首先贴出最重要的模型图
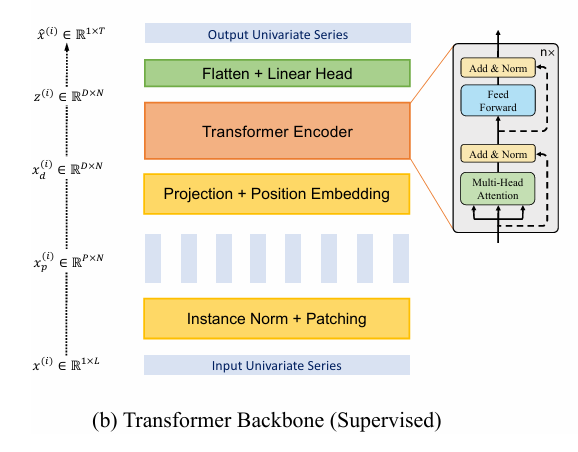
分别从两部分进行讲解
1.patch部分
2.Encoder部分
3.预测部分(Flatten部分)
1.patch部分
主要是class PatchTST_backbone
和TSTiEncoder(分patch主要核心)
2.Encoder部分
还是在PatchTST_backbone.py文件中
主要由TSTEncoderLayer和_MultiheadAttention类组成
2.1先给出TSTEncoderLayer主体代码
class TSTEncoderLayer(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, q_len, d_model, n_heads, d_k=None, d_v=None, d_ff=256, store_attn=False,
norm='BatchNorm', attn_dropout=0, dropout=0., bias=True, activation="gelu", res_attention=False, pre_norm=False):
super().__init__()
assert not d_model%n_heads, f"d_model ({d_model}) must be divisible by n_heads ({n_heads})"
d_k = d_model // n_heads if d_k is None else d_k
d_v = d_model // n_heads if d_v is None else d_v
# Multi-Head attention
self.res_attention = res_attention
self.self_attn = _MultiheadAttention(d_model, n_heads, d_k, d_v, attn_dropout=attn_dropout, proj_dropout=dropout, res_attention=res_attention)
# Add & Norm
self.dropout_attn = nn.Dropout(dropout)#随机丢弃
if "batch" in norm.lower():
self.norm_attn = nn.Sequential(Transpose(1,2), nn.BatchNorm1d(d_model), Transpose(1,2))
else:
self.norm_attn = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)#层归一化
# Position-wise Feed-Forward
self.ff = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(d_model, d_ff, bias=bias),# d_model ->d_ff
get_activation_fn(activation),#gelu
nn.Dropout(dropout),#随机丢弃
nn.Linear(d_ff, d_model, bias=bias))#还原
# Add & Norm
self.dropout_ffn = nn.Dropout(dropout)
if "batch" in norm.lower():
self.norm_ffn = nn.Sequential(Transpose(1,2), nn.BatchNorm1d(d_model), Transpose(1,2))
else:
self.norm_ffn = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)
self.pre_norm = pre_norm
self.store_attn = store_attn
def forward(self, src:Tensor, prev:Optional[Tensor]=None, key_padding_mask:Optional[Tensor]=None, attn_mask:Optional[Tensor]=None) -> Tensor:
# Multi-Head attention sublayer
if self.pre_norm:
src = self.norm_attn(src)#层归一化
## Multi-Head attention
if self.res_attention:#默认false
src2, attn, scores = self.self_attn(src, src, src, prev, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, attn_mask=attn_mask)
else:#三个src是Q,K,V self_attn -> _MultiheadAttention方法
src2, attn = self.self_attn(src, src, src, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, attn_mask=attn_mask)
if self.store_attn:
self.attn = attn
## Add & Norm
src = src + self.dropout_attn(src2) # Add: residual connection with residual dropout #残差连接src是原本的内容
if not self.pre_norm:
src = self.norm_attn(src)
# Feed-forward sublayer
if self.pre_norm:
src = self.norm_ffn(src)
## Position-wise Feed-Forward
src2 = self.ff(src)
## Add & Norm
src = src + self.dropout_ffn(src2) # Add: residual connection with residual dropout
if not self.pre_norm:
src = self.norm_ffn(src)#归一化
if self.res_attention:#默认false
return src, scores#一般不开
else:
return srcdef __init__定义方法:多头注意力-Add Norm-Feed Forward-Add Norm
1.Multi-Head attention里调用了另一个类_MultiheadAttention,这也是多头注意力核心
# Multi-Head attention
self.res_attention = res_attention
self.self_attn = _MultiheadAttention(d_model, n_heads, d_k, d_v, attn_dropout=attn_dropout, proj_dropout=dropout, res_attention=res_attention)2.Add & Norm总结起来就两句,先随机丢弃,然后合并完后调用归一化
# Add & Norm
self.dropout_attn = nn.Dropout(dropout)#随机丢弃
self.norm_attn = nn.LayerNorm(d_model)#层归一化3.Feed Forward 他是先用Linear扩展d_model至更高维度,然后relu后随机丢弃一部分,然后Linear还原
self.ff = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(d_model, d_ff, bias=bias),# d_model ->d_ff
get_activation_fn(activation),#gelu
nn.Dropout(dropout),#随机丢弃
nn.Linear(d_ff, d_model, bias=bias))#还原其余从def forward开始看
由于很多默认false所以总结起来就下面几段代码:
## Multi-Head attention
else:#三个src是Q,K,V self_attn -> _MultiheadAttention方法
src2, attn = self.self_attn(src, src, src, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, attn_mask=attn_mask)
## Add & Norm
src = src + self.dropout_attn(src2) # Add: residual connection with residual dropout #残差连接src是原本的内容
if not self.pre_norm:
src = self.norm_attn(src)#层归一化
## Position-wise Feed-Forward
src2 = self.ff(src)
## Add & Norm
src = src + self.dropout_attn(src2) # Add: residual connection with residual dropout #残差连接src是原本的内容
if not self.pre_norm:
src = self.norm_attn(src)#层归一化
return src2.2给出_MultiheadAttention代码
首先给出参数解释:n_heads:多头量 d_model:维度 K和V都是空
class _MultiheadAttention(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, d_model, n_heads, d_k=None, d_v=None, res_attention=False, attn_dropout=0., proj_dropout=0., qkv_bias=True, lsa=False):
"""Multi Head Attention Layer
Input shape:
Q: [batch_size (bs) x max_q_len x d_model]
K, V: [batch_size (bs) x q_len x d_model]
mask: [q_len x q_len]
"""
super().__init__()
d_k = d_model // n_heads if d_k is None else d_k
d_v = d_model // n_heads if d_v is None else d_v
self.n_heads, self.d_k, self.d_v = n_heads, d_k, d_v
self.W_Q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k * n_heads, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_K = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k * n_heads, bias=qkv_bias)
self.W_V = nn.Linear(d_model, d_v * n_heads, bias=qkv_bias)
# Scaled Dot-Product Attention (multiple heads)
self.res_attention = res_attention
self.sdp_attn = _ScaledDotProductAttention(d_model, n_heads, attn_dropout=attn_dropout, res_attention=self.res_attention, lsa=lsa)
# Poject output
self.to_out = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(n_heads * d_v, d_model), nn.Dropout(proj_dropout))
def forward(self, Q:Tensor, K:Optional[Tensor]=None, V:Optional[Tensor]=None, prev:Optional[Tensor]=None,
key_padding_mask:Optional[Tensor]=None, attn_mask:Optional[Tensor]=None):
bs = Q.size(0)
if K is None: K = Q
if V is None: V = Q
# Linear (+ split in multiple heads)
q_s = self.W_Q(Q).view(bs, -1, self.n_heads, self.d_k).transpose(1,2) # q_s : [bs x n_heads x max_q_len x d_k]
k_s = self.W_K(K).view(bs, -1, self.n_heads, self.d_k).permute(0,2,3,1) # k_s : [bs x n_heads x d_k x q_len] - transpose(1,2) + transpose(2,3)
v_s = self.W_V(V).view(bs, -1, self.n_heads, self.d_v).transpose(1,2) # v_s : [bs x n_heads x q_len x d_v]
# Apply Scaled Dot-Product Attention (multiple heads)
if self.res_attention:
output, attn_weights, attn_scores = self.sdp_attn(q_s, k_s, v_s, prev=prev, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, attn_mask=attn_mask)
else:
output, attn_weights = self.sdp_attn(q_s, k_s, v_s, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, attn_mask=attn_mask)
# output: [bs x n_heads x q_len x d_v], attn: [bs x n_heads x q_len x q_len], scores: [bs x n_heads x max_q_len x q_len]
# back to the original inputs dimensions
output = output.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(bs, -1, self.n_heads * self.d_v) # output: [bs x q_len x n_heads * d_v]
output = self.to_out(output)
if self.res_attention: return output, attn_weights, attn_scores
else: return output, attn_weights首先处理维度,讲d_model展平为n_heads × d_k维度,前者是多头数
d_k = d_model // n_heads if d_k is None else d_k#Q,K维度
d_v = d_model // n_heads if d_v is None else d_v#V维度然后计算矩阵:[混合后的batch,patch数量,多头数,d_k]
self.W_Q = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k * n_heads, bias=qkv_bias)#算Q [bs x q_len x n_heads x d_k]
self.W_K = nn.Linear(d_model, d_k * n_heads, bias=qkv_bias)#算K
self.W_V = nn.Linear(d_model, d_v * n_heads, bias=qkv_bias)#算V点积注意力(就是transformer源码)
self.sdp_attn = _ScaledDotProductAttention(d_model, n_heads, attn_dropout=attn_dropout, res_attention=self.res_attention, lsa=lsa)
#调用了点积注意力输出
self.to_out = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(n_heads * d_v, d_model), nn.Dropout(proj_dropout))#还原维度+丢弃一部分从def forward开始看流程
首先分配QKV,K,V复制Q的内容
bs = Q.size(0)
if K is None: K = Q
if V is None: V = Q做矩阵运算,QKV采用不同方式做
# Linear (+ split in multiple heads)
q_s = self.W_Q(Q).view(bs, -1, self.n_heads, self.d_k).transpose(1,2) # q_s : [bs x n_heads x max_q_len x d_k]
k_s = self.W_K(K).view(bs, -1, self.n_heads, self.d_k).permute(0,2,3,1) # k_s : [bs x n_heads x d_k x q_len] - transpose(1,2) + transpose(2,3)
v_s = self.W_V(V).view(bs, -1, self.n_heads, self.d_v).transpose(1,2) # v_s : [bs x n_heads x q_len x d_v]
做之前维度是[bs x q_len x d_model]
Q先拆分d_model维度变为n_heads x d_k,然后置换q_len和n_heads
K拆分d_model维度,然后换成了bs x n_heads x d_k x q_len
V拆分维度,然后同Q然后做点积(调用_ScaledDotProductAttention新类后面放上来)
output, attn_weights = self.sdp_attn(q_s, k_s, v_s, key_padding_mask=key_padding_mask, attn_mask=attn_mask)最后输出
# back to the original inputs dimensions
output = output.transpose(1, 2).contiguous().view(bs, -1, self.n_heads * self.d_v) # output: [bs x q_len x n_heads * d_v]
output = self.to_out(output)#还原维度+丢弃一部分2.3给出_ScaledDotProductAttention代码(transformer)
class _ScaledDotProductAttention(nn.Module):
r"""Scaled Dot-Product Attention module (Attention is all you need by Vaswani et al., 2017) with optional residual attention from previous layer
(Realformer: Transformer likes residual attention by He et al, 2020) and locality self sttention (Vision Transformer for Small-Size Datasets
by Lee et al, 2021)"""
def __init__(self, d_model, n_heads, attn_dropout=0., res_attention=False, lsa=False):
super().__init__()
self.attn_dropout = nn.Dropout(attn_dropout)
self.res_attention = res_attention
head_dim = d_model // n_heads
self.scale = nn.Parameter(torch.tensor(head_dim ** -0.5), requires_grad=lsa)
self.lsa = lsa
def forward(self, q:Tensor, k:Tensor, v:Tensor, prev:Optional[Tensor]=None, key_padding_mask:Optional[Tensor]=None, attn_mask:Optional[Tensor]=None):
'''
Input shape:
q : [bs x n_heads x max_q_len x d_k]
k : [bs x n_heads x d_k x seq_len]
v : [bs x n_heads x seq_len x d_v]
prev : [bs x n_heads x q_len x seq_len]
key_padding_mask: [bs x seq_len]
attn_mask : [1 x seq_len x seq_len]
Output shape:
output: [bs x n_heads x q_len x d_v]
attn : [bs x n_heads x q_len x seq_len]
scores : [bs x n_heads x q_len x seq_len]
'''
# Scaled MatMul (q, k) - similarity scores for all pairs of positions in an input sequence
attn_scores = torch.matmul(q, k) * self.scale # attn_scores : [bs x n_heads x max_q_len x q_len]
# Add pre-softmax attention scores from the previous layer (optional)
if prev is not None: attn_scores = attn_scores + prev
# Attention mask (optional)
if attn_mask is not None: # attn_mask with shape [q_len x seq_len] - only used when q_len == seq_len
if attn_mask.dtype == torch.bool:
attn_scores.masked_fill_(attn_mask, -np.inf)
else:
attn_scores += attn_mask
# Key padding mask (optional)
if key_padding_mask is not None: # mask with shape [bs x q_len] (only when max_w_len == q_len)
attn_scores.masked_fill_(key_padding_mask.unsqueeze(1).unsqueeze(2), -np.inf)
# normalize the attention weights
attn_weights = F.softmax(attn_scores, dim=-1) # attn_weights : [bs x n_heads x max_q_len x q_len]
attn_weights = self.attn_dropout(attn_weights)
# compute the new values given the attention weights
output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, v) # output: [bs x n_heads x max_q_len x d_v]
if self.res_attention: return output, attn_weights, attn_scores
else: return output, attn_weightsforward开始看:
第一句就是核心
attn_scores = torch.matmul(q, k) * self.scale # attn_scores : [bs x n_heads x max_q_len x q_len]也就是下图的QK/根号d
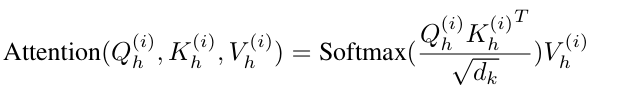
其他的都没开,默认做上图接下来的softmax
# normalize the attention weights
attn_weights = F.softmax(attn_scores, dim=-1) # attn_weights : [bs x n_heads x max_q_len x q_len]
attn_weights = self.attn_dropout(attn_weights)接下来×V
# compute the new values given the attention weights
output = torch.matmul(attn_weights, v) # output: [bs x n_heads x max_q_len x d_v]3.Flatten部分
最后Flatten_Head类
class Flatten_Head(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, individual, n_vars, nf, target_window, head_dropout=0):
super().__init__()
self.individual = individual
self.n_vars = n_vars
if self.individual:
self.linears = nn.ModuleList()
self.dropouts = nn.ModuleList()
self.flattens = nn.ModuleList()
for i in range(self.n_vars):
self.flattens.append(nn.Flatten(start_dim=-2))
self.linears.append(nn.Linear(nf, target_window))
self.dropouts.append(nn.Dropout(head_dropout))
else:
self.flatten = nn.Flatten(start_dim=-2)
self.linear = nn.Linear(nf, target_window)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(head_dropout)
def forward(self, x): # x: [bs x nvars x d_model x patch_num]
if self.individual:
x_out = []
for i in range(self.n_vars):
z = self.flattens[i](x[:,i,:,:]) # z: [bs x d_model * patch_num]
z = self.linears[i](z) # z: [bs x target_window]
z = self.dropouts[i](z)
x_out.append(z)
x = torch.stack(x_out, dim=1) # x: [bs x nvars x target_window]
else:
x = self.flatten(x)
x = self.linear(x)
x = self.dropout(x)
return x依旧拆分,其中论文提供了通道独立和通道混合两种方法:
主要集中在下面代码中,标注已在代码写出
其中flattens做的是一个个取通道,linears做的预测,dropouts扔一点,stack拼接通道得到最终的预测
def forward(self, x): # x: [bs x nvars x d_model x patch_num]
if self.individual:#开启通道独立情况
x_out = []
for i in range(self.n_vars):#一个个取通道
z = self.flattens[i](x[:,i,:,:]) # z: [bs x d_model * patch_num]
z = self.linears[i](z) #用d_model * patch_num做预测输出target_window # z: [bs x target_window]
z = self.dropouts[i](z) #随机扔一点
x_out.append(z)
x = torch.stack(x_out, dim=1) #7个通道拼回去 # x: [bs x nvars x target_window]题外:
论文提供了M,S,MS三种,分别代表只有单变量,多变量但通道独立,多变量并且通道混合的情况,论文中默认开启的是S
如果你想自己复现 S 或 MS,只要改两行:
# S版本(单变量)
c_in=1, n_vars=1
# MS版本(多变量共享)
individual=False # ← 只改这一行就行!