Hooks(钩子)是 iFlow CLI 中的事件驱动机制,允许您在特定的生命周期事件发生时自动执行自定义命令。通过配置 Hooks,您可以实现工具调用前后的自动化处理、环境设置增强、会话停止时的清理操作等功能。
Hooks配置官方介绍见:Hooks | 心流开放平台
配置方法概述
1. Hook 类型(事件类型)
Hook 类型决定了 Hook 在何时触发。iFlow CLI 目前支持 9 种 Hooks 类型:
| 事件 | 触发时机 | 典型用途 |
|---|---|---|
| PreToolUse | 工具执行前 | 阻止危险命令、参数校验 |
| PostToolUse | 工具执行后 | 自动格式化、运行 linter |
| SetUpEnvironment | 会话开始时,环境信息设置阶段 | 动态生成项目信息、增强 AI 上下文 |
| Stop | 主会话结束时 | 清理资源、保存会话信息 |
| SubagentStop | 子代理会话结束时 | 任务完成度验证、错误检测 |
| SessionStart | 会话开始时(启动、恢复、清理、压缩) | 环境初始化、加载配置 |
| SessionEnd | 会话正常结束时 | 生成会话总结、归档记录 |
| UserPromptSubmit | 用户提交提示词前 | 内容过滤、敏感信息拦截 |
| Notification | iFlow 发送通知时 | 通知记录、第三方系统集成 |
2. Matcher(匹配器)
"matcher": 精确控制哪些工具调用会触发该 Hook
bash
{
"matcher": "Bash", // 针对 Bash 命令
"matcher": "Write|Edit", // 针对文件写入或编辑
"matcher": "*", // 针对所有工具
"matcher": "startup", // 仅在新会话启动时触发
"matcher": ".*permission.*" // 正则表达式:匹配包含"permission"的通知
}3. Command(命令)
Command 是 Hook 触发时执行的具体命令:
-
可以是简单的 Shell 命令:echo 'Subagent task completed'
-
可以是 Python 脚本:python3 .iflow/hooks/security_check.py
4. 配置路径
bash
your-project 或根目录~/
├── .iflow/
│ ├── settings.json
│ └── hooks/
│ └── security_check.py
├── .env # 敏感文件
├── .env.example
└── src/
└── main.py5. Hook 配置
配置文件路径:.iflow/seetings.json
多个 hooks 示例:
bash
{
"hooks": {
"SessionStart": [
{
"matcher": "startup",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "python3 ~/.iflow/hooks/session_start.py"
}
]
}
],
"SessionEnd": [
{
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "python3 ~/.iflow/hooks/session_summary.py",
"timeout": 30
}
]
}
],
"UserPromptSubmit": [
{
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "python3 ~/.iflow/hooks/content_filter.py",
"timeout": 10
}
]
}
]
}
}Hook类型
1. PreToolUse Hook
触发时机:在工具执行之前
用途:
-
验证工具参数
-
设置执行环境
-
记录工具调用日志
-
阻止不安全的操作
配置说明:
配置文件位置: ~/.iflow/settings.json
Hook 脚本位置: ~/.iflow/hooks/
示例配置:
添加一个钩子,记录 iFlow cli 运行的 shell 命令,在命令行中安装 jq 以进行 JSON 处理。
配置前,先本地安装 jq :
bash
npm install jq在 settings.json 文件中配置以下 Hook ,该 Hook 可以输出 ToolUse 的 bash 相关命令和描述
bash
{
"hooks": {
"PreToolUse": [
{
"matcher": "Bash",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "jq -r '\"\\(.tool_input.command) - \\(.tool_input.description // \"No description\")\"' >> ~/.iflow/bash-command-log.txt"
}
]
}
]
}
}如想查看具体的log信息,可通过命令 cat ~/.iflow/bash-command-log.txt 示例如下:

2. PostToolUse Hook
触发时机 :在工具执行之后 用途:
-
处理工具执行结果
-
清理临时文件
-
发送通知
-
记录执行统计
和 PreToolUse Hook 一样可以使用 "matcher" 精确控制哪些工具调用会触发该 Hook
示例配置:
尝试添加一个 tool 编辑后自动格式化 TypeScript 文件的 Hook :
bash
{
"hooks": {
"PostToolUse": [
{
"matcher": "Edit|Write",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "jq -r '.tool_input.file_path' | { read file_path; if echo \"$file_path\" | grep -q '\\.ts$'; then npx prettier --write \"$file_path\"; fi; }"
}
]
}
]
}
}3. SetUpEnvironment Hook
触发时机 :会话开始时,环境信息设置阶段 用途:
-
动态生成项目信息
-
设置运行时环境变量
-
增强 AI 的上下文信息
-
加载项目特定配置
示例配置:
创建一个 hook ,可以在每次会话开始时,调用 initial.py 打印所有进程信息
bash
{
"hooks": {
"SetUpEnvironment": [
{
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "python3 ~/.iflow/hooks/initial.py",
"timeout": 30
}
]
}
]
}
}initial.py 脚本代码:(保存路径为 .iflow/hooks/initial.py)
bash
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
import subprocess
import datetime
timestamp = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
# 扫描所有进程
try:
result = subprocess.run(['ps', 'aux'], capture_output=True, text=True)
all_processes = result.stdout
except Exception as e:
all_processes = f'Error: {str(e)}'
# 记录启动时的所有进程
with open(os.path.expanduser('~/.iflow/start.txt'), 'w') as f:
f.write(f'{timestamp}\n')
f.write('All Processes:\n')
f.write(all_processes)启动后打印示例如下:
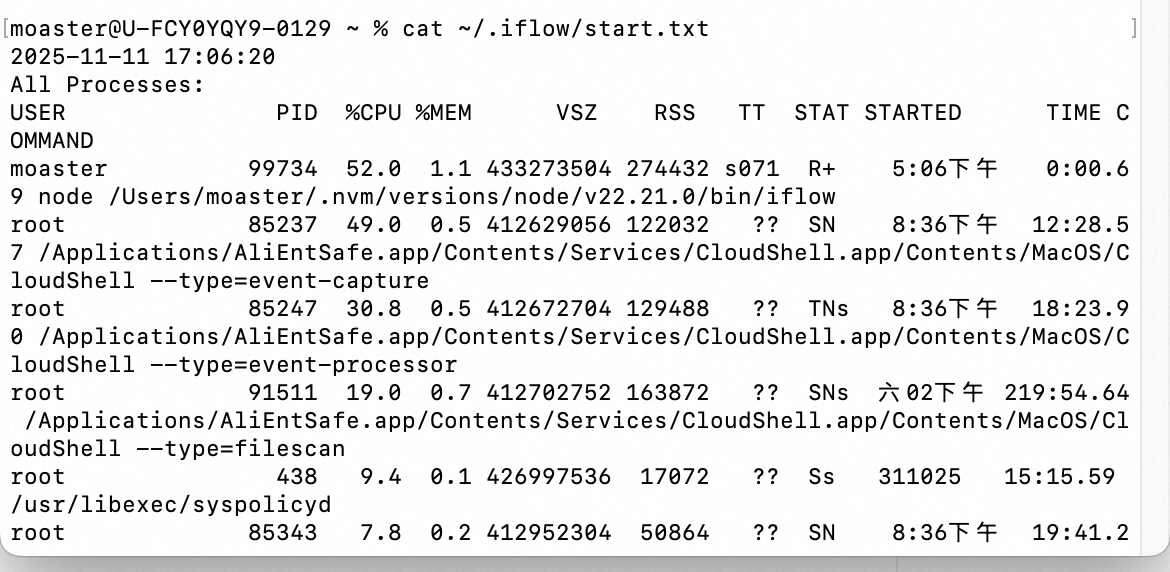
4. Stop Hook
触发时机 :主会话结束时 用途:
-
清理会话资源
-
保存会话信息
-
发送会话总结
-
执行清理脚本
示例配置:
尝试添加一个主会话结束的 hook ,每次退出后记录退出时间
bash
{
"hooks": {
"Stop": [
{
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "python3 ~/.iflow/hooks/save.py",
"timeout": 30
}
]
}
]
}
}save.py 脚本代码:(保存路径为 .iflow/hooks/save.py)
bash
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
import datetime
timestamp = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
with open(os.path.expanduser('~/.iflow/stop-time.txt'), 'w') as f:
f.write(timestamp + '\n')打开终端,进行操作后退出
cat ~/.iflow/stop-time.txt 查看退出时间
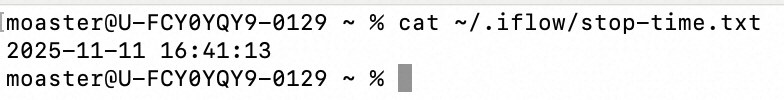
5. SubagentStop Hook
触发时机:子代理会话结束时
用途:在子代理停止前进行决策评估
使用场景:
-
任务完成度验证:确保子代理真正完成任务
-
错误检测:发现并阻止有错误的子代理停止
-
上下文完整性检查:确保已收集足够信息
-
质量控制:在子代理停止前进行智能审核
6. SessionStart Hook
触发时机:会话开始时(启动、恢复、清理、压缩)
用途:在会话开始时(启动、恢复、清理、压缩)执行初始化操作,设置环境变量、加载配置或提供上下文信息
支持的matcher值:
-
"startup" - 新会话启动
-
"resume" - 恢复已有会话
-
"clear" - 清理会话
-
"compress" - 压缩会话
7. SessionEnd Hook
触发时机:会话正常结束时
用途 :在会话结束时运行。它们不能阻止会话终止,但可以执行清理任务
**实战案例:**每次会话结束时,自动生成包含会话 ID、时间戳和 Git 活动记录的 Markdown 文件,方便后续回顾和分析工作历史。
示例配置:
bash
{
"hooks": {
"SessionEnd": [
{
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "python3 ~/.iflow/hooks/session_summary.py",
"timeout": 30
}
]
}
]
}
}session_summary.py 脚本代码:(保存路径为 .iflow/hooks/session_summary.py)
bash
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import os
import datetime
import subprocess
session_id = os.environ.get('IFLOW_SESSION_ID', 'unknown')
timestamp = datetime.datetime.now().strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S')
summary_dir = os.path.expanduser('~/.iflow/session-summaries')
os.makedirs(summary_dir, exist_ok=True)
try:
git_log = subprocess.check_output(['git', 'log', '--oneline', '-3']).decode().strip()
except:
git_log = 'No git repository'
summary_content = f'''# Session Summary
**ID:** {session_id}
**Time:** {timestamp}
**Git Log:**
```
{git_log}
```
'''
with open(f'{summary_dir}/session-{session_id}.md', 'w') as f:
f.write(summary_content)8. UserPromptSubmit Hook
触发时机:用户提交提示词和iFlow处理之前
用途:在用户提交提示词前进行内容过滤,检测并阻止包含敏感信息的输入
示例配置:
可使用 matcher 匹配特定内容,例如:"matcher": ".sensitive."
bash
{
"hooks": {
"UserPromptSubmit": [
{
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "python3 ~/.iflow/hooks/content_filter.py",
"timeout": 10
}
]
}
]
}
}content_filter.py 脚本代码:(保存路径为 .iflow/hooks/content_filter.py)
bash
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import json
import sys
import re
import datetime
# Load input from stdin
try:
input_data = json.load(sys.stdin)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"Error: Invalid JSON input: {e}", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
prompt = input_data.get("prompt", "")
# Check for sensitive patterns
sensitive_patterns = [
(r"(?i)\b(password|secret|key|token)\s*[:=]", "Prompt contains potential secrets"),
]
for pattern, message in sensitive_patterns:
if re.search(pattern, prompt):
# Use JSON output to block with a specific reason
output = {
"decision": "block",
"reason": f"Security policy violation: {message}. Please rephrase your request without sensitive information."
}
print(json.dumps(output))
sys.exit(0)
# Add current time to context
context = f"Current time: {datetime.datetime.now()}"
print(context)
"""
The following is also equivalent:
print(json.dumps({
"hookSpecificOutput": {
"hookEventName": "UserPromptSubmit",
"additionalContext": context,
},
}))
"""
# Allow the prompt to proceed with the additional context
sys.exit(0)实战案例
案例 1: 敏感文件保护 Hook
阻止 iFlow CLI 编辑敏感文件,防止意外修改关键配置。
Hook 配置:
bash
{
"hooks": {
"PreToolUse": [
{
"matcher": "Edit|Write|Shell",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "python3 .iflow/hooks/security_check.py"
}
]
}
]
}
}Python 脚本实现:
创建 .iflow/hooks/security_check.py 文件:
bash
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
敏感文件保护 Hook
阻止对敏感文件和目录的编辑、写入和删除操作
"""
import json
import sys
# 从 stdin 读取 Hook 输入数据
try:
data = json.load(sys.stdin)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"Error: Invalid JSON input: {e}", file=sys.stderr)
sys.exit(1)
# 获取工具输入参数
tool_input = data.get('tool_input', {})
# 获取文件路径或命令内容
path = tool_input.get('file_path', '') or tool_input.get('command', '')
# 定义敏感文件列表
sensitive_files = [
'.env',
'package-lock.json',
'.git/'
]
# 检查路径中是否包含敏感文件
matched = [p for p in sensitive_files if p in path]
if matched:
# 构建详细的错误消息
error_message = f"""⚠️ 安全保护:禁止操作敏感文件/目录
检测到操作涉及敏感内容: {", ".join(matched)}
敏感文件列表包括:
- .env (环境变量配置,可能包含密钥)
- package-lock.json (依赖锁定文件,不应手动编辑)
- .git/ (Git 内部文件,不应直接修改)
如需操作这些文件,请手动执行或联系管理员。"""
print(error_message, file=sys.stderr)
# 退出码 2 表示阻止操作并将 stderr 显示给 LLM
sys.exit(2)
# 退出码 0 表示允许操作
sys.exit(0)脚本权限设置:
bash
chmod +x .iflow/hooks/security_check.py工作原理:
-
使用 PreToolUse hook 在文件编辑前检查
-
通过 matcher: "Edit|Write" 匹配编辑和写入操作
-
使用 Python 一行脚本检查文件路径
-
如果路径包含敏感文件(.env、package-lock.json、.git/),返回退出码 2 阻止操作
-
退出码 0 表示允许操作继续
保护文件列表:
-
.env - 环境变量配置文件(可能包含密钥)
-
package-lock.json - 依赖锁定文件(不应手动编辑)
-
.git/ - Git 内部文件(不应直接修改)
案例 2: TypeScript 代码自动格式化
在编辑 TypeScript 文件后自动进行代码格式化,确保代码风格一致。
Hook 配置:
bash
{
"hooks": {
"PostToolUse": [
{
"matcher": "Edit|Write",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "jq -r '.tool_input.file_path' | { read file_path; if echo \"$file_path\" | grep -q '\\.ts$'; then npx prettier --write \"$file_path\"; fi; }"
}
]
}
]
}
}工作原理:
-
使用 PostToolUse hook 在文件编辑后触发
-
通过 matcher: "Edit|Write" 匹配编辑和写入操作
-
使用 jq 提取文件路径
-
检查文件扩展名是否为 .ts
-
如果是 TypeScript 文件,自动运行 prettier --write 格式化
案例 3: Markdown 文件自动格式化
自动修复 Markdown 文件中缺失的代码块语言标签和格式问题,提升文档可读性。
Hook 配置:
bash
{
"hooks": {
"PostToolUse": [
{
"matcher": "Edit|Write",
"hooks": [
{
"type": "command",
"command": "python3 .iflow/hooks/markdown_formatter.py"
}
]
}
]
}
}Python 脚本实现:
创建 .iflow/hooks/markdown_formatter.py 文件:
bash
#!/usr/bin/env python3
"""
Markdown formatter for iFlow CLI output.
Fixes missing language tags and spacing issues while preserving code content.
"""
import json
import sys
import re
import os
def detect_language(code):
"""Best-effort language detection from code content."""
s = code.strip()
# JSON detection
if re.search(r'^\s*[{\[]', s):
try:
json.loads(s)
return 'json'
except:
pass
# Python detection
if re.search(r'^\s*def\s+\w+\s*\(', s, re.M) or \
re.search(r'^\s*(import|from)\s+\w+', s, re.M) or \
re.search(r'^\s*class\s+\w+', s, re.M):
return 'python'
# JavaScript/TypeScript detection
if re.search(r'\b(function\s+\w+\s*\(|const\s+\w+\s*=|let\s+\w+\s*=|var\s+\w+\s*=)', s) or \
re.search(r'=>|console\.(log|error)|import\s+.*from', s):
return 'javascript'
# Bash detection
if re.search(r'^#!.*\b(bash|sh)\b', s, re.M) or \
re.search(r'\b(echo|grep|sed|awk)\b', s) or \
re.search(r'^\s*\$\s+', s, re.M):
return 'bash'
# SQL detection
if re.search(r'\b(SELECT|INSERT|UPDATE|DELETE|CREATE|DROP|ALTER)\s+', s, re.I):
return 'sql'
# YAML detection
if re.search(r'^\s*\w+:\s*$', s, re.M) and re.search(r'^\s+-\s+', s, re.M):
return 'yaml'
return 'text'
def format_markdown(content):
"""Format markdown content with language detection."""
# Fix unlabeled code fences
def add_lang_to_fence(match):
indent, info, body, closing = match.groups()
if not info.strip():
lang = detect_language(body)
return f"{indent}```{lang}\n{body}{closing}\n"
return match.group(0)
fence_pattern = r'(?ms)^([ \t]{0,3})```([^\n]*)\n(.*?)(\n\1```)\s*$'
content = re.sub(fence_pattern, add_lang_to_fence, content)
# Fix excessive blank lines
content = re.sub(r'\n{3,}', '\n\n', content)
return content.rstrip() + '\n'
def get_file_path(input_data):
"""Extract file path from various possible input structures."""
if not input_data:
return None
# Try tool_input first (most common)
tool_input = input_data.get('tool_input', {})
if isinstance(tool_input, dict):
for key in ['file_path', 'target_file', 'path', 'filepath']:
file_path = tool_input.get(key)
if file_path and isinstance(file_path, str):
return file_path
# Try direct keys
for key in ['file_path', 'target_file', 'path', 'filepath']:
file_path = input_data.get(key)
if file_path and isinstance(file_path, str):
return file_path
# Try tool_result
tool_result = input_data.get('tool_result', {})
if isinstance(tool_result, dict):
for key in ['file_path', 'target_file', 'path', 'filepath']:
file_path = tool_result.get(key)
if file_path and isinstance(file_path, str):
return file_path
return None
# Main execution
try:
if sys.stdin.isatty():
sys.exit(0)
input_data = json.load(sys.stdin)
file_path = get_file_path(input_data)
if not file_path:
sys.exit(0)
if not file_path.endswith(('.md', '.mdx')):
sys.exit(0)
if not os.path.exists(file_path):
sys.exit(0)
with open(file_path, 'r', encoding='utf-8') as f:
content = f.read()
formatted = format_markdown(content)
if formatted != content:
with open(file_path, 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
f.write(formatted)
except (json.JSONDecodeError, Exception):
sys.exit(0)脚本权限设置:
bash
chmod +x .iflow/hooks/markdown_formatter.py功能特性:
-
自动检测未标记代码块的编程语言
-
添加适当的语言标签以实现语法高亮
-
修复过多的空白行,同时保留代码内容
-
仅处理 Markdown 文件(.md、.mdx)
最佳实践总结
-
明确 Hook 用途: 每个 hook 应该专注于单一职责,便于维护和调试
-
安全第一: 始终审查 hook 脚本,避免执行不受信任的代码
-
性能考虑: PostToolUse hooks 会在每次工具调用后执行,注意脚本执行时间
-
错误处理: Hook 脚本应包含适当的错误处理,避免中断工作流
-
测试验证: 在生产环境使用前,先在测试项目中验证 hook 行为
-
文档记录: 为团队共享的 hooks 编写清晰的文档说明