一.栈的定义
栈(Stack)是只允许在一段进行插入或删除操作的线性表;
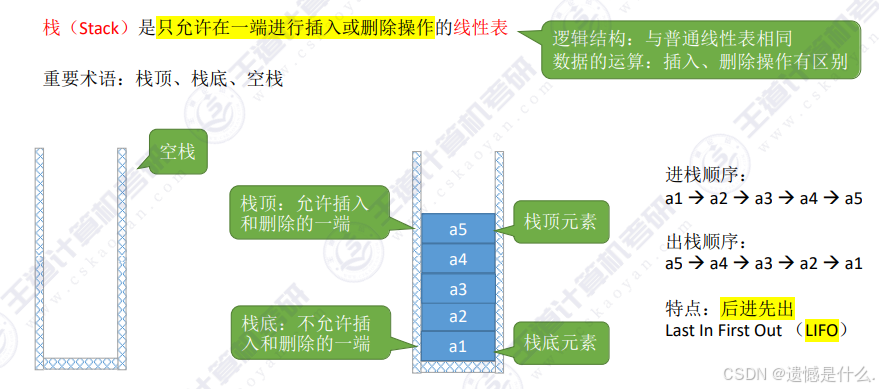
栈和线性表的基本操作:


出栈顺序:

二.栈的初始化
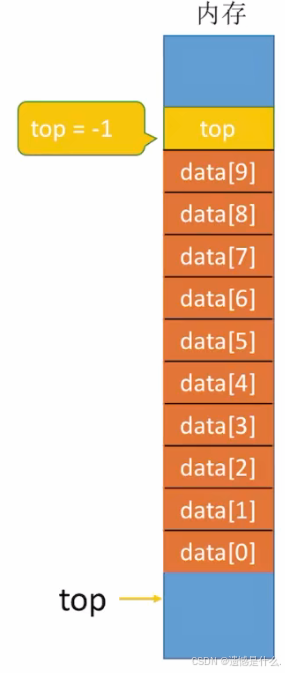 当栈空时, data[0] - data[9]全空, 则top指向data[0]上一个元素, 即top = -1.
当栈空时, data[0] - data[9]全空, 则top指向data[0]上一个元素, 即top = -1.
所以判断栈是否为空, 只需观察top指向哪里,
当top = -1时, 栈空;当top != -1时,栈非空.
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using ElemType = int;
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MaxSize]; //静态数组存放栈中元素
int top; //栈顶指针
}SqStack;
//初始化栈
void InitStack(SqStack& S) {
S.top = -1;
}
//判断栈空
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S) {
if (S.top = -1) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
int main() {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
cout << (StackEmpty(S) ? "栈空" : "栈非空") << endl;
}三.进栈,出栈操作
1.进栈操作
 现在内存中有a元素, top指向data[0], 即top = 0;
现在内存中有a元素, top指向data[0], 即top = 0;
如果想在a后面插入一个元素b, 则需要先将top值 + 1, 再将b填入data[1]中;
用代码表示为:
S.top = S.top + 1;
S.data[S.top] = x;
等价于:
S.data[++S.top] = x;
注意:
是"++S.top"不是"S.top++"
入栈不要忘记判断栈满(栈满不能进)
cpp
//新元素入栈
bool Push(SqStack& S, ElemType x) {
if (StackFull(S)) {
return false;
}
S.top = S.top + 1; //指针先加1
S.data[S.top] = x; //新元素入栈
//等价于:
S.data[++S.top] = x;
return true;
}2.出栈操作
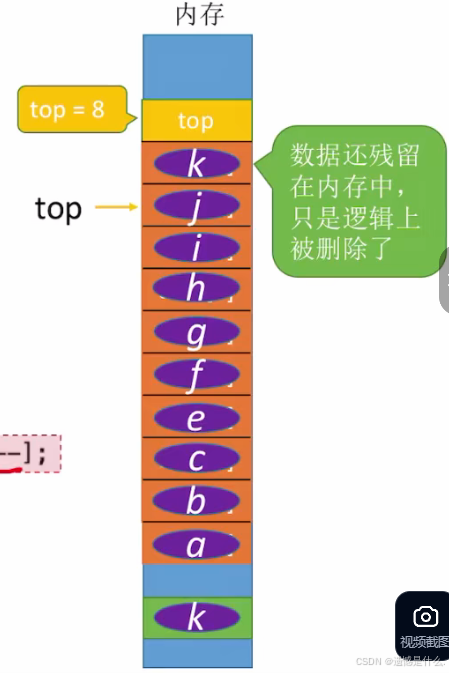 现在内存中存在10个元素, 现在要将栈顶元素k删除, 需要在内存中留一个ElemType x的内存空间,
现在内存中存在10个元素, 现在要将栈顶元素k删除, 需要在内存中留一个ElemType x的内存空间,
然后将k复制到该位置;
现在将data[9]位置的k删去,即top指向data[8],即top = 8:x = S.data[S.top];
再将top-1:S.top = S.top - 1;
等价于:
x = S.data[S.top--];
注意:
是"S.top--"而不是"--S.top"
出栈不要忘记判断栈空(空栈不能出)
cpp
//出栈
bool Pop(SqStack& S, ElemType& x) {
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
return false;
}
x = S.data[S.top];
S.top = S.top - 1;
//等价于: x = S.data[S.top--];
return true;
}3.读栈顶元素
cpp
// 出栈操作
bool Pop(SqStack &S, ElemType &x) {
if (S.top == -1) // 栈空,报错
return false;
x = S.data[S.top--]; // 先出栈,指针再减1
return true;
}
// 读栈顶元素
bool GetTop(SqStack S, ElemType &x) {
if (S.top == -1) // 栈空,报错
return false;
x = S.data[S.top]; // x 记录栈顶元素
return true;
}出栈操作和读栈顶元素的操作的区别:出栈操作指针需要减一,top--;
4.完整代码
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using ElemType = int;
#define MaxSize 10
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top;
}SqStack;
void InitStack(SqStack& S) {
S.top = -1;
}
//栈空
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S) {
if (S.top == -1) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
//栈满
bool StackFull(SqStack S) {
if (S.top == MaxSize - 1) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
//入栈
bool Push(SqStack& S, ElemType x) {
if (StackFull(S)) {
return false;
}
S.top = S.top + 1; //指针先加1
S.data[S.top] = x; //新元素入栈
//等价于: S.data[++S.top] = x;
return true;
}
//出栈
bool Pop(SqStack& S, ElemType& x) {
if (StackEmpty(S)) {
return false;
}
x = S.data[S.top];
S.top = S.top - 1;
//等价于: x = S.data[S.top--];
return true;
}
//读栈顶
bool GetTop(SqStack& S, ElemType& x) {
if (StackEmpty(S)) return false;
x = S.data[S.top];
return true;
}
/*---------------- 测试 ----------------*/
int main() {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
for (int i = 1; i <= MaxSize + 1; ++i) // 故意多 push 一次
if (!Push(S, i))
cout << "第" << i << "次入栈失败(栈满)\n";
ElemType x;
while (Pop(S, x))
cout << x << " 出栈\n";
return 0;
}5.注意问题
(1) 区别:
cpp
//入栈
bool Push(SqStack& S, ElemType x)
//出栈
bool Pop(SqStack& S, ElemType& x)1.
形参里的 & 位置不同
Push 只有 栈 带 & : SqStack& S
Pop 除了 栈 带 & ,还多了 出栈元素 的 & : ElemType& x
2.
作用不同
Push 把 x 的值"复制"进栈,不需要 改 x ,所以 x 按值传递。
Pop 要把栈顶值"送"给调用者,必须 改 x ,所以 x 按引用传递。
一句话:
" Push 只改栈, Pop 既要改栈又要改调用者的变量,因此多一个 & 。"
(2): StackEmpty 和 StackFull 里把"比较"写成了"赋值":
cpp
//栈空
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S) {
if (S.top == -1) {
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
//栈满
bool StackFull(SqStack S) {
if (S.top == MaxSize - 1) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}S.top 是和 -1,MaxSize-1 比较的,而不是复制,这里使用"=="而不是"=".
6.另一种方式
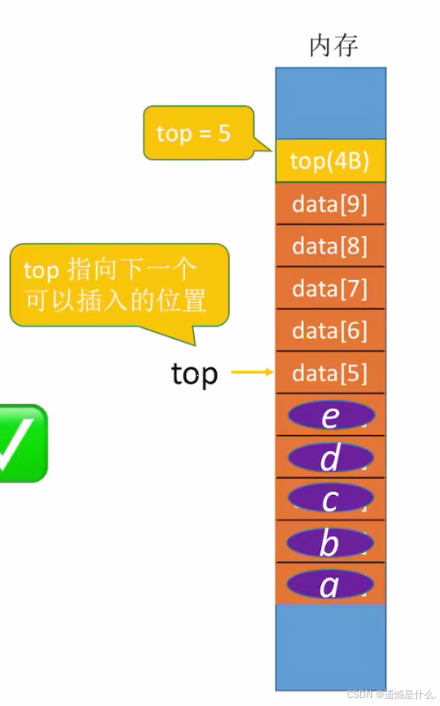 另一种进栈的方式:
另一种进栈的方式:
top指向下一个可以插入的位置, 如图在e元素后面插入元素, 直接让top指向data[5],
此时添加元素则要先填入x, 再top++;
进栈代码为:
S.data[S.top] = x;
S.top = S.top + 1;
等价于:
S.data[S.top++] = x;
出栈代码为:
S.top = S.top - 1;
x = S.data[S.top];
等价于:
x = S.data[--S.top];
四.共享栈
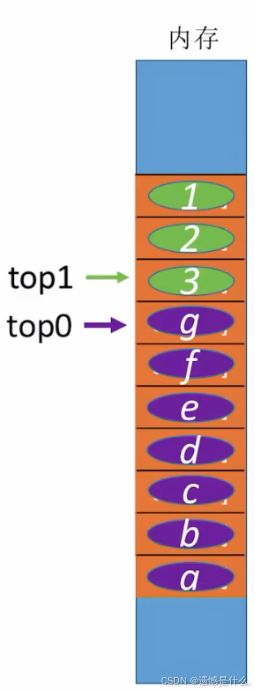 定义:
定义:
两个栈共享同一片内存空间,两个栈从两边往中间增长
初始化:
0号栈栈顶指针初始化时 top0 = -1;
1号栈栈顶指针初始化时 top1 = MaxSize;
栈满条件:
top0 + 1 == top1;
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
constexpr int MaxSize = 10;
using ElemType = int;
/*---------- 共享栈结构 ----------*/
struct ShStack {
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top0; // 左栈顶,空时为 -1
int top1; // 右栈顶,空时为 MaxSize
};
/*---------- 基本操作 ----------*/
void InitStack(ShStack &S) {
S.top0 = -1;
S.top1 = MaxSize; // 原代码缺分号,已补
}
bool Stack0Empty(const ShStack &S) { return S.top0 == -1; }
bool Stack1Empty(const ShStack &S) { return S.top1 == MaxSize; }
bool StackFull(const ShStack &S) { return S.top0 + 1 == S.top1; }
/* 左栈进栈 */
bool Push0(ShStack &S, ElemType x) {
if (StackFull(S)) return false;
S.data[++S.top0] = x;
return true;
}
/* 右栈进栈 */
bool Push1(ShStack &S, ElemType x) {
if (StackFull(S)) return false;
S.data[--S.top1] = x;
return true;
}
/* 左栈出栈 */
bool Pop0(ShStack &S, ElemType &x) {
if (Stack0Empty(S)) return false;
x = S.data[S.top0--];
return true;
}
/* 右栈出栈 */
bool Pop1(ShStack &S, ElemType &x) {
if (Stack1Empty(S)) return false;
x = S.data[S.top1++];
return true;
}
/*---------- 测试 ----------*/
int main() {
ShStack S;
InitStack(S);
for (int i = 1; i <= 6; ++i) Push0(S, i); // 左栈:1 2 3 4 5 6
for (int i = 10; i >= 7; --i) Push1(S, i); // 右栈:10 9 8 7
ElemType x;
while (!Stack0Empty(S)) { Pop0(S, x); cout << "左栈出: " << x << '\n'; }
while (!Stack1Empty(S)) { Pop1(S, x); cout << "右栈出: " << x << '\n'; }
return 0;
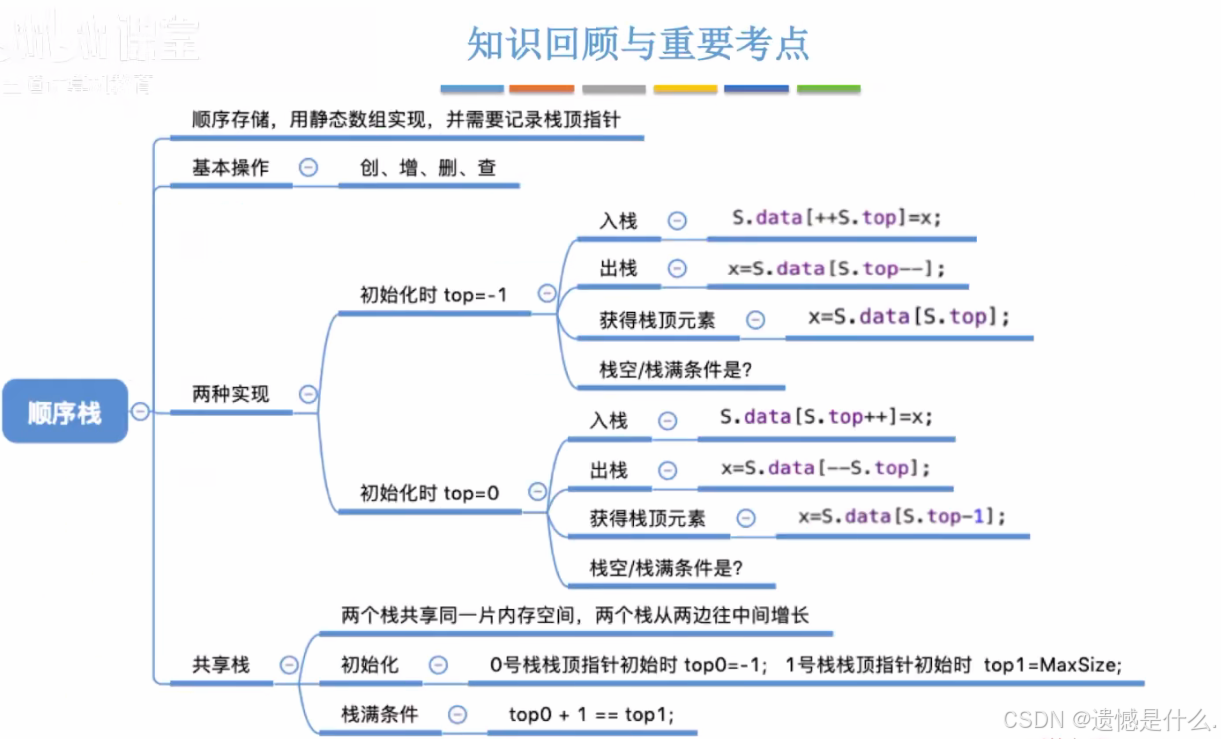
}五.知识回顾
六.链栈的增,删,查(栈顶元素)操作
cpp
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
using ElemType = int;
/*---------- 结点定义 ----------*/
struct StackNode {
ElemType data;
StackNode* next;
};
/*---------- 1. 初始化 ----------*/
void InitStack(StackNode*& S) { // 引用指针,调用后 S 为 nullptr
S = nullptr; // 不带头结点,空栈时栈顶就是 nullptr
}
/*---------- 2. 判空 ----------*/
bool StackEmpty(StackNode* S) {
return S == nullptr;
}
/*---------- 3. 入栈(增)----------*/
bool Push(StackNode*& S, ElemType x) {
StackNode* p = new StackNode; // 新建结点
if (!p) return false; // 内存分配失败
p->data = x;
p->next = S; // 头插法
S = p; // 更新栈顶
return true;
}
/*---------- 4. 出栈(删)----------*/
bool Pop(StackNode*& S, ElemType& x) {
if (StackEmpty(S)) return false;
StackNode* p = S; // 暂存栈顶结点
x = p->data;
S = S->next; // 栈顶下移
delete p; // 释放原栈顶
return true;
}
/*---------- 5. 获取栈顶元素(查)----------*/
bool GetTop(StackNode* S, ElemType& x) {
if (StackEmpty(S)) return false;
x = S->data;
return true;
}
/*---------- 6. 测试 ----------*/
int main() {
StackNode* S;
InitStack(S);
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; ++i) Push(S, i); // 入栈 1 2 3 4 5
ElemType x;
while (!StackEmpty(S)) {
GetTop(S, x);
cout << "栈顶: " << x << " ";
Pop(S, x);
cout << "出栈: " << x << '\n';
}
return 0;
}