目录
-
-
- [7.1 类的引入](#7.1 类的引入)
- [7.2 `struct` VS `class`](#7.2
structVSclass) - [7.3 设计类](#7.3 设计类)
-
- [7.3.1 构造函数](#7.3.1 构造函数)
- [7.3.2 私有成员变量/函数](#7.3.2 私有成员变量/函数)
- [7.3.3 公有成员函数(供用户使用的接口)](#7.3.3 公有成员函数(供用户使用的接口))
- [7.3.4 析构函数](#7.3.4 析构函数)
- [7.3.5 整体例子](#7.3.5 整体例子)
- [7.3.6 类的存储&函数的存储](#7.3.6 类的存储&函数的存储)
- [7.4 类的其他性质](#7.4 类的其他性质)
-
7.1 类的引入
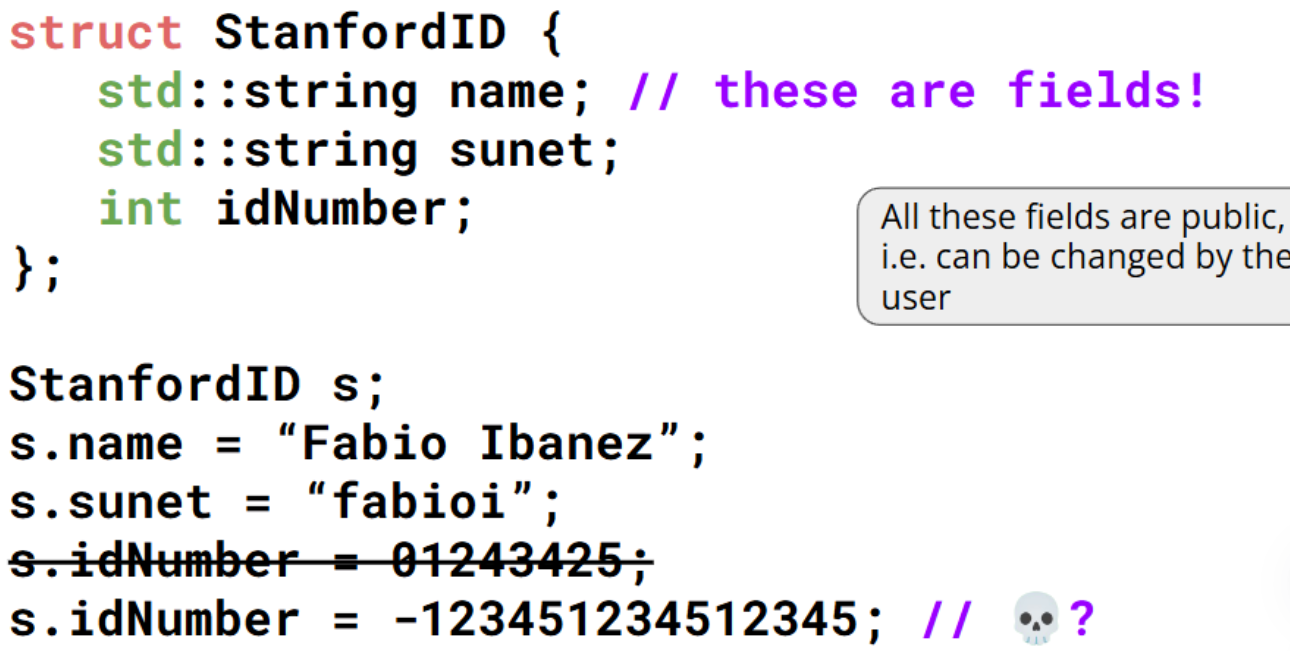
为什么需要类?
- C 语言没有对象
- 无法封装数据以及对这些数据进行操作的函数
- 不具备实现面向对象编程(OOP)设计模式的能力
类将对象的数据和方法捆绑在一起!
什么是OOP?
- 面向对象编程(Object-oriented Programming,简称 OOP)以对象为核心。
- 侧重于类的设计与实现!
- 类(Classes)是用户自定义的类型,可被声明为(实例化)对象!
容器(Containers)是标准模板库(STL)中定义的类!
7.2 struct VS class
类(class)包含:
- 一系列不同类型的对象
- 一组用于操作这些对象的函数
- 一组对这些对象和函数的访问权限限制;
而结构体(struct)是不设访问权限限制的类。
使用结构体(structs)时,不存在直接的访问控制(机制)。


| 头文件(.h) | 源文件(.cpp) | |
|---|---|---|
| 用途(Purpose) | 定义接口 | 实现类的函数 |
| 包含内容(Contains) | 函数原型、类声明、类型定义、宏定义、常量 | 函数实现、可执行代码 |
| 访问与编译(Access) | 供多个源文件共享使用 | 会被编译为目标文件(object file) |
| 示例(Example) | void someFunction (); | void someFunction () {...}; |
7.3 设计类
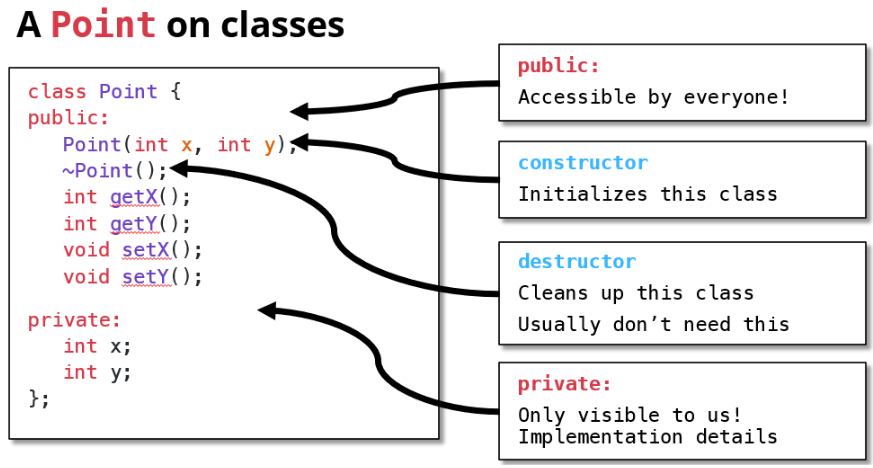
7.3.1 构造函数
构造函数初始化新创建对象的状态。
构造函数声明(.h文件)
cpp
class StanfordID {
private:
std::string name;
std::string sunet;
int idNumber;
public:
// constructor for our StudentID
// 构造函数的函数名必须与所属类的类名完全一致,且无需指定返回值类型(连void都不能写)。
StanfordID(std::string name, std::string sunet, int idNumber);
// method to get name, sunet, and idNumber, respectively
std::string getName();
std::string getSunet();
int getID();
}带参数的构造函数定义(.cpp文件)
cpp
#include "StanfordID.h"
#include <string>
// 要记住命名空间(namespace),比如 std::(标准命名空间)。
// 在我们的 .cpp 文件中,定义成员函数时,需要将我们的类作为命名空间来使用(即通过类限定成员函数的作用域)。
StanfordID::StanfordID(std::string name, std::string sunet, int idNumber) {
name = name;
sunet = sunet;
// 现在,我们还可以对用于初始化或修改成员变量的值强制执行校验(或 "检查")!
if (idNumber > 0) idNumber = idNumber;
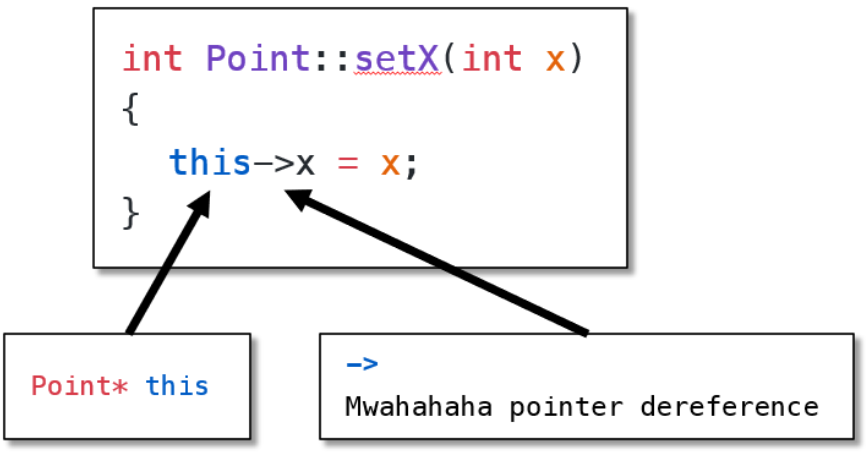
}this关键字(.cpp文件)
this是指向当前类的指针。
cpp
#include "StanfordID.h"
#include <string>
StanfordID::StanfordID(std::string name, std::string sunet, int idNumber) {
// 使用 this 关键字来明确区分你所指代的是哪个 "name"。
this->name = name;
this->state = state;
this->age = age;
}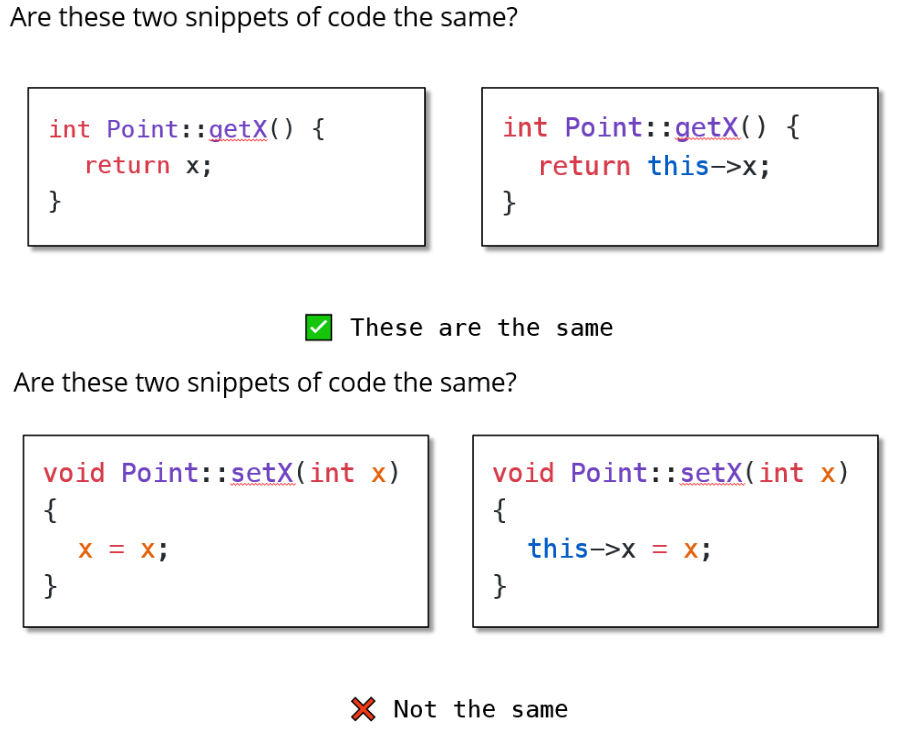
this->x
this在幕后作为参数传递给类函数
统一初始化构造函数定义(.cpp文件)
cpp
#include "StanfordID.h"
#include <string>
// list initialization constructor
// 这是统一初始化语法,不过当前这种(方式)虽与之类似,但并不完全相同!
StanfordID::StanfordID(std::string name, std::string sunet, int idNumber):
name{name}, sunet{sunet}, idNumber{idNumber} {};函数重载------参数可有可无(.cpp文件)
默认构造函数定义与带参数构造函数定义
cpp
#include "StanfordID.h"
#include <string>
// default constructor
// 如果我们调用无参数的构造函数,就可以设置默认值!
StanfordID::StanfordID() {
name = "John Appleseed";
sunet = "jappleseed";
idNumber = 00000001;
}
// parameterized constructor
// 编译器会根据输入的参数来判断我们想要使用哪一个(函数 / 构造函数)!
StanfordID::StanfordID(std::string name, std::string sunet, int idNumber) {
this->name = name;
this->state = state;
this->age = age;
}7.3.2 私有成员变量/函数
在.h文件中体现
7.3.3 公有成员函数(供用户使用的接口)
cpp
#include "StanfordID.h"
#include <string>
std::string StanfordID::getName() {
return this->name;
}
std::string StanfordID::getSunet() {
return this->sunet;
}
int StanfordID::getID() {
return this->idNumber;
}设值函数返回类型为空
cpp
#include "StanfordID.h"
#include <string>
void StanfordID::setName(std::string name) {
this->name = name;
}
void StanfordID::setSunet(std::string sunet) {
this->sunet = sunet;
}
void StanfordID::setID(int idNumber) {
if (idNumber >= 0){
this->idNumber = idNumber;
}7.3.4 析构函数
cpp
#include "StanfordID.h" // 包含StanfordID类的头文件
#include <string> // 包含string类的标准头文件
// 实现StanfordID类的析构函数
StanfordID::~StanfordID() {
// 在此处释放/归还所有(动态分配的)数据
delete[] my_array; // 示例:释放动态数组my_array的内存}
// 析构函数无需显式调用,当对象超出作用域(如离开所在代码块、程序结束)时,会被自动调用
}7.3.5 整体例子
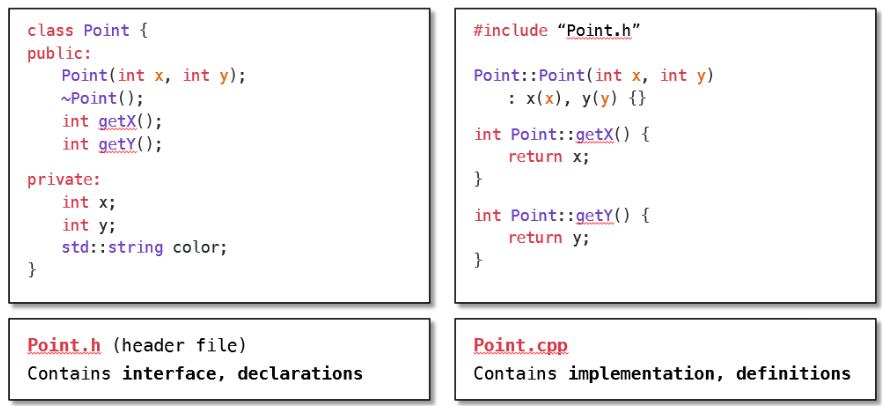
7.3.6 类的存储&函数的存储
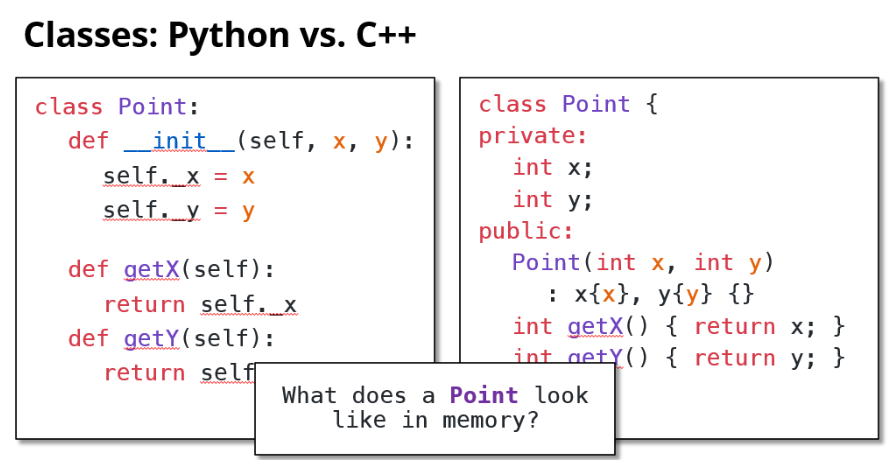
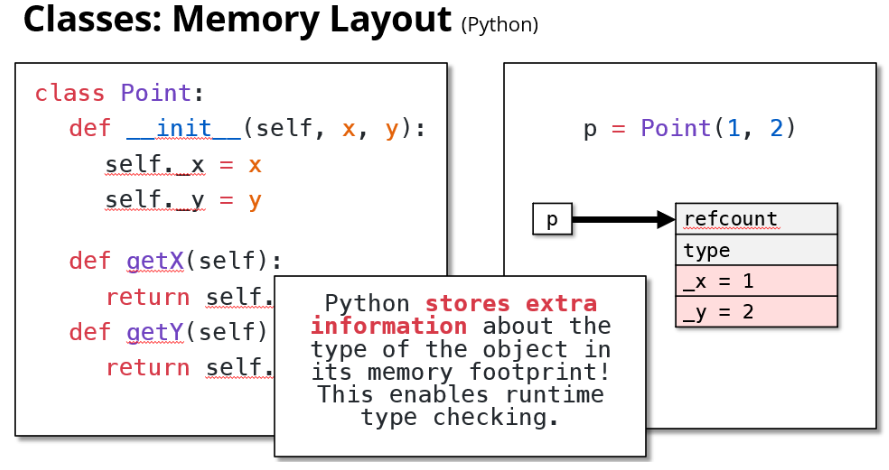
Python会存关于对象类型的额外信息,来确保运行时类型检查。
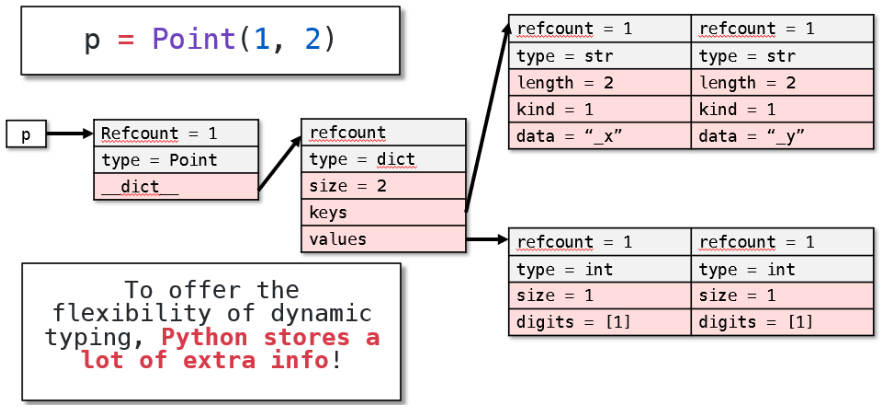
但C++不会,C++只在对象中存数据。类型检查全部交给编译器。
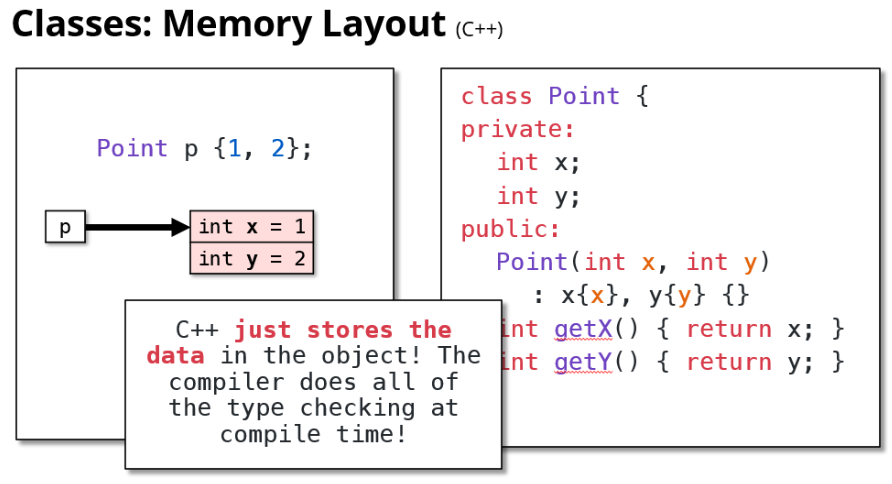
函数并非存储在对象本身中,而是单独存储的。
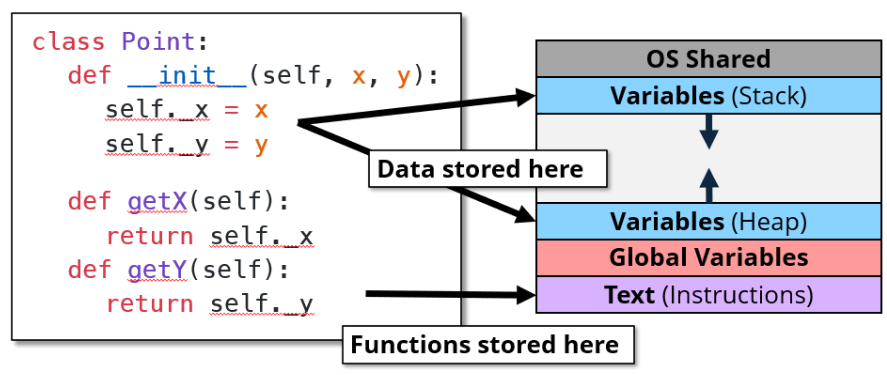
7.4 类的其他性质
类别名
用using实现
cpp
class StanfordID {
private:
// An example of type aliasing
using String = std::string;
String name; String sunet;
int idNumber;
public:
// constructor for our student
StanfordID(String name, String sunet, int idNumber);
// method to get name, state, and age, respectively
String getName();
String getSunet();
int getID();
}