大家好,我是 方圆 。最近学习了一下 Nacos 源码,顺便为 Nacos 开源项目提交了 10+ 个 PR,成为了 Nacos 项目的 Contributor。Nacos 是一个非常活跃且包容的社区,大家可以在 Github-Nacos 关注并认领 ISSUE。本篇文章基于 Nacos 的 3.1.0 版本,准备详细解释一下 Nacos 对配置管理的核心流程,方便之后了解和学习 Nacos 的同学。
本文将主要分成两大部分:
- 当配置发生变更时,Nacos Server 服务端是如何保证配置数据的一致性的,在这个小节内我们会讨论两种情况,分别关于 Nacos Server 的单机部署和集群部署
- 当配置发生变更时,Nacos Client 客户端是如何保证及时更新配置,并保证配置内容是最新的
在每个部分我都会在讲解源码前将具体的逻辑使用图示整理出来,方便想理解原理而不想看源码的同学,同时也能让想看源码的同学快速入手。如果大家对 Nacos 感兴趣,可以将源码 clone 下来,Debug 调试整个流程,这样学习和理解的效果更佳。
Nacos Server 服务端
当我们在 Nacos 控制台变更配置时,不论是单机部署还是集群部署都会经过以下逻辑,请求会由 ConsoleConfigController 来承接,调用其中的 publishConfig 发布配置的方法,如下所示:
java
@NacosApi
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/v3/console/cs/config")
@ExtractorManager.Extractor(httpExtractor = ConfigDefaultHttpParamExtractor.class)
public class ConsoleConfigController {
private final ConfigProxy configProxy;
public ConsoleConfigController(ConfigProxy configProxy) {
this.configProxy = configProxy;
}
@PostMapping()
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.WRITE, signType = SignType.CONFIG, apiType = ApiType.CONSOLE_API)
public Result<Boolean> publishConfig(HttpServletRequest request, ConfigFormV3 configForm) throws NacosException {
// check required
configForm.validateWithContent();
final boolean namespaceTransferred = NamespaceUtil.isNeedTransferNamespace(configForm.getNamespaceId());
configForm.setNamespaceId(NamespaceUtil.processNamespaceParameter(configForm.getNamespaceId()));
// check param
ParamUtils.checkParam(configForm.getDataId(), configForm.getGroup(), "datumId", configForm.getContent());
ParamUtils.checkParamV2(configForm.getTag());
if (StringUtils.isBlank(configForm.getSrcUser())) {
configForm.setSrcUser(RequestUtil.getSrcUserName(request));
}
if (!ConfigType.isValidType(configForm.getType())) {
configForm.setType(ConfigType.getDefaultType().getType());
}
ConfigRequestInfo configRequestInfo = new ConfigRequestInfo();
configRequestInfo.setSrcIp(RequestUtil.getRemoteIp(request));
configRequestInfo.setRequestIpApp(RequestUtil.getAppName(request));
configRequestInfo.setBetaIps(request.getHeader("betaIps"));
configRequestInfo.setCasMd5(request.getHeader("casMd5"));
configRequestInfo.setNamespaceTransferred(namespaceTransferred);
return Result.success(configProxy.publishConfig(configForm, configRequestInfo));
}
}Controller 中并没有值得特别关注的逻辑,包含必要的参数校验和执行 ConfigProxy#publishConfig 方法,后者从命名来看,包含了 Proxy 字样,暗示它是一个代理类,具体的实现逻辑如下所示:
java
@Service
public class ConfigProxy {
private final ConfigHandler configHandler;
@Autowired
public ConfigProxy(ConfigHandler configHandler) {
this.configHandler = configHandler;
}
/**
* Add or update configuration.
*/
public Boolean publishConfig(ConfigForm configForm, ConfigRequestInfo configRequestInfo) throws NacosException {
return configHandler.publishConfig(configForm, configRequestInfo);
}
// ...
}可以发现它使用了 静态代理模式 ,并没有做发布配置的逻辑,而是注入了 ConfigHandler 类,并调用其 publishConfig 方法,那么它代理了什么呢?如下图所示:
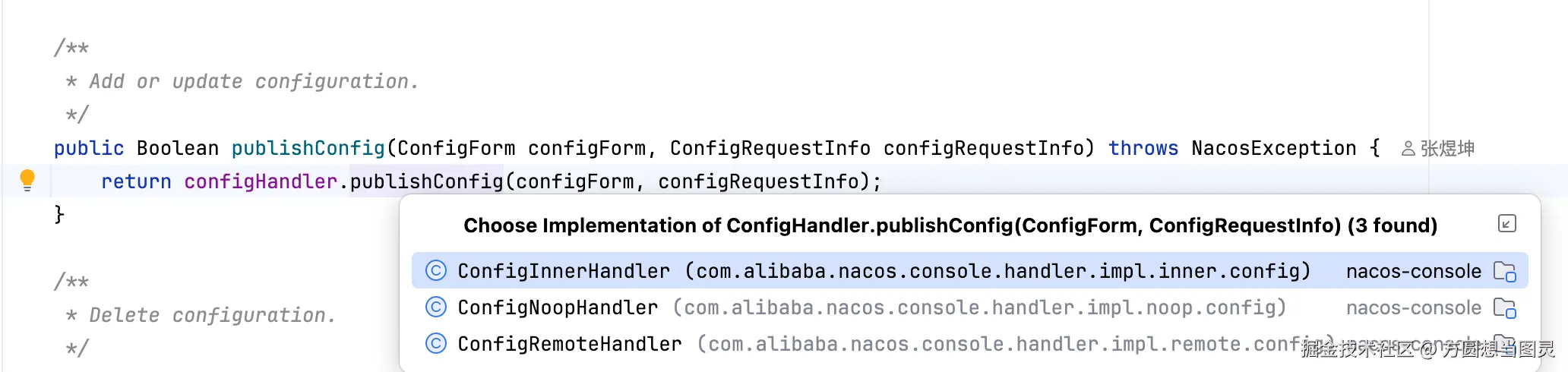
ConfigHandler 是一个接口,它有多个实现类,当在 Nacos 中采用不同的配置时,会注入不同的实现类,所以这部分代理操作实际上根据不同的配置来选择不同的策略。在这里我们仅关注 ConfigInnerHandler 实现策略,它会执行到 ConfigOperationService#publishConfig 发布配置的核心逻辑。这个方法的逻辑虽然很长,但是其中值得关注的内容我已经用序号标注了,分别为 "写入数据库的逻辑" 和 "发布 ConfigDataChangeEvent 配置变更事件":
java
public class ConfigOperationService {
private ConfigInfoPersistService configInfoPersistService;
private ConfigInfoGrayPersistService configInfoGrayPersistService;
private ConfigMigrateService configMigrateService;
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ConfigOperationService.class);
public ConfigOperationService(ConfigInfoPersistService configInfoPersistService,
ConfigInfoGrayPersistService configInfoGrayPersistService,
ConfigMigrateService configMigrateService) {
this.configInfoPersistService = configInfoPersistService;
this.configInfoGrayPersistService = configInfoGrayPersistService;
this.configMigrateService = configMigrateService;
}
public Boolean publishConfig(ConfigForm configForm, ConfigRequestInfo configRequestInfo, String encryptedDataKey) throws NacosException {
Map<String, Object> configAdvanceInfo = getConfigAdvanceInfo(configForm);
ParamUtils.checkParam(configAdvanceInfo);
configForm.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);
ConfigInfo configInfo = new ConfigInfo(configForm.getDataId(), configForm.getGroup(),
configForm.getNamespaceId(), configForm.getAppName(), configForm.getContent());
// set old md5
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(configRequestInfo.getCasMd5())) {
configInfo.setMd5(configRequestInfo.getCasMd5());
}
configInfo.setType(configForm.getType());
configInfo.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);
// 1. 写入数据库的逻辑:区分了 md5 是否为空
if (StringUtils.isNotBlank(configRequestInfo.getCasMd5())) {
// 非空会执行 CAS 比较并交换的操作
configOperateResult = configInfoPersistService.insertOrUpdateCas(configRequestInfo.getSrcIp(),
configForm.getSrcUser(), configInfo, configAdvanceInfo);
if (!configOperateResult.isSuccess()) {
LOGGER.warn(
"[cas-publish-config-fail] srcIp = {}, dataId= {}, casMd5 = {}, msg = server md5 may have changed.",
configRequestInfo.getSrcIp(), configForm.getDataId(), configRequestInfo.getCasMd5());
throw new NacosApiException(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), ErrorCode.RESOURCE_CONFLICT,
"Cas publish fail, server md5 may have changed.");
}
} else {
if (configRequestInfo.getUpdateForExist()) {
configOperateResult = configInfoPersistService.insertOrUpdate(configRequestInfo.getSrcIp(),
configForm.getSrcUser(), configInfo, configAdvanceInfo);
} else {
try {
configOperateResult = configInfoPersistService.addConfigInfo(configRequestInfo.getSrcIp(),
configForm.getSrcUser(), configInfo, configAdvanceInfo);
} catch (DataIntegrityViolationException ive) {
configOperateResult = new ConfigOperateResult(false);
}
}
}
if (!configOperateResult.isSuccess()) {
LOGGER.warn("[publish-config-failed] config already exists. dataId: {}, group: {}, namespaceId: {}",
configForm.getDataId(), configForm.getGroup(), configForm.getNamespaceId());
throw new ConfigAlreadyExistsException(
String.format("config already exist, dataId: %s, group: %s, namespaceId: %s",
configForm.getDataId(), configForm.getGroup(), configForm.getNamespaceId()));
}
// 2. 发布 ConfigDataChangeEvent 配置变更事件
ConfigChangePublisher.notifyConfigChange(
new ConfigDataChangeEvent(configForm.getDataId(), configForm.getGroup(), configForm.getNamespaceId(),
configOperateResult.getLastModified()));
return true;
}
}接下来我们根据 "单机部署,采用 MySQL 数据库" 和 "集群部署,采用内嵌 Derby 数据库" 来讨论具体的逻辑。
单机部署,采用 MySQL 数据库
在单机部署并采用 MySQL 数据库时,Nacos 服务端在配置变更后执行逻辑的流程图如下所示:
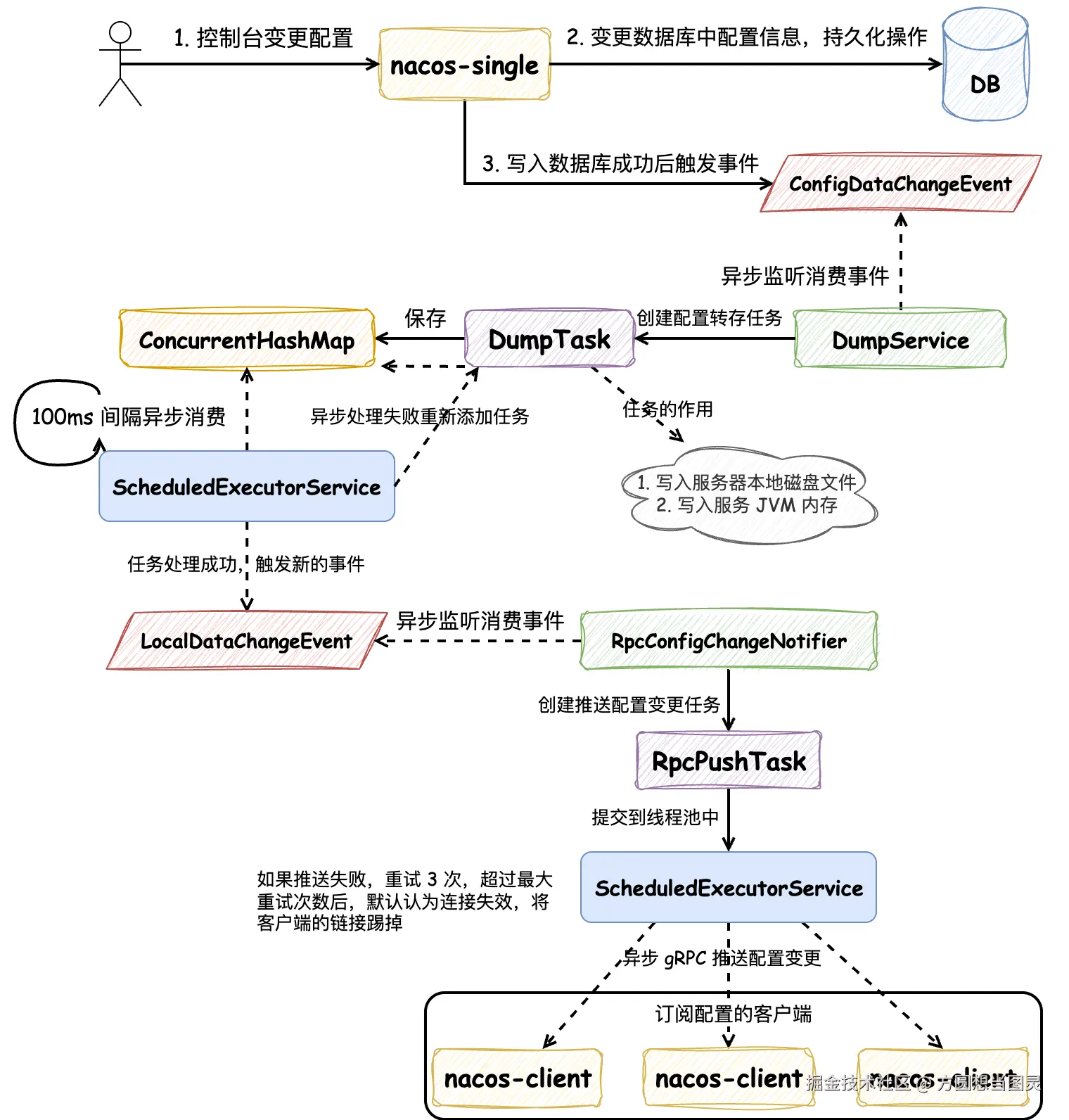
在控制台变更配置后,会先写入 MySQL 数据库,写入成功继续执行,如果写入失败则抛出异常,控制台会提示配置写入失败,就不再执行后续的逻辑了。
在写入 MySQL 数据库成功后,会触发 ConfigDataChangeEvent 配置发生变更的事件,由 DumpService 监听并消费。消费这个事件时,会创建 DumpTask 任务,这个任务的作用有两个:将配置信息 写入本地磁盘文件 和 写入服务 JVM 内存 ,这样 即使在 MySQL 数据库发生宕机时,客户端也能正常读取配置信息 ,写入本地磁盘相当于做了数据库的容灾。DumpTask 被创建后会被保存在一个 ConcurrentHashMap 中,由一个 ScheduledExecutorService 定时 100ms 执行的线程池定期处理任务,如果任务在执行时失败,都会被重新添加到 ConcurrentHashMap 中,无限次重试处理。
DumpTask 处理完成后,会再次发出 LocalDataChangeEvent 本地缓存变更事件,这个事件由 RpcConfigChangeNotifier 监听并消费。RpcConfigChangeNotifier 处理这个事件时会创建 RpcPushTask 为客户端推送配置变更的任务,这个任务同样会被添加到另一个 ScheduledExecutorService 中去执行,但是异步推送变更的任务不会无限重试,最多只会重试 3 次。在这里大家可能会有疑问:如果重试超过 3 次没有成功,那么 Nacos 客户端该如何获取到最新的配置变更呢?其实 Nacos 客户端不只是通过 Nacos 服务端推送获取配置变更,而且还能通过主动从 Nacos 服务端拉取获取配置变更,这个逻辑在后续的内容中解释。
以上便是 Nacos 服务端在单机部署并采用 MySQL 数据库时主要的逻辑流程,接下来我们深入分析具体的源码。
在 "写入数据库的逻辑" 中,Nacos 区分了 MD5 是否为空的两种情况,MD5 在 Nacos 表示的是什么含义呢?Nacos 中的每项配置都会根据其 配置的内容 计算出 MD5 值,并将其存储在数据库中,因为 MD5 加密后输出长度固定,所以可以根据配置的 MD5 值快速判断配置内容是否发生变更。
MD5(Message Digest Algorithm 5)是一种广泛使用的密码散列函数,可以产生出一个128位(16字节)的散列值(hash value),用来确保信息传输完整一致。不过现在更推荐使用 SHA-256 或更新的散列算法来替代 MD5。
Nacos 在发布配置时,如果 MD5 值不为空则调用 ConfigInfoPersistService#insertOrUpdateCas 方法,这个方法使用了 CAS 操作,在执行 UPDATE SQL 时会先判断数据库中配置的 MD5 值是否与请求中的 MD5 值相同,如果相同则执行更新操作,否则不执行更新操作,这样能够避免多人在控制台同时修改配置造成的并发写入问题。
如果 MD5 值为空的话,那么直接调用 ConfigInfoPersistService#insertOrUpdate 方法,直接落库。
在数据库操作完成后,配置变更已经在保存在数据库了 ,之后会发布 ConfigDataChangeEvent 配置变更事件,这是一个异步处理的操作,在单机部署模式下,需要关注 DumpService 对这个事件的消费,它会执行 DumpService#handleConfigDataChange 方法,将配置变更事件转换为配置转储任务 DumpTask:
java
/**
* 监听并处理 ConfigDataChangeEvent 事件
* 将 ConfigDataChangeEvent 转换为 DumpRequest,交给 DumpProcessor 处理
* 作用:将配置变更事件转换为配置转储任务,更新本地缓存
*/
public abstract class DumpService {
private TaskManager dumpTaskMgr;
void handleConfigDataChange(Event event) {
// Generate ConfigDataChangeEvent concurrently
if (event instanceof ConfigDataChangeEvent) {
ConfigDataChangeEvent evt = (ConfigDataChangeEvent) event;
DumpRequest dumpRequest = DumpRequest.create(evt.dataId, evt.group, evt.tenant, evt.lastModifiedTs,
NetUtils.localIp());
dumpRequest.setGrayName(evt.grayName);
// 执行 dump 转储操作,由 DumpProcessor 处理
DumpService.this.dump(dumpRequest);
}
}
public void dump(DumpRequest dumpRequest) {
dumpFormal(dumpRequest.getDataId(), dumpRequest.getGroup(), dumpRequest.getTenant(),
dumpRequest.getLastModifiedTs(), dumpRequest.getSourceIp());
}
private void dumpFormal(String dataId, String group, String tenant, long lastModified, String handleIp) {
// 生成 Task 的 Key 值,格式为:dataId+group+tenant
// eg: default_config+DEFAULT_GROUP+public 其中 default_config 为配置的名称,DEFAULT_GROUP 为分组ID,public 为命名空间ID
String groupKey = GroupKey2.getKey(dataId, group, tenant);
String taskKey = groupKey;
// 生成转储任务 DumpTask
dumpTaskMgr.addTask(taskKey, new DumpTask(groupKey, null, lastModified, handleIp));
DUMP_LOG.info("[dump] add formal task. groupKey={}", groupKey);
}
}调用 TaskManager#addTask 方法添加配置转储任务 DumpTask,最终会执行以下逻辑:
java
public class NacosDelayTaskExecuteEngine extends AbstractNacosTaskExecuteEngine<AbstractDelayTask> {
protected final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
protected final ConcurrentHashMap<Object, AbstractDelayTask> tasks;
@Override
public void addTask(Object key, AbstractDelayTask newTask) {
lock.lock();
try {
AbstractDelayTask existTask = tasks.get(key);
if (null != existTask) {
newTask.merge(existTask);
}
tasks.put(key, newTask);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}在这个方法中有两点需要注意:
ReentrantLock lock变量:在向ConcurrentHashMap<Object, AbstractDelayTask> tasks添加任务时执行了加锁操作ConcurrentHashMap<Object, AbstractDelayTask> tasks变量:该变量是并发安全的,但是仍然在操作前执行了加锁操作
因为 AbstractDelayTask#merge 方法并不是并发安全的,多线程操作时可能发生未知的情况,所以便需要注意以上两点。现在,转储任务 DumpTask 已经被添加到 ConcurrentHashMap<Object, AbstractDelayTask> tasks 中了,那么这个任务是如何被执行的呢?
我们先看一下 NacosDelayTaskExecuteEngine 的构造方法,在构造方法中创建了 ScheduledExecutorService processingExecutor 变量用于定期(100ms)执行 ProcessRunnable 任务,ProcessRunnable 是静态内部类,调用 processTasks 方法来处理任务:
java
public class NacosDelayTaskExecuteEngine extends AbstractNacosTaskExecuteEngine<AbstractDelayTask> {
private final ScheduledExecutorService processingExecutor;
protected final ConcurrentHashMap<Object, AbstractDelayTask> tasks;
protected final ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
// processInterval 处理间隔默认值为 100ms
public NacosDelayTaskExecuteEngine(String name, int initCapacity, Logger logger, long processInterval) {
super(logger);
tasks = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(initCapacity);
processingExecutor = ExecutorFactory.newSingleScheduledExecutorService(new NameThreadFactory(name));
processingExecutor.scheduleWithFixedDelay(new ProcessRunnable(), processInterval, processInterval, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
private class ProcessRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
processTasks();
} catch (Throwable e) {
getEngineLog().error(e.toString(), e);
}
}
}
protected void processTasks() {
Collection<Object> keys = getAllTaskKeys();
for (Object taskKey : keys) {
// 逐个删除而不是在上面统一删除,删除的时候而且加了锁,这样即使被多个线程拿到多个 Key,也能通过加锁避免执行重复的任务
AbstractDelayTask task = removeTask(taskKey);
if (null == task) {
continue;
}
// 此处使用了策略模式,可以针对不同的 key 来定义不同的处理策略,这里默认使用了 DumpProcessor
NacosTaskProcessor processor = getProcessor(taskKey);
try {
// 处理失败或者抛出异常都会重试
if (!processor.process(task)) {
retryFailedTask(taskKey, task);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
getEngineLog().error("Nacos task execute error ", e);
retryFailedTask(taskKey, task);
}
}
}
private void retryFailedTask(Object key, AbstractDelayTask task) {
task.setLastProcessTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
// 重新调用上文中的 NacosDelayTaskExecuteEngine#addTask 方法
addTask(key, task);
}
@Override
public Collection<Object> getAllTaskKeys() {
Collection<Object> keys = new HashSet<>();
lock.lock();
try {
// 将 DumpService 执行时添加的 Key 在这里获取,但没有删除操作,而是在后续的步骤中遍历一个加锁删除一个
keys.addAll(tasks.keySet());
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
return keys;
}
@Override
public AbstractDelayTask removeTask(Object key) {
lock.lock();
try {
AbstractDelayTask task = tasks.get(key);
if (null != task && task.shouldProcess()) {
return tasks.remove(key);
} else {
return null;
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}在上述逻辑中,getAllTaskKeys 和 removeTask 方法中仍然使用了 ReentrantLock 加锁,但是在这两个方法中都是读操作,而且是定时线程池定期执行,发生并发问题的概率非常小,实际上我认为可以采用不加锁的方案,或者可以考虑将 ConcurrentHashMap 换成 ConcurrentLinkedDeque 队列,任务在队列尾部添加,每次线程在执行任务时直接将队列头部的任务取出,执行失败或者不满足执行条件再将它放回到队列中 。不过,这种异步执行任务的多线程设计采用的是 "生产者消费者"模式,这种设计方法还是非常值得学习的。
接下来我们看一下 DumpProcessor#process 方法中,到底执行了什么逻辑,如下所示,大部分都是参数赋值,重点是 从数据库中将配置查询出来 后,执行了 DumpConfigHandler#configDump 方法:
java
public class DumpProcessor implements NacosTaskProcessor {
final ConfigInfoPersistService configInfoPersistService;
@Override
public boolean process(NacosTask task) {
DumpTask dumpTask = (DumpTask) task;
String[] pair = GroupKey2.parseKey(dumpTask.getGroupKey());
String dataId = pair[0];
String group = pair[1];
String tenant = pair[2];
long lastModifiedOut = dumpTask.getLastModified();
String handleIp = dumpTask.getHandleIp();
String grayName = dumpTask.getGrayName();
ConfigDumpEvent.ConfigDumpEventBuilder build = ConfigDumpEvent.builder().namespaceId(tenant).dataId(dataId)
.group(group).grayName(grayName).handleIp(handleIp);
String type = "formal";
// 从数据库读取配置信息,构建 ConfigDumpEvent 事件
ConfigInfoWrapper cf = configInfoPersistService.findConfigInfo(dataId, group, tenant);
build.remove(Objects.isNull(cf));
build.content(Objects.isNull(cf) ? null : cf.getContent());
build.type(Objects.isNull(cf) ? null : cf.getType());
build.encryptedDataKey(Objects.isNull(cf) ? null : cf.getEncryptedDataKey());
build.lastModifiedTs(Objects.isNull(cf) ? lastModifiedOut : cf.getLastModified());
return DumpConfigHandler.configDump(build.build());
}
}为了方便理解,省略一系列不重要的源码,最终会执行到 ConfigCacheService#dumpWithMd5 方法,在这个方法中修改缓存前会添加写锁 tryWriteLock,添加写锁成功后才能继续处理,后续处理逻辑中有两步比较重要:"写入到本地文件" 和 "更新 JVM 本地缓存对象":
java
public class ConfigCacheService {
public static boolean dumpWithMd5(String dataId, String group, String tenant, String content, String md5,
long lastModifiedTs, String type, String encryptedDataKey) {
String groupKey = GroupKey2.getKey(dataId, group, tenant);
CacheItem ci = makeSure(groupKey, encryptedDataKey);
ci.setType(type);
// 对某个缓存的操作添加了写锁
final int lockResult = tryWriteLock(groupKey);
if (lockResult < 0) {
DUMP_LOG.warn("[dump-error] write lock failed. {}", groupKey);
return false;
}
try {
// 校验修改时间
boolean lastModifiedOutDated = lastModifiedTs < ConfigCacheService.getLastModifiedTs(groupKey);
if (lastModifiedOutDated) {
DUMP_LOG.warn("[dump-ignore] timestamp is outdated,groupKey={}", groupKey);
return true;
}
boolean newLastModified = lastModifiedTs > ConfigCacheService.getLastModifiedTs(groupKey);
if (md5 == null) {
md5 = MD5Utils.md5Hex(content, PERSIST_ENCODE);
}
// 1. 写入到本地文件中
String localContentMd5 = ConfigCacheService.getContentMd5(groupKey);
boolean md5Changed = !md5.equals(localContentMd5);
if (md5Changed) {
DUMP_LOG.info("[dump] md5 changed, save to disk cache ,groupKey={}, newMd5={},oldMd5={}", groupKey, md5, localContentMd5);
ConfigDiskServiceFactory.getInstance().saveToDisk(dataId, group, tenant, content);
} else {
DUMP_LOG.warn("[dump-ignore] ignore to save to disk cache. md5 consistent,groupKey={}, md5={}", groupKey, md5);
}
// 2. 更新 JVM 本地缓存对象 CacheItem
if (md5Changed) {
DUMP_LOG.info(
"[dump] md5 changed, update md5 and timestamp in jvm cache ,groupKey={}, newMd5={},oldMd5={},lastModifiedTs={}",
groupKey, md5, localContentMd5, lastModifiedTs);
updateMd5(groupKey, md5, content, lastModifiedTs, encryptedDataKey);
} else if (newLastModified) {
DUMP_LOG.info(
"[dump] md5 consistent ,timestamp changed, update timestamp only in jvm cache ,groupKey={},lastModifiedTs={}",
groupKey, lastModifiedTs);
updateTimeStamp(groupKey, lastModifiedTs, encryptedDataKey);
} else {
DUMP_LOG.warn(
"[dump-ignore] ignore to save to jvm cache. md5 consistent and no new timestamp changed.groupKey={}",
groupKey);
}
return true;
} catch (IOException ioe) {
DUMP_LOG.error("[dump-exception] save disk error. " + groupKey + ", " + ioe);
if (ioe.getMessage() != null) {
String errMsg = ioe.getMessage();
if (errMsg.contains(NO_SPACE_CN) || errMsg.contains(NO_SPACE_EN) || errMsg.contains(DISK_QUOTA_CN)
|| errMsg.contains(DISK_QUOTA_EN)) {
// Protect from disk full.
FATAL_LOG.error("Local Disk Full,Exit", ioe);
EnvUtil.systemExit();
}
}
return false;
} finally {
releaseWriteLock(groupKey);
}
}
}我们先来看一下 "写入到本地文件" 的逻辑,它最终会执行到 ConfigDiskService#saveToDisk 方法:
java
public class ConfigRawDiskService implements ConfigDiskService {
// 将配置信息写入磁盘文件
public void saveToDisk(String dataId, String group, String tenant, String content) throws IOException {
File targetFile = targetFile(dataId, group, tenant);
FileUtils.writeStringToFile(targetFile, content, ENCODE_UTF8);
}
}在这个方法中,它会将配置信息写入磁盘文件中,也就是说:Nacos 配置变更后,会异步将配置信息写入磁盘文件。这个文件何时被读取我们先不关注,我们先来考虑一下,如果配置变更在写入数据库成功后,服务立即宕机,也就是说磁盘文件还没有来得及写入,那么磁盘文件的数据该如何和数据库数据保持一致呢?
Nacos 借助 @PostConstruct 注解,在服务启动时,会执行 DumpService#dumpOperate 方法,这个方法的源码就不在这里贴了,它最终会执行到 DumpAllProcessor#process 方法,分页查询出所有的配置信息,逐一异步写入本地磁盘文件中,这样就保证了磁盘文件和数据库数据的一致性。
接下来我们再来看一下 "更新 JVM 本地缓存对象" 的逻辑,这段逻辑并不复杂,首先它需要保证在 JVM 本地缓存中创建了 CacheItem 本地缓存对象,然后创建 ConfigCache 对象记录必要的信息,注意在这段逻辑中,并没有为配置的内容 content 定义字段保存,这些逻辑完成后,发送了 LocalDataChangeEvent 事件:
发送
LocalDataChangeEvent事件的逻辑比较隐蔽,就像分布式事务中协同式 Saga 的设计模式(参见《微服务设计模式》),一个事件处理完成再去处理下一个事件,这使得代码的复杂度增加。
java
public class ConfigCacheService {
/**
* groupKey -> cacheItem.
*/
static final ConcurrentHashMap<String, CacheItem> CACHE = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
public static void updateMd5(String groupKey, String md5, String content, long lastModifiedTs, String encryptedDataKey) {
CacheItem cache = makeSure(groupKey, encryptedDataKey);
ConfigCache configCache = cache.getConfigCache();
if (configCache.getMd5() == null || !configCache.getMd5().equals(md5)) {
configCache.setMd5(md5);
configCache.setLastModifiedTs(lastModifiedTs);
configCache.setEncryptedDataKey(encryptedDataKey);
ConfigCachePostProcessorDelegate.getInstance().postProcess(configCache, content);
// 更新本地 JVM 缓存后,发布 LocalDataChangeEvent 事件
NotifyCenter.publishEvent(new LocalDataChangeEvent(groupKey));
}
}
static CacheItem makeSure(final String groupKey, final String encryptedDataKey) {
CacheItem item = CACHE.get(groupKey);
if (null != item) {
return item;
}
CacheItem tmp = new CacheItem(groupKey, encryptedDataKey);
item = CACHE.putIfAbsent(groupKey, tmp);
return (null == item) ? tmp : item;
}
}现在,配置变更已经成功写入数据库、磁盘文件和 JVM 内存,保证了在 Nacos Server 端配置数据的一致性。接下来便是由 Nacos Server 推送给 Nacos Client 的流程,这个逻辑便是在 LocalDataChangeEvent 事件的处理逻辑中完成的,RpcConfigChangeNotifier#onEvent 方法会监听 LocalDataChangeEvent 事件,并执行 configDataChanged 方法,这个方法的逻辑比较复杂,我们分段来看:
java
public class RpcConfigChangeNotifier extends Subscriber<LocalDataChangeEvent> {
@Autowired
ConfigChangeListenContext configChangeListenContext;
@Autowired
private ConnectionManager connectionManager;
@Override
public void onEvent(LocalDataChangeEvent event) {
String groupKey = event.groupKey;
String[] strings = GroupKey.parseKey(groupKey);
String dataId = strings[0];
String group = strings[1];
String tenant = strings.length > 2 ? strings[2] : "";
// 监听LocalDataChangeEvent事件,通过 gRPC 双向流推送配置变更通知到客户端
configDataChanged(groupKey, dataId, group, tenant);
}
public void configDataChanged(String groupKey, String dataId, String group, String tenant) {
// 获取所有监听该配置的客户端连接
Set<String> listeners = configChangeListenContext.getListeners(groupKey);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(listeners)) {
return;
}
int notifyClientCount = 0;
for (final String client : listeners) {
Connection connection = connectionManager.getConnection(client);
if (connection == null) {
continue;
}
boolean ifNamespaceTransfer = configChangeListenContext.getConfigListenState(client, groupKey).isNamespaceTransfer();
if (ifNamespaceTransfer) {
tenant = null;
}
ConnectionMeta metaInfo = connection.getMetaInfo();
String clientIp = metaInfo.getClientIp();
// 构建 ConfigChangeNotifyRequest 请求,包含变更的配置信息
ConfigChangeNotifyRequest notifyRequest = ConfigChangeNotifyRequest.build(dataId, group, tenant);
// 创建 RpcPushTask 异步推送任务,支持重试机制
RpcPushTask rpcPushRetryTask = new RpcPushTask(notifyRequest,
ConfigCommonConfig.getInstance().getMaxPushRetryTimes(), client, clientIp, metaInfo.getAppName());
// 异步推送通知
push(rpcPushRetryTask, connectionManager);
notifyClientCount++;
}
}
// 处理推送任务重试逻辑,支持延迟重试和连接管理
private static void push(RpcPushTask retryTask, ConnectionManager connectionManager) {
ConfigChangeNotifyRequest notifyRequest = retryTask.getNotifyRequest();
if (retryTask.isOverTimes()) {
// 重试次数超限,注销客户端连接
connectionManager.unregister(retryTask.getConnectionId());
} else if (connectionManager.getConnection(retryTask.getConnectionId()) != null) {
// 客户端连接存在,延迟重试推送(首次延迟0s,第二次2s,第三次4s),
// 本质上执行的是 ScheduledExecutorService#schedule(Runnable command, long delay, TimeUnit unit); 方法
ConfigExecutor.scheduleClientConfigNotifier(retryTask, retryTask.getTryTimes() * 2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} else {
// 客户端已离线,忽略推送任务
}
}
}在 configDataChanged 方法中,会先获取当前连接到 Nacos Server 的 所有订阅某个配置 groupKey 的 Nacos Client 连接,创建 RpcPushTask 异步推送任务,并调用 push 方法异步推送配置变更通知,注意这里执行配置推送任务时,使用的是 ScheduledExecutorService#schedule 它会根据重试次数指定延迟推送时间,首次推送是不延迟的,如果超过重试次数,表示客户端无法响应,则注销客户端连接,接下来我们看一下 RpcPushTask 的逻辑,它是 RpcConfigChangeNotifier 的内部类:
java
public class RpcConfigChangeNotifier extends Subscriber<LocalDataChangeEvent> {
class RpcPushTask implements Runnable {
ConfigChangeNotifyRequest notifyRequest;
int maxRetryTimes;
int tryTimes = 0;
String connectionId;
String clientIp;
String appName;
public RpcPushTask(ConfigChangeNotifyRequest notifyRequest, int maxRetryTimes, String connectionId,
String clientIp, String appName) {
this.notifyRequest = notifyRequest;
this.maxRetryTimes = maxRetryTimes;
this.connectionId = connectionId;
this.clientIp = clientIp;
this.appName = appName;
}
public boolean isOverTimes() {
return maxRetryTimes > 0 && this.tryTimes >= maxRetryTimes;
}
// 异步执行配置推送任务
@Override
public void run() {
// 累加推送配置的重试次数
tryTimes++;
TpsCheckRequest tpsCheckRequest = new TpsCheckRequest();
tpsCheckRequest.setPointName(POINT_CONFIG_PUSH);
if (!tpsControlManager.check(tpsCheckRequest).isSuccess()) {
// TPS限流检查失败,延迟重试推送任务
push(this, connectionManager);
} else {
// TPS检查通过,通过 gRPC 双向流推送配置变更通知到客户端
rpcPushService.pushWithCallback(connectionId, notifyRequest,
new RpcPushCallback(this, tpsControlManager, connectionManager),
ConfigExecutor.getClientConfigNotifierServiceExecutor());
}
}
}
}RpcPushTask#run 方法中会先检查限流配置,如果限流检查通过会通过 gRPC 推送配置变更到 Nacos Client,借助的是 gRPC 的双向流接口,并根据结果调用 RpcPushCallback 中的回调方法,RpcPushCallback 是 RpcConfigChangeNotifier 的内部类。如果配置推送成功会记录推送成功统计,否则调用 RpcConfigChangeNotifier#push 方法重试推送配置,如果超过最大重试次数(3次)则注销掉客户端:
java
public class RpcConfigChangeNotifier extends Subscriber<LocalDataChangeEvent> {
static class RpcPushCallback extends AbstractPushCallBack {
RpcPushTask rpcPushTask;
TpsControlManager tpsControlManager;
ConnectionManager connectionManager;
public RpcPushCallback(RpcPushTask rpcPushTask, TpsControlManager tpsControlManager,
ConnectionManager connectionManager) {
super(3000L);
this.rpcPushTask = rpcPushTask;
this.tpsControlManager = tpsControlManager;
this.connectionManager = connectionManager;
}
@Override
public void onSuccess() {
// 客户端成功接收配置变更通知,记录推送成功统计
TpsCheckRequest tpsCheckRequest = new TpsCheckRequest();
tpsCheckRequest.setPointName(POINT_CONFIG_PUSH_SUCCESS);
tpsControlManager.check(tpsCheckRequest);
}
@Override
public void onFail(Throwable e) {
// 推送失败,记录失败统计并进行重试
TpsCheckRequest tpsCheckRequest = new TpsCheckRequest();
tpsCheckRequest.setPointName(POINT_CONFIG_PUSH_FAIL);
tpsControlManager.check(tpsCheckRequest);
Loggers.REMOTE_PUSH.warn("Push fail, dataId={}, group={}, tenant={}, clientId={}",
rpcPushTask.getNotifyRequest().getDataId(), rpcPushTask.getNotifyRequest().getGroup(),
rpcPushTask.getNotifyRequest().getTenant(), rpcPushTask.getConnectionId(), e);
push(rpcPushTask, connectionManager);
}
}
}注意,RpcPushTask 在执行过程中都是没有被持久化的,也就是说一旦在执行过程中发生服务宕机,这些任务也会丢失,没有办法重新拉起向订阅配置的客户端推送,这样会不会导致客户端无法收到配置变更通知呢?实际上是不会的,配置变更除了服务端会主动推送以外,客户端还存在主动拉取的机制,也就是说 配置同步是推、拉结合的,保证客户端能够及时感知到配置变更,客户端的具体逻辑我们在后文中再解释。
以上我们讲解了 Nacos Server 单机采用 MySQL 数据库部署时,保证配置变更高可用的机制,接下来我们再看一下当集群部署并使用内嵌 Derby 数据库时,保证配置变更高可用的实现。
集群部署,采用内嵌 Derby 数据库
Nacos Server 在集群模式部署时,也可以使用 MySQL 数据库,不过因为集群模式使用 MySQL 数据库与单机模式使用 MySQL 数据库对数据一致性的保证没有区别,所以我们就不再讨论这种情况了。值得讨论的是:在集群模式下,Nacos Server 还支持使用内嵌数据库 Derby 部署,这种情况下,Nacos 采用了 Raft 算法保证了集群的强一致性,Raft 算法的实现它使用的是 开源项目 JRaft。在本文中,我们不会具体讲解 Raft 算法的流程,如果大家感兴趣可以参考文章 深入理解分布式共识算法 Raft。如下图所示:
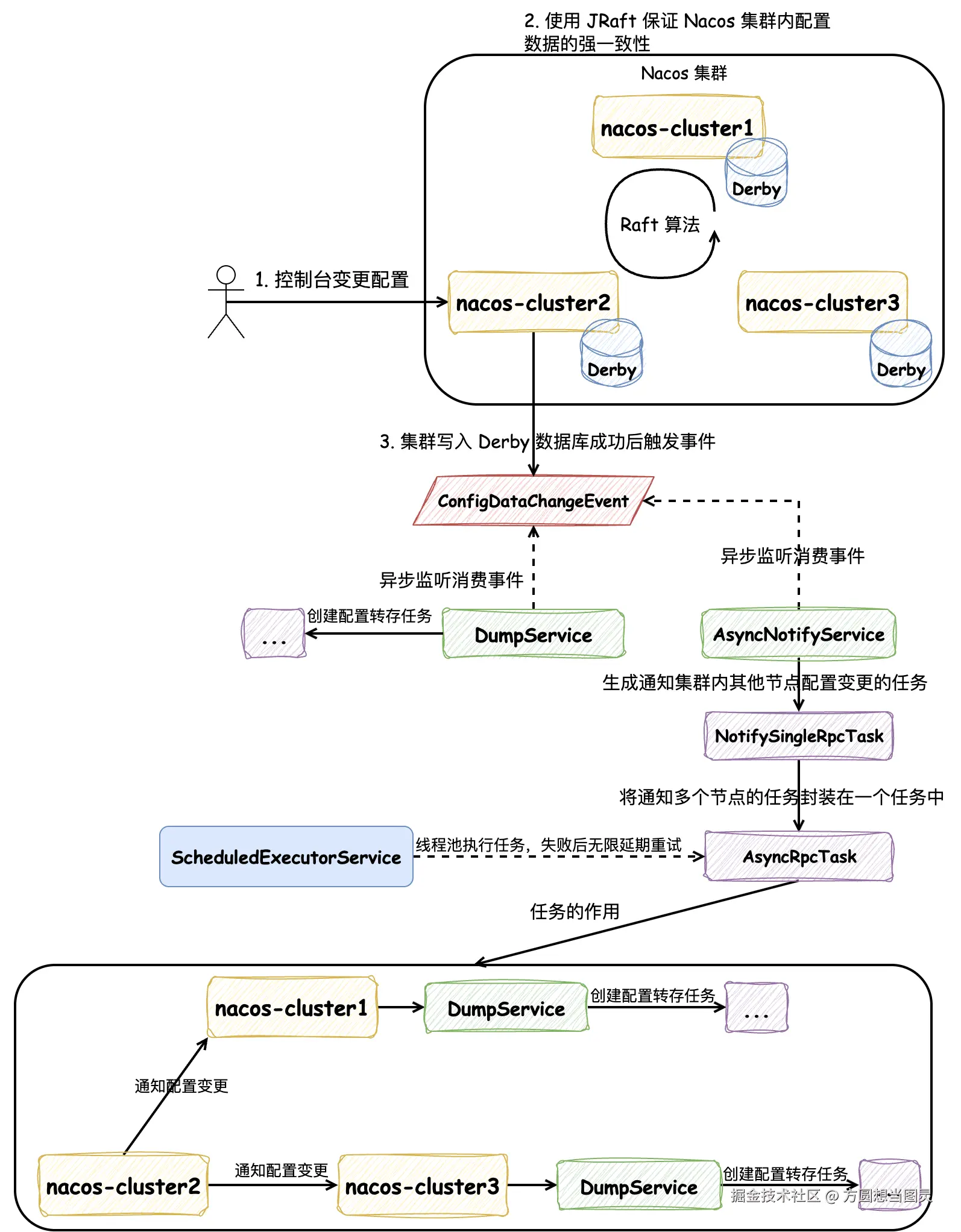
Nacos 在集群部署时,在控制台进行配置变更后,请求只会打到其中一台服务上,在这一台服务上会触发 JRaft 算法来完成各个服务内的 Derby 数据的写入,同样地,与写入 MySQL 的流程一致,只有在 JRaft 写入执行成功后才能继续处理。
在接收到请求的这台服务上,它会像单机模式一样发送 ConfigDataChangeEvent 事件,触发文件转存的操作,因为这部分内容是重复的就不再赘述了。集群模式与单机模式不同的是还有一个 AsyncNotifyService 服务会监听消费 ConfigDataChangeEvent 事件。AsyncNotifyService 的功能是 通知集群内其他节点触发文件转存的操作 ,如图所示,它会将通知集群内每个节点的请求封装成 NotifySingleRpcTask,创建所有节点的通知任务后,打包创建 AsyncRpcTask 任务,这个任务会被添加到 ScheduledExecutorService 线程池中,由线程池异步延时处理,如果发生处理失败的情况,会重新提交到线程池中,作为新的任务进行处理,以此来保证通知任务的处理成功。
以上就是 Nacos 在集群模式下采用 Derby 数据库时配置变更的处理流程,下面的内容我们根据源码来分析:当在 Nacos 控制台对配置进行修改时,Nacos 是如何借助 JRaft 保证数据一致性的。
同样地,ConsoleConfigController#publishConfig 方法是在 Nacos 控制台修改配置的入口,承接配置变更的 POST 请求:
java
@NacosApi
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/v3/console/cs/config")
@ExtractorManager.Extractor(httpExtractor = ConfigDefaultHttpParamExtractor.class)
public class ConsoleConfigController {
private final ConfigProxy configProxy;
public ConsoleConfigController(ConfigProxy configProxy) {
this.configProxy = configProxy;
}
@PostMapping()
@Secured(action = ActionTypes.WRITE, signType = SignType.CONFIG, apiType = ApiType.CONSOLE_API)
public Result<Boolean> publishConfig(HttpServletRequest request, ConfigFormV3 configForm) throws NacosException {
// ...
return Result.success(configProxy.publishConfig(configForm, configRequestInfo));
}
}因为 Nacos Server 启动时配置内嵌(Embedded)数据库 Derby,所以它会执行到 EmbeddedConfigInfoPersistServiceImpl 相关的方法中,我们以其中的 EmbeddedConfigInfoPersistServiceImpl#updateConfigInfoCas 方法为例,在这个方法中有一个私有方法 updateConfigInfoAtomicCas 特别关键,它主要在这里封装 SQL 的参数,并生成一条 SQL 并不立即执行,而是封装到上下文 EmbeddedStorageContextHolder 中:
java
@Service("embeddedConfigInfoPersistServiceImpl")
public class EmbeddedConfigInfoPersistServiceImpl implements ConfigInfoPersistService {
private ConfigOperateResult updateConfigInfoAtomicCas(final ConfigInfo configInfo, final String srcIp,
final String srcUser, Map<String, Object> configAdvanceInfo) {
// 处理 SQL 的入参
MapperContext context = new MapperContext();
context.putUpdateParameter(FieldConstant.CONTENT, configInfo.getContent());
// ...
// 生成 SQL 而不执行(ConfigInfoMapper#updateConfigInfoAtomicCas 在接口中定义的 default 方法)
MapperResult mapperResult = configInfoMapper.updateConfigInfoAtomicCas(context);
// 保存在上下文中
EmbeddedStorageContextHolder.addSqlContext(Boolean.TRUE, mapperResult.getSql(),
mapperResult.getParamList().toArray());
return getConfigInfoOperateResult(configInfo.getDataId(), configInfo.getGroup(), tenantTmp);
}
}
public interface ConfigInfoMapper extends Mapper {
default MapperResult updateConfigInfoAtomicCas(MapperContext context) {
List<Object> paramList = new ArrayList<>();
// 封装 set 中的参数
paramList.add(context.getUpdateParameter(FieldConstant.CONTENT));
// ...
// 封装 where 中的参数
paramList.add(context.getWhereParameter(FieldConstant.MD5));
// ...
String sql = "UPDATE config_info SET " + "content=?, md5=?, src_ip=?, src_user=?, gmt_modified="
+ getFunction("NOW()")
+ ", app_name=?, c_desc=?, c_use=?, effect=?, type=?, c_schema=?, encrypted_data_key=? "
+ "WHERE data_id=? AND group_id=? AND tenant_id=? AND (md5=? OR md5 IS NULL OR md5='')";
return new MapperResult(sql, paramList);
}
}在这里有两个点值得注意:
- 生成 Update SQL 而不执行,却放在了上下文
EmbeddedStorageContextHolder中,它是一个ThreadLocal对象 - 生成的 SQL 使用 CAS 的策略,在 WHERE 条件中它会将前端控制台配置的 MD5 值作为条件传入,防止并发修改配置时的脏写问题
现在既然已经将变更 Derby 数据库 Update SQL 保存在了上下文中,接下来就是看它什么时候被执行了,它会继续执行 DatabaseOperate#blockUpdate 方法,从它的命名中也能发现它是同步阻塞执行的逻辑:
java
public interface DatabaseOperate {
// ...
// 阻塞更新逻辑
default Boolean blockUpdate(BiConsumer<Boolean, Throwable> consumer) {
try {
// 在上下文中获取 SQL
return update(EmbeddedStorageContextHolder.getCurrentSqlContext(), consumer);
} finally {
EmbeddedStorageContextHolder.cleanAllContext();
}
}
}它是一个 default 方法,会调用 DistributedDatabaseOperateImpl#update 方法,它会将 SQL 封装在 WriteRequest 中,调用封装好的 Raft 协议的 write 方法:
java
public class DistributedDatabaseOperateImpl extends RequestProcessor4CP implements BaseDatabaseOperate {
private CPProtocol protocol;
@Override
public Boolean update(List<ModifyRequest> sqlContext, BiConsumer<Boolean, Throwable> consumer) {
try {
final String key =
System.currentTimeMillis() + "-" + group() + "-" + memberManager.getSelf().getAddress() + "-"
+ MD5Utils.md5Hex(sqlContext.toString(), PersistenceConstant.DEFAULT_ENCODE);
WriteRequest request = WriteRequest.newBuilder().setGroup(group()).setKey(key)
// 将 SQL 序列化成字节数组保存在 WriteRequest 中
.setData(ByteString.copyFrom(serializer.serialize(sqlContext)))
.putAllExtendInfo(EmbeddedStorageContextHolder.getCurrentExtendInfo())
.setType(sqlContext.getClass().getCanonicalName()).build();
if (Objects.isNull(consumer)) {
// 重要:raft 协议 write 开始执行,同步阻塞调用
Response response = this.protocol.write(request);
if (response.getSuccess()) {
return true;
}
LOGGER.error("execute sql modify operation failed : {}", response.getErrMsg());
return false;
} else {
// ...
}
return true;
} catch (TimeoutException e) {
LOGGER.error("An timeout exception occurred during the update operation");
throw new NacosRuntimeException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR, e.toString());
} catch (Throwable e) {
LOGGER.error("An exception occurred during the update operation : {}", e);
throw new NacosRuntimeException(NacosException.SERVER_ERROR, e.toString());
}
}
}其中 Response response = this.protocol.write(request); 逻辑为执行 Raft 算法的写流程:
java
public class JRaftProtocol extends AbstractConsistencyProtocol<RaftConfig, RequestProcessor4CP>
implements CPProtocol<RaftConfig, RequestProcessor4CP> {
@Override
public Response write(WriteRequest request) throws Exception {
// 依靠 CompletableFuture 实现阻塞同步调用
CompletableFuture<Response> future = writeAsync(request);
return future.get(10_000L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
@Override
public CompletableFuture<Response> writeAsync(WriteRequest request) {
return raftServer.commit(request.getGroup(), request, new CompletableFuture<>());
}
}在这段逻辑中依靠 CompletableFuture 实现了同步阻塞的写调用。JRaftServer#commit 方法是处理 Raft 算法中写请求的流程:
java
public class JRaftServer {
/**
* [raft] 处理写请求,所有写操作必须通过 Leader 节点处理
*/
public CompletableFuture<Response> commit(final String group, final Message data,
final CompletableFuture<Response> future) {
LoggerUtils.printIfDebugEnabled(Loggers.RAFT, "data requested this time : {}", data);
final RaftGroupTuple tuple = findTupleByGroup(group);
if (tuple == null) {
future.completeExceptionally(new IllegalArgumentException("No corresponding Raft Group found : " + group));
return future;
}
FailoverClosureImpl closure = new FailoverClosureImpl(future);
final Node node = tuple.node;
if (node.isLeader()) {
// 当前节点是 Leader,直接应用写操作到状态机
applyOperation(node, data, closure);
} else {
// 当前节点不是 Leader,将请求转发给 Leader 处理
invokeToLeader(group, data, rpcRequestTimeoutMs, closure);
}
return future;
}
}如果是 Leader 节点的话,直接操作日志写入,在这里的逻辑都是与 JRaft 框架相关了,不过我们只需要关注与 Raft 算法有关的流程,注意注释信息:
java
public class JRaftServer {
public void applyOperation(Node node, Message data, FailoverClosure closure) {
// Task 是用户使用 jraft 最核心的类之一,用于向一个 raft 集群提交一个任务,这个任务提交到 leader,并复制到其他 follower 节点
// 通俗的理解为让 Leader 节点记录 log 日志,并同步到其他 Follower 节点
final Task task = new Task();
// done 表示任务的回调方法,在任务完成的时候,即 apply 的时候,通知此回调对象,无论成功还是失败。
task.setDone(new NacosClosure(data, status -> {
NacosClosure.NacosStatus nacosStatus = (NacosClosure.NacosStatus) status;
closure.setThrowable(nacosStatus.getThrowable());
closure.setResponse(nacosStatus.getResponse());
closure.run(nacosStatus);
}));
// add request type field at the head of task data.
byte[] requestTypeFieldBytes = new byte[2];
requestTypeFieldBytes[0] = ProtoMessageUtil.REQUEST_TYPE_FIELD_TAG;
if (data instanceof ReadRequest) {
requestTypeFieldBytes[1] = ProtoMessageUtil.REQUEST_TYPE_READ;
} else {
requestTypeFieldBytes[1] = ProtoMessageUtil.REQUEST_TYPE_WRITE;
}
// data 任务的数据,在本次逻辑中是变更配置的 SQL,用户应当将要复制的业务数据通过一定序列化方式(比如 java/hessian2) 序列化成一个 ByteBuffer,放到 task 里
byte[] dataBytes = data.toByteArray();
task.setData((ByteBuffer) ByteBuffer.allocate(requestTypeFieldBytes.length + dataBytes.length)
.put(requestTypeFieldBytes).put(dataBytes).position(0));
// 使用 node 提交任务,node 可以为是 Raft 集群的 Leader 节点,操作 apply 方法之后表示将日志记录下来并给其他 Follower 节点同步
node.apply(task);
}
}当在 Raft 集群中有超过半数节点已经将本次任务的日志持久化后,它会自动调用 StateMachineAdapter#onApply 方法,表示将日志应用到状态机,即使写请求生效:
java
class NacosStateMachine extends StateMachineAdapter {
/**
* 最核心的方法,应用任务列表应用到状态机,任务将按照提交顺序应用。
* 请注意,当这个方法返回的时候,我们就认为这一批任务都已经成功应用到状态机上,如果你没有完全应用(比如错误、异常),
* 将会被当做一个 critical 级别的错误,报告给状态机的 StateMachineAdapter#onError 方法,错误类型为 ERROR_TYPE_STATE_MACHINE
*/
@Override
public void onApply(Iterator iter) {
int index = 0;
int applied = 0;
Message message;
NacosClosure closure = null;
try {
// 遍历处理本次应用的任务(日志)
while (iter.hasNext()) {
// 结果通过 Status 告知,Status#isOk() 告诉你成功还是失败
Status status = Status.OK();
try {
// 如果 task 没有设置 closure,那么 done 会是 null,
// 另外在 follower 节点上,done 也是 null,因为 done 不会被复制到除了 leader 节点之外的其他 raft 节点
if (iter.done() != null) {
// 获取回调函数
closure = (NacosClosure) iter.done();
// 从 Leader 节点的日志条目中获取消息
message = closure.getMessage();
} else {
// 从 Follower 节点复制的日志条目中解析消息
final ByteBuffer data = iter.getData();
// 解析成 SQL
message = ProtoMessageUtil.parse(data.array());
if (message instanceof ReadRequest) {
// Follower 节点忽略读请求,只处理写请求
applied++;
index++;
iter.next();
continue;
}
}
LoggerUtils.printIfDebugEnabled(Loggers.RAFT, "receive log : {}", message);
// 应用写请求到业务状态机,实现数据的持久化存储
if (message instanceof WriteRequest) {
// 使 Update SQL 执行并生效,在 Response 中返回执行结果
Response response = processor.onApply((WriteRequest) message);
// 对结果的后置处理
postProcessor(response, closure);
}
// 处理读请求(仅在 Leader 节点)
if (message instanceof ReadRequest) {
Response response = processor.onRequest((ReadRequest) message);
postProcessor(response, closure);
}
} catch (Throwable e) {
index++;
status.setError(RaftError.UNKNOWN, e.toString());
Optional.ofNullable(closure).ifPresent(closure1 -> closure1.setThrowable(e));
throw e;
} finally {
Optional.ofNullable(closure).ifPresent(closure1 -> closure1.run(status));
}
applied++;
index++;
iter.next();
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 状态机应用失败时进行回滚,保证数据一致性
Loggers.RAFT.error("processor : {}, stateMachine meet critical error: {}.", processor, t);
iter.setErrorAndRollback(index - applied,
new Status(RaftError.ESTATEMACHINE, "StateMachine meet critical error: %s.",
ExceptionUtil.getStackTrace(t)));
}
}
}因为将任务应用到状态机时会在 Leader 和 Follower 节点都执行,所以以上逻辑会包含针对 Leader 节点和 Follower 节点的执行逻辑。它会在 Response response = processor.onApply((WriteRequest) message); 逻辑中完成 Update SQL 的执行,如下 DistributedDatabaseOperateImpl#onApply 方法:
java
@Conditional(ConditionDistributedEmbedStorage.class)
@Component
public class DistributedDatabaseOperateImpl extends RequestProcessor4CP implements BaseDatabaseOperate {
@Override
public Response onApply(WriteRequest log) {
LoggerUtils.printIfDebugEnabled(LOGGER, "onApply info : log : {}", log);
final ByteString byteString = log.getData();
Preconditions.checkArgument(byteString != null, "Log.getData() must not null");
final Lock lock = readLock;
lock.lock();
try {
// 将任务中的数据转换成本次修改配置要执行的 SQL
List<ModifyRequest> sqlContext = serializer.deserialize(byteString.toByteArray(), List.class);
sqlLimiter.doLimitForModifyRequest(sqlContext);
boolean isOk = false;
// 区分导入和非导入逻辑
if (log.containsExtendInfo(DATA_IMPORT_KEY)) {
isOk = doDataImport(jdbcTemplate, sqlContext);
} else {
sqlContext.sort(Comparator.comparingInt(ModifyRequest::getExecuteNo));
// 执行修改 SQL
isOk = update(transactionTemplate, jdbcTemplate, sqlContext);
PersistenceExecutor.executeEmbeddedDump(() -> {
for (EmbeddedApplyHook each : EmbeddedApplyHookHolder.getInstance().getAllHooks()) {
each.afterApply(log);
}
});
}
return Response.newBuilder().setSuccess(isOk).build();
} catch (BadSqlGrammarException | DataIntegrityViolationException e) {
return Response.newBuilder().setSuccess(false).setErrMsg(e.toString()).build();
} catch (DataAccessException e) {
throw new ConsistencyException(e.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
LoggerUtils.printIfWarnEnabled(LOGGER, "onApply warn : log : {}", log, e);
return Response.newBuilder().setSuccess(false).setErrMsg(e.toString()).build();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}执行完成后,通过 Response 对象来判断执行成功还是执行失败,postProcessor 方法负责后置处理,最终回调的逻辑如下:
java
public class FailoverClosureImpl implements FailoverClosure {
// ...
private final CompletableFuture<Response> future;
@Override
public void run(Status status) {
// 调用 CompletableFuture#complete 方法标记任务完成,同步阻塞调用恢复,并返回结果值
if (status.isOk()) {
future.complete(data);
return;
}
final Throwable throwable = this.throwable;
future.completeExceptionally(Objects.nonNull(throwable) ? new ConsistencyException(throwable.getMessage())
: new ConsistencyException("operation failure"));
}
}其中 future 字段为在执行 Raft 的写请求时保证同步阻塞调用的 CompletableFuture,如果执行成功调用 CompletableFuture#complete 方法便能让停止阻塞并返回结果,以上便是在 Nacos 集群中执行写请求的流程。在 Nacos 源码的 DistributedDatabaseOperateImpl 类上有以下流程图注释能非常清晰的反映整个流程:
- 用户
user执行配置变更时执行publishConfig的逻辑,要执行的 SQL 会被保存在上下文SqlContextUtils中 - 对数据库的操作都会被提交到 JRaft 协议状态机
JRaftProtocol中执行,应用onApply到状态机时会从上下文SqlContextUtils中获取 SQL 并执行 - 同步阻塞返回用户
user结果
text
┌────────────────────┐
┌──▶│ PersistService │
│ └────────────────────┘ ┌─────────────────┐
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ │ ▼
│ │ │ ┌────────────────────┐ save sql
│ ▼ │ │ saveConfig │──────────context─────────────┐
│ ┌────────────────┐ │ └────────────────────┘ │
│ │ publishConfig │───┘ │ │
│ └────────────────┘ │ │
│ ▼ ▼
│ ┌─────────────────────────┐ save sql ┌────────────────────┐
│ │ saveConfigTagRelations │────context────▶│ SqlContextUtils │◀─┐
publish config └─────────────────────────┘ └────────────────────┘ │
│ │ ▲ │
│ │ │ │
│ ▼ │ │
│ ┌───────────────────────┐ save sql │ │
┌────┐ │ saveConfigHistory │─────────context────────────┘ │
│user│ └───────────────────────┘ │
└────┘ │
▲ │
│ ┌1:getCurrentSqlContexts───────────────────────────────┘
│ │
│ │
│ │
│ ┌───────────────┐ ┌─────────────────────┐
│ │ JdbcTemplate │◀───│ DatabaseOperate │───┐
4:execute result └───────────────┘ └─────────────────────┘ │
│ │ ▲ │
│ │ │ │
│ │ 3:onApply 2:submit(List<ModifyRequest>)
│ │ │ │
│ ▼ │ │
│ ┌──────────────┐ │ │
│ │ Apache Derby │ ┌───────────────────────┐ │
│ └──────────────┘ │ JRaftProtocol │◀─┘
│ └───────────────────────┘
│ │
│ │
└───────────────────────────────────────────┘当 Raft 的流程执行完成后,会回到在文章开头我们提到的 ConfigOperationService#publishConfig 方法中,在单机部署的模式下,我们提到过:Nacos 会触发 ConfigDataChangeEvent 事件来触发 DumpTask 来将配置信息写入到本地磁盘文件和 JVM 缓存中,并在随后触发 LocalDataChangeEvent 事件通知连接到该单机上所有的 Nacos Client 保证配置变更的通知。现在我们来考虑一个问题:当我们在控制台修改配置信息时,配置变更的请求只会打到 Nacos 集群的某一台服务上,在这一台服务上会执行 Dump 文件的操作并通知连接到该台服务器上的 Nacos Client 配置变更,那 集群中其他节点是不是也需要通知连接到本身的 Nacos Client 配置变更 呢?答案是肯定的。
在集群模式下,ConfigDataChangeEvent 事件会被 AsyncNotifyService 消费,其中的 AsyncNotifyService#handleConfigDataChangeEvent 方法会处理 ConfigDataChangeEvent 事件来完成通知集群内其他节点配置发生变更的操作:
java
@Service
public class AsyncNotifyService {
private ServerMemberManager memberManager;
// 处理 ConfigDataChangeEvent 事件
void handleConfigDataChangeEvent(Event event) {
if (event instanceof ConfigDataChangeEvent) {
ConfigDataChangeEvent evt = (ConfigDataChangeEvent) event;
MetricsMonitor.incrementConfigChangeCount(evt.tenant, evt.group, evt.dataId);
// 集群中除了自己的所有节点
Collection<Member> ipList = memberManager.allMembersWithoutSelf();
Queue<NotifySingleRpcTask> rpcQueue = new LinkedList<>();
for (Member member : ipList) {
// 生成通知其他节点数据变更的任务,包含配置信息和节点IP信息
NotifySingleRpcTask notifySingleRpcTask = generateTask(evt, member);
// 加入队列
rpcQueue.add(notifySingleRpcTask);
}
// 异步执行任务
if (!rpcQueue.isEmpty()) {
ConfigExecutor.executeAsyncNotify(new AsyncRpcTask(rpcQueue));
}
}
}
}它会将变更的配置和要通知的节点信息封装成一个个 NotifySingleRpcTask 异步任务,并放在队列 Queue<NotifySingleRpcTask> 中,随后使用线程池异步执行 ConfigExecutor#executeAsyncNotify 队列中所有的任务。AsyncRpcTask 是在 AsyncNotifyService 封装的内部类,执行通知的逻辑为 AsyncNotifyService#executeAsyncRpcTask 方法,借助 gRPC 通知其他节点,并在失败后重试,请关注以下逻辑的注释信息:
java
@Service
public class AsyncNotifyService {
private static final int MIN_RETRY_INTERVAL = 500;
private static final int INCREASE_STEPS = 1000;
private static final int MAX_COUNT = 6;
@Autowired
private ConfigClusterRpcClientProxy configClusterRpcClientProxy;
private ServerMemberManager memberManager;
public class AsyncRpcTask implements Runnable {
private Queue<NotifySingleRpcTask> queue;
public AsyncRpcTask(Queue<NotifySingleRpcTask> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 处理通知其他节点配置变更的任务
executeAsyncRpcTask(queue);
}
}
void executeAsyncRpcTask(Queue<NotifySingleRpcTask> queue) {
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
NotifySingleRpcTask task = queue.poll();
ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequest syncRequest = new ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequest();
syncRequest.setDataId(task.getDataId());
syncRequest.setTenant(task.getTenant());
syncRequest.setGroup(task.getGroup());
syncRequest.setLastModified(task.getLastModified());
syncRequest.setGrayName(task.getGrayName());
syncRequest.setBeta(task.isBeta());
syncRequest.setTag(task.getTag());
Member member = task.member;
String event = getNotifyEvent(task);
if (memberManager.hasMember(member.getAddress())) {
// 将可能下线的服务放入异步队列延迟执行,健康的服务器直接通知
boolean unHealthNeedDelay = isUnHealthy(member.getAddress());
if (unHealthNeedDelay) {
ConfigTraceService.logNotifyEvent(task.getDataId(), task.getGroup(), task.getTenant(), null,
task.getLastModified(), InetUtils.getSelfIP(), event,
ConfigTraceService.NOTIFY_TYPE_UNHEALTH, 0, member.getAddress());
asyncTaskExecute(task);
} else {
try {
// gRPC 通知配置发生变更
configClusterRpcClientProxy.syncConfigChange(member, syncRequest,
new AsyncRpcNotifyCallBack(AsyncNotifyService.this, task));
} catch (Exception e) {
// 无限重试,直到重试成功或服务停止
MetricsMonitor.getConfigNotifyException().increment();
asyncTaskExecute(task);
}
}
} else {
//No nothing if member has offline.
}
}
}
private void asyncTaskExecute(NotifySingleRpcTask task) {
// 获取重试延迟时间
int delay = getDelayTime(task);
Queue<NotifySingleRpcTask> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.add(task);
// 借助 ScheduledExecutorService 线程池延迟执行的任务
AsyncRpcTask asyncTask = new AsyncRpcTask(queue);
ConfigExecutor.scheduleAsyncNotify(asyncTask, delay, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
// 执行失败后获取延迟执行的时间
private static int getDelayTime(NotifySingleRpcTask task) {
// 失败次数
int failCount = task.getFailCount();
// 指数级计算重试间隔
int delay = MIN_RETRY_INTERVAL + failCount * failCount * INCREASE_STEPS;
// 最大重试次数限制,超过后仍然继续重试,只是限制了重试间隔的指数爆炸
if (failCount <= MAX_COUNT) {
task.setFailCount(failCount + 1);
}
return delay;
}
}集群中其他节点在收到 ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequest 请求后,会在 ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequestHandler 类中处理:
java
@Component
@InvokeSource(source = {RemoteConstants.LABEL_SOURCE_CLUSTER})
public class ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequestHandler
extends RequestHandler<ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequest, ConfigChangeClusterSyncResponse> {
private final DumpService dumpService;
private ConfigMigrateService configMigrateService;
public ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequestHandler(DumpService dumpService,
ConfigMigrateService configMigrateService) {
this.dumpService = dumpService;
this.configMigrateService = configMigrateService;
}
@Override
@NamespaceValidation
@TpsControl(pointName = "ClusterConfigChangeNotify")
@ExtractorManager.Extractor(rpcExtractor = ConfigRequestParamExtractor.class)
@Secured(signType = SignType.CONFIG, apiType = ApiType.INNER_API)
public ConfigChangeClusterSyncResponse handle(ConfigChangeClusterSyncRequest configChangeSyncRequest,
RequestMeta meta) throws NacosException {
// 参数校验
checkCompatity(configChangeSyncRequest, meta);
ParamUtils.checkParam(configChangeSyncRequest.getTag());
// 执行 Dump 操作
DumpRequest dumpRequest = DumpRequest.create(configChangeSyncRequest.getDataId(),
configChangeSyncRequest.getGroup(), configChangeSyncRequest.getTenant(),
configChangeSyncRequest.getLastModified(), meta.getClientIp());
dumpRequest.setGrayName(configChangeSyncRequest.getGrayName());
dumpService.dump(dumpRequest);
return new ConfigChangeClusterSyncResponse();
}
// ...
}它的逻辑非常简单,接受到请求后,执行文件 Dump 操作并通知连接到服务本身的所有 Nacos Client 客户端配置发生变更。接下来,我们再看一下在 Nacos Server 端通过控制台查询配置数据时,读取 Derby 数据库是如何读取的。在开始具体的逻辑前,先给大家留一个问题:在集群模式部署时,每个集群实例都有一份配置数据的副本,当请求打到不同的实例时,如果存在实例未完成最新配置数据的写入,会不会存在多次请求不一致的情况呢?
在 Nacos Server 端通过控制台读取配置数据
在 Nacos 集群模式下使用内嵌 Derby 数据库时遵循 Raft 算法,如果要查询配置信息时它采用的是 ReadIndex Read 实现线性一致性读,我们直接略过非核心代码,分析与 Raft 相关的源码部分:
java
public class JRaftServer {
/**
* [raft] 处理读请求,使用 ReadIndex 机制保证线性一致性读
*/
CompletableFuture<Response> get(final ReadRequest request) {
final String group = request.getGroup();
CompletableFuture<Response> future = new CompletableFuture<>();
final RaftGroupTuple tuple = findTupleByGroup(group);
if (Objects.isNull(tuple)) {
future.completeExceptionally(new NoSuchRaftGroupException(group));
return future;
}
final Node node = tuple.node;
final RequestProcessor processor = tuple.processor;
try {
// 使用 ReadIndex Read 机制确保读取到的数据是最新的已提交数据
// 其中 requestContext (第一个入参)提供给用户作为请求的附加上下文,可以在 closure 里再次拿到继续处理
node.readIndex(BytesUtil.EMPTY_BYTES, new ReadIndexClosure() {
@Override
public void run(Status status, long index, byte[] reqCtx) {
// ReadIndex 成功,传入的 closure 将被调用,可以安全地从本地状态机读取数据
if (status.isOk()) {
try {
Response response = processor.onRequest(request);
future.complete(response);
} catch (Throwable t) {
MetricsMonitor.raftReadIndexFailed();
future.completeExceptionally(new ConsistencyException(
"The conformance protocol is temporarily unavailable for reading", t));
}
return;
}
MetricsMonitor.raftReadIndexFailed();
Loggers.RAFT.error("ReadIndex has error : {}, go to Leader read.", status.getErrorMsg());
MetricsMonitor.raftReadFromLeader();
// ReadIndex 失败,降级到 Leader 读取保证一致性
readFromLeader(request, future);
}
});
return future;
} catch (Throwable e) {
// ReadIndex 异常,直接从 Leader 读取
MetricsMonitor.raftReadFromLeader();
Loggers.RAFT.warn("Raft linear read failed, go to Leader read logic : {}", e.toString());
// run raft read
readFromLeader(request, future);
return future;
}
}
// raft log process
public void readFromLeader(final ReadRequest request, final CompletableFuture<Response> future) {
commit(request.getGroup(), request, future);
}
}这部分源码比较简单,因为 JRaft 框架将 ReadIndex Read 的实现封装起来了,开放出了 readIndex 方法来直接复用,注意如果在 ReadIndex 时失败,会走 Raft Log 流程来处理读请求,这个开销就相对来说比较大了。如果大家对 Raft 算法不了解,可以阅读参考 深入理解分布式共识算法 Raft。
至此,变更配置后 Nacos Server 端对配置数据一致性的保证相关的源码逻辑就已经讲解完了,接下来我们就要看看 Nacos Client 是如何接收配置变更并更新配置信息的。
由于社区最大字数限制,请看下篇:Nacos 源码深度畅游:Nacos 配置同步详解(下)。