进程创建
在Linux中fork函数可以在已经存在的进程中创建出一个新进程。这个新进程称为子进程,而原进程称为父进程。
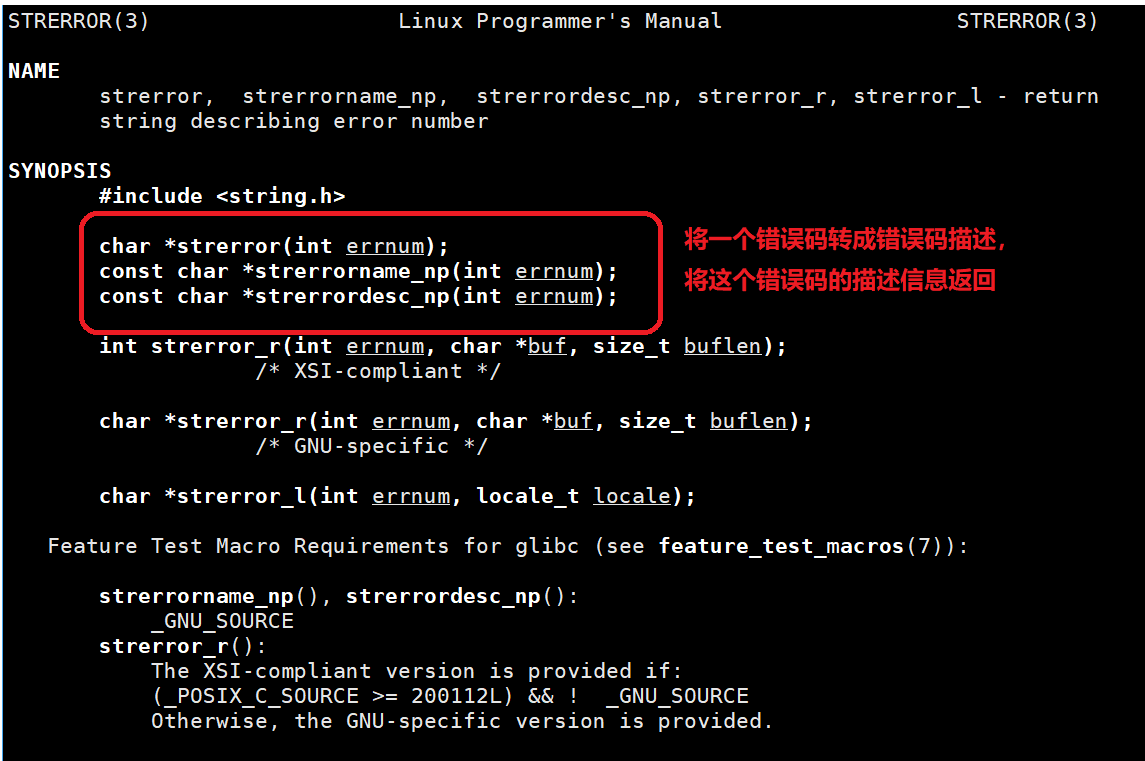
- 头文件#include<unistd.h>
- pid_t fork(void);
- 返回值:子进程返回0,父进程返回子进程的id,出错返回-1.
当进程创建fork函数,操作系统会进行:
- 分配新的内存块和内核数据结构(PCB,进程地址空间、页表)给子进程
- 将父进程的部分数据结构内容拷贝给子进程
- 添加子进程到系统进程列表中
- fork返回,开始由调度器调度
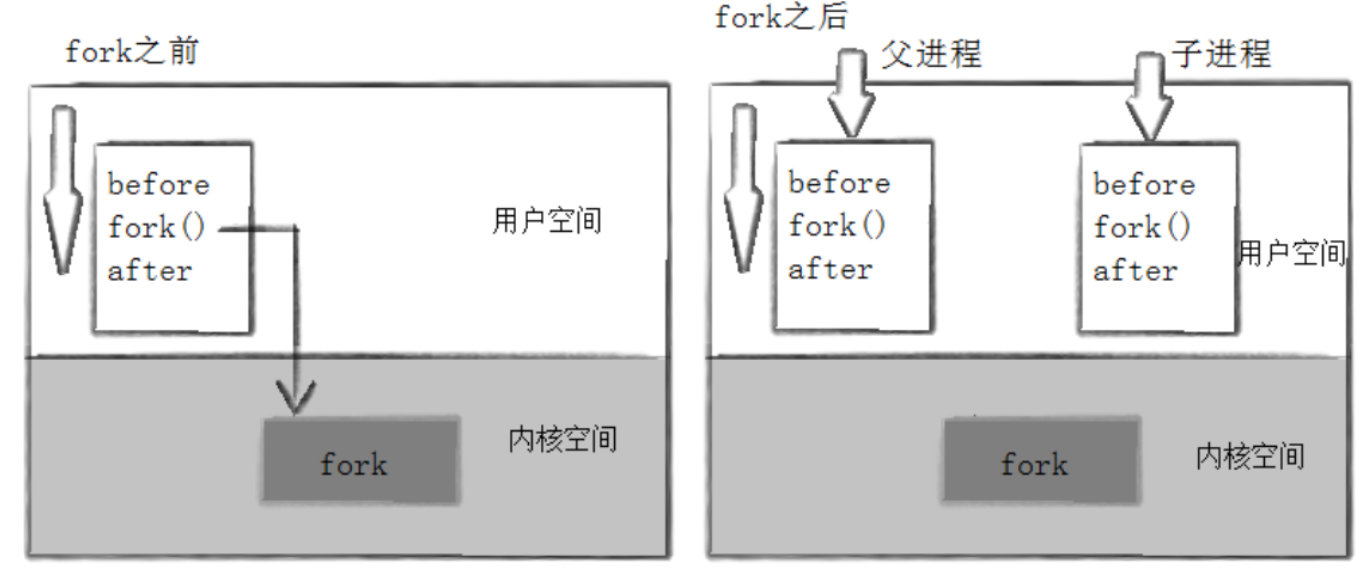
当一个寄存调用fork函数后,就有存在两个二进制代码相同的进程,且运行到相同地址。
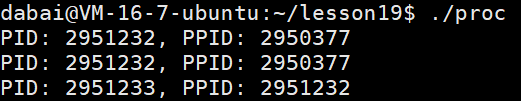
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
int main()
{
printf("PID: %d, PPID: %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
fork();
printf("PID: %d, PPID: %d\n", getpid(), getppid());
return 0;
} 
写时拷贝
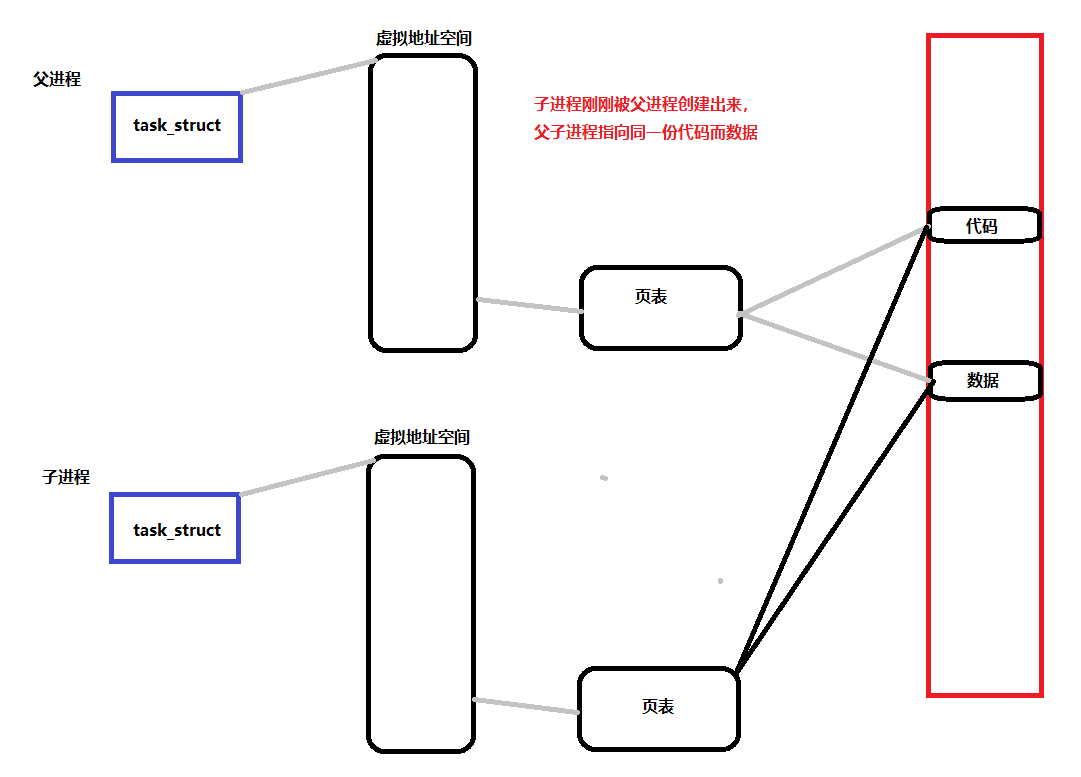
- 子进程在刚创建出来的时候,父子进程指向的是同一份代码和数据,此时子进程和父进程的代码和数据默认是不可被写入的------进程独立性
- 父子进程任意一方在对数据进行写入的时候,就会触发写时拷贝,就会用写时拷贝的方式各自拷贝一份副本
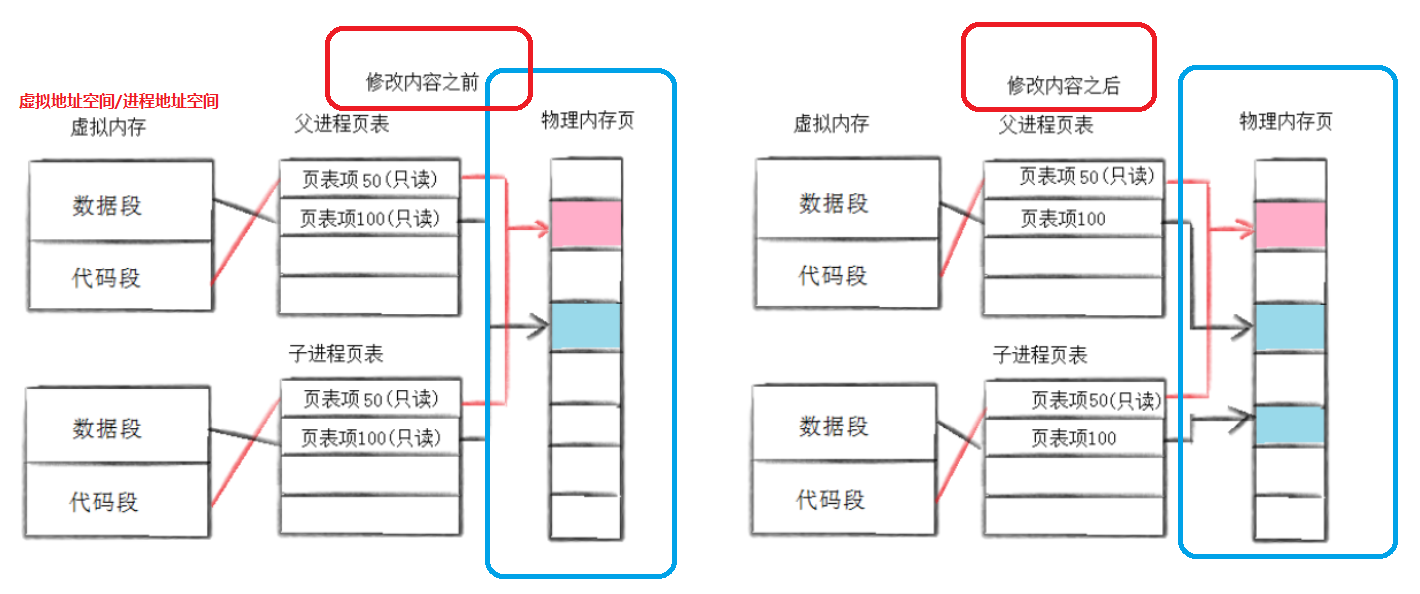
进程在刚被创建出来的时候,操作系统会将父子进程页表的内容都设置成只读权限的,当一个进程触发修改的时候,触发写时拷贝,让修改后的数据重新在物理内存中开辟一段空间,并建立映射,同时将这部分数据在页表中修改成可写权限
fork函数的常规用法
- 父进程希望子进程做复制自己,使得父子进程同时执行不同的代码段。
- 一个进程要执行一个不同的程序。
fork函数调用失败的原因
- 系统中存在过多的进程
- 实际用户的进程数超过了限制
进程终止
cpp
#define N 5
void runChild()
{
int cnt = 5;
while(cnt--)
{
printf("child pid : %d ; ppid : %d \n", getpid(), getppid());
sleep(1);
}
}
int main()
{
for(size_t i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id == 0)
{
// 子进程开始
runChild();
exit(1);
// 子进程结束
}
}
// 让父进程先不要退出
sleep(50);
return 0;
}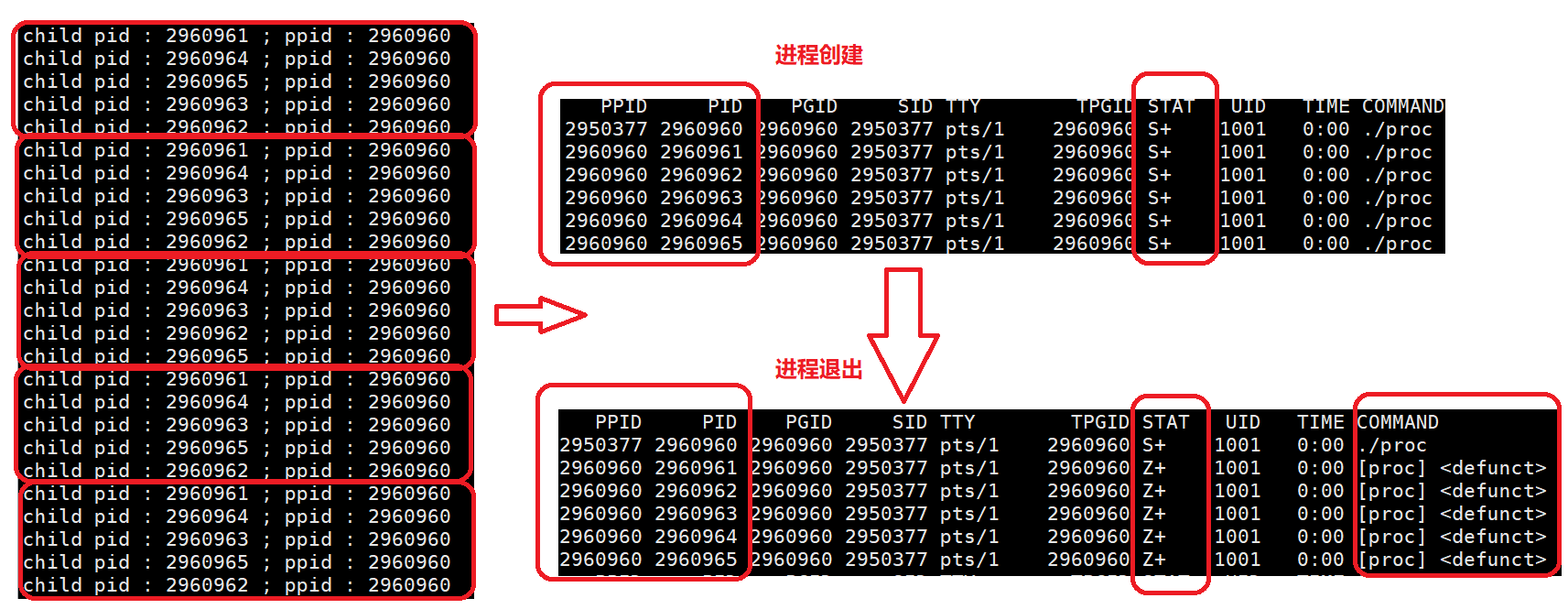
- 使用循环的方式创建出5个进程,由于父进程没有对这5个进程进行回收,导致这5个进程变成僵尸进程。
- 当创建多进程程序的时候,不管是父子进程还是兄弟进程,谁用运行这件事情是由调度器来决定的,由于这几个进程的优先级相等,谁先被调度器放在运行队列中,谁就会被先运行。
- exit();会终止一个进场。
进程退出的场景
- 代码运行完毕,结果正确
- 代码运行完毕,结果不正确
- 代码异常终止
问题:为什么main函数总是return 0?会返回其他值吗??这个返回值返回到哪里了?为什么?
- return 0; // 表示进程的退出码,表征进程的运行结果是否正确。
- 0->表示success
- return 0;这个退出码会被这个进程的父进程获取到,也就是bash进程获取到。
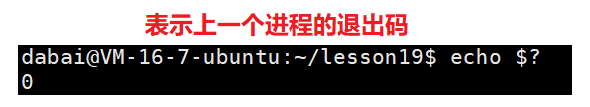
一般而言,只有父进程才会关心子进程退出是否正常,尤其是当代码运行结束,结果不正确的情况------这里就可以用return的不同的返回值数字,来表示不同的出错原因------退出码。
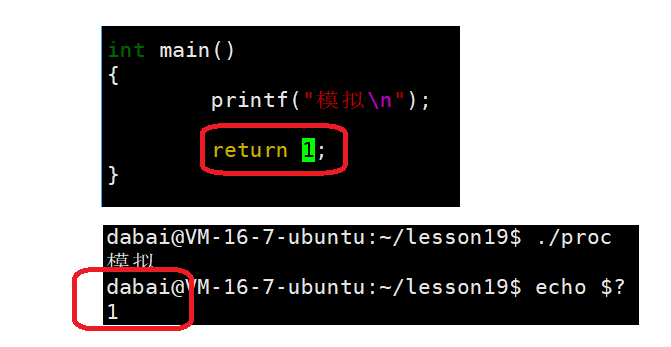
main函数的返回值,其本质是进程运行完成时,是否是正确的结果,如果不是,可以用不同的数字,表示不同的出错原因!
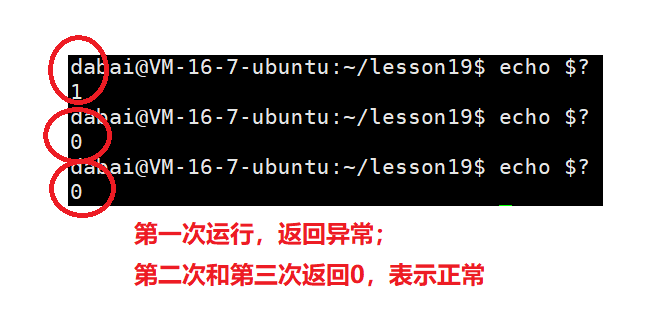
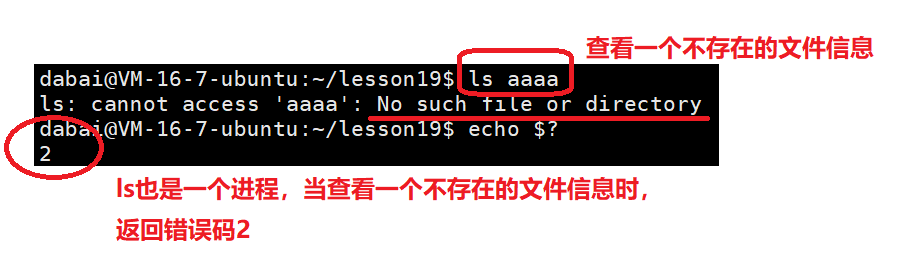
$? 表示最近一次进程的退出码。第一次打印的退出码是上一个进程的退出码,第二次和第三次表示的是执行echo命令进程的退出码。
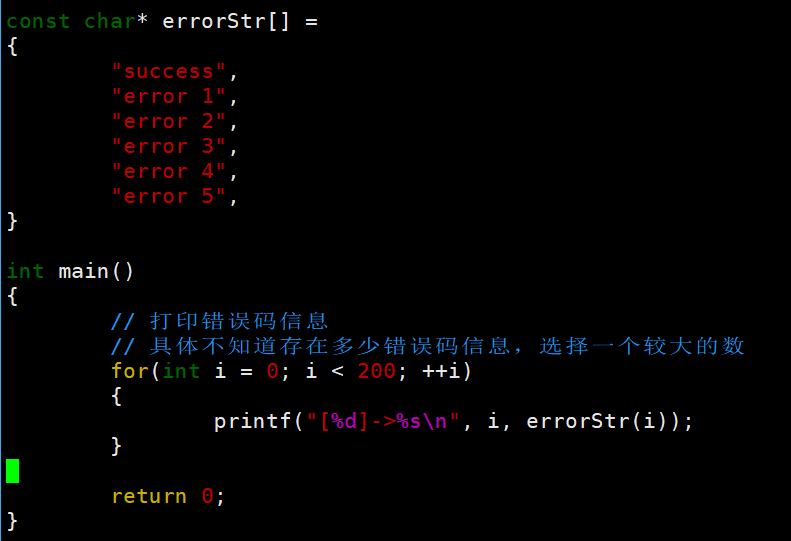
cpp
int main()
{
// 打印错误码信息
// 具体不知道存在多少错误码信息,选择一个较大的数
for(int i = 0; i < 200; ++i)
{
printf("[%d]->%s\n", i, strerror(i));
}
return 0;
}
bash
[0]->Success
[1]->Operation not permitted
[2]->No such file or directory
[3]->No such process
[4]->Interrupted system call
[5]->Input/output error
[6]->No such device or address
[7]->Argument list too long
[8]->Exec format error
[9]->Bad file descriptor
[10]->No child processes
[11]->Resource temporarily unavailable
[12]->Cannot allocate memory
[13]->Permission denied
[14]->Bad address
[15]->Block device required
[16]->Device or resource busy
[17]->File exists
[18]->Invalid cross-device link
[19]->No such device
[20]->Not a directory
[21]->Is a directory
[22]->Invalid argument
[23]->Too many open files in system
[24]->Too many open files
[25]->Inappropriate ioctl for device
[26]->Text file busy
[27]->File too large
[28]->No space left on device
[29]->Illegal seek
[30]->Read-only file system
[31]->Too many links
[32]->Broken pipe
[33]->Numerical argument out of domain
[34]->Numerical result out of range
[35]->Resource deadlock avoided
[36]->File name too long
[37]->No locks available
[38]->Function not implemented
[39]->Directory not empty
[40]->Too many levels of symbolic links
[41]->Unknown error 41
[42]->No message of desired type
[43]->Identifier removed
[44]->Channel number out of range
[45]->Level 2 not synchronized
[46]->Level 3 halted
[47]->Level 3 reset
[48]->Link number out of range
[49]->Protocol driver not attached
[50]->No CSI structure available
[51]->Level 2 halted
[52]->Invalid exchange
[53]->Invalid request descriptor
[54]->Exchange full
[55]->No anode
[56]->Invalid request code
[57]->Invalid slot
[58]->Unknown error 58
[59]->Bad font file format
[60]->Device not a stream
[61]->No data available
[62]->Timer expired
[63]->Out of streams resources
[64]->Machine is not on the network
[65]->Package not installed
[66]->Object is remote
[67]->Link has been severed
[68]->Advertise error
[69]->Srmount error
[70]->Communication error on send
[71]->Protocol error
[72]->Multihop attempted
[73]->RFS specific error
[74]->Bad message
[75]->Value too large for defined data type
[76]->Name not unique on network
[77]->File descriptor in bad state
[78]->Remote address changed
[79]->Can not access a needed shared library
[80]->Accessing a corrupted shared library
[81]->.lib section in a.out corrupted
[82]->Attempting to link in too many shared libraries
[83]->Cannot exec a shared library directly
[84]->Invalid or incomplete multibyte or wide character
[85]->Interrupted system call should be restarted
[86]->Streams pipe error
[87]->Too many users
[88]->Socket operation on non-socket
[89]->Destination address required
[90]->Message too long
[91]->Protocol wrong type for socket
[92]->Protocol not available
[93]->Protocol not supported
[94]->Socket type not supported
[95]->Operation not supported
[96]->Protocol family not supported
[97]->Address family not supported by protocol
[98]->Address already in use
[99]->Cannot assign requested address
[100]->Network is down
[101]->Network is unreachable
[102]->Network dropped connection on reset
[103]->Software caused connection abort
[104]->Connection reset by peer
[105]->No buffer space available
[106]->Transport endpoint is already connected
[107]->Transport endpoint is not connected
[108]->Cannot send after transport endpoint shutdown
[109]->Too many references: cannot splice
[110]->Connection timed out
[111]->Connection refused
[112]->Host is down
[113]->No route to host
[114]->Operation already in progress
[115]->Operation now in progress
[116]->Stale file handle
[117]->Structure needs cleaning
[118]->Not a XENIX named type file
[119]->No XENIX semaphores available
[120]->Is a named type file
[121]->Remote I/O error
[122]->Disk quota exceeded
[123]->No medium found
[124]->Wrong medium type
[125]->Operation canceled
[126]->Required key not available
[127]->Key has expired
[128]->Key has been revoked
[129]->Key was rejected by service
[130]->Owner died
[131]->State not recoverable
[132]->Operation not possible due to RF-kill
[133]->Memory page has hardware error
[134]->Unknown error 134
[135]->Unknown error 135
[136]->Unknown error 136
[137]->Unknown error 137
[138]->Unknown error 138
[139]->Unknown error 139
在Linux操作系统中,系统提供了[0, 133]个错误码信息。
系统提供的错误码和错误码描述是有对应关系的。
自己设计一套退出码体系
【总结】进程退出的时候,会返回退出码来表示进程运行的结果。例如,0表示成功等等。
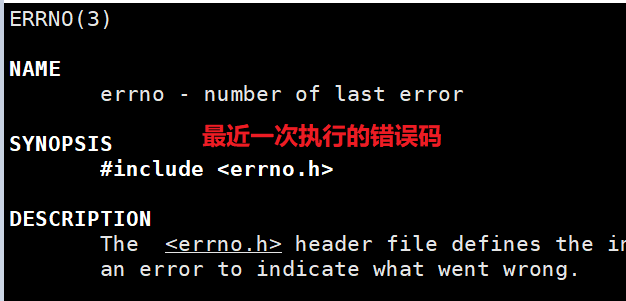
与进程退出码类似的,系统提供了一个全局变量:errno
cpp
int main()
{
int ret = 0;
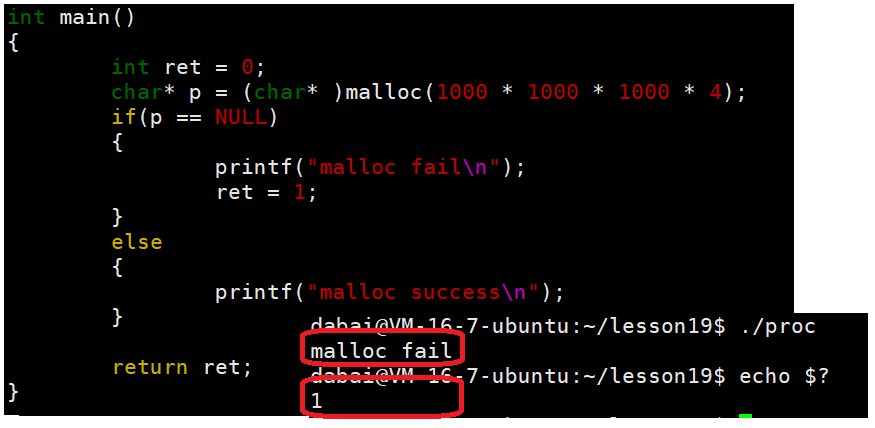
char* p = (char* )malloc(1000 * 1000 * 1000 * 4);
if(p == NULL)
{
// 描述错误信息
printf("malloc fail, %d : %s\n", errno, strerror(errno));
ret = errno; // 使用系统的错误返回值
}
else
{
printf("malloc success\n");
}
return ret;
}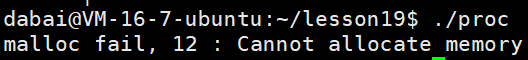

通过这段代码可以获取到错误码,也可以得到错误码信息,同时也可以将错误码返回给父进程,让父进程获取到错误码信息,errno是C语言库实现的一个全局变量。
程序异常退出
【程序异常退出】当程序异常退出的时候,本质可能就是代码没有跑完,所以其进程的退出码没有任何意义,不需要关心。
在程序退出时,需要注意程序是否时异常退出,如果没有出异常,再看结果是否正确。
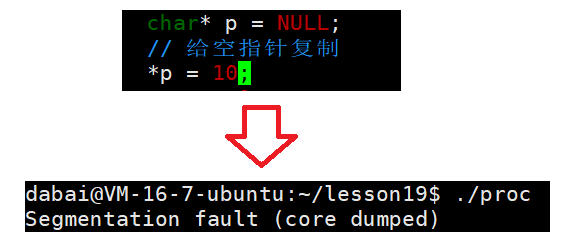
进程出现异常,本质就是进程收到了对应的信号。
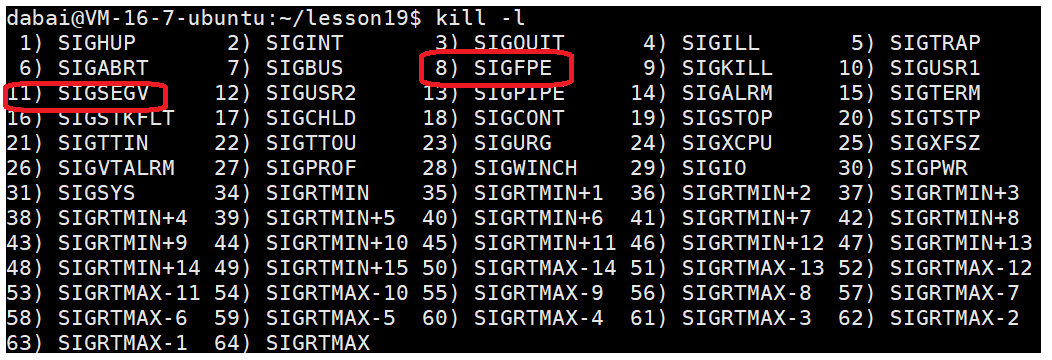
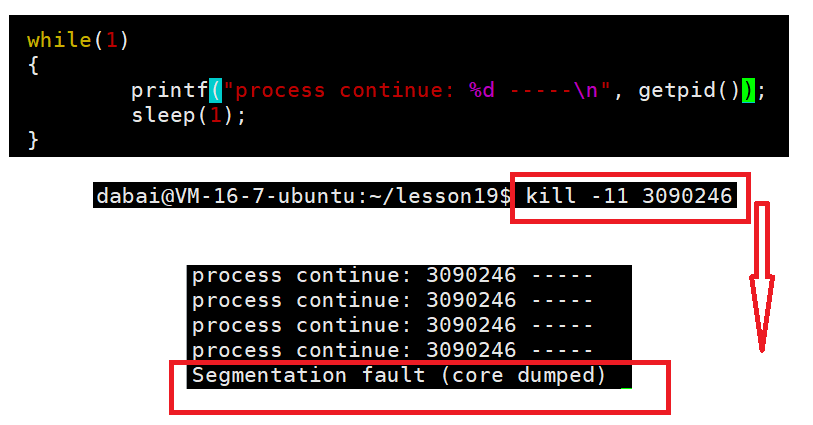
这段内容证明了进程异常结束是收到了信号
进程退出的方式
exit函数
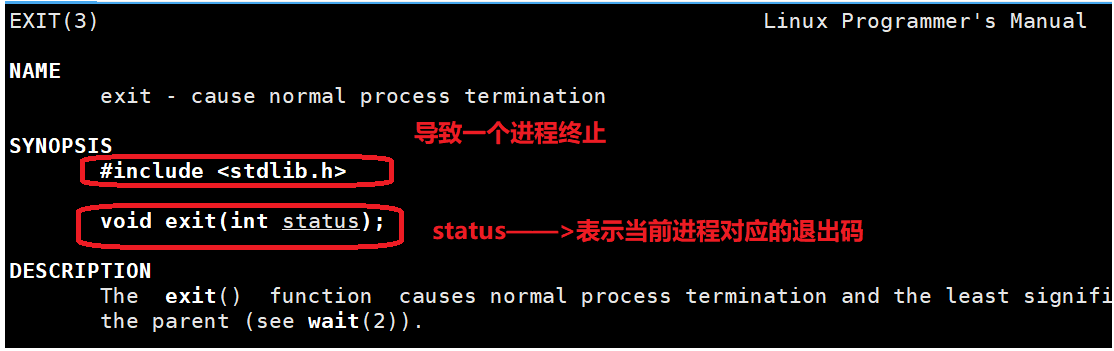
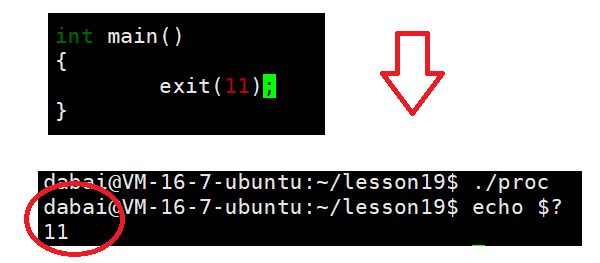
在main函数中exit()函数和return函数具有相同的效果。
exit和return的区别
cpp
void show()
{
printf("show begin-------\n");
printf("show begin-------\n");
printf("show begin-------\n");
printf("show begin-------\n");
exit(13);
printf("show end-------\n");
printf("show end-------\n");
printf("show end-------\n");
printf("show end-------\n");
}
int main()
{
show();
printf("success show");
printf("success show");
printf("success show");
return 0;
}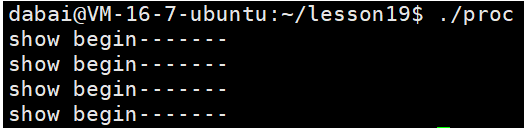
exit函数表示在任意地方被调用,都表示调用进程之间退出。而return只表示当前函数返回,程序仍然会继续向后运行。
_exit函数
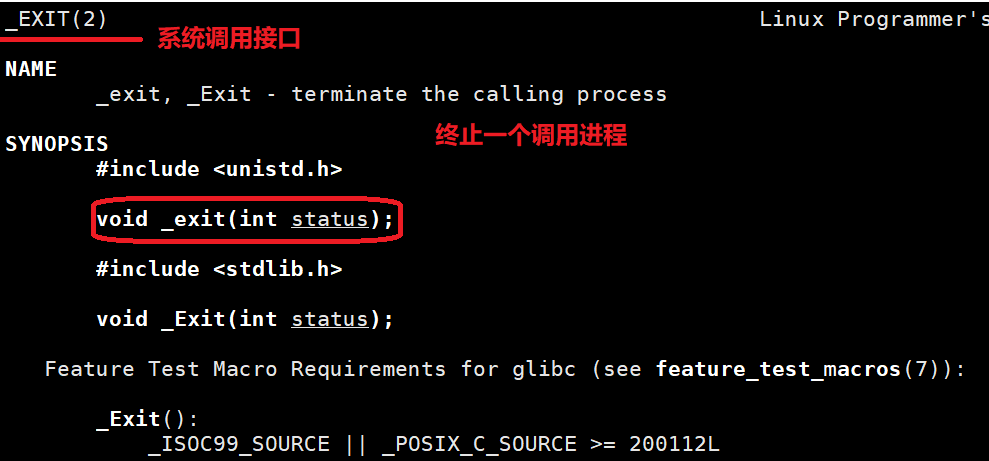
exit和_exit都可以让进程退出,但是却有不同,_exit系统调用接口,而exit是C语言封装的_exit函数,相当于exit最有也会调用_exit,但是在调用_exit之前,还做了其他工作:
- 执行用户通过atexit或者on_exit定义的清理函数
- 关闭所有打开的流,所有的缓存数据均被写入
- 调用_exit函数。
【总结】_exit是系统调用,当终止的时候,_exit会直接终止进程,缓冲区数据不做刷新,而exit在终止进程之前会冲刷缓冲区等操作。
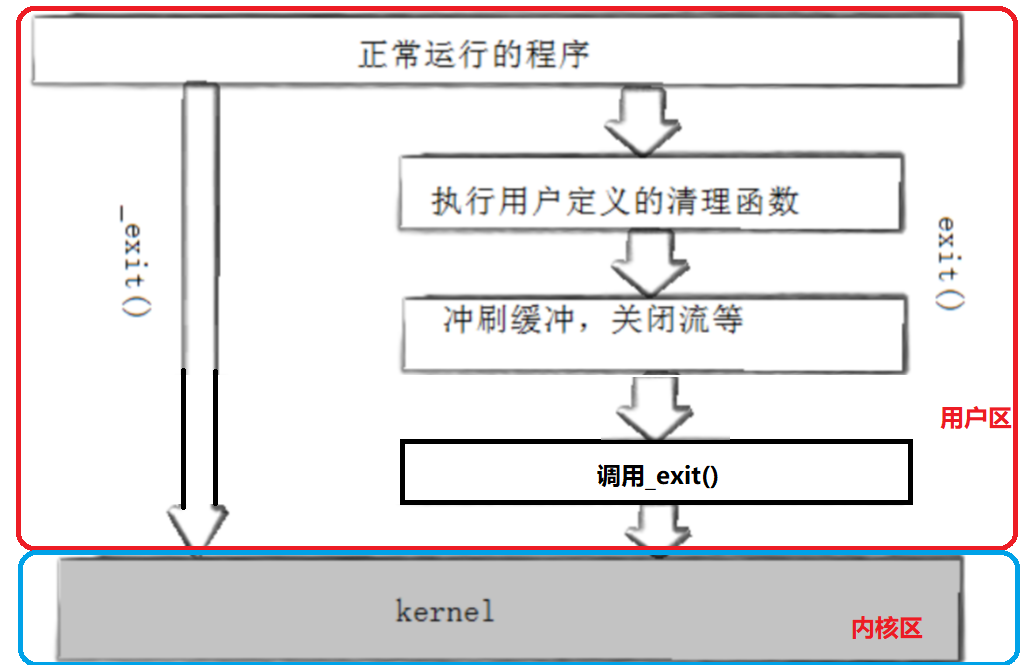
printf()函数会先将数据写入缓冲区内,在合适的时候(例如\n)进行刷新,因此缓冲区一定不会在内核中,因为如果缓冲区在内核区,则_exit一定会将内核区中的数据刷新出来。