1.1红黑树的概念
红黑树,是一种二叉搜索树,但是每个节点上增加一个存储位表示节点的颜色,可以是Red也可以是Black,通过对任何一条从根到叶子的路径上各节点着色方式限制,红黑树确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出两倍,因此接近平衡的。
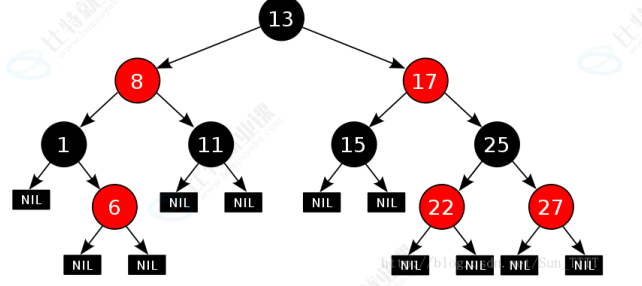
1.2红黑树的性质
1,最长路径最多是最短路径的二倍。
2,每个节点不是红色就是黑色。
3,根节点是黑色的。
4,如果一个节点的颜色为红色那么它的两个孩子的颜色均为黑色,【没有两个连续的红色节点】
5,对于每个节点,从该节点到其他所有后代的最简路径上,均包含相同的数目的黑色节点。
6,每个叶子节点都是黑色的(此处的叶子节点是指空节点)。
1.3红黑树节点的定义
代码展示
java
class RBTreeNode{
RBTreeNode lft=null;
RBTreeNode right=null;
RBTreeNode parent=null;
COLOR color=RED;
int val;
public RBTreeNode(int val){
this.val=val;
}
}1.4红黑树的插入
红黑树是在二叉搜索树的基础上加以平衡限制条件,因此红黑树的插入可以分为两部:
1,按照二叉搜索的树规则插入新节点
2,检测新节点插入后,红黑树的性质是否造到破坏
因为新节点的默认颜色是红色 ,因此:如果其双亲节点的颜色是黑色,没有违反红黑树任何性质,则不需要 调整;但当新插入节点的双亲节点颜色为红色时,就违反了性质三不能有连在一起的红色节点,此时需要对 红黑树分情况来讨论:
1,插入的节点是根节点➡️直接变黑。
2,插入节点的叔叔是红色➡️叔叔爷爷变色,爷爷变插入节点(cur指向爷爷)。
3,插入节点的叔叔是黑色➡️(LL,RR,LR,RL)旋转,然后变色。
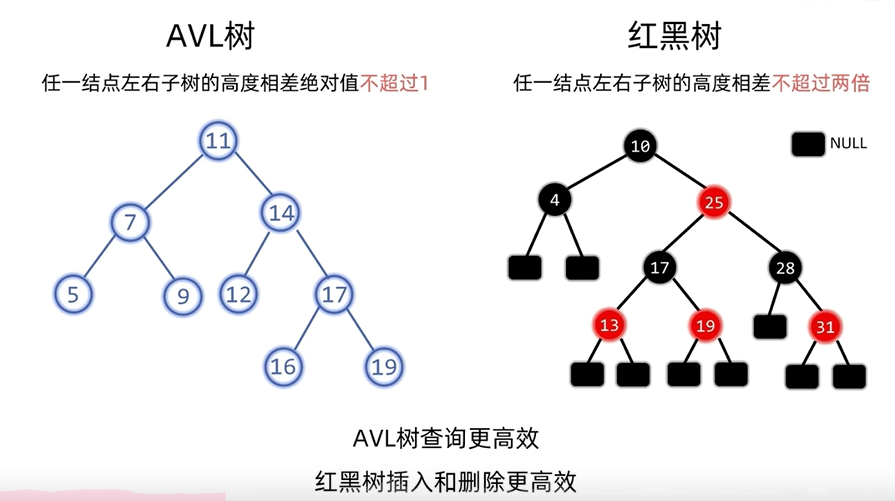
1.5与AVL树的比较
1.6代码全套案例
java
/**
* 红黑树 (Red-Black Tree) 的 Java 实现
*
* 性质:
* 1. 每个节点要么是红色,要么是黑色。
* 2. 根节点是黑色。
* 3. 所有的叶子节点(NIL节点)都是黑色。
* 4. 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个子节点都是黑色。(从每个叶子到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点)
* 5. 从任一节点到其每个叶子的所有简单路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点。
*/
public class RedBlackTree {
// 定义节点颜色常量
private static final boolean RED = true;
private static final boolean BLACK = false;
/**
* 内部类:表示红黑树的节点
*/
private class Node {
int data; // 节点存储的数据
boolean color; // 节点的颜色 (RED 或 BLACK)
Node left; // 左子节点
Node right; // 右子节点
Node parent; // 父节点
/**
* 构造函数
* @param data 节点数据
* @param color 节点颜色
* @param parent 父节点引用
*/
public Node(int data, boolean color, Node parent) {
this.data = data;
this.color = color;
this.parent = parent;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
// 红黑树的根节点
private Node root;
// 代表所有叶子节点的哨兵 NIL 节点。它始终是黑色的。
// 使用哨兵可以简化边界条件的处理,避免频繁检查 null。
private final Node NIL;
/**
* 红黑树构造函数
* 初始化 NIL 哨兵节点,并将根节点指向 NIL。
*/
public RedBlackTree() {
// 创建 NIL 哨兵节点,它是黑色的,父、左、右指针都指向自己或 null
// 在实际应用中,通常让所有节点的空指针都指向同一个全局 NIL 实例
NIL = new Node(0, BLACK, null);
NIL.left = NIL;
NIL.right = NIL;
root = NIL; // 初始时,树为空,根为 NIL
}
/* ---------------------- 辅助方法 ---------------------- */
/**
* 获取节点颜色
* @param node 要查询的节点
* @return 节点颜色,NIL 节点返回 BLACK
*/
private boolean getColor(Node node) {
if (node == null || node == NIL) {
return BLACK; // NIL 节点被视为黑色
}
return node.color;
}
/**
* 设置节点颜色
* @param node 要设置颜色的节点
* @param color 新的颜色 (RED 或 BLACK)
*/
private void setColor(Node node, boolean color) {
if (node != null && node != NIL) {
node.color = color;
}
}
/**
* 执行左旋转操作
* 将指定节点 y 向左旋转。这是维持红黑树性质的关键操作之一。
*
* py py
* | |
* y x
* / \ -----> / \
* ly x y rx
* / \ / \
* lx rx ly lx
*
* @param y 要进行左旋的节点
*/
private void leftRotate(Node y) {
if (y == null || y.right == NIL) {
return; // 无法左旋
}
Node x = y.right; // 设置 x
// 1. 将 x 的左子树 lx 连接到 y 的右边
y.right = x.left;
if (x.left != NIL) {
x.left.parent = y;
}
// 2. 将 x 上移到 y 的位置
x.parent = y.parent;
if (y.parent == null) { // y 是根节点
this.root = x;
} else if (y == y.parent.left) { // y 是左子节点
y.parent.left = x;
} else { // y 是右子节点
y.parent.right = x;
}
// 3. 将 y 作为 x 的左子节点
x.left = y;
y.parent = x;
}
/**
* 执行右旋转操作
* 将指定节点 x 向右旋转。这是维持红黑树性质的关键操作之一。
*
* px px
* | |
* x y
* / \ -----> / \
* y rx ly x
* / \ / \
* ly ry ry rx
*
* @param x 要进行右旋的节点
*/
private void rightRotate(Node x) {
if (x == null || x.left == NIL) {
return; // 无法右旋
}
Node y = x.left; // 设置 y
// 1. 将 y 的右子树 ry 连接到 x 的左边
x.left = y.right;
if (y.right != NIL) {
y.right.parent = x;
}
// 2. 将 y 上移到 x 的位置
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent == null) { // x 是根节点
this.root = y;
} else if (x == x.parent.right) { // x 是右子节点
x.parent.right = y;
} else { // x 是左子节点
x.parent.left = y;
}
// 3. 将 x 作为 y 的右子节点
y.right = x;
x.parent = y;
}
/* ---------------------- 插入操作 ---------------------- */
/**
* 公开的插入方法
* @param data 要插入的数据
*/
public void insert(int data) {
Node newNode = new Node(data, RED, null); // 新插入的节点初始为红色
newNode.left = NIL;
newNode.right = NIL;
root = insertNode(root, newNode);
fixInsert(newNode); // 插入后可能违反红黑树性质,需要修复
}
/**
* 在以 node 为根的子树中递归查找并插入新节点
* @param node 当前子树的根节点
* @param newNode 要插入的新节点
* @return 插入完成后的子树根节点
*/
private Node insertNode(Node node, Node newNode) {
if (node == NIL) {
// 找到插入位置,直接返回新节点作为根
newNode.parent = null; // 新节点将成为新的根
return newNode;
}
if (newNode.data < node.data) {
Node newLeft = insertNode(node.left, newNode);
node.left = newLeft;
newLeft.parent = node;
} else if (newNode.data > node.data) {
Node newRight = insertNode(node.right, newNode);
node.right = newRight;
newRight.parent = node;
}
// 如果 newNode.data == node.data,则不插入重复值(可根据需求修改)
return node;
}
/**
* 修复因插入红色节点而可能违反的红黑树性质
* 主要处理"连续红色"问题。
* @param k 刚刚插入的节点(红色)
*/
private void fixInsert(Node k) {
Node u; // uncle
while (k.parent != null && k.parent.color == RED) { // 当父节点为红色时才需要修复
if (k.parent == k.parent.parent.right) { // 父节点是祖父节点的右子节点 (Case 1: 父亲是右孩子)
u = k.parent.parent.left; // 叔叔是祖父的左子节点
if (getColor(u) == RED) { // Case 1.1: 叔叔是红色
// LLr, RRr (同侧且叔叔红): 变色,然后向上检查祖父
setColor(u, BLACK);
setColor(k.parent, BLACK);
setColor(k.parent.parent, RED);
k = k.parent.parent; // 继续向上检查祖父节点
} else { // Case 1.2: 叔叔是黑色或NIL
if (k == k.parent.left) { // LRr: k是父亲的左孩子
// LRr -> RRr: 对父亲进行一次右旋
k = k.parent;
rightRotate(k);
}
// RRr (父亲和孩子在同侧): 对祖父进行一次左旋,并交换父亲和祖父的颜色
setColor(k.parent, BLACK);
setColor(k.parent.parent, RED);
leftRotate(k.parent.parent);
}
} else { // 父节点是祖父节点的左子节点 (Case 2: 父亲是左孩子)
u = k.parent.parent.right; // 叔叔是祖父的右子节点
if (getColor(u) == RED) { // Case 2.1: 叔叔是红色
// RRl, LLl (同侧且叔叔红): 变色,然后向上检查祖父
setColor(u, BLACK);
setColor(k.parent, BLACK);
setColor(k.parent.parent, RED);
k = k.parent.parent; // 继续向上检查祖父节点
} else { // Case 2.2: 叔叔是黑色或NIL
if (k == k.parent.right) { // RLl: k是父亲的右孩子
// RLl -> LLl: 对父亲进行一次左旋
k = k.parent;
leftRotate(k);
}
// LLl (父亲和孩子在同侧): 对祖父进行一次右旋,并交换父亲和祖父的颜色
setColor(k.parent, BLACK);
setColor(k.parent.parent, RED);
rightRotate(k.parent.parent);
}
}
}
setColor(root, BLACK); // 最后确保根节点是黑色
}
/* ---------------------- 删除操作 ---------------------- */
/**
* 公开的删除方法
* @param data 要删除的数据
*/
public void delete(int data) {
deleteNodeHelper(this.root, data);
}
/**
* 查找包含特定数据的节点
* @param node 开始搜索的节点
* @param key 要查找的数据
* @return 找到的节点,如果未找到则返回 NIL
*/
private Node search(Node node, int key) {
if (node == NIL || key == node.data) {
return node;
}
if (key < node.data) {
return search(node.left, key);
}
return search(node.right, key);
}
/**
* 删除操作的核心辅助方法
* @param node 当前考虑的节点
* @param key 要删除的键
*/
private void deleteNodeHelper(Node node, int key) {
// 1. 找到要删除的节点 z 和替代节点 y
Node z = NIL; // 要删除的节点
Node x, y; // x: 移动到 y 原来位置的节点; y: 真正被删除/替换的节点
// 遍历找到要删除的节点
while (node != NIL){
if (node.data == key) {
z = node;
}
if (node.data <= key) {
node = node.right;
} else {
node = node.left;
}
}
if (z == NIL) {
System.out.println("Couldn't find key " + key + " in the tree");
return; // 未找到要删除的节点
}
y = z; // 初始化 y
boolean y_original_color = y.color; // 记录 y 的原始颜色,用于后续判断是否需要修复
// 2. 执行删除逻辑,确定替代节点 x
if (z.left == NIL) {
// 情况1: z 的左子树为空,则用右子树替代 z
x = z.right;
rbTransplant(z, z.right); // 用 z.right 替换 z
} else if (z.right == NIL) {
// 情况2: z 的右子树为空,则用左子树替代 z
x = z.left;
rbTransplant(z, z.left); // 用 z.left 替换 z
} else {
// 情况3: z 的左右子树都非空
// 找到 z 的后继节点 y (右子树中的最小节点)
y = minimum(z.right);
y_original_color = y.color; // 更新 y 的原始颜色
x = y.right; // x 是 y 的右子节点 (y 的左子节点必为 NIL)
if (y.parent == z) {
// 3a. 如果 y 是 z 的直接右子节点
x.parent = y; // 即使 x 是 NIL,也更新其父指针
} else {
// 3b. 如果 y 不是 z 的直接子节点
// 先用 y 的右子节点 x 替换 y
rbTransplant(y, y.right);
// 然后将 z 的右子树连接为 y 的右子树
y.right = z.right;
y.right.parent = y;
}
// 用 y 替换 z
rbTransplant(z, y);
// 将 z 的左子树连接为 y 的左子树
y.left = z.left;
y.left.parent = y;
// y 继承 z 的颜色
y.color = z.color;
}
// 3. 如果被删除的节点 y 原本是黑色,则需要修复红黑树性质
if (y_original_color == BLACK){
fixDelete(x);
}
}
/**
* 用 anotherNode 替换 node 在树中的位置
* @param node 被替换的节点
* @param anotherNode 替换上去的节点
*/
private void rbTransplant(Node node, Node anotherNode) {
if (node.parent == null) {
root = anotherNode;
} else if (node == node.parent.left){
node.parent.left = anotherNode;
} else {
node.parent.right = anotherNode;
}
anotherNode.parent = node.parent;
}
/**
* 找到以指定节点为根的子树中的最小节点
* @param node 子树的根
* @return 最小节点
*/
private Node minimum(Node node) {
while (node.left != NIL) {
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
/**
* 修复因删除黑色节点而可能违反的红黑树性质
* 主要处理"黑色高度减少"的问题。
* @param x 补位的节点(可能是 NIL)
*/
private void fixDelete(Node x) {
Node s; // sibling
while (x != root && getColor(x) == BLACK) {
if (x == x.parent.left) { // x 是左子节点
s = x.parent.right; // 兄弟节点
if (getColor(s) == RED) { // Case 1: 兄弟是红色
// 通过旋转将其转换为兄弟是黑色的情况
setColor(s, BLACK);
setColor(x.parent, RED);
leftRotate(x.parent);
s = x.parent.right; // 更新兄弟节点
}
// 此时兄弟 s 必为黑色
if (getColor(s.left) == BLACK && getColor(s.right) == BLACK) { // Case 2: 兄弟的两个子节点都是黑色
// 将兄弟染红,将"双重黑色"问题向上传递给父节点
setColor(s, RED);
x = x.parent; // 向上检查父节点
} else {
if (getColor(s.right) == BLACK) { // Case 3: 兄弟是黑色,远侄子(兄弟的右子)是黑色,近侄子(兄弟的左子)是红色
// 将兄弟染红,近侄子染黑,对兄弟右旋,转换为 Case 4
setColor(s.left, BLACK);
setColor(s, RED);
rightRotate(s);
s = x.parent.right; // 更新兄弟节点
}
// Case 4: 兄弟是黑色,远侄子(兄弟的右子)是红色
// 将兄弟染成父节点的颜色,父节点染黑,远侄子染黑,对父节点左旋
setColor(s, x.parent.color);
setColor(x.parent, BLACK);
setColor(s.right, BLACK);
leftRotate(x.parent);
x = root; // 修复完成,将 x 设为根节点以退出循环
}
} else { // x 是右子节点 (镜像情况)
s = x.parent.left; // 兄弟节点
if (getColor(s) == RED) { // Case 1: 兄弟是红色
setColor(s, BLACK);
setColor(x.parent, RED);
rightRotate(x.parent);
s = x.parent.left;
}
if (getColor(s.left) == BLACK && getColor(s.right) == BLACK) { // Case 2: 兄弟的两个子节点都是黑色
setColor(s, RED);
x = x.parent;
} else {
if (getColor(s.left) == BLACK) { // Case 3: 兄弟是黑色,远侄子(兄弟的左子)是黑色,近侄子(兄弟的右子)是红色
setColor(s.right, BLACK);
setColor(s, RED);
leftRotate(s);
s = x.parent.left;
}
// Case 4: 兄弟是黑色,远侄子(兄弟的左子)是红色
setColor(s, x.parent.color);
setColor(x.parent, BLACK);
setColor(s.left, BLACK);
rightRotate(x.parent);
x = root;
}
}
}
setColor(x, BLACK); // 最终将 x(现在是根或通过旋转上来的节点)染黑
}
/* ---------------------- 遍历和打印 ---------------------- */
/**
* 中序遍历 (In-order Traversal)
* 对于二叉搜索树,这将以升序输出所有元素。
*/
public void inorder() {
inorderHelper(this.root);
}
private void inorderHelper(Node node) {
if (node != NIL) {
inorderHelper(node.left);
System.out.print(node.data + "(" + (node.color == RED ? "R" : "B") + ") ");
inorderHelper(node.right);
}
}
/**
* 打印红黑树的结构(简单的文本形式)
*/
public void printTree() {
printTreeHelper(this.root, "", true);
}
private void printTreeHelper(Node node, String indent, boolean last) {
if (node != NIL) {
System.out.print(indent);
if (last) {
System.out.print("R----");
indent += " ";
} else {
System.out.print("L----");
indent += "| ";
}
String color = node.color == RED ? "RED" : "BLACK";
System.out.println(node.data + "(" + color + ")");
printTreeHelper(node.left, indent, false);
printTreeHelper(node.right, indent, true);
}
}
/* ---------------------- 测试主函数 ---------------------- */
/**
* 主函数,用于测试红黑树的功能
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
RedBlackTree bst = new RedBlackTree();
System.out.println("--- 插入操作 ---");
int[] keysToInsert = {10, 85, 15, 70, 20, 60, 30, 50, 65, 80, 90, 40, 5, 55};
for (int key : keysToInsert) {
System.out.println("插入: " + key);
bst.insert(key);
// 可选:每次插入后打印树结构以观察变化
// bst.printTree();
// System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("\n--- 中序遍历结果 ---");
bst.inorder();
System.out.println("\n");
System.out.println("--- 树结构 ---");
bst.printTree();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("\n--- 删除操作 ---");
int[] keysToDelete = {5, 10, 55, 60}; // 测试不同情况的删除
for (int key : keysToDelete) {
System.out.println("删除: " + key);
bst.delete(key);
// 可选:每次删除后打印树结构以观察变化
// bst.printTree();
// System.out.println();
}
System.out.println("\n--- 删除后的中序遍历结果 ---");
bst.inorder();
System.out.println("\n");
System.out.println("--- 删除后的树结构 ---");
bst.printTree();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--- 尝试删除不存在的节点 ---");
bst.delete(100);
System.out.println("\n--- 最终中序遍历结果 ---");
bst.inorder();
System.out.println("\n");
}
}