一.list介绍
list是C++标准模版库(STL)中的一个双向链表容器,提供了高效的元素插入和删除。
基本特性
- 双向链表结构:每个元素包含指向前后元素的指针
- 非连续内存存储:元素在内存中不一定是连续存储的
- 动态大小:可以在运行时自由增长或缩小
- 高效操作:在任意位置插入/删除元素的时间复杂度为 O(1)
- 不支持随机访问:访问元素需要通过迭代器遍历,时间复杂度为 O(n)、
链表结构图:
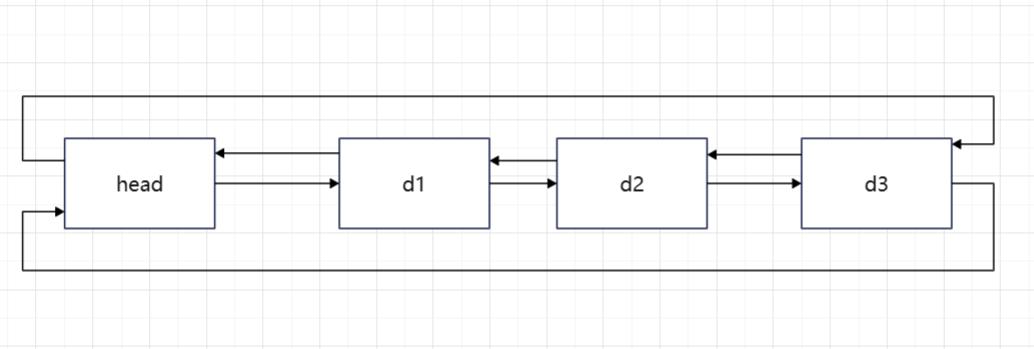
二.list常用接口
1.构造函数
|---------------------------------------------------------------|--------------------------------------|
| list (size_type n, const value_type& val = value_type()) | 构造的list中包含n个值为val的 元素 |
| list() | 构造空的list |
| list (const list& x) | 拷贝构造函数 |
| list (InputIterator first, InputIterator last) | 用[first, last)区间中的元素构造 list |
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
list<int> s1(10, 6); //构造的list中包含n个值为val的元素
for (auto& x : s1)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
list<int> s2(); //构造空的list
list<int> s3(s1); //拷贝构造函数
for (auto& x : s3)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
list<int> s4(arr, arr + n); //用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list
for (auto& x : s4)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
return 0;
}
2.list iterator
|-----------------------|----------------------------------------------------------------------------------|
| begin + end | 返回第一个元素的迭代器 + 返回最后一个元素下一个位置的迭代器 |
| rbegin + rend | 返回第一个元素的reverse_iterator,即end位置 ,返回最后一个元素下一个位置的reverse_iterator,即begin位置 |
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
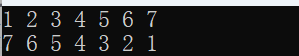
list<int> s4(arr, arr + n); //用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list
auto it = s4.begin();
auto rit = s4.rbegin();
for (it; it != s4.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
for (rit; rit != s4.rend(); ++rit) {
cout << *rit << " ";
}
return 0;
}
3.list 空间有关函数
|-----------|---------------------------------|
| empty | 判断list是否为空,是返回true,否返回false |
| size | 返回list中有效节点的个数 |
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
list<int> s4(arr, arr + n); //用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list
cout << s4.size() << endl;
cout << s4.empty() << endl;//false打印出来是0
return 0;
}
4.list front和back
|-----------|-----------------------|
| front | 返回list第一个节点中值的引用 |
| back | 返回list最后一个节点中值的引用 |
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
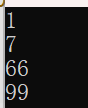
list<int> s4(arr, arr + n); //用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list
cout << s4.front() << endl;
cout << s4.back() << endl;
s4.front() = 66;//修改list第一个节点的值的引用
s4.back() = 99; // 修改list最后一个节点的值的引用
cout << s4.front() << endl;
cout << s4.back() << endl;
return 0;
}
5.list 修改相关函数
|----------------|-----------------------|
| push_front | 在list首元素前插入新元素 |
| pop_front | 删除list中第一个元素 |
| push_back | 在list尾部插入新元素 |
| pop_back | 删除list中最后一个元素 |
| insert | 在pos位置中插入值为val的元素 |
| erase | 删除pos位置的元素 |
| swap | 交换两个list中的元素 |
| clear | 清空list中的有效元素 |
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void Print(list<int>& s)
{
for (auto& x: s)
{
cout << x << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
int arr[] = { 1,2,3,4,5,6,7 };
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
list<int> s(arr, arr + n); //用[first, last)区间中的元素构造list
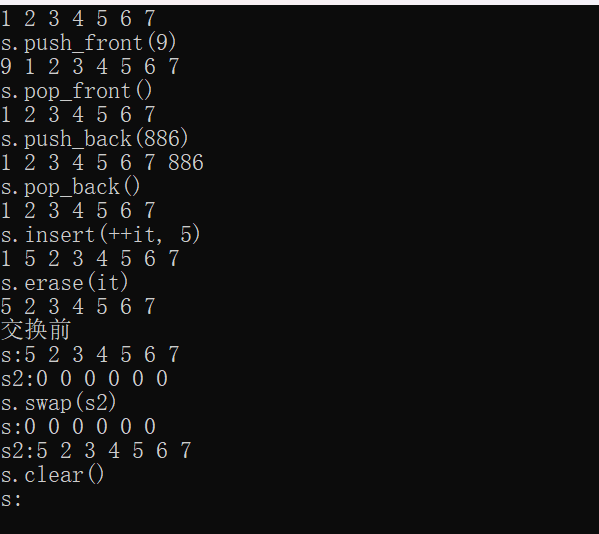
Print(s);
s.push_front(9); //在list首元素前插入新元素
cout << "s.push_front(9)" << endl;
Print(s);
s.pop_front(); //删除list中第一个元素
cout << "s.pop_front()" << endl;
Print(s);
s.push_back(886); //在list尾部插入新元素
cout << "s.push_back(886)" << endl;
Print(s);
s.pop_back(); //删除list中最后一个元素
cout << "s.pop_back()" << endl;
Print(s);
auto it = s.begin();
it++;//it原本是第一个节点位置现在++指向第二个节点位置
s.insert(it, 5);//在第二个位置插入新的元素5;
cout << "s.insert(++it, 5)" << endl;
Print(s);
it = s.begin();//it指向的是第一个节点位置
s.erase(it);//删除it位置的元素
cout << "s.erase(it)" << endl;
Print(s);
list<int> s2(6,0);
cout << "交换前" << endl;
cout << "s:";
Print(s);
cout << "s2:";
Print(s2);
s.swap(s2);//交换两个list中的元素
cout << "s.swap(s2)"<<endl;
cout << "s:";
Print(s);
cout << "s2:";
Print(s2);
s.clear();
cout << "s.clear()" << endl;
cout << "s:";
Print(s);
return 0;
}
三.list模拟实现
1.list的节点
cpp
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode(const T& val = T())
{
_val = val;
}
ListNode<T>* _pre = nullptr;//前一个节点
ListNode<T>* _next = nullptr;//后一个节点
T _val;//节点内的数据
};list的节点是双向的说以内部必须存在一个指向前一个节点和一个指向后一个节点的指针
2.list的迭代器
list的迭代器需要定义一个类,因为list里的节点的在物理上并不一定连续,不能像vector那样直接使用数据的原生指针。
2.1基本框架
迭代器里面的成员变量只需存节点的指针就行了, 其中的模版参数Ref和Ptr重载*和->会用到;
cpp
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;//节点指针
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self//迭代器;
PNode _pNode;
};2.2迭代器构造
接着我们写一下迭代器的构造和拷贝构造,很简单只需要传入一个节点指针即可,拷贝构造把其他迭代器里的节点指针复制过来即可
cpp
ListIterator(PNode pNode = nullptr)
{
_pNode = pNode;
}
ListIterator(const Self& l)
{
_pNode = l._pNode;
}2.3operator*()和operator->()
cpp
Ref operator*()
{
return _pNode->_val;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_pNode->_val;
}这里operator*()我们能理解,就是拿取节点里面的值,因为pNode是类指针要访问类里面的成员就要使用->来获的里面的成员变量,可是operator->()是怎么回事,访问里面的值又把这个值的地址给返回?这里我们就得从表层看起!
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <list>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
class B
{
public:
int val = 10;
};
int main()
{
list<B> l1;
B b1;
l1.push_back(b1);
auto it = l1.begin();
cout << it->val << endl;
return 0;
}这里我们定义了一个类B,里面有公共成员变量val,我们用这个类实例化了一个对象b1,然后把这个对象存入到list里面,然后我们创建一个迭代器it,it里面装的是第一个节点的指针,这个指针指向的是装着b1的那个节点,关系图如下:
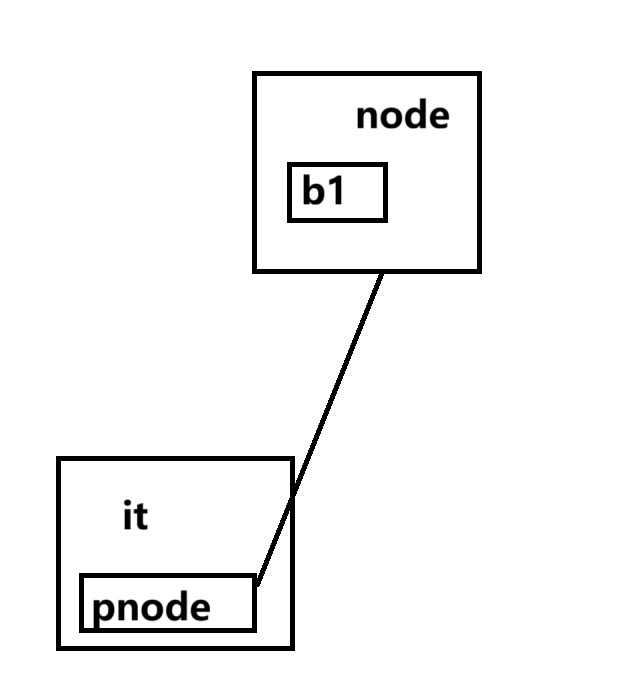
当我对it进行->的时候会返回pnode指向那个节点里面的值的地址就是b1的地址,这里我们又有问题
返回的是地址的话不应该是it->->val 才能访问到b1里面的val吗?为什么只用了一个->就轻松访问到b1里面的val了?答案就是编译器做了优化,帮我们省略了一个箭头;其实我们it->val原型是这样的
cpp
it.operator->()->val我们来运行一下看看:
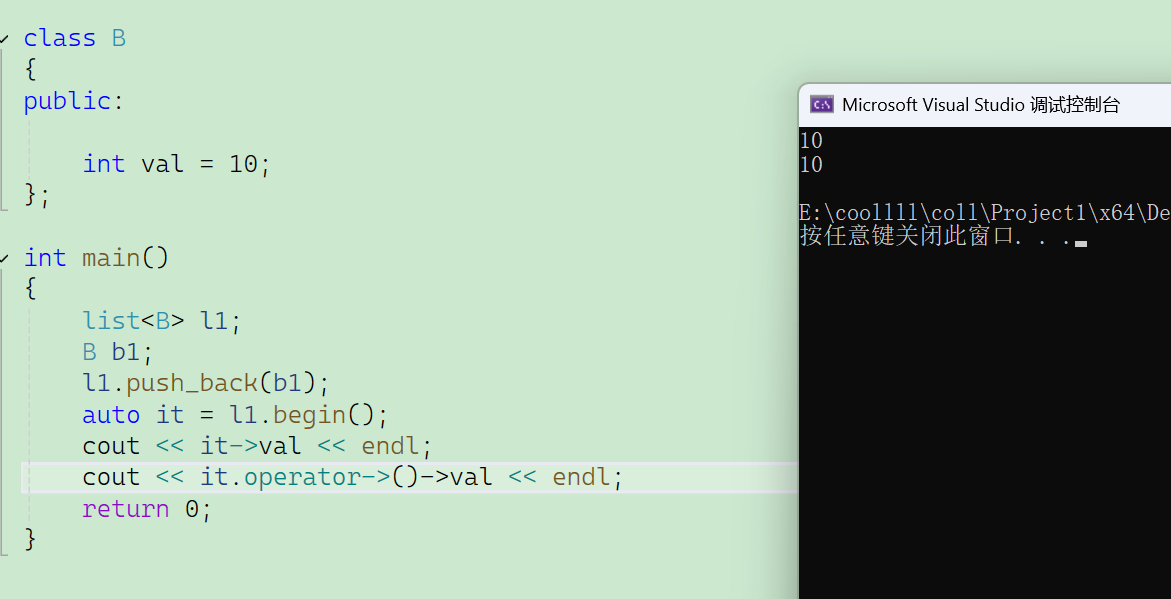
可以看到结果是一样的,实际上我们使用->访问list里面存储的对象的成员变量时是先调用operator->()返回对象的地址,然后再使用->访问里面的成员变量!
回到正题,我们继续重载其他运算符
2.4前置++和后置++
cpp
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_next;//指向下一个节点
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self node = _pNode;
_pNode = _pNode->_next;//指向下一个节点
return node;
}前置++和后置++都很简单,前置++只需要把当前存储的节点指针指向下一个节点就行,前置++就返回当前迭代器,后置++就先创建一个迭代器保存当前节点位置,然后自身指向下一个节点,然后返回创建的那个迭代器。
2.5前置--和后置--
因为我们的list的是双向的所以可以支持迭代器--;原理和++差不多,只不过是访问前一个节点;
cpp
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pre;//指向前一个节点
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self node = _pNode;
_pNode = _pNode->_pre;//指向前一个节点
return node;
}2.6!=和==
这个也很简单,只需要对比两个迭代器里存储的节点指针是否一样就行了
cpp
bool operator!=(const Self& l)
{
return _pNode != l._pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& l)
{
return _pNode == l._pNode;
}2.7 迭代器代码
cpp
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
ListIterator(PNode pNode = nullptr)
{
_pNode = pNode;
}
ListIterator(const Self& l)
{
_pNode = l._pNode;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _pNode->_val;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_pNode->_val;
}
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self node = _pNode;
_pNode = _pNode->_next;
return node;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pre;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self node = _pNode;
_pNode = _pNode->_pre;
return node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& l)
{
return _pNode != l._pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& l)
{
return _pNode == l._pNode;
}
PNode _pNode;
};3.list类基本框架
cpp
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef Node* PNode;
public:
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T&> const_iterator;
public:
list();
list(int n, const T& value = T());
template <class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last);
list(const list<T>& l);
list<T>& operator=(list<T> l);
~list();
iterator begin();
iterator end();
const_iterator begin() const;
const_iterator end() const;
size_t size()const;
bool empty()const;
T& front();
const T& front()const;
T& back();
const T& back()const;
void push_back(const T& val);
void pop_back();
void push_front(const T& val);
void pop_front();
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val);
iterator erase(iterator pos);
void clear();
void swap(list<T>& l);
private:
size_t _size = 0;
void CreateHead();
PNode _pHead;
};我们list类必须要有个头节点知道从哪开始和节点个数, _pHead list开头也是结尾_size记录有效节点个数。
4.CreateHead()创造头结点
cpp
void CreateHead()
{
PNode tmp = new Node();
tmp->_next = tmp;
tmp->_pre = tmp;
_pHead = tmp;
}这个函数比较简单,创造一个节点然后把这个节点的前一个节点和后一个节点指向自己形成循环,
然后把这个节点的指针存入list的_pHead 里作为头结点。
5.构造函数
有四个构造函数,分别是空构造,构造n个val,用迭代区间构造,拷贝构造
cpp
list()
{
CreateHead();//空构造直接建一个头结点就可以了
}
list(int n, const T& value = T())//构造n个value直接调用尾插插入n个val就行
{
CreateHead();
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
template <class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)//迭代区间也是如此调用尾插进行插入
{
CreateHead();
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
first++;
}
}
list(const list<T>& l)//拷贝构造用范围for进行遍历尾插
{
CreateHead();
for (auto& x : l)
{
push_back(x);
}
}6.begin和end
begin和end就非常简单了,头结点的下一个位置就是第一个节点,头结点自己则是尾
注意要区分const迭代器和普通迭代器
cpp
iterator begin()
{
return _pHead->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _pHead;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _pHead->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _pHead;
}7.size和empty
size和empty只需要看_size就行了,size直接返回_size就知道节点个数,如果_size==0就说明没有有效节点。
cpp
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()const
{
return _size == 0;
}8.front 和back
front和back是获取第一个节点和最后一个节点,front我们可以直接复用一下begin;
begin返回的是第一个节点,back直接返回_pHead的上一个节点,因为list是双向循环链表所以_pHead上一个就是最后一个节点
cpp
T& front()
{
//it begin()
iterator it = begin();
return it._pNode->_val;
}
const T& front()const
{
const_iterator it = begin();
return it._pNode->_val;
}
T& back()
{
iterator it = _pHead->_pre;
return it._pNode->_val;
}
const T& back()const
{
const_iterator it = _pHead->_pre;
return it._pNode->_val;
}9.insert
cpp
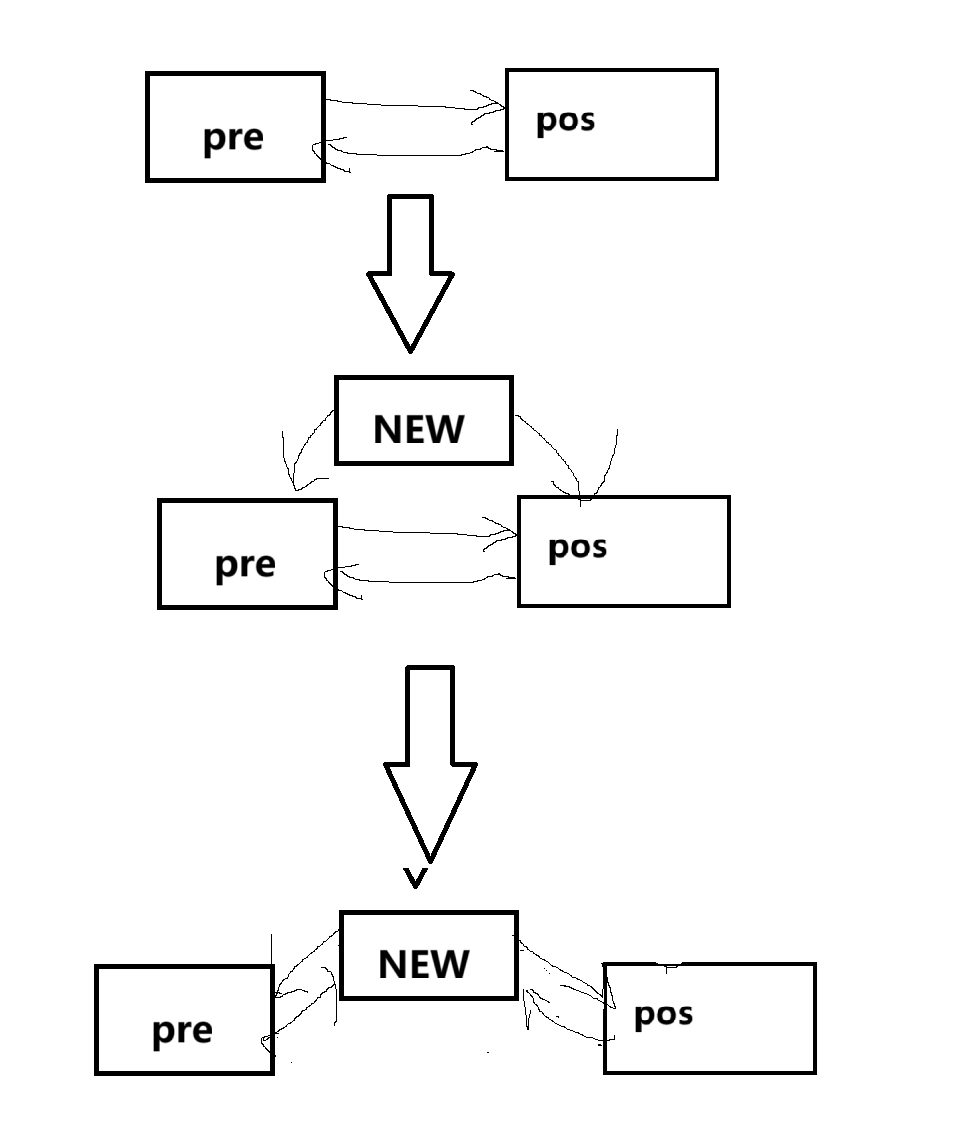
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{
PNode tmp = new Node(val); //创建一个新节点用传入的val进行这个节点的构造
PNode cur = pos._pNode;//记录插入位置的节点
PNode prv = cur->_pre;//记录插入位置节点的前一个节点
tmp->_next = cur;//新节点的下一个节点指向被插入的那个节点
tmp->_pre = prv;//新节点的上一个节点指向被插入节点的上一个节点
prv->_next = tmp; //被插入节点的上一个节点的下一个节点指向新节点
cur->_pre = tmp;//被插入节点的上一个节点指向新节点
_size++;//有效节点+1;
return tmp;//返回新插入节点的位置
}这一块用文字不好解释,用图来表达一下
10.erase
cpp
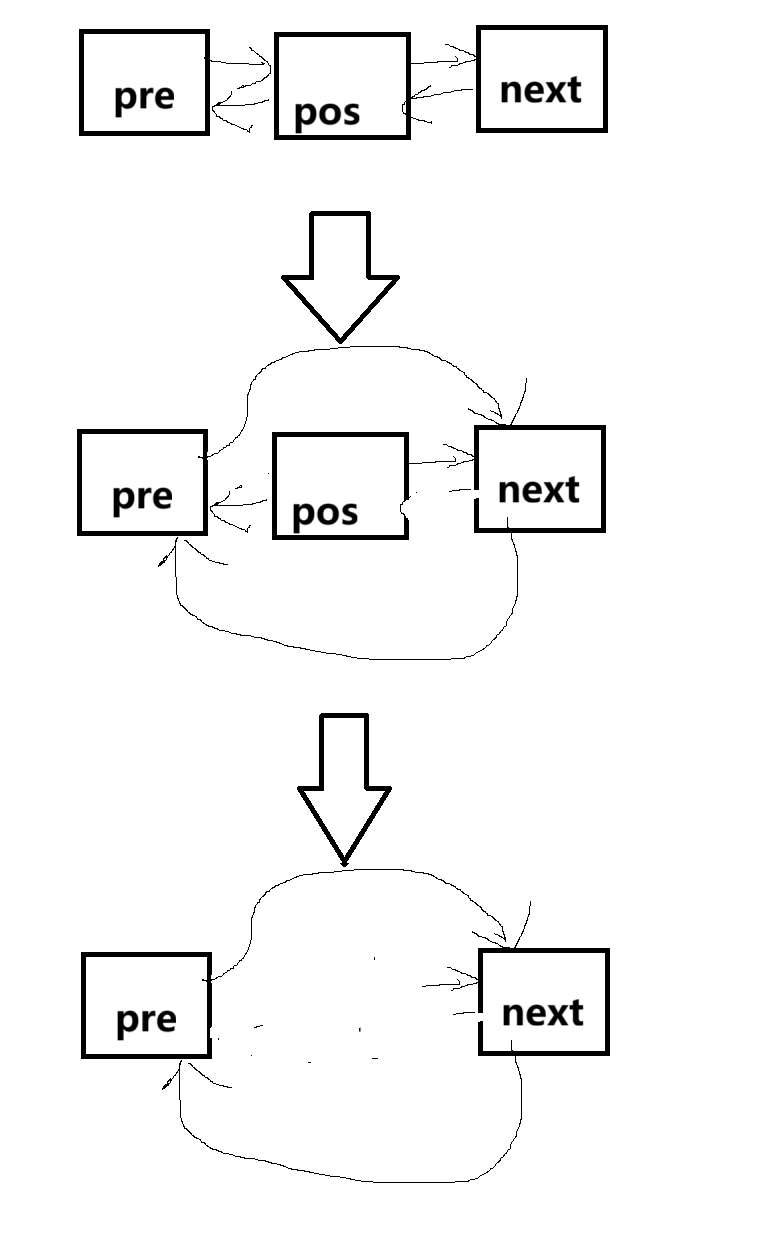
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());//不能把头结点给删了
PNode pre = pos._pNode->_pre;//记录pos位置前一个节点
PNode next = pos._pNode->_next;//记录pos位置后一个节点
pre->_next = next;//pre的下一个节点指向next
next->_pre = pre;//next的前一个节点执行pre
delete(pos._pNode);//删除pso节点
_size--;//有效节点-1
return next;
}erase相对简单:
11.clear
清空list
cpp
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}用begin获得第一个节点然后依次删除,直到end停下,要注意删除的时候一定要用it重新接受删除位置的下一个迭代器不然当前节点被销毁了当前节点的迭代器就会失效!
12.swap
swap交换两个list的数据,这个很简单,交换一下双方的头结点和size就可以了
cpp
void swap(list<T>& l)
{
std::swap(_pHead, l._pHead);
std::swap(_size, l._size);
}13.operator=
重载赋值,这个很简单我使用传值操作,传值产生临时变量,交换一下临时变量里的数据,然后函数结束销毁临时变量里的数据也就是原来list里的数据。
cpp
list<T>& operator=(list<T> l)
{
swap(l);
return *this;
}14.析构函数
析构函数很简单,如果_size不为0表示还有有效节点,直接使用迭代器遍历有效节点然后一个一个释放,但是要记住,释放前要保存下一个节点位置,以免迭代器失效。
cpp
~list()
{
if (_size != 0)
{
iterator it = begin();
iterator cur = begin();
while (it != end())
{
cur = it++;
delete cur._pNode;
}
}
delete _pHead;
}15.完整代码
为了防止污染标准库里的list我们要使用命名空间
mylist.h
cpp
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
#include<assert.h>
using namespace std;
namespace Ysz
{
// List的节点类
template<class T>
struct ListNode
{
ListNode(const T& val = T())
{
_val = val;
}
ListNode<T>* _pre = nullptr;
ListNode<T>* _next = nullptr;
T _val;
};
//List的迭代器类
template<class T, class Ref, class Ptr>
struct ListIterator
{
typedef ListNode<T>* PNode;
typedef ListIterator<T, Ref, Ptr> Self;
ListIterator(PNode pNode = nullptr)
{
_pNode = pNode;
}
ListIterator(const Self& l)
{
_pNode = l._pNode;
}
Ref operator*()
{
return _pNode->_val;
}
Ptr operator->()
{
return &_pNode->_val;
}
Self& operator++()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_next;
return *this;
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self node = _pNode;
_pNode = _pNode->_next;
return node;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_pNode = _pNode->_pre;
return *this;
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self node = _pNode;
_pNode = _pNode->_pre;
return node;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& l)
{
return _pNode != l._pNode;
}
bool operator==(const Self& l)
{
return _pNode == l._pNode;
}
PNode _pNode;
};
//list类
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef ListNode<T> Node;
typedef Node* PNode;
public:
typedef ListIterator<T, T&, T*> iterator;
typedef ListIterator<T, const T&, const T&> const_iterator;
public:
// List的构造
list()
{
CreateHead();
}
list(int n, const T& value = T())
{
CreateHead();
for (size_t i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
push_back(value);
}
}
template <class Iterator>
list(Iterator first, Iterator last)
{
CreateHead();
while (first != last)
{
push_back(*first);
first++;
}
}
list(const list<T>& l)
{
CreateHead();
for (auto& x : l)
{
push_back(x);
}
}
list<T>& operator=(list<T> l)
{
swap(l);
return *this;
}
~list()
{
if (_size != 0)
{
iterator it = begin();
iterator cur = begin();
while (it != end())
{
cur = it++;
delete cur._pNode;
}
}
delete _pHead;
}
// List Iterator
iterator begin()
{
return _pHead->_next;
}
iterator end()
{
return _pHead;
}
const_iterator begin() const
{
return _pHead->_next;
}
const_iterator end() const
{
return _pHead;
}
// List Capacity
size_t size()const
{
return _size;
}
bool empty()const
{
return _size == 0;
}
// List Access
T& front()
{
//it begin()
iterator it = begin();
return it._pNode->_val;
}
const T& front()const
{
const_iterator it = begin();
return it._pNode->_val;
}
T& back()
{
iterator it = _pHead->_pre;
return it._pNode->_val;
}
const T& back()const
{
const_iterator it = _pHead->_pre;
return it._pNode->_val;
}
// List Modify
void push_back(const T& val) { insert(end(), val); }
void pop_back() { erase(--end()); }
void push_front(const T& val) { insert(begin(), val); }
void pop_front() { erase(begin()); }
// 在pos位置前插入值为val的节点
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)
{
PNode tmp = new Node(val);
PNode cur = pos._pNode;
PNode prv = cur->_pre;
tmp->_next = cur;
tmp->_pre = prv;
prv->_next = tmp;
cur->_pre = tmp;
_size++;
return tmp;
}
// 删除pos位置的节点,返回该节点的下一个位置
iterator erase(iterator pos)
{
assert(pos != end());
PNode pre = pos._pNode->_pre;
PNode next = pos._pNode->_next;
pre->_next = next;
next->_pre = pre;
delete(pos._pNode);
_size--;
return next;
}
void clear()
{
iterator it = begin();
while (it != end())
{
it = erase(it);
}
}
void swap(list<T>& l)
{
std::swap(_pHead, l._pHead);
std::swap(_size, l._size);
}
private:
size_t _size = 0;
void CreateHead()
{
PNode tmp = new Node();
tmp->_next = tmp;
tmp->_pre = tmp;
_pHead = tmp;
}
PNode _pHead;
};
};