目录
-
-
- [3.1 流概览](#3.1 流概览)
- [3.2 stringstreams](#3.2 stringstreams)
-
- [3.2.1 定义与使用](#3.2.1 定义与使用)
- [3.2.1 getline()](#3.2.1 getline())
- [3.3 输出流](#3.3 输出流)
- [3.4 输入流](#3.4 输入流)
-
3.1 流概览
Streams------a general input/output(IO) abstraction for C++
流作为一种通用的输入输出抽象机制,为 C++ 程序处理数据的读取(输入)和写入(输出)提供了统一的接口,屏蔽了不同数据来源 / 目的地的底层差异。
std::cout << "Hello, World" << std::endl;
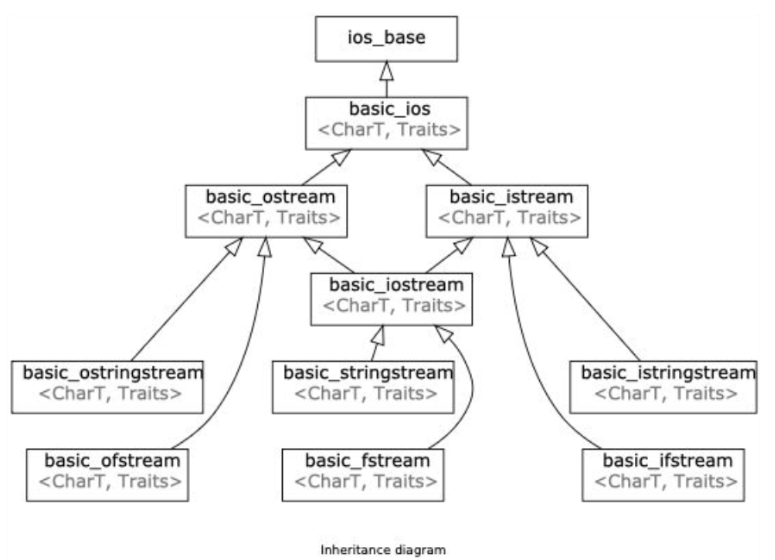
std::cout 是 std::ostream 的实例
同理,std::cin 是 std::istream 的实例
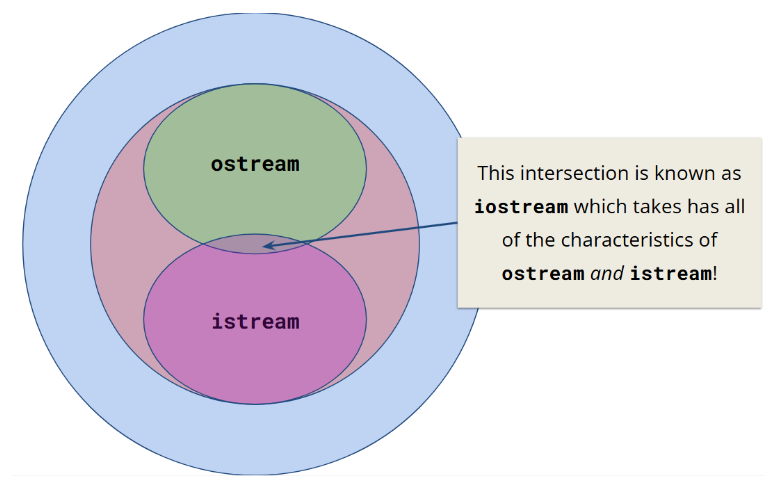
集成图:
包含关系:
3.2 stringstreams
3.2.1 定义与使用
std::stringstreams是一种把字符串当作流处理的方式。
在处理数据类型混合的场景中十分实用。
cpp
void foo() {
/// partial Bjarne Quote
std::string initial_quote = "Bjarne Stroustrup C makes it easy to shoot yourself in the foot";
/// create a stringstream
// 方法一:用字符串构造函数初始化字符串流(initialize stringstream with string constructor)
std::stringstream ss(initial_quote);
// 方法二:由于是流所以也可以这样插入字符串
std::stringstream ss;
ss << initial_quote;
/// data destinations
std::string first;
std::string last;
std::string language, extracted_quote;
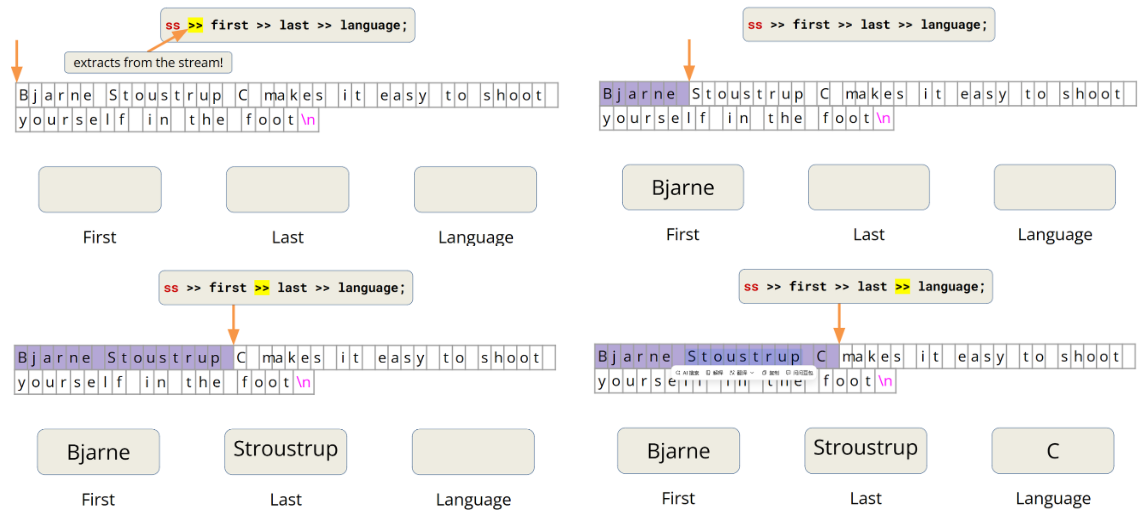
// 问题:>> 只读取到下一个空格,所以此情况extracted_quote只能读取到makes!
ss >> first >> last >> language >> extracted_quote;
std::cout << first << " " << last << " said this: "<< language << " " << extracted_quote << std::endl;
}
3.2.1 getline()
istream& getline(istream& is, string& str, char delim)
getline()函数会读取输入流is中的数据,直到遇到分隔符字符delim为止,并将读取到的数据存储到字符串缓冲区str中。- 分隔符字符(delim char)的默认值为'\n'(换行符)。
getline()函数会 "消耗" 掉分隔符字符(delim character)!
cpp
void foo() {
/// partial Bjarne Quote
std::string initial_quote = "Bjarne Stroustrup C makes it easy to shoot yourself in the foot";
/// create a stringstream
// 方法一:用字符串构造函数初始化字符串流(initialize stringstream with string constructor)
std::stringstream ss(initial_quote);
// 方法二:由于是流所以也可以这样插入字符串
std::stringstream ss;
ss << initial_quote;
/// data destinations
std::string first;
std::string last;
std::string language, extracted_quote;
ss >> first >> last >> language;
// 使用getline
std::getline(ss, extracted_quote);
std::cout << first << " " << last << " said this: "<< language << " " << extracted_quote << std::endl;
}cppreference------std::getline
3.3 输出流
std::ostream
输出流:一种把输入写入目的源或外部源的方式。
std::cout
用 << 把一些东西输出到控制台。
输出流中的字符会先存储在中间缓冲区中,然后再刷新(flush)到目标位置。

std::cout 流是行缓冲的,在发生显式刷新操作之前,缓冲区中的内容不会显示在外部输出源上!
std::endl
std::endl通知std::cout流结束当前行,也通知流进行刷新操作!
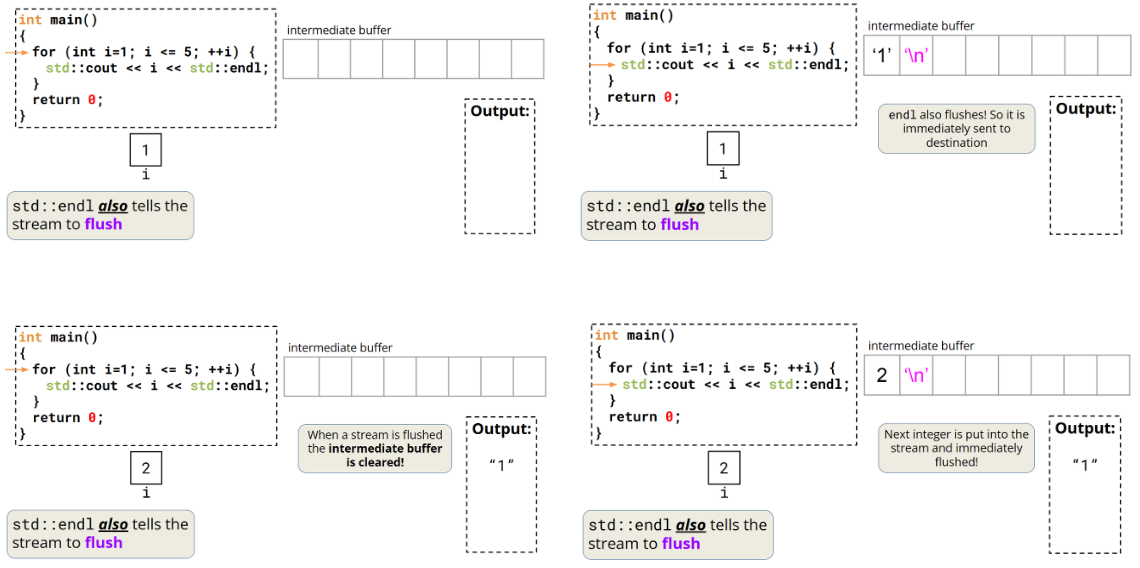
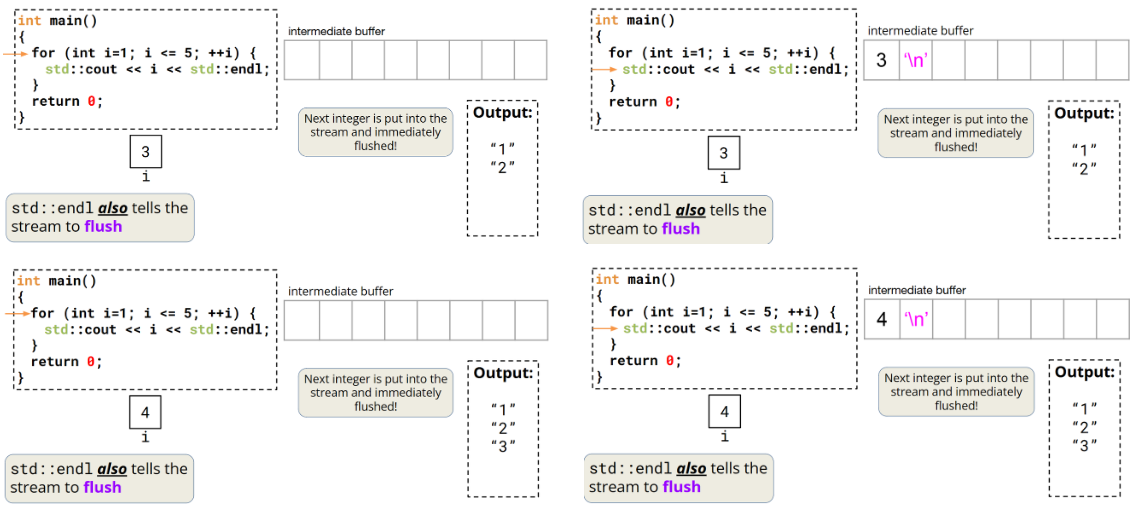
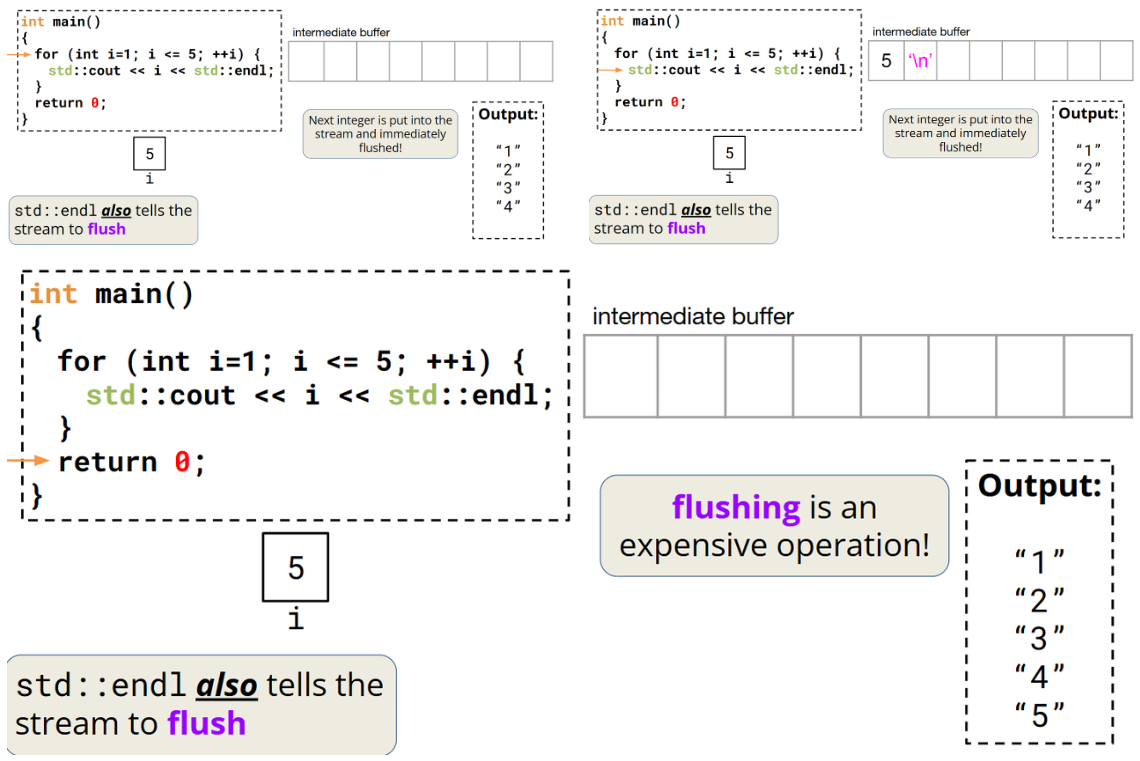
用std::endl可以,但是刷新操作开销很大!
'\n'
'\n'会存到中间缓冲区,减少刷新操作!
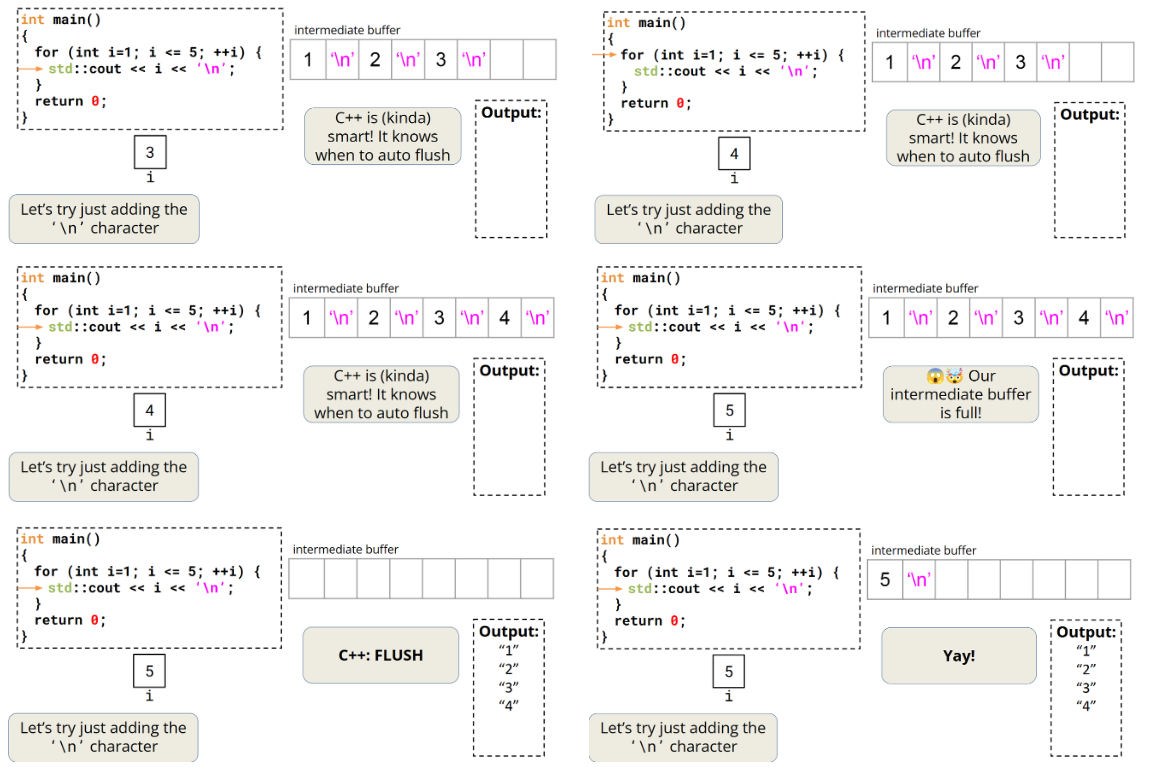
注意:
然而,在测试这些示例时,我发现 '\n' 似乎会以类似于 std::cout 的方式刷新缓冲区。进一步研究后,我查阅了 C++ 参考中关于 std::endl 的内容,其中指出:"在许多实现中,标准输出是行缓冲的,写入 '\n' 无论如何都会导致刷新,除非执行了 std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false)。" 这表明在许多标准输出中,'\n' 的行为与 std::cout 是相同的。此外,当我在程序中附加 | cat(通过管道将输出传给 cat 命令)时,我注意到在文件输出中,'\n' 并不会立即刷新缓冲区。

std::ios::sync_with_stdio(false)链接
cerr&clog
- cerr(character error):用于输出可能导致系统崩溃的错误信息(无缓冲),类比std::endl,效率低
- clog(character logging):用于非关键事件的日志记录(有缓冲),类比'\n',效率高
std::ofstream&std::ifstream
std::ofstream
一种向文件写入数据的方式!
○ 使用 << 插入运算符(insertion operator)将数据写入文件
○ std::ofstream 类提供了一些成员方法,可自行查阅了解
○ 需要掌握的方法:
■ is_open ():判断文件流是否成功打开文件,返回 bool 值(true 表示已打开,false 表示未打开)
■ open ():打开指定文件,将文件与 std::ofstream 对象关联,需传入文件路径等参数
■ close ():关闭已打开的文件,释放文件资源,避免资源泄漏
■ fail ():检查文件流操作是否失败(如打开不存在的文件、无写入权限等),返回 bool 值(true 表示操作失败,false
表示操作正常)
ofstream示例:
cpp
int main() {
/// associating file on construction
std::ofstream ofs("hello.txt"); // 创建一个指向 "hello.txt" 文件的输出文件流。
if (ofs.is_open()) { // 检查文件是否已打开,若已打开,则尝试向该文件写入数据!
ofs << "Hello CS106L!" << '\n';
}
ofs.close(); // 这会关闭与 "hello.txt" 文件关联的输出文件流。
ofs << "this will not get written"; // 会静默失败。
ofs.open("hello.txt"); // 重新打开流。10和11行选其一
ofs.open("hello.txt", std::ios::app); // 重新打开流,以追加的方式,而不是截断!
ofs << "this will though! It's open again"; // 成功写入流
return 0;
}ifstream示例:
cpp
int inputFileStreamExample() {
std::ifstream ifs("input.txt");
if (ifs.is_open()) {
std::string line;
std::getline(ifs, line);
std::cout << "Read from the file: " << line << '\n';
}
if (ifs.is_open()) {
std::string lineTwo;
std::getline(ifs, lineTwo);
std::cout << "Read from the file: " << lineTwo << '\n';
}
return 0;
}同一源 / 目标类型的输入流与输出流是互补的!
3.4 输入流
std::istream
一种从目的源或外界源读取数据的方式
std::cin
用>>从外界读取内容
std::cin是带缓冲的!可以将其理解为一个 "临时存储区":用户先将数据存入这里,之后程序再从这里读取数据
std::cin 的缓冲区会在遇到空白字符时停止(读取 / 存储)
C++的空白字符包括:" ",\n,\t
错误示例一
cpp
#include <iostream>
void cinGetlineBug() {
double pi;
double tao;
std::string name;
std::cin >> pi;
std::cin >> name; // 仅仅是吃掉了之前的换行符
std::cin >> tao;
std::cout << "my name is : " << name << " tao is : " << tao
<< " pi is : " << pi << '\n';
}
int main() {
cinGetlineBug();
return 0;
}错误示例二
cpp
#include <iostream>
void cinGetlineBug() {
double pi;
double tao;
std::string name;
std::cin >> pi;
std::getline(std::cin, name); // 仅仅是吃掉了之前的换行符
std::cin >> tao;
std::cout << "my name is : " << name << " tao is : " << tao
<< " pi is : " << pi << '\n';
}
int main() {
cinGetlineBug();
return 0;
}正确示例
cpp
#include <iostream>
void cinGetline() {
double pi;
double tao;
std::string name;
std::cin >> pi; // 读取一个浮点数到pi,此时输入缓冲区会留下一个换行符\n
std::getline(std::cin, name); // !会直接读取到缓冲区中残留的\n,导致读取到空字符串,实际作用是 "吃掉" 前面留下的换行符
std::getline(std::cin, name); // 读取用户输入
std::cin >> tao;
std::cout << "my name is : " << name << " tao is : " << tao
<< " pi is : " << pi << '\n';
}
int main() {
cinGetline();
return 0;
}