1、简介
作为一个内核工程师, 会经常见到vmlinux ELF文件,如果没有对这个ELF文件熟悉,不能称之为合格的内核工程师。在分析中断向量表的定义和内存布局时,发现自己没有写过一个和内核vmlinux ELF布局的文章。下面开始详细介绍vmlinux ELF是如何生成的以及段布局。
2、ELF布局
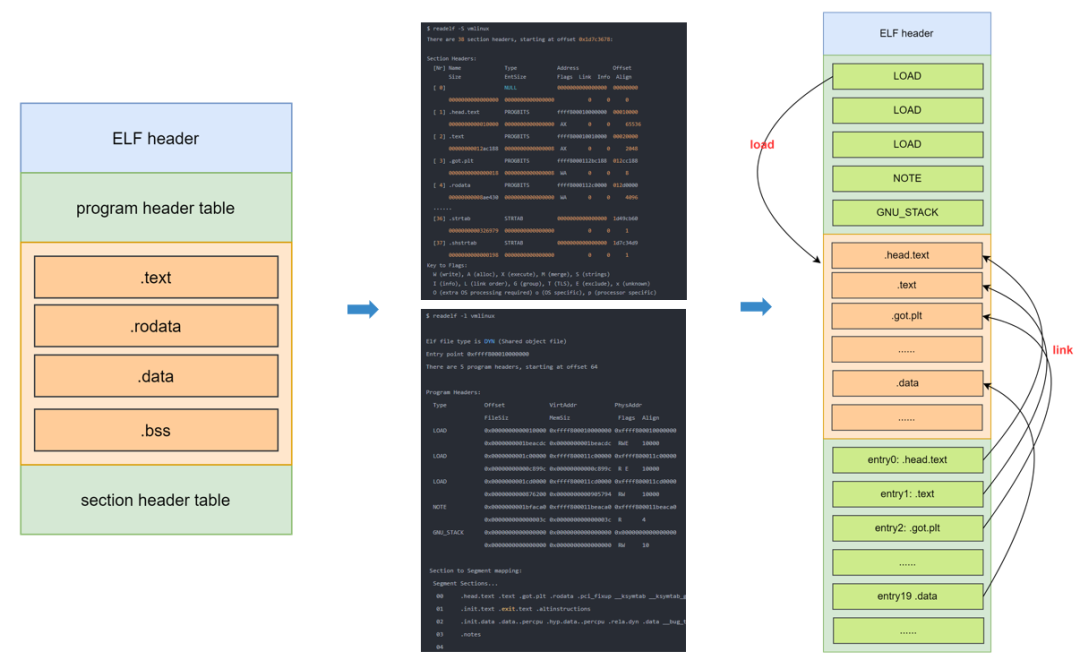
vmlinux 属于 ELF 文件,要想了解如何启动 vmlinux,首先需要知道 ELF 的格式。
- text段
代码段,通常是指用来存放程序执行代码的一块内存区域。这部分区域的大小在程序运行前就已经确定。
- data段
数据段,通常是指用来存放程序中已初始化的全局变量的一块内存区域。数据段属于静态内存分配。
- bss段
通常是指用来存放程序中未初始化的全局变量和静态变量的一块内存区域。BSS段属于静态内存分配。
- init段
linux定义的一种初始化过程中才会用到的段,一旦初始化完成,那么这些段所占用的内存会被释放掉,后续会继续说明。
3、vmlinux 入口:第一行运行的代码
Linux启动,会启动内核编译后的文件 vmlinux,vmlinux 是一个 ELF 文件,按照 ./arch/arm64/kernel/vmlinux.lds 设定的规则进行链接,vmlinux.lds 是 vmlinux.lds.S 编译之后生成的。所以为了确定 vmlinux 内核的起始地址, 首先通过 vmlinux.lds.S 链接脚本进行分析。如下所示:
$ readelf -h vmlinux
ELF Header:
Magic: 7f 45 4c 46 02 01 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 00
Class: ELF64
Data: 2's complement, little endian
Version: 1 (current)
OS/ABI: UNIX - System V
ABI Version: 0
Type: DYN (Shared object file)
Machine: AArch64
Version: 0x1
Entry point address: 0xffff800010000000
Start of program headers: 64 (bytes into file)
Start of section headers: 494679672 (bytes into file)
Flags: 0x0
Size of this header: 64 (bytes)
Size of program headers: 56 (bytes)
Number of program headers: 5
Size of section headers: 64 (bytes)
Number of section headers: 38
Section header string table index: 37
$ readelf -l vmlinux
Elf file type is DYN (Shared object file)
Entry point 0xffff800010000000
There are 5 program headers, starting at offset 64
Program Headers:
Type Offset VirtAddr PhysAddr
FileSiz MemSiz Flags Align
LOAD 0x0000000000010000 0xffff800010000000 0xffff800010000000
0x0000000001beacdc 0x0000000001beacdc RWE 10000
LOAD 0x0000000001c00000 0xffff800011c00000 0xffff800011c00000
0x00000000000c899c 0x00000000000c899c R E 10000
LOAD 0x0000000001cd0000 0xffff800011cd0000 0xffff800011cd0000
0x0000000000876200 0x0000000000905794 RW 10000
NOTE 0x0000000001bfaca0 0xffff800011beaca0 0xffff800011beaca0
0x000000000000003c 0x000000000000003c R 4
GNU_STACK 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000 RW 10
Section to Segment mapping:
Segment Sections...
00 .head.text .text .got.plt .rodata .pci_fixup __ksymtab __ksymtab_gpl __ksymtab_strings __param __modver __ex_table .notes
01 .init.text .exit.text .altinstructions
02 .init.data .data..percpu .hyp.data..percpu .rela.dyn .data __bug_table .mmuoff.data.write .mmuoff.data.read .pecoff_edata_padding .bss
03 .notes
04通过上面的查询可知,此 vmlinux 为一个 aarch64 架构平台的 ELF 可执行文件,其程序入口的地址为 0xffff800010000000,此段对应的 section 为.head.text .text .got.plt......,所以 vmlinux 的入口在 .head.text 文本段。
详细查看各个段:readelf -S vmlinux
There are 38 section headers, starting at offset 0xd7dc238:
Section Headers:
[Nr] Name Type Address Offset
Size EntSize Flags Link Info Align
[ 0] NULL 0000000000000000 00000000
0000000000000000 0000000000000000 0 0 0
[ 1] .head.text PROGBITS ffffffc010080000 00010000
0000000000001000 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 4096
[ 2] .text PROGBITS ffffffc010081000 00011000
00000000008dcfd8 0000000000000008 AX 0 0 2048
[ 3] .rodata PROGBITS ffffffc010960000 008f0000
00000000003032b8 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 65536
[ 4] .modinfo PROGBITS ffffffc010c632b8 00bf32b8
00000000000115d2 0000000000000000 A 0 0 1
[ 5] .init.eh_frame PROGBITS ffffffc010c74890 00c04890
0000000000001bb0 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8
[ 6] .pci_fixup PROGBITS ffffffc010c76440 00c06440
00000000000022b0 0000000000000000 A 0 0 16
[ 7] __ksymtab PROGBITS ffffffc010c786f0 00c086f0
000000000000d500 0000000000000000 A 0 0 4
[ 8] __ksymtab_gpl PROGBITS ffffffc010c85bf0 00c15bf0
000000000000da04 0000000000000000 A 0 0 4
[ 9] __ksymtab_strings PROGBITS ffffffc010c935f4 00c235f4
000000000002c292 0000000000000000 A 0 0 1
[10] __param PROGBITS ffffffc010cbf888 00c4f888
0000000000002710 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8
[11] __modver PROGBITS ffffffc010cc1f98 00c51f98
00000000000000c0 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8
[12] __ex_table PROGBITS ffffffc010cc3000 00c53000
0000000000001f10 0000000000000000 A 0 0 8
[13] .notes NOTE ffffffc010cc4f10 00c54f10
000000000000003c 0000000000000000 A 0 0 4
[14] .init.text PROGBITS ffffffc010cd0000 00c60000
0000000000049180 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 16
[15] .exit.text PROGBITS ffffffc010d19180 00ca9180
0000000000002e1c 0000000000000000 AX 0 0 4
[16] .altinstructions PROGBITS ffffffc010d1bf9c 00cabf9c
0000000000024bc4 0000000000000000 A 0 0 1
[17] .init.data PROGBITS ffffffc010d41000 00cd1000
00000000000169b0 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 256
[18] .data..percpu PROGBITS ffffffc010d58000 00ce8000
000000000000c258 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 64
[19] .rela.dyn RELA ffffffc010d64258 00cf4258
0000000000100050 0000000000000018 A 0 0 8
[20] .data PROGBITS ffffffc010e70000 00e00000
000000000008f640 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 4096
[21] .got.plt PROGBITS ffffffc010eff640 00e8f640
0000000000000018 0000000000000008 WA 0 0 8
[22] __bug_table PROGBITS ffffffc010eff658 00e8f658
0000000000010824 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 4
[23] .mmuoff.data[...] PROGBITS ffffffc010f10000 00ea0000
0000000000000018 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 2048
[24] .mmuoff.data.read PROGBITS ffffffc010f10800 00ea0800
0000000000000008 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 8
[25] .pecoff_edat[...] PROGBITS ffffffc010f10808 00ea0808
00000000000001f8 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 1
[26] .bss NOBITS ffffffc010f11000 00ea0a00
0000000000060628 0000000000000000 WA 0 0 4096
[27] .comment PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00ea0a00
000000000000005a 0000000000000001 MS 0 0 1
[28] .debug_line PROGBITS 0000000000000000 00ea0a5a
00000000011db9fa 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[29] .debug_info PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0207c454
0000000009285ce2 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[30] .debug_abbrev PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0b302136
000000000048bc4e 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[31] .debug_aranges PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0b78dd90
0000000000021cc0 0000000000000000 0 0 16
[32] .debug_str PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0b7afa50
0000000000291d0d 0000000000000001 MS 0 0 1
[33] .debug_ranges PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0ba41760
0000000000ca18c0 0000000000000000 0 0 16
[34] .debug_loc PROGBITS 0000000000000000 0c6e3020
0000000000d6e817 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[35] .symtab SYMTAB 0000000000000000 0d451838
0000000000230d90 0000000000000018 36 76147 8
[36] .strtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 0d6825c8
0000000000159acb 0000000000000000 0 0 1
[37] .shstrtab STRTAB 0000000000000000 0d7dc093
000000000000019f 0000000000000000 0 0 1
Key to Flags:
W (write), A (alloc), X (execute), M (merge), S (strings), I (info),
L (link order), O (extra OS processing required), G (group), T (TLS),
C (compressed), x (unknown), o (OS specific), E (exclude),
p (processor specific)注意一个点: .head.text 的大小 0x1000, 一个页的大小。后面紧接着就是 exceptions.
3.1 .head.text 文本段
通过 vmlinux.lds.S 找到 vmlinux 的入口函数。具体分析如下:
/* SPDX-License-Identifier: GPL-2.0 */
/*
* ld script to make ARM Linux kernel
* taken from the i386 version by Russell King
* Written by Martin Mares <mj@atrey.karlin.mff.cuni.cz>
*/
#define RO_EXCEPTION_TABLE_ALIGN 8
#define RUNTIME_DISCARD_EXIT
#include <asm-generic/vmlinux.lds.h>
#include <asm/cache.h>
#include <asm/hyp_image.h>
#include <asm/kernel-pgtable.h>
#include <asm/memory.h>
#include <asm/page.h>
#include "image.h"
OUTPUT_ARCH(aarch64)
ENTRY(_text)根据链接脚本语法,可以知道 OUTPUT_ARCH 关键字指定了链接之后的输出文件的体系结构是 aarch64。ENTRY 关键字指定了输出文件 vmlinux 的入口 地址是 _text, 因此只需找到 _text 的定义就可以知道 vmlinux 的入口函数。接下来的代码是:
SECTIONS
{
/*
* XXX: The linker does not define how output sections are
* assigned to input sections when there are multiple statements
* matching the same input section name. There is no documented
* order of matching.
*/
/DISCARD/ : {
ARM_EXIT_DISCARD(EXIT_TEXT)
ARM_EXIT_DISCARD(EXIT_DATA)
EXIT_CALL
*(.discard)
*(.discard.*)
*(.interp .dynamic)
*(.dynsym .dynstr .hash .gnu.hash)
*(.eh_frame)
}
. = KIMAGE_VADDR + TEXT_OFFSET; //这个当前段开始的位置
.head.text : {
_text = .; //将上面的段的开始位置赋值给_text
HEAD_TEXT
}
.text : { /* Real text segment */
_stext = .; /* Text and read-only data */
__exception_text_start = .;
*(.exception.text)
__exception_text_end = .;
IRQENTRY_TEXT
SOFTIRQENTRY_TEXT
ENTRY_TEXT
TEXT_TEXT
SCHED_TEXT
CPUIDLE_TEXT
LOCK_TEXT
KPROBES_TEXT
HYPERVISOR_TEXT
IDMAP_TEXT
HIBERNATE_TEXT
TRAMP_TEXT
*(.fixup)
*(.gnu.warning)
. = ALIGN(16);
*(.got) /* Global offset table */
}
. = ALIGN(SEGMENT_ALIGN);
_etext = .; /* End of text section */
RO_DATA(PAGE_SIZE) /* everything from this point to */
EXCEPTION_TABLE(8) /* __init_begin will be marked RO NX */
NOTES
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
idmap_pg_dir = .;
. += IDMAP_DIR_SIZE;
idmap_pg_end = .;
#ifdef CONFIG_UNMAP_KERNEL_AT_EL0
tramp_pg_dir = .;
. += PAGE_SIZE;
#endif
reserved_pg_dir = .;
. += PAGE_SIZE;
swapper_pg_dir = .;
. += PAGE_SIZE;
. = ALIGN(SEGMENT_ALIGN);
__init_begin = .;
__inittext_begin = .;
INIT_TEXT_SECTION(8)
__exittext_begin = .;
.exit.text : {
ARM_EXIT_KEEP(EXIT_TEXT)
}
__exittext_end = .;
. = ALIGN(4);
.altinstructions : {
__alt_instructions = .;
*(.altinstructions)
__alt_instructions_end = .;
}
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
__inittext_end = .;
__initdata_begin = .;
.init.data : {
INIT_DATA
INIT_SETUP(16)
INIT_CALLS
CON_INITCALL
INIT_RAM_FS
*(.init.rodata.* .init.bss) /* from the EFI stub */
}
.exit.data : {
ARM_EXIT_KEEP(EXIT_DATA)
}
PERCPU_SECTION(L1_CACHE_BYTES)
.rela.dyn : ALIGN(8) {
*(.rela .rela*)
}
__rela_offset = ABSOLUTE(ADDR(.rela.dyn) - KIMAGE_VADDR);
__rela_size = SIZEOF(.rela.dyn);
#ifdef CONFIG_RELR
.relr.dyn : ALIGN(8) {
*(.relr.dyn)
}
__relr_offset = ABSOLUTE(ADDR(.relr.dyn) - KIMAGE_VADDR);
__relr_size = SIZEOF(.relr.dyn);
#endif
. = ALIGN(SEGMENT_ALIGN);
__initdata_end = .;
__init_end = .;
_data = .;
_sdata = .;
RW_DATA_SECTION(L1_CACHE_BYTES, PAGE_SIZE, THREAD_ALIGN)
/*
* Data written with the MMU off but read with the MMU on requires
* cache lines to be invalidated, discarding up to a Cache Writeback
* Granule (CWG) of data from the cache. Keep the section that
* requires this type of maintenance to be in its own Cache Writeback
* Granule (CWG) area so the cache maintenance operations don't
* interfere with adjacent data.
*/
.mmuoff.data.write : ALIGN(SZ_2K) {
__mmuoff_data_start = .;
*(.mmuoff.data.write)
}
. = ALIGN(SZ_2K);
.mmuoff.data.read : {
*(.mmuoff.data.read)
__mmuoff_data_end = .;
}
PECOFF_EDATA_PADDING
__pecoff_data_rawsize = ABSOLUTE(. - __initdata_begin);
_edata = .;
BSS_SECTION(0, 0, 0)
. = ALIGN(PAGE_SIZE);
init_pg_dir = .;
. += INIT_DIR_SIZE;
init_pg_end = .;
__pecoff_data_size = ABSOLUTE(. - __initdata_begin);
_end = .;
STABS_DEBUG
HEAD_SYMBOLS
}对上面做个简化:
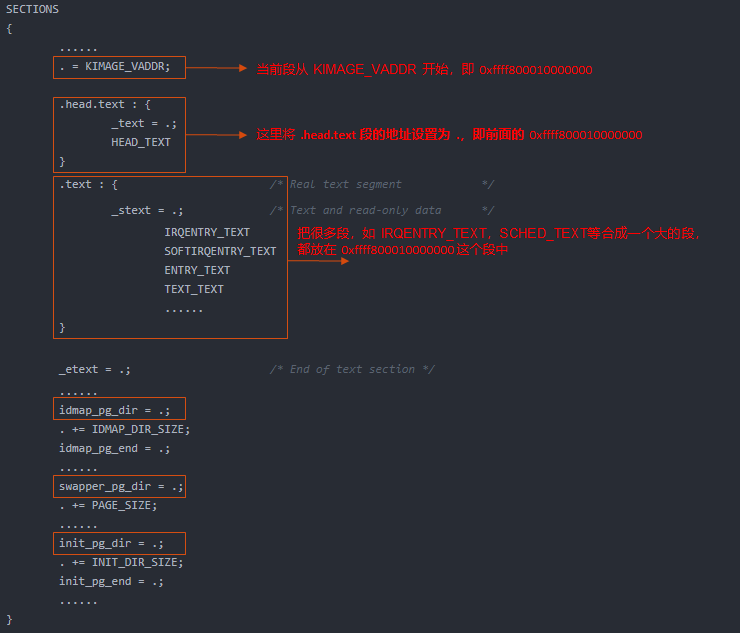
上面这个简化图和 readelf -S vmlinux 看到的各个段是一致的。
-
上图中的宏 HEAD_TEXT 定义在文件 include/asm-generic/vmlinux.lds.S 中,其定义为 .head.text 文本段。
-
上图中的 idmap_pg_dir,init_pg_dir 是页表映射,idmap_pg_dir 是 identity mapping 用到的页表,init_pg_dir 是 kernel_image_mapping 用到的页表。
/* include/asm-generic/vmlinux.lds.h文件 /
#define HEAD_TEXT KEEP((.head.text))/* include/linux/init.h 文件*/
#define __HEAD .section ".head.text","ax"
上面是 HEAD_TEXT 定义的宏,最终找到__HEAD;故转向 arch/arm64/kernel/head.S 中继续执行。
__HEAD
_head:
/*
* DO NOT MODIFY. Image header expected by Linux boot-loaders.
*/
#ifdef CONFIG_EFI
/*
* This add instruction has no meaningful effect except that
* its opcode forms the magic "MZ" signature required by UEFI.
*/
add x13, x18, #0x16
b primary_entry
#else
b primary_entry // branch to kernel start, magic
.long 0 // reserved
#endif3.2 primary_entry
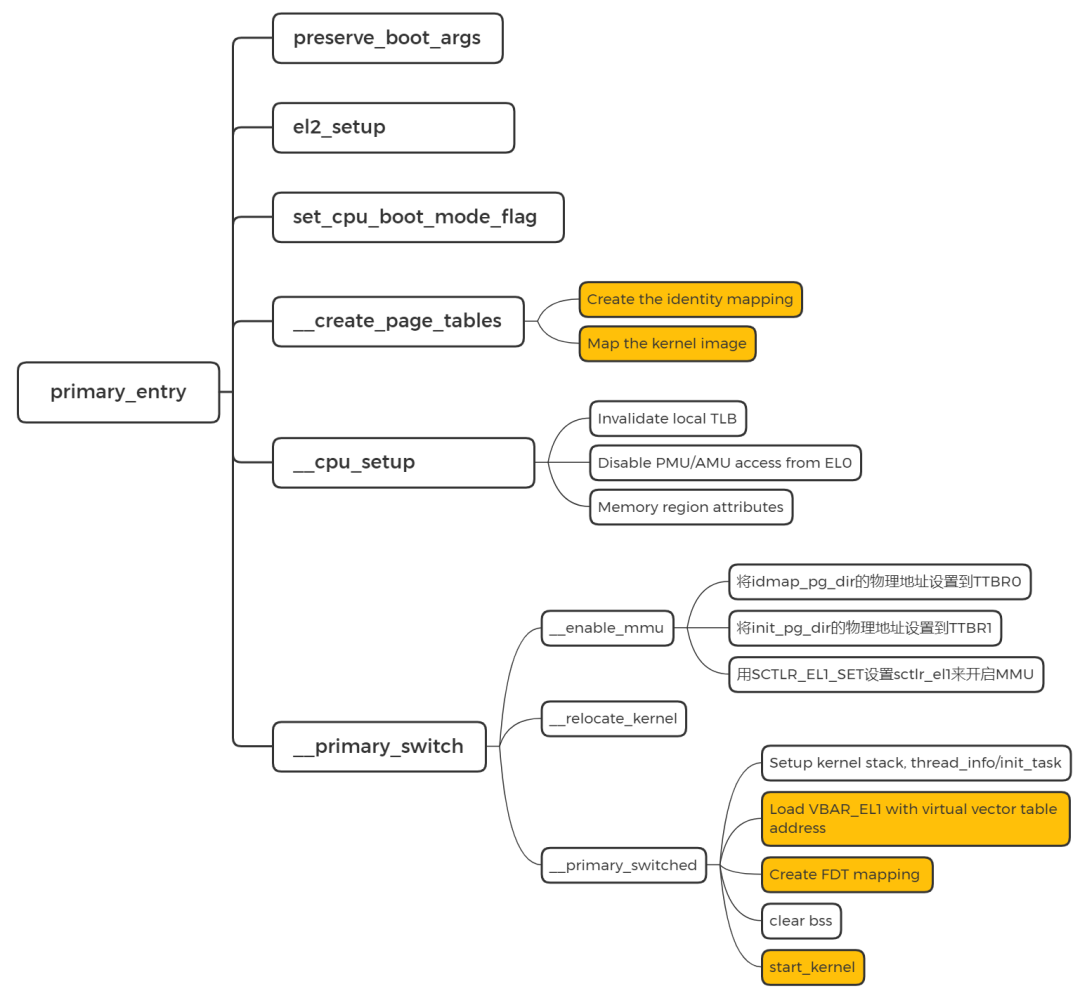
进入正式的初始化流程。
SYM_CODE_START(primary_entry)
bl preserve_boot_args
bl el2_setup // Drop to EL1, w0=cpu_boot_mode
adrp x23, __PHYS_OFFSET
and x23, x23, MIN_KIMG_ALIGN - 1 // KASLR offset, defaults to 0
bl set_cpu_boot_mode_flag
bl __create_page_tables
/*
* The following calls CPU setup code, see arch/arm64/mm/proc.S for
* details.
* On return, the CPU will be ready for the MMU to be turned on and
* the TCR will have been set.
*/
bl __cpu_setup // initialise processor
b __primary_switch
SYM_CODE_END(primary_entry)preserve_boot_args 是用来保存从 bootloader 传递的参数,使 dcache 失效。
el2_setup 设定 core 启动状态。
set_cpu_boot_mode_flag 设置 core 启动的 EL。
__create_page_tables 创建页表
我们知道 idmap_pg_dir 是 identity mapping 用到的页表,init_pg_dir 是 kernel_image_mapping 用到的页表。这里通过 __create_page_tables 来填充这两个页表。(具体如何实现的代码细节,请查看我写的内存管理文章)
SYM_FUNC_START_LOCAL(__create_page_tables)
mov x28, lr
......
/*
* Create the identity mapping.
*/
adrp x0, idmap_pg_dir
adrp x3, __idmap_text_start // __pa(__idmap_text_start)
......
adrp x5, __idmap_text_end
......
/*
* Map the kernel image (starting with PHYS_OFFSET).
*/
adrp x0, init_pg_dir
mov_q x5, KIMAGE_VADDR // compile time __va(_text)
add x5, x5, x23 // add KASLR displacement
mov x4, PTRS_PER_PGD
adrp x6, _end // runtime __pa(_end)
adrp x3, _text // runtime __pa(_text)
sub x6, x6, x3 // _end - _text
add x6, x6, x5 // runtime __va(_end)
......
SYM_FUNC_END(__create_page_tables)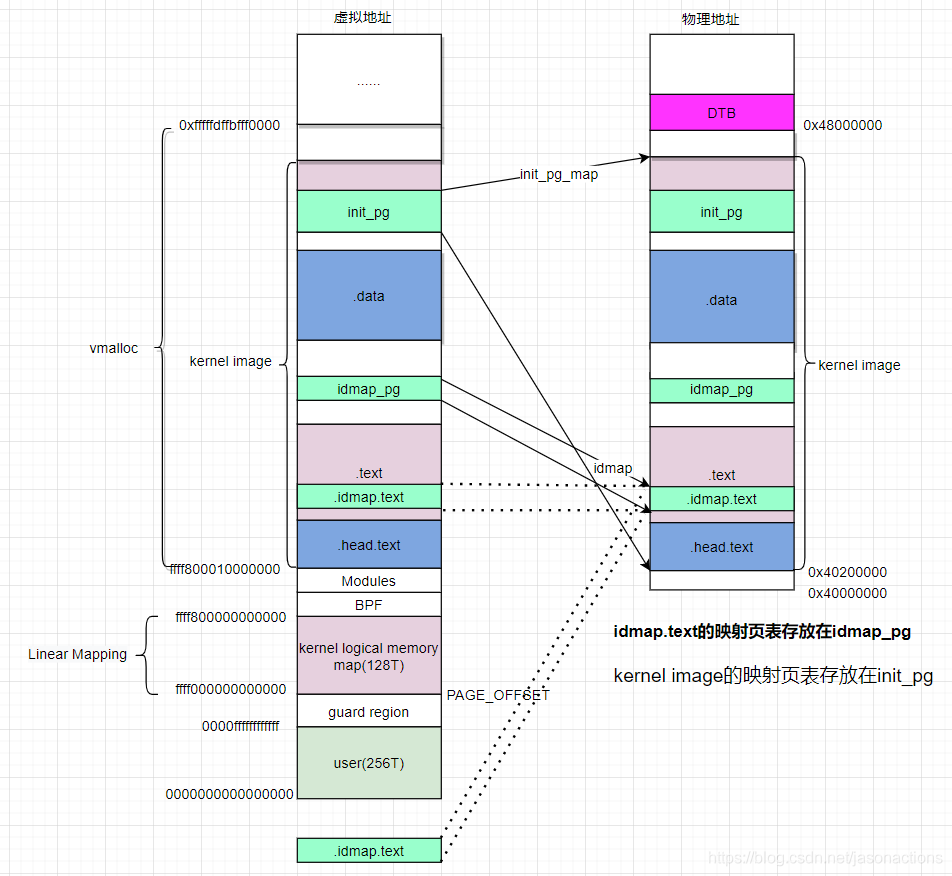
这里可以留一个 问题,让大家去查一下: idmap.text 恒等映射的原因是什么?
kernel 镜像的各个段分布, 就是由链接脚本组成的虚拟地址分布布局。至于物理地址, 是由bootloader 加载到内存的地址。然后CPU 访问虚拟地址,经过MMU,访问到物理内存上的二进制。
3.3 __cpu_setup 初始化 CPU
为开启 MMU 做一些 CPU 的初始化工作。前面都是关闭MMU。
SYM_FUNC_START(__cpu_setup)
tlbi vmalle1 // Invalidate local TLB
dsb nsh
mov x1, #3 << 20
msr cpacr_el1, x1 // Enable FP/ASIMD
mov x1, #1 << 12 // Reset mdscr_el1 and disable
msr mdscr_el1, x1 // access to the DCC from EL0
isb // Unmask debug exceptions now,
enable_dbg // since this is per-cpu
reset_pmuserenr_el0 x1 // Disable PMU access from EL0
reset_amuserenr_el0 x1 // Disable AMU access from EL0
/*
* Memory region attributes
*/
mov_q x5, MAIR_EL1_SET前面做 TLB/FP/ASIMD/DCC/PMU/AMU 的初始化,后面做 Memory region attributes。
3.4__primary_switch 开启MMU
切换到虚拟地址,并调用 __primary_switched。
3.5 __primary_switched
__primary_switched主要完成了如下的工作:
- 为init进程设置好堆栈地址和大小,保存当前进程描述符地址到sp_el0;
- 设置异常向量表基址寄存器;
- 保存FDT地址到__fdt_pointer变量;
- 将kimage的虚拟地址和物理地址的偏移保存到kimage_voffset
- clear bss
- 跳转到start_kernel
3.6 用一张图概括: