深度学习
自动微分模块
基本概念
训练神经网络时,最常用的算法就是反向传播。在该算法中,参数(模型权重)会根据损失函数关于对应参数的梯度进行调整。为了计算这些梯度,PyTorch 内置了名为 torch.autograd 的微分模块(通过 backward 方法、grad 属性来实现计算和访问)。它支持任意计算图的自动梯度计算:
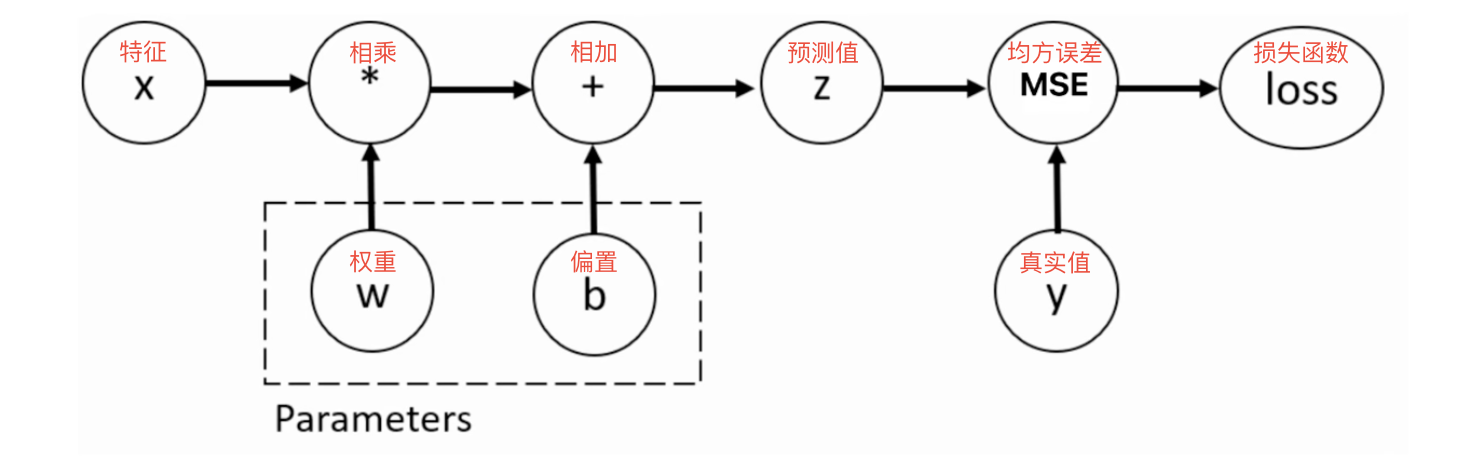
自动微分就是对损失函数求导,结合反向传播,更新权重参数
W、b
梯度下降(Gradient Descent)中对于任意参数 θ \theta θ(权重 W W W 或偏置 b b b),更新公式为:
θ new = θ old − η ⋅ ∇ θ L ( θ old ) \theta_{\text{new}} = \theta_{\text{old}} - \eta \cdot \nabla_{\theta} \mathcal{L}(\theta_{\text{old}}) θnew=θold−η⋅∇θL(θold)
其中:
-
θ new \theta_{\text{new}} θnew:更新后的参数
-
θ old \theta_{\text{old}} θold:更新前的参数
-
η \eta η(学习率):步长系数(通常取 1 0 − 3 ∼ 1 0 − 5 10^{−3}∼10^{−5} 10−3∼10−5,需通过验证集调优)
-
∇ θ L \nabla_{\theta} \mathcal{L} ∇θL:损失函数关于 θ \theta θ 的梯度(偏导数)
反向传播就是通过对损失函数求导更新权重,而从特征到预测值的过程则是正向传播
梯度基本计算
PyTorch 不支持向量张量对向量张量的求导,只支持标量张量对向量张量的求导( x x x 如果是张量, y y y 必须是标亮(一个值)才可以进行求导)
计算梯度:y.backward(), y y y 是一个标量
获取 x x x 点的梯度值:x.grad,会累加上一次的梯度
python
import torch
# 1. 定义变量,记录初始的的权重w(旧)
# 参数1: 初始值,参数2: 是否需要自动微分(求导),参数3: 数据类型
w = torch.tensor(10, requires_grad=True, dtype=torch.float)
# 2. 定义loss变量表示损失函数(模拟)
loss = 2 * w ** 2 # loss = 2w^2 -> 求导:4w
# 3. 打印梯度函数类型(了解)
print(f"梯度函数类型:{type(loss.grad_fn)}")
print(f"loss: {loss.sum()}")
# 4. 对loss进行求导,计算完后会记录到w.grad中
loss.sum().backward() # 保证loss是标量
# loss.backward()
# 也可以使用该方法求导,因为w本身就是标量,所以效果与backward()相同
print(f"w.grad: {w.grad}")
# 5. 代入权重更新公式
w.data = w.data - 0.01 * w.grad
# 6. 打印更新后的权重w(新)
print(f"更新后的w: {w}")输出结果如下:
mathematica
梯度函数类型:<class 'MulBackward0'>
loss: 200.0
w.grad: 40.0
更新后的w: 9.600000381469727梯度下降法求最优解
梯度下降法公式: W n e w = W o l d − η ⋅ ∇ W L ( W o l d ) W_{new} = W_{old} - \eta \cdot \nabla_{W} \mathcal{L}(W_{old}) Wnew=Wold−η⋅∇WL(Wold)
清空上一次的梯度值:w.grad.zero()(如果不清空的话每次的梯度都会累加)
python
import torch
# 1. 定义点 w=10 requires_grad=True dtype=torch.float
w = torch.tensor(10, requires_grad=True, dtype=torch.float)
# 2. 定义函数 loss = w**2 + 20
loss = w**2 + 20
# 3. 利用梯度下降法,循环迭代10求最优解
print(f"开始 权重初始值:{w},(0.01 * w.grad):无,loss:{loss}")
# 循环迭代100求最优解
for i in range(10):
# 3.1 正向计算(前向传播)
loss = w**2 + 20
# 3.2梯度清零
if w.grad is not None:
w.grad.zero_()
# 3.3 反向传播
loss.backward()
# 3.4 梯度更新
print(f"第{i}次迭代 梯度值:{w.grad}")
w.data = w.data - 0.01 * w.grad
# 3.5 打印本次梯度更新后的权重参数结果
print(f"第{i}次迭代 权重值:{w:.5f},(0.01 * w.grad):{0.01 * w.grad:.5f},loss:{loss:.5f}")
# 4. 打印最终结果
print(f"最终 权重值:{w:.5f},梯度:{w.grad:.5f},loss:{loss:.5f}")输出结果如下:
mathematica
开始 权重初始值:10.0,(0.01 * w.grad):无,loss:120.0
第0次迭代 梯度值:20.0
第0次迭代 权重值:9.80000,(0.01 * w.grad):0.20000,loss:120.00000
第1次迭代 梯度值:19.600000381469727
第1次迭代 权重值:9.60400,(0.01 * w.grad):0.19600,loss:116.04000
第2次迭代 梯度值:19.20800018310547
第2次迭代 权重值:9.41192,(0.01 * w.grad):0.19208,loss:112.23682
第3次迭代 梯度值:18.823841094970703
第3次迭代 权重值:9.22368,(0.01 * w.grad):0.18824,loss:108.58425
第4次迭代 梯度值:18.447364807128906
第4次迭代 权重值:9.03921,(0.01 * w.grad):0.18447,loss:105.07632
第5次迭代 梯度值:18.07841682434082
第5次迭代 权重值:8.85842,(0.01 * w.grad):0.18078,loss:101.70729
第6次迭代 梯度值:17.716848373413086
第6次迭代 权重值:8.68126,(0.01 * w.grad):0.17717,loss:98.47168
第7次迭代 梯度值:17.362510681152344
第7次迭代 权重值:8.50763,(0.01 * w.grad):0.17363,loss:95.36420
第8次迭代 梯度值:17.015260696411133
第8次迭代 权重值:8.33748,(0.01 * w.grad):0.17015,loss:92.37978
第9次迭代 梯度值:16.674955368041992
第9次迭代 权重值:8.17073,(0.01 * w.grad):0.16675,loss:89.51353
最终 权重值:8.17073,梯度:16.67496,loss:89.51353detach() 函数
自动微分存在的问题:一个张量一旦设置了自动微分,就无法直接转换成 Numpy 的 ndarray 对象
这种情况就需要用 detach() 函数来解决
python
import torch
import numpy as np
# 1,定义张量
t1 = torch.tensor([10, 20], dtype =torch.float)
t2 = torch.tensor([20, 30], requires_grad=True, dtype =torch.float)
print(f"t1:{t1},type:{type(t1)}")
print(f"t2:{t2},type:{type(t2)}")
# 2.尝试把张量 t1 转换为 numpy ndarray 对象
n1 = t1.numpy()
print(f"n1: {n1},type:{type(n1)}")
# 3. 尝试把张量 t2 转换为 numpy ndarray 对象
# n2 = t2.numpy()
# print(f"n2: {n2},type:{type(n2)}")
# 报错:Traceback (most recent call last):
# File "/Users/PycharmProjects/DL_learn/day03/03_自动微分模块_detach函数.py", line 20, in <module>
# n2 = t2.numpy()
# ^^^^^^^^^^
# RuntimeError: Can't call numpy() on Tensor that requires grad. Use tensor.detach().numpy() instead.
# 4. 尝试把张量 t2 转换为 numpy ndarray 对象,使用 detach() 函数
t3 = t2.detach()
print(f"t3: {t3},type:{type(t3)}")
# 测试:t3 是否与 t2 共享内存
t3[0] = 100
print(f"t3: {t3}")
print(f"t2: {t2}")
# 查看 t2 和 t3 哪个可以自动微分
print(f"t2.requires_grad: {t2.requires_grad}")
print(f"t3.requires_grad: {t3.requires_grad}")
n2 = t3.numpy()
print(f"n2: {n2},type:{type(n2)}")输出结果如下:
mathematica
t1:tensor([10., 20.]),type:<class 'torch.Tensor'>
t2:tensor([20., 30.], requires_grad=True),type:<class 'torch.Tensor'>
n1: [10. 20.],type:<class 'numpy.ndarray'>
t3: tensor([20., 30.]),type:<class 'torch.Tensor'>
t3: tensor([100., 30.])
t2: tensor([100., 30.], requires_grad=True)
t2.requires_grad: True
t3.requires_grad: False
n2: [100. 30.],type:<class 'numpy.ndarray'>自动微分应用
python
import torch
# 1. 定义x,表示:特征(输入数据),假设:2行5列的全1矩阵
x = torch.ones(2, 5)
print(f"x: {x}")
# 2. 定义y,表示:标签(真实值),假设:2行3列的全0矩阵
y = torch.zeros(2, 3)
print(f"y: {y}")
# 3. 初始化(可自动微分的)权重和偏置
w = torch.randn(5, 3, requires_grad=True)
print(f"w: {w}")
b = torch.randn(3, requires_grad=True)
print(f"b: {b}")
# 新建一个 MSELoss 对象
criterion = torch.nn.MSELoss()
# 设置学习率
learning_rate = 0.01
for i in range(10):
# 4. 前向传播计算出预测值(每次迭代都需要重新计算)
z = torch.matmul(x, w) + b
# 5. 定义损失函数
loss = criterion(z, y)
# 6. 梯度清零
if w.grad is not None:
w.grad.data.zero_()
if b.grad is not None:
b.grad.data.zero_()
# 7. 计算损失函数关于权重和偏置的梯度
loss.backward()
print(f"第{i}次迭代:")
print(f"w.grad: {w.grad}")
print(f"b.grad: {b.grad}")
# 8. 基于梯度,更新权重和偏置
with torch.no_grad():
w.data -= learning_rate * w.grad
b.data -= learning_rate * b.grad
# 打印本次梯度更新后的权重参数结果
print(f"权重值w:{w},偏置值b:{b}")
print(f"损失函数值loss:{loss}")输出结果如下:
mathematica
x: tensor([[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1., 1., 1.]])
y: tensor([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
w: tensor([[ 0.1683, -1.3922, 0.0113],
[-0.3075, -0.5632, 0.1783],
[ 0.6182, -0.4339, -1.5849],
[-1.3927, -0.1006, 1.0168],
[-0.4363, -0.7434, -0.3629]], requires_grad=True)
b: tensor([-1.4458, -0.6056, -1.8829], requires_grad=True)
第0次迭代:
w.grad: tensor([[-1.8639, -2.5593, -1.7495],
[-1.8639, -2.5593, -1.7495],
[-1.8639, -2.5593, -1.7495],
[-1.8639, -2.5593, -1.7495],
[-1.8639, -2.5593, -1.7495]])
b.grad: tensor([-1.8639, -2.5593, -1.7495])
权重值w:tensor([[ 0.1870, -1.3666, 0.0288],
[-0.2889, -0.5376, 0.1958],
[ 0.6368, -0.4083, -1.5674],
[-1.3741, -0.0750, 1.0343],
[-0.4177, -0.7178, -0.3454]], requires_grad=True),偏置值b:tensor([-1.4272, -0.5800, -1.8654], requires_grad=True)
损失函数值loss:9.813471794128418
第1次迭代:
w.grad: tensor([[-1.7893, -2.4569, -1.6795],
[-1.7893, -2.4569, -1.6795],
[-1.7893, -2.4569, -1.6795],
[-1.7893, -2.4569, -1.6795],
[-1.7893, -2.4569, -1.6795]])
b.grad: tensor([-1.7893, -2.4569, -1.6795])
权重值w:tensor([[ 0.2049, -1.3421, 0.0456],
[-0.2710, -0.5130, 0.2126],
[ 0.6547, -0.3837, -1.5506],
[-1.3562, -0.0504, 1.0511],
[-0.3998, -0.6932, -0.3286]], requires_grad=True),偏置值b:tensor([-1.4093, -0.5555, -1.8486], requires_grad=True)
损失函数值loss:9.044095993041992
第2次迭代:
w.grad: tensor([[-1.7177, -2.3586, -1.6123],
[-1.7177, -2.3586, -1.6123],
[-1.7177, -2.3586, -1.6123],
[-1.7177, -2.3586, -1.6123],
[-1.7177, -2.3586, -1.6123]])
b.grad: tensor([-1.7177, -2.3586, -1.6123])
权重值w:tensor([[ 0.2221, -1.3185, 0.0617],
[-0.2538, -0.4895, 0.2287],
[ 0.6719, -0.3601, -1.5345],
[-1.3390, -0.0268, 1.0673],
[-0.3826, -0.6696, -0.3125]], requires_grad=True),偏置值b:tensor([-1.3921, -0.5319, -1.8325], requires_grad=True)
损失函数值loss:8.335038185119629
第3次迭代:
w.grad: tensor([[-1.6490, -2.2643, -1.5478],
[-1.6490, -2.2643, -1.5478],
[-1.6490, -2.2643, -1.5478],
[-1.6490, -2.2643, -1.5478],
[-1.6490, -2.2643, -1.5478]])
b.grad: tensor([-1.6490, -2.2643, -1.5478])
权重值w:tensor([[ 0.2385, -1.2958, 0.0772],
[-0.2373, -0.4668, 0.2442],
[ 0.6884, -0.3375, -1.5190],
[-1.3225, -0.0042, 1.0827],
[-0.3661, -0.6470, -0.2970]], requires_grad=True),偏置值b:tensor([-1.3756, -0.5092, -1.8170], requires_grad=True)
损失函数值loss:7.6815714836120605
第4次迭代:
w.grad: tensor([[-1.5831, -2.1737, -1.4859],
[-1.5831, -2.1737, -1.4859],
[-1.5831, -2.1737, -1.4859],
[-1.5831, -2.1737, -1.4859],
[-1.5831, -2.1737, -1.4859]])
b.grad: tensor([-1.5831, -2.1737, -1.4859])
权重值w:tensor([[ 0.2544, -1.2741, 0.0920],
[-0.2215, -0.4451, 0.2591],
[ 0.7042, -0.3157, -1.5041],
[-1.3067, 0.0175, 1.0976],
[-0.3503, -0.6253, -0.2822]], requires_grad=True),偏置值b:tensor([-1.3598, -0.4875, -1.8022], requires_grad=True)
损失函数值loss:7.0793375968933105
第5次迭代:
w.grad: tensor([[-1.5198, -2.0868, -1.4265],
[-1.5198, -2.0868, -1.4265],
[-1.5198, -2.0868, -1.4265],
[-1.5198, -2.0868, -1.4265],
[-1.5198, -2.0868, -1.4265]])
b.grad: tensor([-1.5198, -2.0868, -1.4265])
权重值w:tensor([[ 0.2696, -1.2532, 0.1063],
[-0.2063, -0.4242, 0.2733],
[ 0.7194, -0.2949, -1.4899],
[-1.2915, 0.0384, 1.1119],
[-0.3351, -0.6044, -0.2679]], requires_grad=True),偏置值b:tensor([-1.3446, -0.4666, -1.7879], requires_grad=True)
损失函数值loss:6.524317264556885
第6次迭代:
w.grad: tensor([[-1.4590, -2.0033, -1.3694],
[-1.4590, -2.0033, -1.3694],
[-1.4590, -2.0033, -1.3694],
[-1.4590, -2.0033, -1.3694],
[-1.4590, -2.0033, -1.3694]])
b.grad: tensor([-1.4590, -2.0033, -1.3694])
权重值w:tensor([[ 0.2842, -1.2332, 0.1200],
[-0.1917, -0.4042, 0.2870],
[ 0.7340, -0.2748, -1.4762],
[-1.2769, 0.0584, 1.1255],
[-0.3205, -0.5844, -0.2542]], requires_grad=True),偏置值b:tensor([-1.3300, -0.4466, -1.7742], requires_grad=True)
损失函数值loss:6.012809753417969
第7次迭代:
w.grad: tensor([[-1.4006, -1.9232, -1.3147],
[-1.4006, -1.9232, -1.3147],
[-1.4006, -1.9232, -1.3147],
[-1.4006, -1.9232, -1.3147],
[-1.4006, -1.9232, -1.3147]])
b.grad: tensor([-1.4006, -1.9232, -1.3147])
权重值w:tensor([[ 0.2982, -1.2140, 0.1331],
[-0.1777, -0.3849, 0.3002],
[ 0.7480, -0.2556, -1.4630],
[-1.2629, 0.0777, 1.1387],
[-0.3065, -0.5651, -0.2411]], requires_grad=True),偏置值b:tensor([-1.3160, -0.4274, -1.7610], requires_grad=True)
损失函数值loss:5.541406154632568
第8次迭代:
w.grad: tensor([[-1.3446, -1.8462, -1.2621],
[-1.3446, -1.8462, -1.2621],
[-1.3446, -1.8462, -1.2621],
[-1.3446, -1.8462, -1.2621],
[-1.3446, -1.8462, -1.2621]])
b.grad: tensor([-1.3446, -1.8462, -1.2621])
权重值w:tensor([[ 0.3116, -1.1955, 0.1458],
[-0.1642, -0.3665, 0.3128],
[ 0.7615, -0.2371, -1.4504],
[-1.2494, 0.0961, 1.1513],
[-0.2930, -0.5467, -0.2284]], requires_grad=True),偏置值b:tensor([-1.3026, -0.4089, -1.7484], requires_grad=True)
损失函数值loss:5.106959819793701
第9次迭代:
w.grad: tensor([[-1.2908, -1.7724, -1.2116],
[-1.2908, -1.7724, -1.2116],
[-1.2908, -1.7724, -1.2116],
[-1.2908, -1.7724, -1.2116],
[-1.2908, -1.7724, -1.2116]])
b.grad: tensor([-1.2908, -1.7724, -1.2116])
权重值w:tensor([[ 0.3245, -1.1778, 0.1579],
[-0.1513, -0.3488, 0.3249],
[ 0.7744, -0.2194, -1.4383],
[-1.2365, 0.1139, 1.1634],
[-0.2801, -0.5289, -0.2163]], requires_grad=True),偏置值b:tensor([-1.2897, -0.3912, -1.7363], requires_grad=True)
损失函数值loss:4.706573963165283案例:模拟线性回归
在 Pytorch 中进行模型构建的整个流程一般分为四个步骤:
- 准备训练集数据
- 构建要使用的模型
- 设置损失函数和优化器
- 模型训练
使用到的 API:
- 使用 Pytorch 的
nn.MSELoss()代替平方损失函数 - 使用 Pytorch 的
data.DataLoader代替数据加载器 - 使用 Pytorch 的
optim.SGD代替优化器 - 使用 Pytorch 的
nn.Linear代替假设函数
python
import torch
from torch.utils.data import TensorDataset # 构造数据集对象
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader # 构造数据加载器对象
# numpy对象 -> 张量Tensor -> 数据集Dataset -> 数据加载器DataLoader
from torch import nn # 神经网络模块
from torch import optim # 优化器模块
from sklearn.datasets import make_regression # 生成模拟回归数据集
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['Arial Unicode MS', 'SimHei', 'DejaVu Sans'] # 用来正常显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 用来正常显示负号
# 定义函数,创建线性回归样本数据
def create_dataset():
# 创建数据集对象
x, y, coef = make_regression(n_samples=100, # 样本数量100
n_features=1, # 特征数量1
noise=10, # 噪声,噪声越大,样本数据越散,噪声越小,样本数据越集中
coef=True, # 是否返回系数,默认False,返回为None
bias=14.5, # 偏置项
random_state=3) # 随机种子
print(f"x_type:{type(x)},y_type:{type(y)},coef_type:{type(coef)}")
# 将构建数据转换为张量类型
x = torch.tensor(x, dtype=torch.float)
y = torch.tensor(y, dtype=torch.float)
return x, y, coef
# 定义函数,表示模型训练
def train(x, y, coef):
# 1. 构造数据集对象
dataset = TensorDataset(x, y)
# 2. 构造数据加载器对象
# 参数1: 数据集对象,参数2: 批次大小,默认1,参数3: 是否打乱数据,默认False(训练集打乱,测试集不打乱)
dataloader = DataLoader(dataset, batch_size=16, shuffle=True)
# 3. 创建初始的线性回归模型
# 参数1: 输入特征数量,参数2: 输出特征数量
model = nn.Linear(1, 1)
# 4. 创建损失函数对象
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
# 5. 创建优化器对象
# 参数1: 模型参数,参数2: 学习率
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# 6. 具体的训练过程
# 6.1 定义变量,分别表示:训练轮数,每轮的(平均)损失值,训练总损失值,训练的样本数
epochs, loss_list, total_loss, total_samples = 100, [], 0, 0
# 6.2 开始训练,按轮训练
for epoch in range(epochs):
# 6.2.1 每轮是分批次训练的,从数据加载器中获取批次数据
for train_x, train_y in dataloader: # 7批(16,16,16,16,16,16,4)
# 6.2.1.1 模型预测
y_pred = model(train_x)
# 6.2.1.2 计算(每批的平均)损失值
loss = criterion(y_pred, train_y.reshape(-1, 1)) # -1 表示自动计算
# 6.2.1.3 计算总损失和样本(批次)数
total_loss += loss.item()
total_samples += 1
# 6.2.1.4 梯度清零,反向传播,梯度更新
optimizer.zero_grad() # 梯度清零
loss.backward() # 反向传播,计算梯度
optimizer.step() # 梯度更新
# 6.2.2 把本轮的(平均)损失值,添加到列表中
loss_list.append(total_loss / total_samples)
print(f"epoch:{epoch+1},loss:{total_loss / total_samples}")
# 7. 打印最终的训练结果
print(f"{epochs}轮的平均损失值为:{loss_list}")
print(f"模型参数,权重:{model.weight.item()},偏置:{model.bias.item()}")
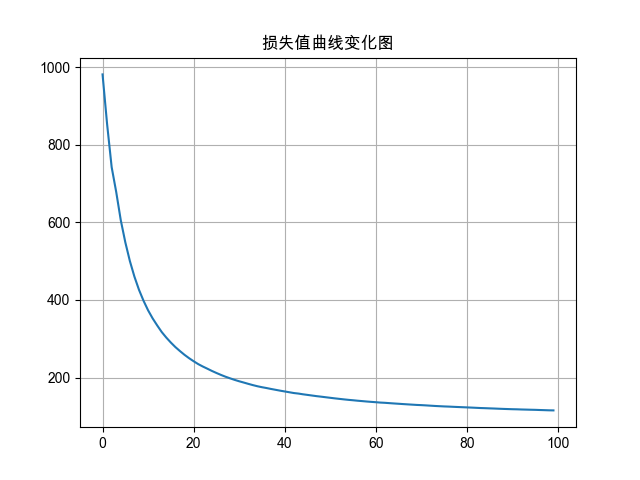
# 8. 绘制损失曲线
plt.plot(range(epochs), loss_list)
plt.title('损失值曲线变化图')
plt.grid() # 显示网格线
plt.show() # 显示损失曲线
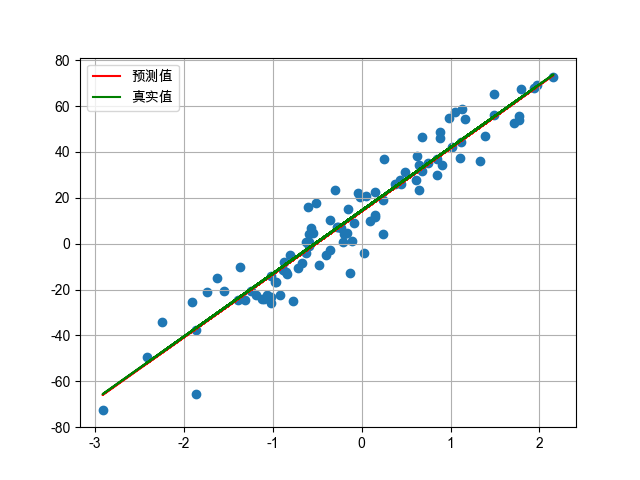
# 9. 绘制预测值和真实值的关系
# 绘制样本点分布情况
plt.scatter(x, y)
# 绘制训练模型的预测值
y_pred = torch.tensor(data = [v * model.weight.item() + model.bias.item() for v in x])
# 计算真实值
y_true = torch.tensor(data = [v * coef.item() + 14.5 for v in x])
# 绘制预测值和真实值的折线图
plt.plot(x, y_pred, color='red', label='预测值')
plt.plot(x, y_true, color='green', label='真实值')
plt.legend() # 显示图例
plt.grid() # 显示网格线
plt.show()
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 创建数据集
x, y, coef = create_dataset()
# print(f"x_shape:{x.shape},y_shape:{y.shape},coef_shape:{coef.shape}")
# print(f"x:{x},y:{y},coef:{coef}")
# 模型训练
train(x, y, coef)输出结果如下:
mathematica
epoch:1,loss:981.5269252232143
epoch:2,loss:853.3959612165179
epoch:3,loss:742.5516124906994
...
epoch:98,loss:116.04389740774305
epoch:99,loss:115.62916484436431
epoch:100,loss:115.40643576894487
100轮的平均损失值为:[981.5269252232143, 853.3959612165179, 742.5516124906994, 678.4569364275251, 605.8102375575475, 548.6587242853074, 500.36826098695093, 460.1560640675681, 426.3043611011808, 398.0191957473755, 373.3733908665645, 352.55637702487763, 334.41243330986947, 317.3166756338003, 303.06303981599353, 290.23163395268574, 278.5381171122319, 268.30006616077725, 258.62909295505153, 249.9824803352356, 242.1277265873085, 234.78329686994675, 228.59299124249762, 222.9695519379207, 217.2016434914725, 211.90159880459964, 206.87735432417935, 202.21674172732295, 198.0625297377262, 194.10351158323743, 190.4825868826308, 187.20595926046371, 183.82109612303896, 180.60866456873276, 177.6812167887785, 175.193129478939, 173.06181149869352, 170.65958882095222, 168.4760366726271, 166.26354225703648, 164.24055067587398, 162.20579415924695, 160.15612860454672, 158.80201498564188, 156.93153119465663, 155.34386212781348, 153.73787305130423, 152.13456554356077, 150.77345948455633, 149.30770564215524, 147.8670169365506, 146.433272254336, 145.1130473273141, 143.80517857919926, 142.58734095437185, 141.55579608070607, 140.3645850351281, 139.37626582178575, 138.30676883762166, 137.38113928295317, 136.51254849579072, 135.57208513004989, 134.959542306913, 134.11099514790945, 133.27229425618935, 132.48517642495952, 131.70074998900327, 130.94415850599273, 130.21998091514067, 129.4918162053945, 128.99063432720345, 128.32033567579967, 127.57748236908138, 126.84413563975036, 126.2349357405163, 125.64247574662804, 125.21943763103025, 124.65178913947864, 124.13279057238891, 123.62976352998189, 123.14717520019154, 122.64006108440174, 122.07807005292987, 121.50720818999673, 121.1260860427087, 120.64489899600463, 120.23127605801537, 119.70435118520415, 119.2549658311504, 118.85111155585638, 118.458202333615, 118.2068915233849, 117.74867322807488, 117.4586065011184, 117.11785009427179, 116.85318271460987, 116.40885656887723, 116.04389740774305, 115.62916484436431, 115.40643576894487]
模型参数,权重:27.481021881103516,偏置:14.157599449157715