Flink是Apache软件基金会下开源的分布式流批一体计算框架,具备实时流计算和高吞吐批处理计算的大数据计算能力。本专栏内容为Flink源码解析的记录与分享。
本文解析的Flink源码版本为:flink-1.19.0
1.Flink计算资源的申请与调度功能概述
在前文《Flink-1.19.0源码详解7-Flink集群端调度》已介绍了Flink开启集群端调度与ExecutionGraph生成源码过程《Flink-1.19.0源码详解8-ExecutionGraph生成-前篇》《Flink-1.19.0源码详解9-ExecutionGraph生成-后篇》,当JobMaster生成了ExecutionGraph并划分好SchedulingPipelinedRegion后,JobMaster开始为每个SchedulingPipelinedRegion向Flink Resource Manager申请CPU/内存计算资源,开始进行Flink计算资源的申请与调度。
本文从Flink为每个SchedulingPipelinedRegion进行计算资源的申请与调度(内容为下流程图的红色部分)开始解析。
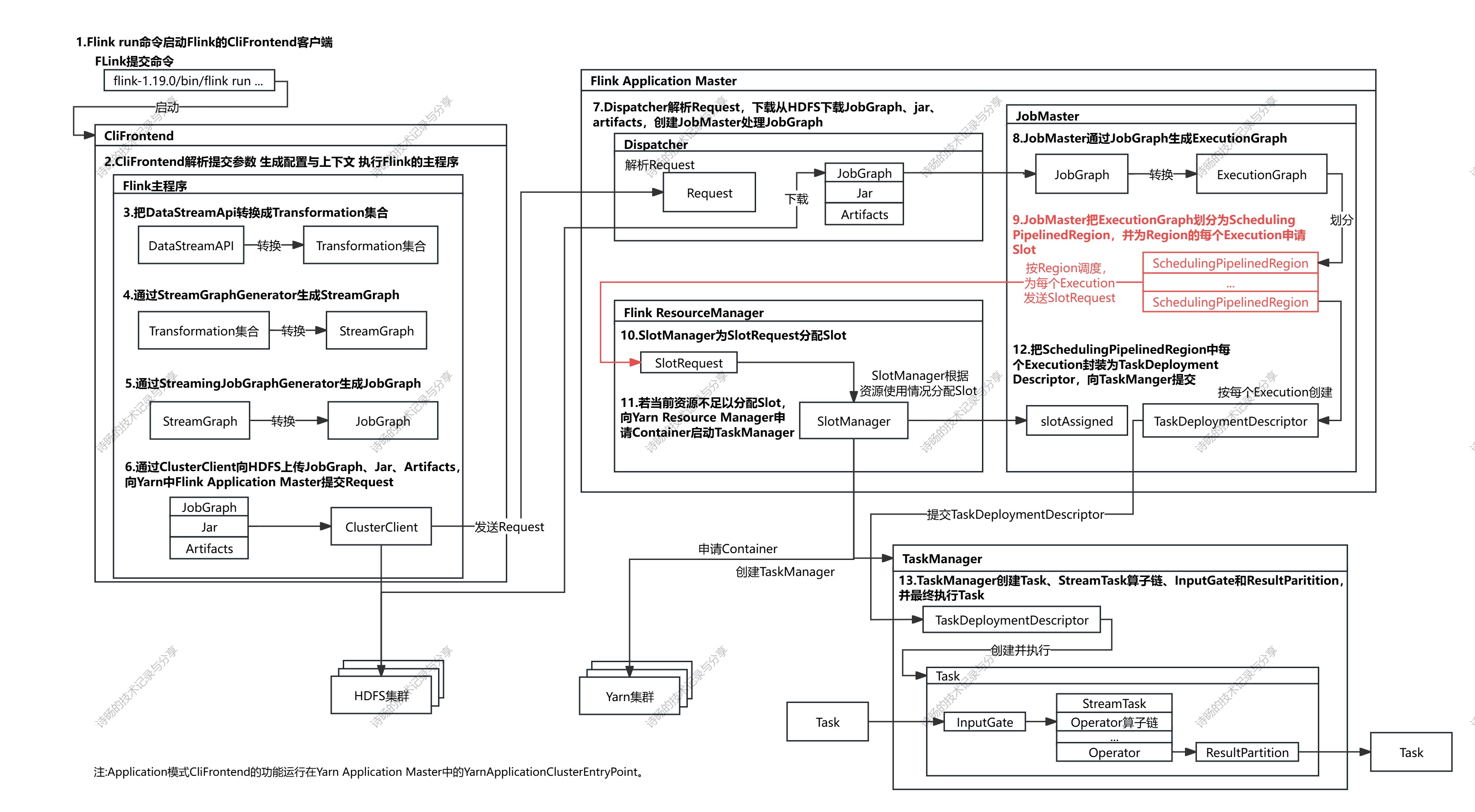
完整源码图解:
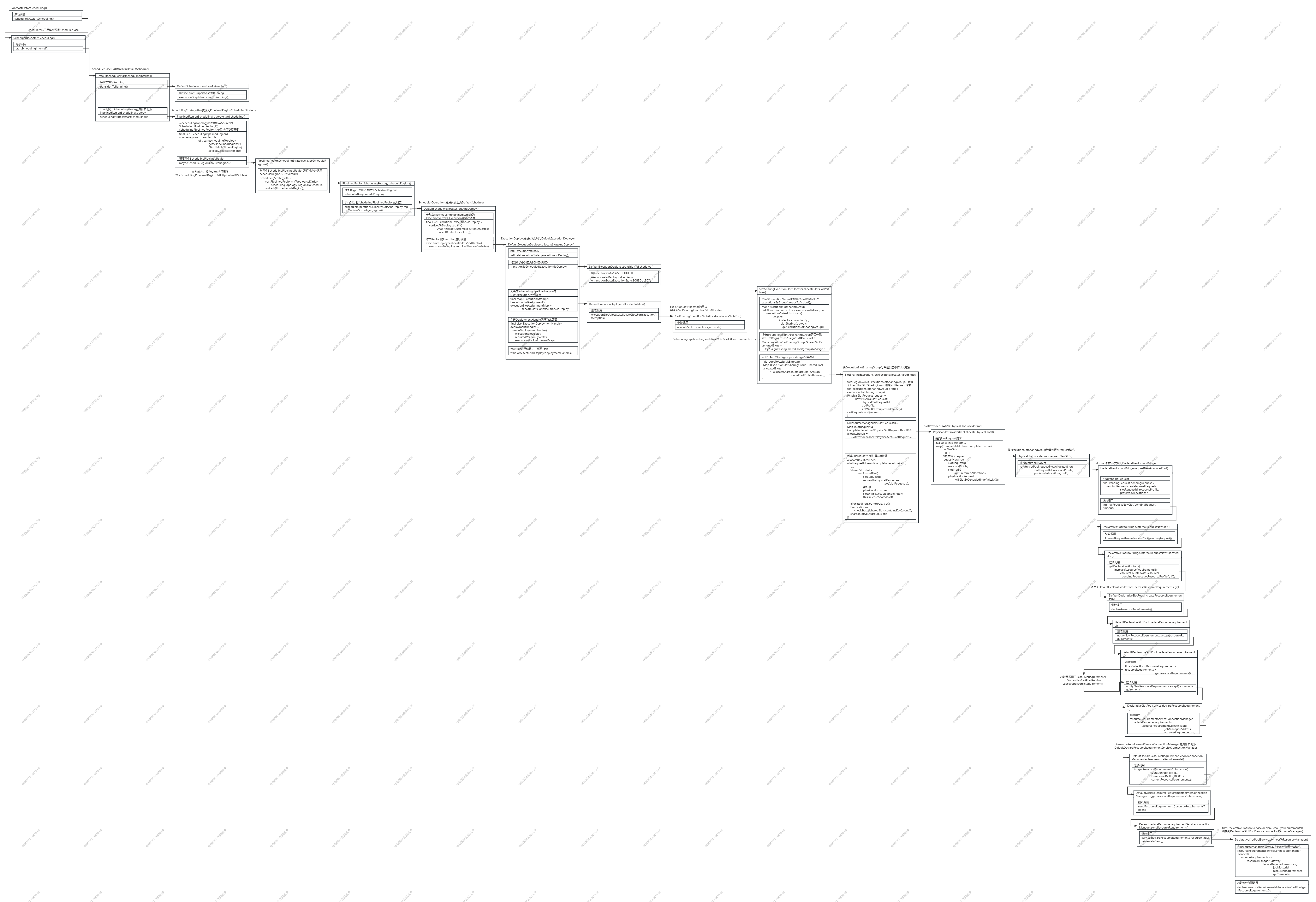
2.SchedulingPipelinedRegion计算资源调度
上文《Flink-1.19.0源码详解7-Flink集群端调度》解析了Flink开启了集群端调度,并通过调用DefaultScheduler的startSchedulingInternal()方法进入Flink的计算资源调度,本文从DefaultScheduler的startSchedulingInternal()方法开始,继续分析Flink计算资源调度的完整源码。
在DefaultScheduler的startSchedulingInternal()方法中,Flink先把ExecutionGraph的状态转为Running,并通过调用PipelinedRegionSchedulingStrategy(SchedulingStrategy的实现)的startScheduling()方法,开始具体调度。
DefaultScheduler.startSchedulingInternal()方法源码:
java
protected void startSchedulingInternal() {
log.info(
"Starting scheduling with scheduling strategy [{}]",
schedulingStrategy.getClass().getName());
//将ExecutionGraph的状态转为Running
transitionToRunning();
//开始调度,SchedulingStrategy具体实现为PipelinedRegionSchedulingStrategy
schedulingStrategy.startScheduling();
}在PipelinedRegionSchedulingStrategy.startScheduling()方法中,Flink从schedulingTopology拓扑中找到包含Source的SchedulingPipelinedRegion,然后继续调用PipelinedRegionSchedulingStrategy的maybeScheduleRegions()方法,进行调度。
PipelinedRegionSchedulingStrategy.startScheduling()方法源码:
java
public void startScheduling() {
//从schedulingTopology拓扑中包含Source的SchedulingPipelinedRegion,以SchedulingPipelinedRegion为单位进行资源调度
final Set<SchedulingPipelinedRegion> sourceRegions =
IterableUtils.toStream(schedulingTopology.getAllPipelinedRegions())
.filter(this::isSourceRegion)
.collect(Collectors.toSet());
//开始调度
maybeScheduleRegions(sourceRegions);
}PipelinedRegionSchedulingStrategy的startScheduling()方法对每个SchedulingPipelinedRegion进行排序,并调用scheduleRegion()方法对单个SchedulingPipelinedRegion进行调度。
PipelinedRegionSchedulingStrategy.startScheduling()方法源码:
java
private void maybeScheduleRegions(final Set<SchedulingPipelinedRegion> regions) {
//将每个SchedulingPipelinedRegion加入regionsToSchedule的set中
final Set<SchedulingPipelinedRegion> regionsToSchedule = new HashSet<>();
Set<SchedulingPipelinedRegion> nextRegions = regions;
while (!nextRegions.isEmpty()) {
nextRegions = addSchedulableAndGetNextRegions(nextRegions, regionsToSchedule);
}
// schedule regions in topological order.
//对每个SchedulingPipelinedRegion进行排序并调用scheduleRegion()方法,对单个SchedulingPipelinedRegion进行调度
SchedulingStrategyUtils.sortPipelinedRegionsInTopologicalOrder(
schedulingTopology, regionsToSchedule)
.forEach(this::scheduleRegion);
}在PipelinedRegionSchedulingStrategy的scheduleRegion()方法中,先把当前SchedulingPipelinedRegion加入正在调度的scheduledRegions数据结构中,然后继续调用DefaultScheduler的allocateSlotsAndDeploy()方法,其中DefaultScheduler为SchedulerOperations的具体实现。
PipelinedRegionSchedulingStrategy.scheduleRegion()方法源码:
java
private void scheduleRegion(final SchedulingPipelinedRegion region) {
checkState(
areRegionVerticesAllInCreatedState(region),
"BUG: trying to schedule a region which is not in CREATED state");
//添加Region到正在调度的ScheduleRegion
scheduledRegions.add(region);
//执行对当前ScheduleRegion的调度
schedulerOperations.allocateSlotsAndDeploy(regionVerticesSorted.get(region));
}DefaultScheduler的allocateSlotsAndDeploy()方法获取了当前SchedulingPipelinedRegion的ExecutionVertex的Execution,并以Execution为单位调用DefaultExecutionDeployer的allocateSlotsAndDeploy()方法进行调度,其中ExecutionDeployer的具体实现为DefaultExecutionDeployer。
DefaultScheduler.allocateSlotsAndDeploy()方法源码:
java
public void allocateSlotsAndDeploy(final List<ExecutionVertexID> verticesToDeploy) {
final Map<ExecutionVertexID, ExecutionVertexVersion> requiredVersionByVertex =
executionVertexVersioner.recordVertexModifications(verticesToDeploy);
//获取当前SchedulingPipelinedRegion的ExecutionVertex的Execution并进行调度
final List<Execution> executionsToDeploy =
verticesToDeploy.stream()
.map(this::getCurrentExecutionOfVertex)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
//对本Region的Execution进行调度
executionDeployer.allocateSlotsAndDeploy(executionsToDeploy, requiredVersionByVertex);
}3.Execution计算资源调度
进入DefaultExecutionDeployer.allocateSlotsAndDeploy()方法后,开始进行SchedulingPipelinedRegion中每个Execution的调度。
DefaultExecutionDeployer的allocateSlotsAndDeploy()方法为Execution调度与执行的主要方法,首先先验证了Execution当前状态并把状态调整为SCHEDULED。然后开始进行调度为当前SchedulingPipelinedRegion的List<Execution>分配slot,最后创建创建DeploymentHandle处理Task部署,并等待Slot分配结果,开始进行Task部署。
DefaultExecutionDeployer.allocateSlotsAndDeploy()方法源码:
java
public void allocateSlotsAndDeploy(
final List<Execution> executionsToDeploy,
final Map<ExecutionVertexID, ExecutionVertexVersion> requiredVersionByVertex) {
//验证Execution当前状态
validateExecutionStates(executionsToDeploy);
//将当前状态调整为SCHEDULED
transitionToScheduled(executionsToDeploy);
//为当前SchedulingPipelinedRegion的List<Execution>分配slot
final Map<ExecutionAttemptID, ExecutionSlotAssignment> executionSlotAssignmentMap =
allocateSlotsFor(executionsToDeploy);
//创建DeploymentHandle处理Task部署
final List<ExecutionDeploymentHandle> deploymentHandles =
createDeploymentHandles(
executionsToDeploy, requiredVersionByVertex, executionSlotAssignmentMap);
//等待Slot分配结果,并部署Task
waitForAllSlotsAndDeploy(deploymentHandles);
}首先关注对SchedulingPipelinedRegion的List<Execution>分配slot,又经过几次调用,先调用DefaultExecutionDeployer的allocateSlotsFor()方法,再调用SlotSharingExecutionSlotAllocator的allocateSlotsFor()方法,最终进入SlotSharingExecutionSlotAllocator的allocateSlotsForVertices()方法,开始调度。
DefaultExecutionDeployer.allocateSlotsFor()方法源码:
java
private Map<ExecutionAttemptID, ExecutionSlotAssignment> allocateSlotsFor(
final List<Execution> executionsToDeploy) {
final List<ExecutionAttemptID> executionAttemptIds =
executionsToDeploy.stream()
.map(Execution::getAttemptId)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
//继续调用
return executionSlotAllocator.allocateSlotsFor(executionAttemptIds);
}SlotSharingExecutionSlotAllocator.allocateSlotsFor()方法源码:
java
public Map<ExecutionAttemptID, ExecutionSlotAssignment> allocateSlotsFor(
List<ExecutionAttemptID> executionAttemptIds) {
//...
//继续调用
return allocateSlotsForVertices(vertexIds).stream()
.collect(
Collectors.toMap(
vertexAssignment ->
vertexIdToExecutionId.get(
vertexAssignment.getExecutionVertexId()),
vertexAssignment ->
new ExecutionSlotAssignment(
vertexIdToExecutionId.get(
vertexAssignment.getExecutionVertexId()),
vertexAssignment.getLogicalSlotFuture())));
}SlotSharingExecutionSlotAllocator的allocateSlotsAndDeploy方法首先把所有ExecutionVertex按共享slot划分成多个groupsToAssign组,按共享slot为单位分配资源。若当前groupsToAssign组所在共享slot已分配计算资源,则把groupsToAssign组分配在本共享slot中,若未分配资源,则调用SlotSharingExecutionSlotAllocatorallocateSharedSlots()方法继续申请资源。
SlotSharingExecutionSlotAllocator.allocateSlotsAndDeploy()方法源码:
java
private List<SlotExecutionVertexAssignment> allocateSlotsForVertices(
List<ExecutionVertexID> executionVertexIds) {
//把所有ExecutionVertexID按共享slot划分成多个executionsByGroup(groupsToAssign组)
SharedSlotProfileRetriever sharedSlotProfileRetriever =
sharedSlotProfileRetrieverFactory.createFromBulk(new HashSet<>(executionVertexIds));
Map<ExecutionSlotSharingGroup, List<ExecutionVertexID>> executionsByGroup =
executionVertexIds.stream()
.collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(
slotSharingStrategy::getExecutionSlotSharingGroup));
Map<ExecutionSlotSharingGroup, SharedSlot> slots = new HashMap<>(executionsByGroup.size());
Set<ExecutionSlotSharingGroup> groupsToAssign = new HashSet<>(executionsByGroup.keySet());
//检查groupsToAssign组所在SharingGroup已分配slot,则将groupsToAssign组分配在该slot上
Map<ExecutionSlotSharingGroup, SharedSlot> assignedSlots =
tryAssignExistingSharedSlots(groupsToAssign);
slots.putAll(assignedSlots);
groupsToAssign.removeAll(assignedSlots.keySet());
//若未分配,则为该groupsToAssign组申请slot
if (!groupsToAssign.isEmpty()) {
//进入slot分配
Map<ExecutionSlotSharingGroup, SharedSlot> allocatedSlots =
allocateSharedSlots(groupsToAssign, sharedSlotProfileRetriever);
slots.putAll(allocatedSlots);
groupsToAssign.removeAll(allocatedSlots.keySet());
Preconditions.checkState(groupsToAssign.isEmpty());
}
Map<ExecutionVertexID, SlotExecutionVertexAssignment> assignments =
allocateLogicalSlotsFromSharedSlots(slots, executionsByGroup);
// we need to pass the slots map to the createBulk method instead of using the allocator's
// 'sharedSlots'
// because if any physical slots have already failed, their shared slots have been removed
// from the allocator's 'sharedSlots' by failed logical slots.
SharingPhysicalSlotRequestBulk bulk = createBulk(slots, executionsByGroup);
bulkChecker.schedulePendingRequestBulkTimeoutCheck(bulk, allocationTimeout);
return executionVertexIds.stream().map(assignments::get).collect(Collectors.toList());
}申请资源的单位为SchedulingPipelinedRegion按共享同个slot在划分的ExecutionSlotSharingGroup组,首先遍历Region里所有ExecutionSlotSharingGroup,为每个ExecutionSlotSharingGroup创建slotRequest请求,然后向ResourceManager提交SlotRequest请求,最后创建SharedSlot实例封装申请到的slot资源。
DefaultExecutionDeployer.allocateSlotsAndDeploy()方法源码:
java
private Map<ExecutionSlotSharingGroup, SharedSlot> allocateSharedSlots(
Set<ExecutionSlotSharingGroup> executionSlotSharingGroups,
SharedSlotProfileRetriever sharedSlotProfileRetriever) {
List<PhysicalSlotRequest> slotRequests = new ArrayList<>();
Map<ExecutionSlotSharingGroup, SharedSlot> allocatedSlots = new HashMap<>();
Map<SlotRequestId, ExecutionSlotSharingGroup> requestToGroup = new HashMap<>();
Map<SlotRequestId, ResourceProfile> requestToPhysicalResources = new HashMap<>();
//遍历Region里所有ExecutionSlotSharingGroup,为每个ExecutionSlotSharingGroup创建slotRequest请求
for (ExecutionSlotSharingGroup group : executionSlotSharingGroups) {
SlotRequestId physicalSlotRequestId = new SlotRequestId();
ResourceProfile physicalSlotResourceProfile = getPhysicalSlotResourceProfile(group);
SlotProfile slotProfile =
sharedSlotProfileRetriever.getSlotProfile(group, physicalSlotResourceProfile);
PhysicalSlotRequest request =
new PhysicalSlotRequest(
physicalSlotRequestId, slotProfile, slotWillBeOccupiedIndefinitely);
slotRequests.add(request);
requestToGroup.put(physicalSlotRequestId, group);
requestToPhysicalResources.put(physicalSlotRequestId, physicalSlotResourceProfile);
}
//向ResourceManager提交SlotRequest请求
Map<SlotRequestId, CompletableFuture<PhysicalSlotRequest.Result>> allocateResult =
slotProvider.allocatePhysicalSlots(slotRequests);
//创建SharedSlot实例封装slot资源
allocateResult.forEach(
(slotRequestId, resultCompletableFuture) -> {
ExecutionSlotSharingGroup group = requestToGroup.get(slotRequestId);
CompletableFuture<PhysicalSlot> physicalSlotFuture =
resultCompletableFuture.thenApply(
PhysicalSlotRequest.Result::getPhysicalSlot);
SharedSlot slot =
new SharedSlot(
slotRequestId,
requestToPhysicalResources.get(slotRequestId),
group,
physicalSlotFuture,
slotWillBeOccupiedIndefinitely,
this::releaseSharedSlot);
allocatedSlots.put(group, slot);
Preconditions.checkState(!sharedSlots.containsKey(group));
sharedSlots.put(group, slot);
});
return allocatedSlots;
}提交SlotRequest请求的方法是PhysicalSlotProviderImpl.allocatePhysicalSlots(),在方法中,遍历了ExecutionSlotSharingGroup,为每个ExecutionSlotSharingGroup调用PhysicalSlotProviderImpl的requestNewSlot()方法提交请求。
java
public Map<SlotRequestId, CompletableFuture<PhysicalSlotRequest.Result>> allocatePhysicalSlots(
Collection<PhysicalSlotRequest> physicalSlotRequests) {
//...
//提交SlotRequest请求
return availablePhysicalSlots.entrySet().stream()
.collect(
//..
CompletableFuture<PhysicalSlot> slotFuture =
availablePhysicalSlot
.map(CompletableFuture::completedFuture)
.orElseGet(
//为每个ExecutionSlotSharingGroup提交请求
() ->
requestNewSlot(
slotRequestId,
resourceProfile,
slotProfile
.getPreferredAllocations(),
physicalSlotRequest
.willSlotBeOccupiedIndefinitely()));
return slotFuture.thenApply(
physicalSlot ->
new PhysicalSlotRequest.Result(
slotRequestId, physicalSlot));
}));
}然后又经历一系列复杂的调用
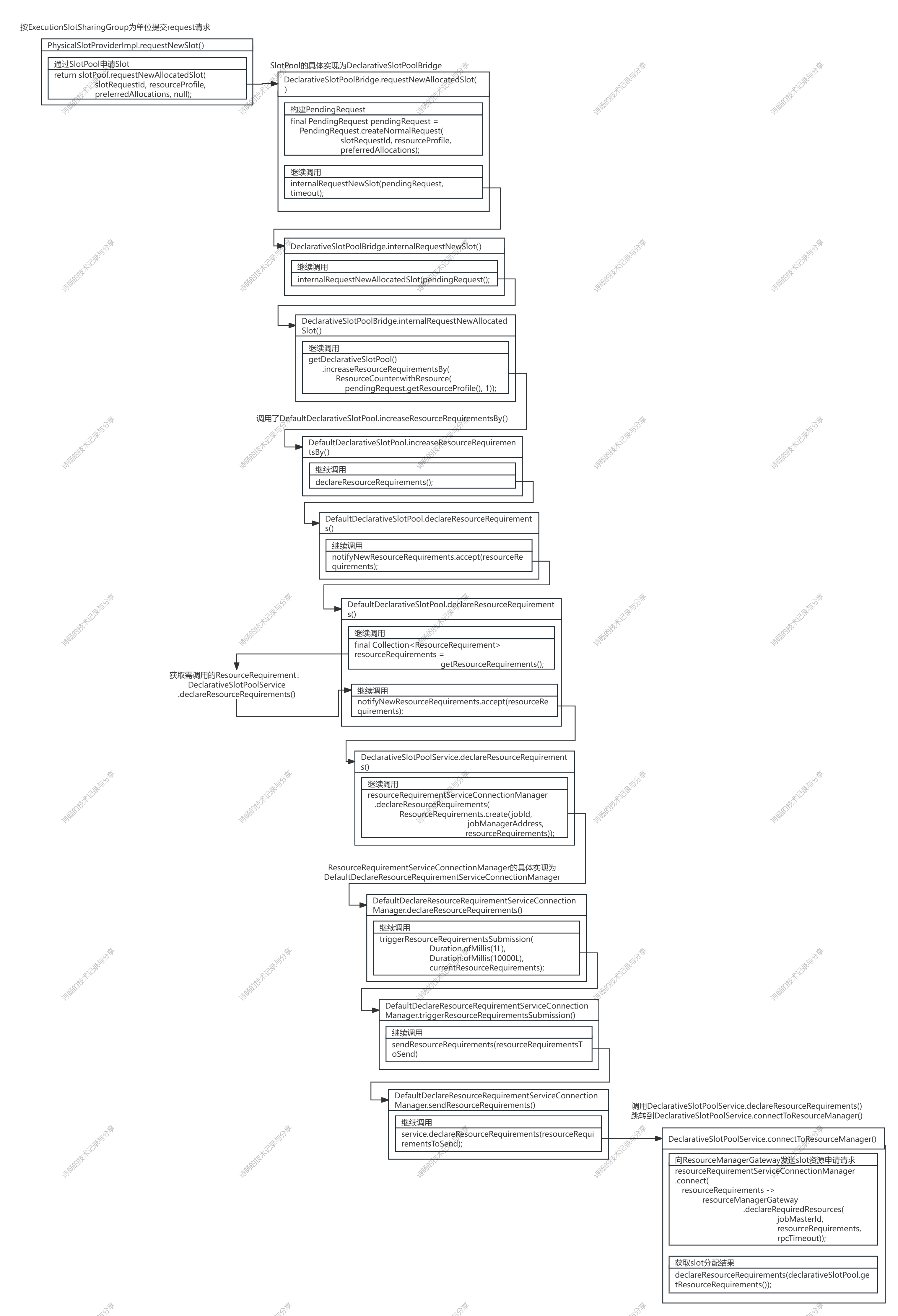
最终调用到DeclarativeSlotPoolService的connectToResourceManager()方法,通过ResourceManagerGateway向Flink的ResourceManager发送slot资源申请请求。
DeclarativeSlotPoolService.connectToResourceManager()方法源码:
java
public void connectToResourceManager(ResourceManagerGateway resourceManagerGateway) {
assertHasBeenStarted();
//向ResourceManagerGateway发送slot资源申请请求
resourceRequirementServiceConnectionManager.connect(
resourceRequirements ->
resourceManagerGateway.declareRequiredResources(
jobMasterId, resourceRequirements, rpcTimeout));
//获取slot分配结果
declareResourceRequirements(declarativeSlotPool.getResourceRequirements());
}4.结语
至此,调度从JobMaster来到了Flink的Resource Manager,进行Resource Manager层面的资源调度,Resource Manager调度的源码解析见《Flink-1.19.0源码详解11-Flink ResourceManager资源调度》。