2>& v);
Point_& operator = (const Point_& pt);
//! conversion to another data type
template<typename _Tp2> operator Point_<_Tp2>() const;
//! conversion to the old-style C structures
operator Vec<_Tp, 2>() const;
//! dot product
_Tp dot(const Point_& pt) const;
//! dot product computed in double-precision arithmetics
double ddot(const Point_& pt) const;
//! cross-product
double cross(const Point_& pt) const;
//! checks whether the point is inside the specified rectangle
bool inside(const Rect_<_Tp>& r) const;
_Tp x; //!< x coordinate of the point
_Tp y; //!< y coordinate of the point
};****x:****矩形的x坐标轴
y: 矩形的y坐标轴
****width:****矩形的宽度
****height:****矩形的高度
1.5. rectangle的API讲解
rectangle函数的作用是绘制矩形,它有两种表示形式
1.5.1. 以两个顶点的方式画矩形
cpp
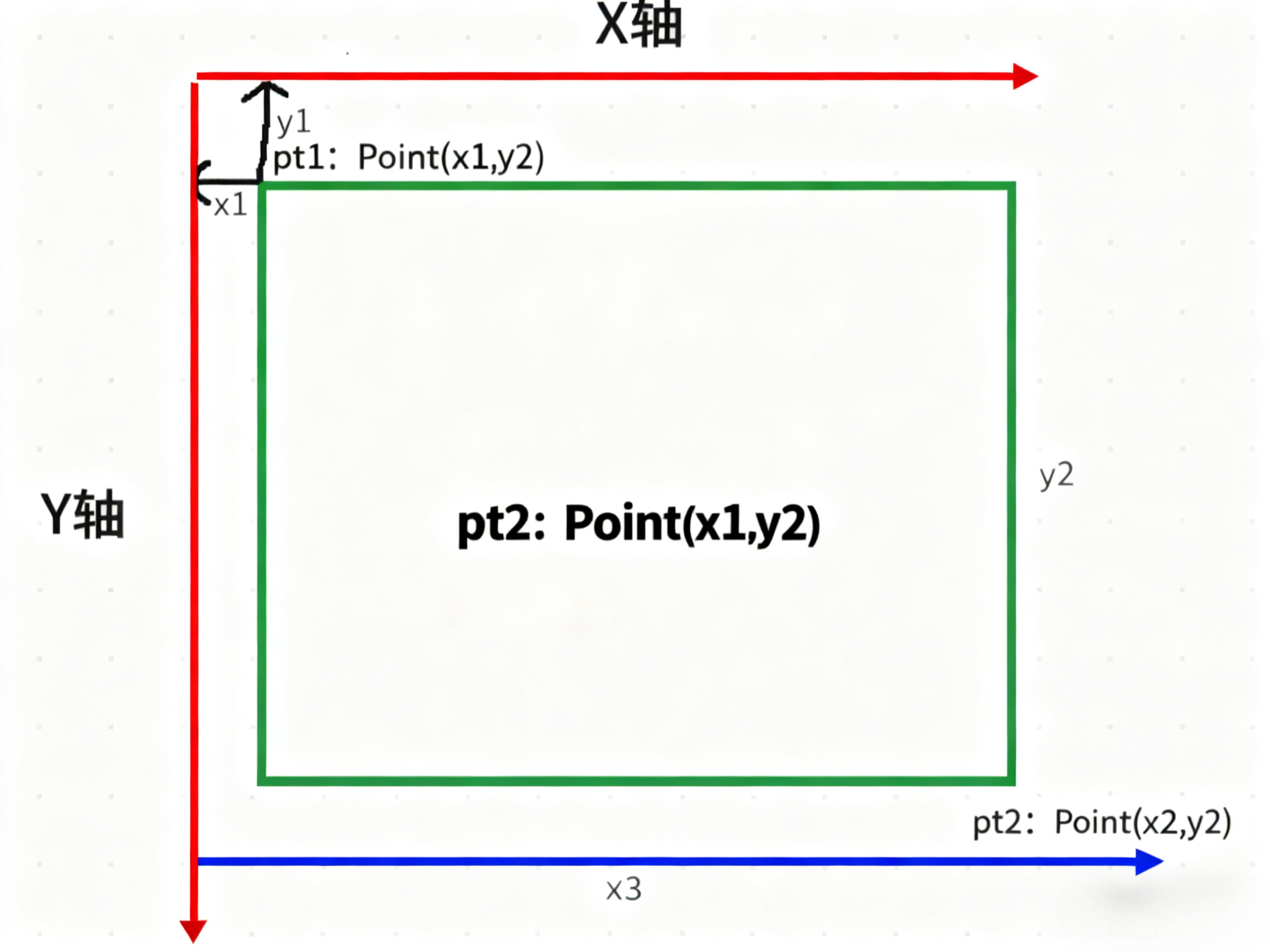
void cv::rectangle(InputOutputArray img, Point pt1, Point pt2, const Scalar & color, int thickness = 1,int lineType = LINE_8, int shift = 0)****第一个参数:****输入的矩阵图像数据
****第二个参数:****pt1是矩形的一个顶点,左上角的顶点
****第三个参数:****pt2矩形中与pt1相对的顶点,也就是两个点在对角线上,也就是右下角的顶点
****第四个参数:****Scalar颜色的标量
****第五个参数:****thickness线宽
****第六个参数:****lineType线的类型,默认是LINE_8就行,具体的类型如下代码:
cpp
//! type of line
enum LineTypes {
FILLED = -1,
LINE_4 = 4, //!< 4-connected line
LINE_8 = 8, //!< 8-connected line
LINE_AA = 16 //!< antialiased line
};****第七个参数:****shift坐标的小数点位,默认为0就可以
1.5.2.以Rect的方式画矩形
cpp
void cv::rectangle(InputOutputArray img, Rect rec, const Scalar & color, int thickness = 1,int lineType = LINE_8, int shift = 0) ****第一个参数:****输入的矩阵图像数据
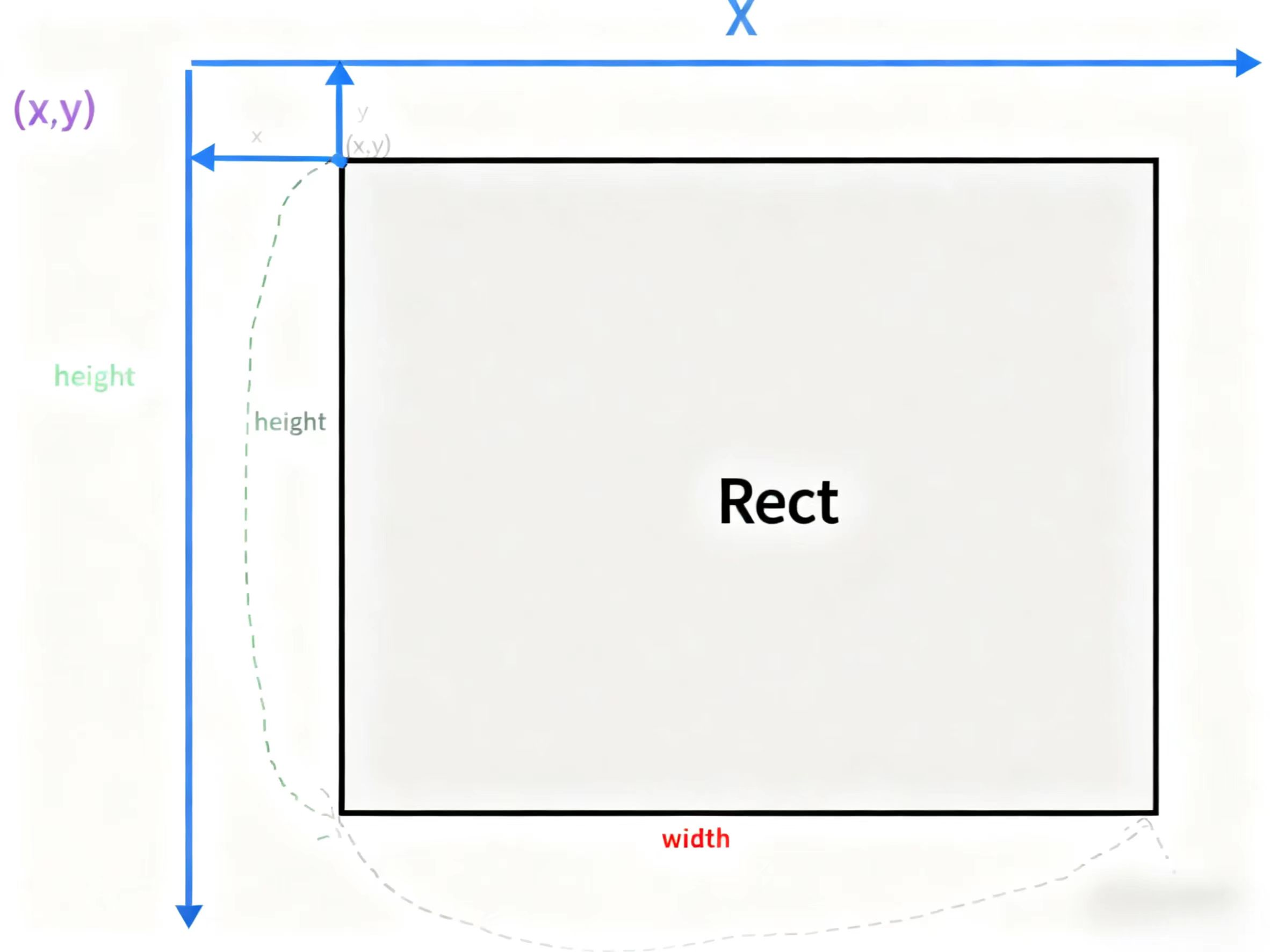
****第二个参数:****Rect的结构体,我们来看看这个Rect的重要成员变量
cpp
template<typename _Tp> class Rect_
{
public:
typedef _Tp value_type;
//! default constructor
Rect_();
Rect_(_Tp _x, _Tp _y, _Tp _width, _Tp _height);
Rect_(const Rect_& r);
Rect_(const Point_<_Tp>& org, const Size_<_Tp>& sz);
Rect_(const Point_<_Tp>& pt1, const Point_<_Tp>& pt2);
Rect_& operator = ( const Rect_& r );
//! the top-left corner
Point_<_Tp> tl() const;
//! the bottom-right corner
Point_<_Tp> br() const;
//! size (width, height) of the rectangle
Size_<_Tp> size() const;
//! area (width*height) of the rectangle
_Tp area() const;
//! true if empty
bool empty() const;
//! conversion to another data type
template<typename _Tp2> operator Rect_<_Tp2>() const;
//! checks whether the rectangle contains the point
bool contains(const Point_<_Tp>& pt) const;
_Tp x; //!< x coordinate of the top-left corner
_Tp y; //!< y coordinate of the top-left corner
_Tp width; //!< width of the rectangle
_Tp height; //!< height of the rectangle
};x:矩形的x坐标轴
y: 矩形的y坐标轴
****width:****矩形的宽度
****height:****矩形的高度
****第三个参数:****Scalar颜色的标量
****第四个参数:****thickness线宽,默认是1
****第五个参数:****lineType线的类型,默认是LINE_8就行,line的类型如下:
cpp
//! type of line
enum LineTypes {
FILLED = -1,
LINE_4 = 4, //!< 4-connected line
LINE_8 = 8, //!< 8-connected line
LINE_AA = 16 //!< antialiased line
};****第六个参数:****shift坐标点的小数点位数
1.6. line的API讲解
line函数的主要作用是通过两个点绘制直线
cpp
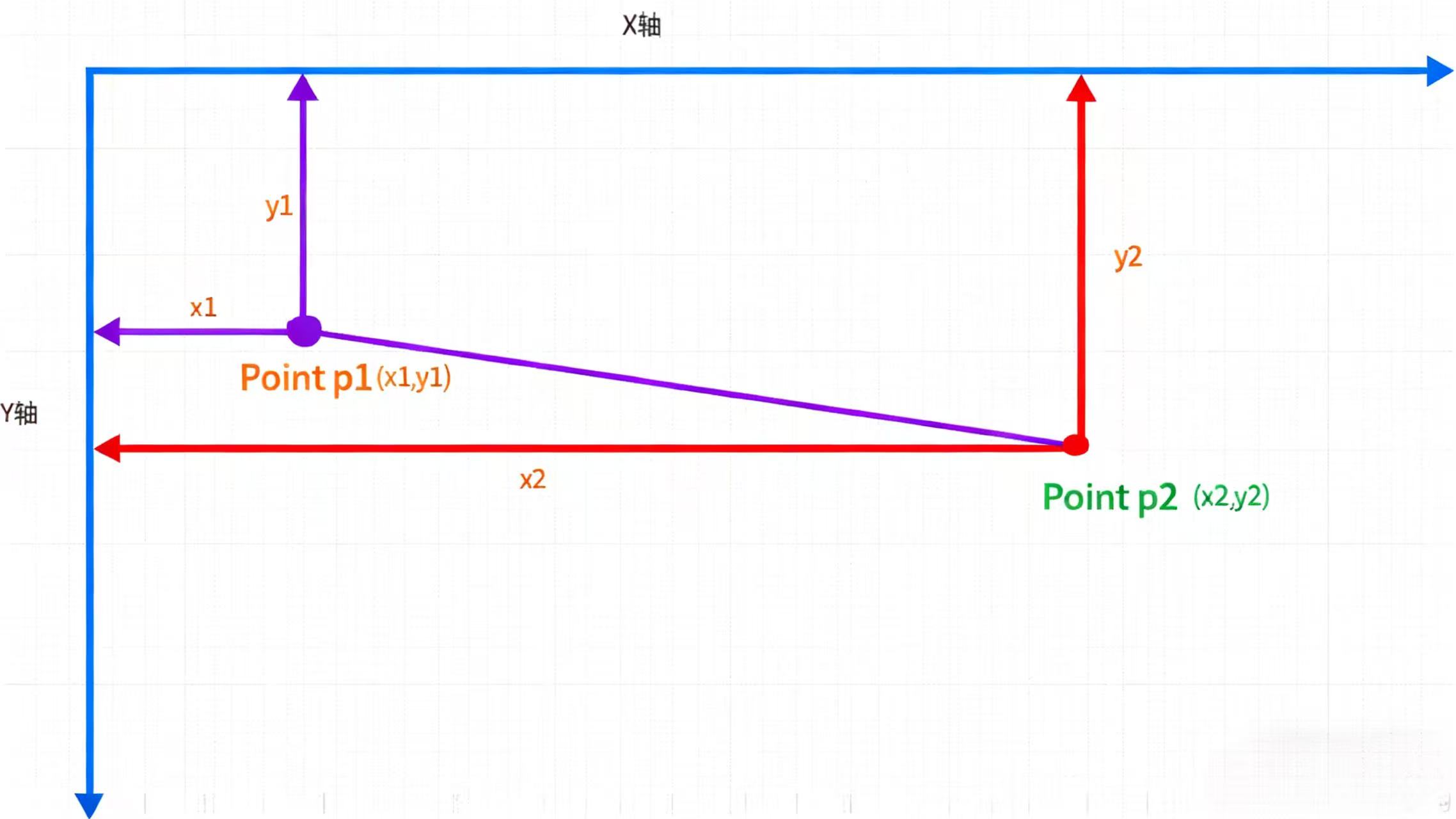
CV_EXPORTS_W void line(InputOutputArray img, Point pt1, Point pt2, const Scalar& color,int thickness = 1, int lineType = LINE_8, int shift = 0);****第一个参数:****输入的矩阵图像数据
第二个参数: pt1是线的起始坐标,也就是图上x1坐标和y1坐标
****第三个参数:****pt2是线的终点坐标,也就是图上x2坐标和y2坐标
第四个参数: Scalar是颜色标量,绘制直线的颜色
****第五个参数:****thickness它是线的粗细程度,默认为1
****第六个参数:****lineType线的类型,默认是LINE_8就行,具体的类型
****第七个参数:****shift坐标点的小数点位数
1.7. threshold的API讲解
threshold主要用途是把图像进行二值化处理,二值化操作可以使图像中的数据量大大降低图像的复杂度,并且能够凸显出图像中的轮廓。
cpp
CV_EXPORTS_W double threshold( InputArray src, OutputArray dst, double thresh, double maxval, int type );第一个参数: src源图像,可以是8位灰度图,也可以是32位的三通道图像
****第二个参数:****dst目标图像
第三个参数: thres h 阈值
第四个参数:maxval 二值图像中灰度最大值,maxval只能在THRESH_BINARY 和THRESH_BINARY_INV 有用,但是其他选项也需要填这个值,不能空着。
第五个参数:type阈值操作类型,具体的阈值操作如下图:
THRESH_BINARY:二值化阈值处理将图像转换为仅包含两个灰度值的二值图像。具体规则为:当像素灰度值超过设定阈值时,将其设为最大值(maxval);若像素灰度值不高于阈值,则将其置为0。

THRESH_BINARY_INV(反二值化阈值处理)同样会将图像转换为二值图像,但其处理逻辑与THRESH_BINARY相反。具体表现为:
- 当像素灰度值大于阈值时,该像素值设为0
- 当像素灰度值小于或等于阈值时,该像素值设为预设的最大值(maxval)

THRESH_TRUNC(截断阈值化)是一种图像处理方法,其规则如下:
- 对于像素值超过设定阈值的点,将其值设为该阈值
- 对于像素值小于或等于阈值的点,保持原值不变
例如设定阈值为127时:
- 像素值大于127的点会被设为127
- 像素值≤127的点保持不变

THRESH_TOZERO_INV 是一种阈值处理方式,其规则如下:
- 当像素值大于设定阈值时,将该像素置为0
- 当像素值小于或等于阈值时,保持原值不变
例如设定阈值为127时:
- 像素值>127 → 置为0
- 像素值≤127 → 保持原值

THRESH_TOZERO阈值处理:当像素值小于或等于设定阈值时,该像素将被置零;高于阈值的像素则保持原值。例如设定阈值为127时,所有≤127的像素会被归零,而>127的像素则保留原始数值。

THRESH_OTSU:OTSU方法会遍历所有可能的阈值,从而找到一个最佳的阈值。值得注意的是,在使用OTSU方法的时候需要把阈值设定为0。这个时候,threshold会自动寻找最优的值。
