单进程版本------实现简单的程序替换

int execl(const char* pathname, const char* arg, ...);
- const char* pathname :表示执行的文件的路径
- const char* arg:表示如何执行这个程序
- ... 表示可变参数列表
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
int main()
{
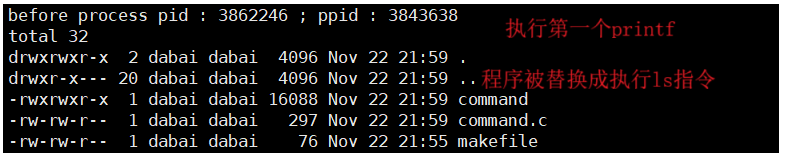
printf("before process pid : %d ; ppid : %d \n", getpid(), getppid());
// 程序替换
execl("/usr/bin/ls", "ls", "-a", "-l", NULL);
printf("after process pid : %d ; ppid : %d \n", getpid(), getppid());
return 0;
}
进程替换的原理
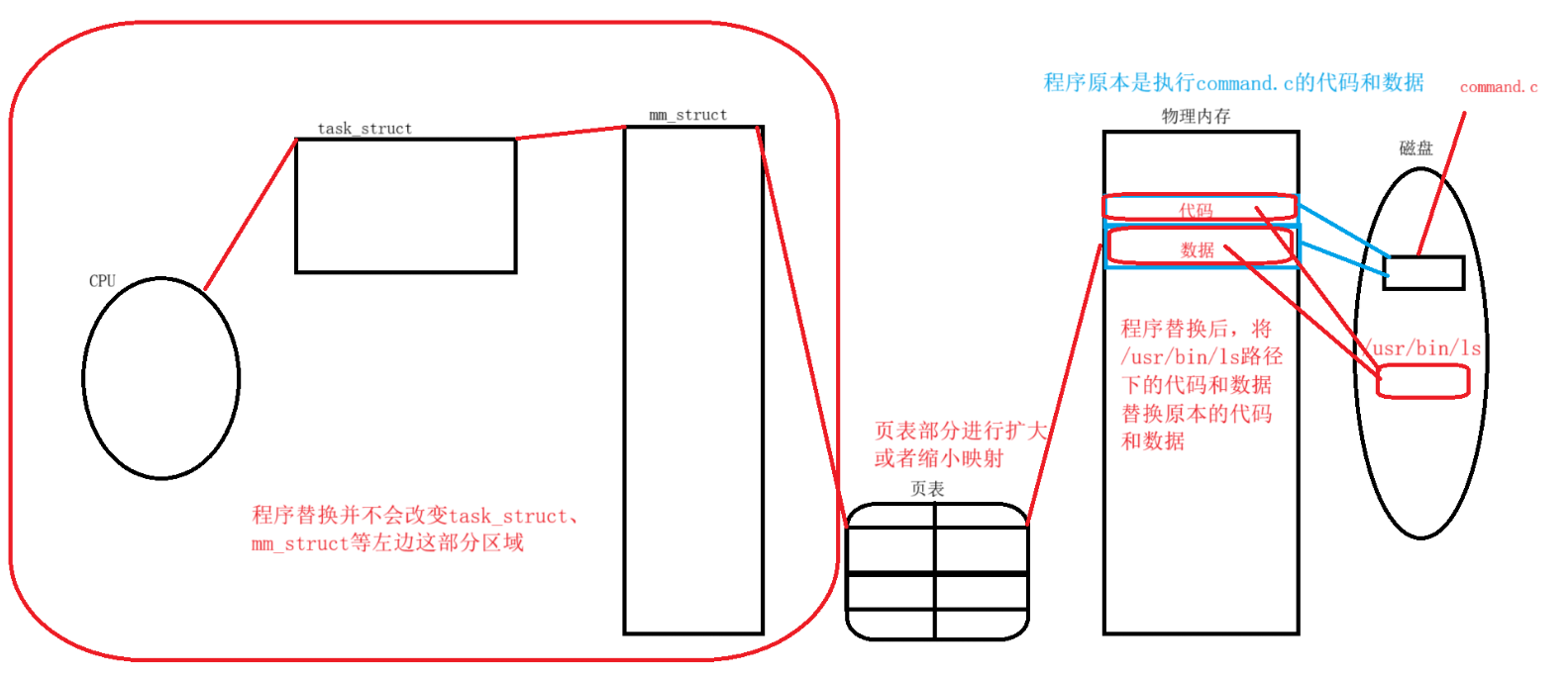
当程序运行到程序替换的位置处,excel会将新程序的代表替换老程序的代码,用新程序的数据替换老程序的数据,将堆区和栈区全部替换,然后让CPU开始执行新程序的mian函数入口。
【注意】整个过程只是将进程的代码和数据进行了替换,没有创建子进程。
多进程版本------验证各种进程替换的结构
cpp
int main()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id == 0)
{
// child
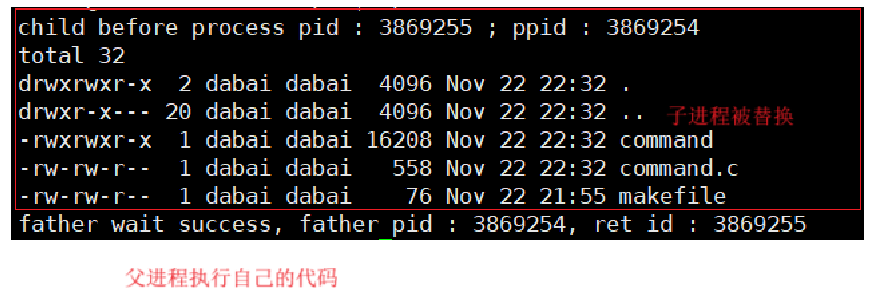
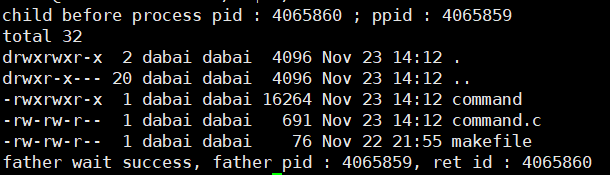
printf("child before process pid : %d ; ppid : %d \n", getpid(), getppid());
// 程序替换
execl("/usr/bin/ls", "ls", "-a", "-l", NULL);
printf("child after process pid : %d ; ppid : %d \n", getpid(), getppid());
exit(1);
}
// father
pid_t ret = waitpid(id, NULL, 0);
if(ret > 0)
{
printf("father wait success, father pid : %d, ret id : %d\n", getpid(), ret);
}
return 0;
}
【结论】
- 在子进程执行的程序替换,父进程并不会受影响。是因为进程之间具有独立性质,并且存在写时拷贝技术,所以也证实了代码也是可以被写时拷贝的。
- 程序替换不会创建子进程,只进行进程的程序代码和数据的替换工作。
当使用fork创建子进程后执行的是和父进程相同的程序(相同的代码和数据,但是可能是不同的代码分支),子进程往往要调用一种exec函数以执行另一个程序。当进程调用exec函数时,该进程的用户空间代码和数据完全被新程序所替换,从新程序的启动例程开始执行。调用exec并不会创建新进程,所以调用exec前后该进程的id并没有改变。
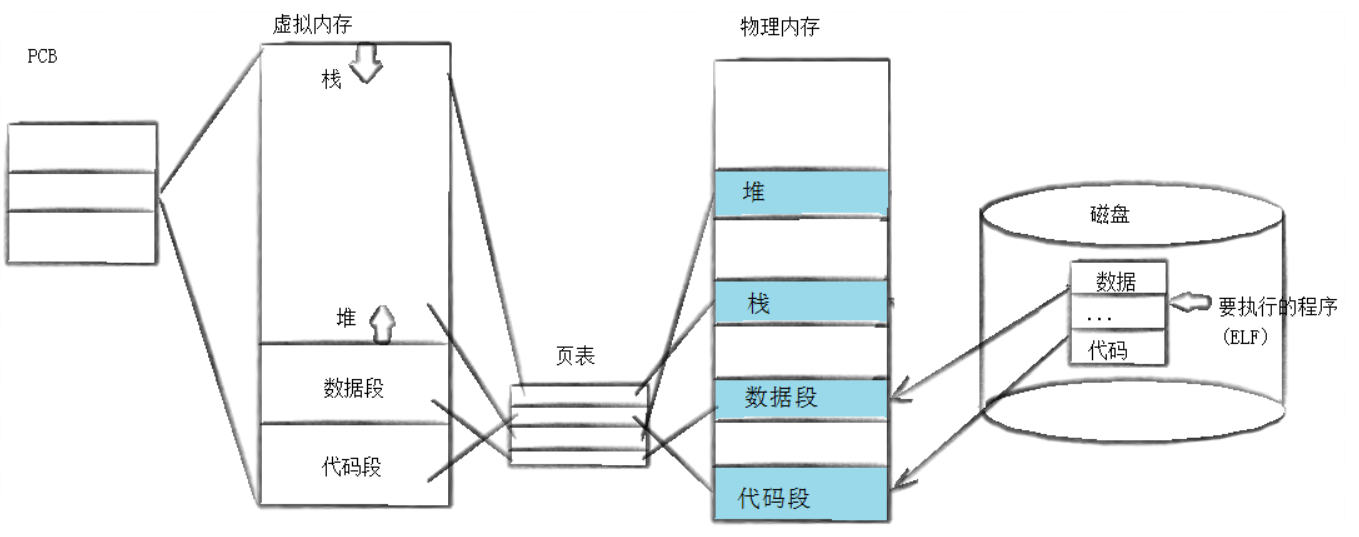
程序替换成功之后,exec*该进程后续的代码不会执行。如果程序替换失败,才可能执行后续代码。因此,exec*函数,只有失败返回值,没有成功返回值。
问题1:进程替换后,CPU如何知道新进程的入口?
Linux中形成的可执行程序是有格式的,即ELF格式,而这个可执行程序中会有一个表头,而这个可执行程序的入口地址就在表头中,进程替换后,会先将表头加载到CPU中。
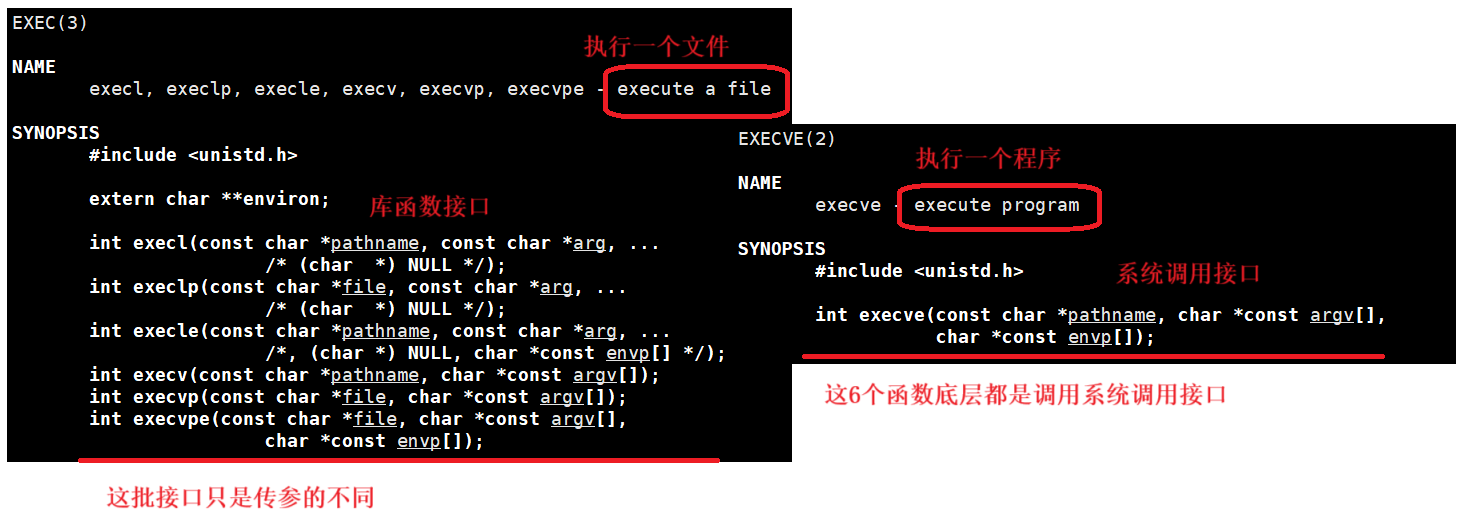
接口总结
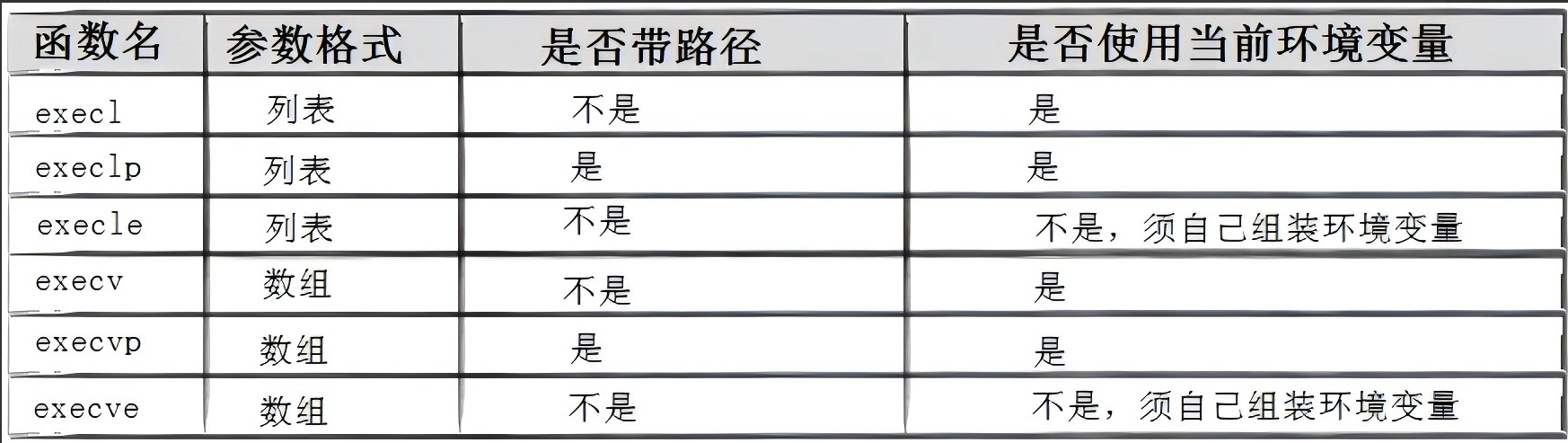
Linux中有7种以exec开头的函数,统称为exec函数:
- int execl(const char *path, const char *arg, ...);
- int execlp(const char *file, const char *arg, ...);
- int execle(const char *path, const char *arg, ..., char *const envp[]);
- int execv(const char *path, char *const argv[]);
- int execvp(const char *file, char *const argv[]);
- int execvpe(const char *file, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
上述六个接口是C语言实现的接口,下面这个是系统调用接口:
int execve(const char *path, char *const argv[], char *const envp[]);
execl接口
execl是exec类型接口的第一个接口,l 可以理解是list的意思,也就是从第二个参数开始,参数是一个一个传递给函数的,l 代表传参是可变参数列表。
cpp
execl("/usr/bin/ls", "ls", "-a", "-l", NULL);
通过上面的这个例子在命令行中如何写指令,从第二个参数开始就是如何传递参数。
第一个参数,代表如果想要执行程序,就需要找到这个程序。而所有带 l 的exec函数的第一个参数就是决定如何找到该程序。通过第一个参数找到这个程序,后面的参数代表如何执行这个程序,主要是要不要涵盖选项,涵盖那些选项。
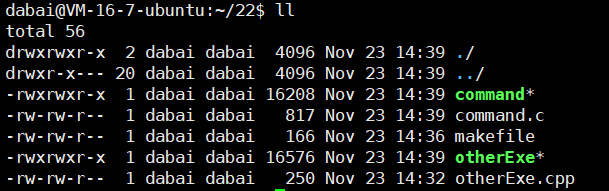
makefile执行多个可执行文件
bash
.PHONY:all
all:otherExe command
command:command.c
gcc -o $@ $^ -std=c99
otherExe:otherExe.cpp
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -f command otherExe使用一个C语言程序调用另一个C++程序
cpp
int main()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id == 0)
{
// child
printf("child before process pid : %d ; ppid : %d \n", getpid(), getppid());
// 程序替换
execl("./otherExe", "otherExe", NULL);
printf("child after process pid : %d ; ppid : %d \n", getpid(), getppid());
exit(1);
}
// father
pid_t ret = waitpid(id, NULL, 0);
if(ret > 0)
{
printf("father wait success, father pid : %d, ret id : %d\n", getpid(), ret);
}
return 0;
}注意,第二个参数不需要带./,是因为系统已经可以通过第一个参数找到该路径
用C语言或者C++调用其他的脚本语言
首先,创建一个shell脚本
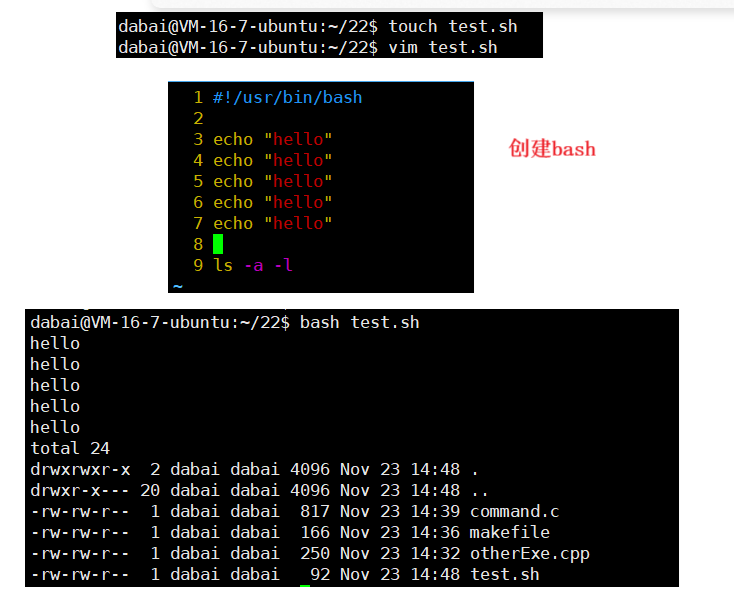
cpp
int main()
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id == 0)
{
// child
printf("child before process pid : %d ; ppid : %d \n", getpid(), getppid());
// 程序替换
execl("/usr/bin/bash", "bash", "test.sh", NULL);
printf("child after process pid : %d ; ppid : %d \n", getpid(), getppid());
exit(1);
}
// father
pid_t ret = waitpid(id, NULL, 0);
if(ret > 0)
{
printf("father wait success, father pid : %d, ret id : %d\n", getpid(), ret);
}
return 0;
}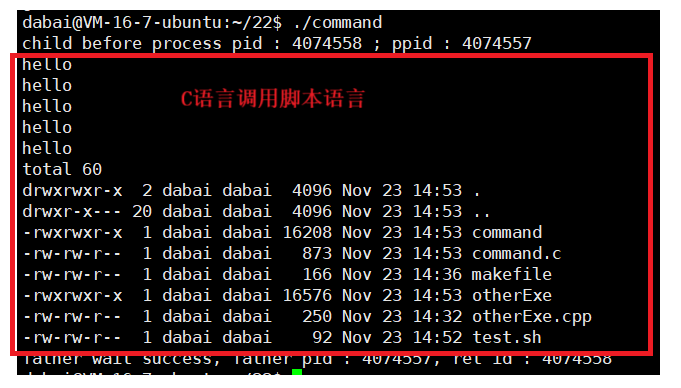
【注意】无论是可执行程序或者脚本,都可以跨语言调用,其核心原因是所有语言运行起来后,都是进程。
execlp接口
execlp在上面的execl的基础上多了p,p代表的是PATH,代表execlp会默认在PATH环境变量中查找某个程序。后面的内容同execl相同。
cpp
execlp("ls", "ls", "-a", "-l", NULL);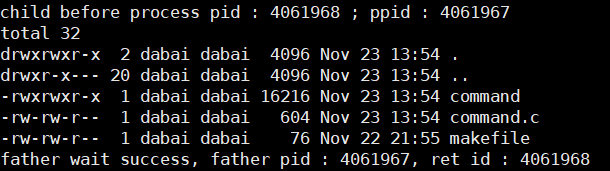
环境变量具有全局属性,所以每一个进程都会有环境变量。

【注意】函数中存在两个ls,第一个ls代表的是找到该程序的路径(同时这个路径需要在PATH环境变量下,才可以缩写),第二个以及后面的参数代表如何执行这个程序。
execv接口
v代表的意思是vector(了解C++的一定清楚,是C++中的一个容器),第一个参数没有带p,说明第一个参数是需要如何找到该程序。第二个参数是字符串指针数组。
在命令行输入指令ls -a -l的时候,程序会将这些指令解释成"ls","-a"."-l"字符串。而execv的第二个参数代表将这些字符串放在一个字符串指针数组中,然后传递过来。
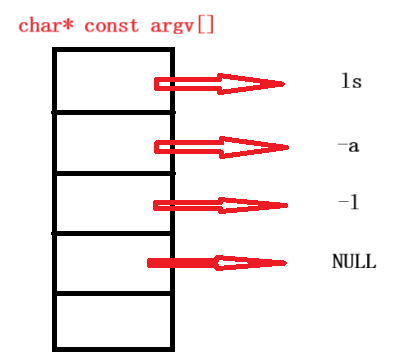
【注意】char *const argv[]代表指针本身不能被修改,而指针所指向的内容不可以被修改。

execvp接口
exec后面多个v和p,p代表在PATH环境变量中查找,v代表可以使用字符指针数组传递参数。
cpp
char *const myargv[] = {"ls", "-a", "-l", NULL};
execvp("ls", myargv);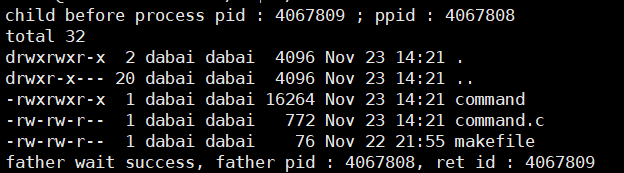
execle接口
execle接口中的e代表的是env环境变量。环境变量也是数据,在创建子进程的时候,环境变量已经被子进程继承下去了。所以,程序替换中环境信息不会被替换。
如何给子进程传递环境变量?
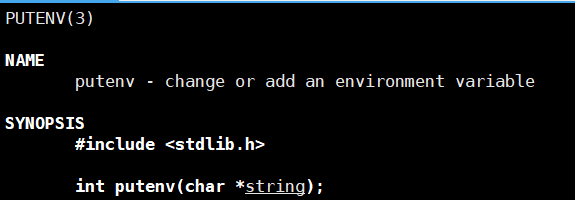
- 新增环境变量------在自己父进程的地址空间中直接putenv()
- 彻底替换
cpp
// 父进程执行
extern char **environ;// 设置环境变量
putenv("PRIVATE_ENV=11111111");// 添加该进程下的环境变量
// 子进程执行
char *const myargv[] = {"ls", "-a", "-l", NULL};
// 此处传递的系统的环境变量
execle("./otherExe", "otherExe", "-a", "-w", "-v", NULL, environ); // 子进程替换后,也可以看到添加后的环境变量传递环境变量的作用,可以给环境变量传递变量的值。这里被替换的进程看到的是传递的系统提供的环境变量
cpp
// 父进程执行
extern char **environ;// 设置环境变量
putenv("PRIVATE_ENV=11111111");// 添加该进程下的环境变量
// 子进程执行
char *const myargv[] = {"ls", "-a", "-l", NULL};
// 自定义环境变量
char *const myenv[] = {"MYVAL=111", "MYPATH=/usr/bin/sss", NULL};
execle("./otherExe", "otherExe", "-a", "-w", "-v", NULL, myenv); // 子进程替换后,也可以看到添加后的环境变量这里被替换的进程只能看到传递的自定义环境变量,当传递自定义环境变量的时候,采取的策略是覆盖,而不是追加。
execve接口
execve不同于其他几个接口,该函数是取自2号手册,
函数解释:
- exec函数承担的是加载器的效果。
- 这些函数如果调用成功加载新的程序从启动代码开始执行,不再返回
- 如果调用出错则返回-1
- exec函数只有出错的返回值而没有成功的返回值。
命名理解:
- l(list):表示参数采用列表
- v(vector):参数用数组
- p(path):有p自动搜索环境变量PATH
- e(env):表示自己维护环境变量
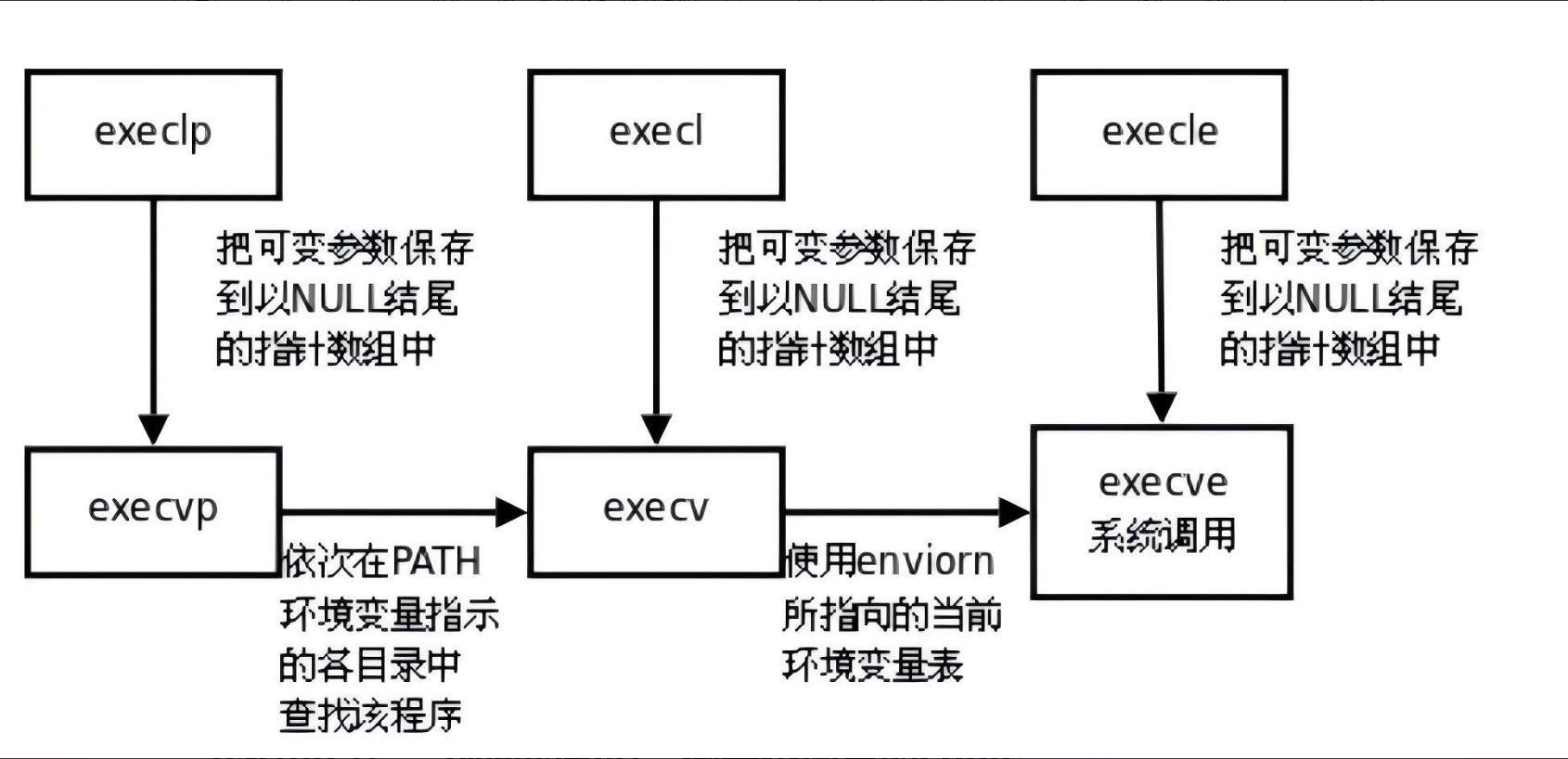
【总结】事实上,只有execve是真正的系统调用,其他五个函数最终都调用execve。
自定义shell
shell是一个外壳程序,shell/bash也是一个进程,本质就是自己创建子进程执行的。
cpp
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<sys/types.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<sys/wait.h>
#define LEFT "["
#define RIGHT "]"
#define LABLE "$"
#define DELIM " \t"
#define LINE_SIZE 1024
#define ARGC_SIZE 32
#define EXIT_CODE 2
int lastcode = 0;
int quit = 0;
extern char **environ;
char commandline[LINE_SIZE];
char *argv[ARGC_SIZE];
char pwd[LINE_SIZE];
// 获取环境变量中的USER变量
const char* getusername()
{
return getenv("USER");
}
// 获取环境变量中的HSITNAME------主机名称
const char* gethostname()
{
return getenv("HOSTNAME");
}
// 获取环境变量的当前路径
void getpwd()
{
getcwd(pwd, sizeof(pwd) - 1);
}
// 交互函数
void Interact(char *cline, int size)
{
getpwd();
printf(LEFT"%s@%s:%s"RIGHT""LABLE" ", getusername(), gethostname(), pwd);
char *s = fgets(cline, size, stdin);
assert(s != NULL);
(void)s; // 防止编译器报错
//"abcd\n\0"
cline[strlen(cline) - 1] = '\0';
}
// 分割子字符串
int splitspring(char cline[], char *_argv[])
{
int i = 0;
_argv[i++] = strtok(cline, DELIM);
while(_argv[i++] = strtok(NULL, DELIM)); // 一行代码将字符串全部切割
return i - 1;
}
// 普通命令的执行
void NormalExcute(char *_argv[])
{
pid_t id = fork();
if(id < 0)
{
perror("fork");
return;
}
else if(id == 0)
{
// 让子进程执行命令
// execvpe(_argv[0], _argv, environ);
execvp(_argv[0], _argv);
exit(EXIT_CODE);
}
else
{
// 父进程
int status = 0;
pid_t ret = waitpid(id, &status, 0);
if(ret == id)
{
// 最近一次进程等待的退出码
lastcode = WEXITSTATUS(status);
}
}
}
int buildCommand(char *_argv[], int _argc)
{
buildCommand(argv, argc);
if(argc == 2 && strcmp(argv[0], "cd") == 0)
{
chdir(argv[1]);
getpwd();
sprintf(getenv("PWD"), "%s", pwd);
return 1;
}
if(strcmp(_argv[0], "ls") == 0)
{
_argv[_argc++] = "--color";
_argv[_argc] = NULL;
}
return 0;
}
// 其他命令
// ... ...
int main()
{
while(!0)
{
// 1.
// 2.交互问题,获取命令行
Interact(commandline, sizeof(commandline));
// "ls -a -l -n\0"将命令字符串进行切割------> "ls" "-a" "-l" "-n"
// 使用strtok接口,第一个参数代码分割的字串,第二个参数代码分割符,返回值代表的是分割出来的字串
// 3.字符串风格,解析命令
int argc = splitspring(commandline, argv);
if(argc == 0) continue;
// 4.指令的判断
// debug测试
// for(int i = 0; argv[i]; ++i) printf("[%d]:%s\n", i, argv[i]);
int n = buildCommand(argv, argc)
// 5.普通命令的执行
if(!n) NormalExcute(argv);
}
return 0;
}