一、对称二叉树
1、题目
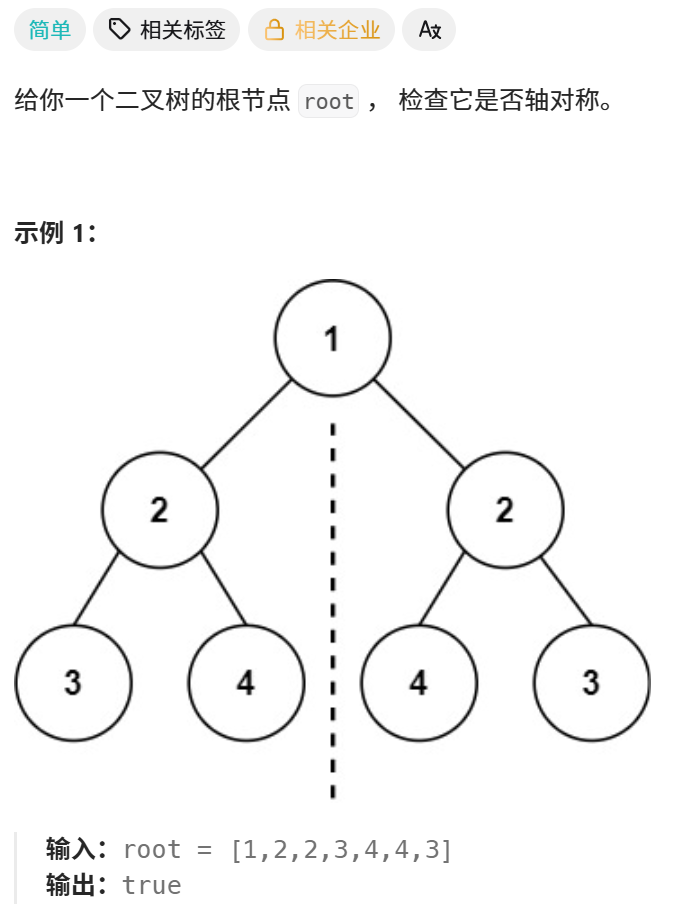
2、分析
递归:
子问题:判断左右根植是否相等、判断左子树的左子树与右子树的右子树书否对称、判断左子树的右子树与右子树的左子树书否对称。
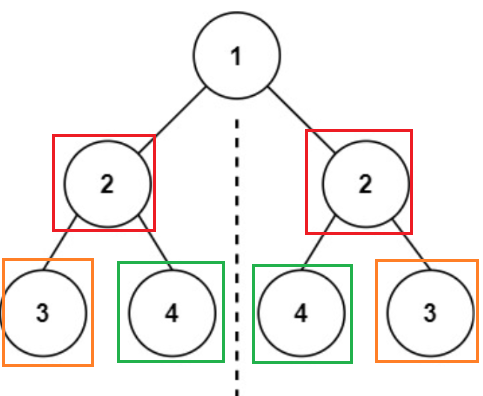
结束条件:左右子树为空,true、只有一个为空,false、左右根不相等,false。
时间复杂度:O(n),空间复杂度:O(n),最高树。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) { // 空树,对称
return true;
}
return isSymmetricChild(root.left, root.right);
}
public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode leftRoot, TreeNode rightRoot) {
// 左根、右根都为空,对称
if(leftRoot == null && rightRoot == null) {
return true;
}
// 左、右根其中一个不为空,另一个为空,不对称
if(leftRoot == null || rightRoot == null) {
return false;
}
// 左右根不为空,但值不等,不对称
if(leftRoot.val != rightRoot.val) {
return false;
}
// 左根的左子树、右根的右子树对称,且左根的右子树、右根的左子树对称,才对称
return isSymmetricChild(leftRoot.left, rightRoot.right) && isSymmetricChild(leftRoot.right, rightRoot.left);
}
}二、二叉树的层序遍历
1、题目
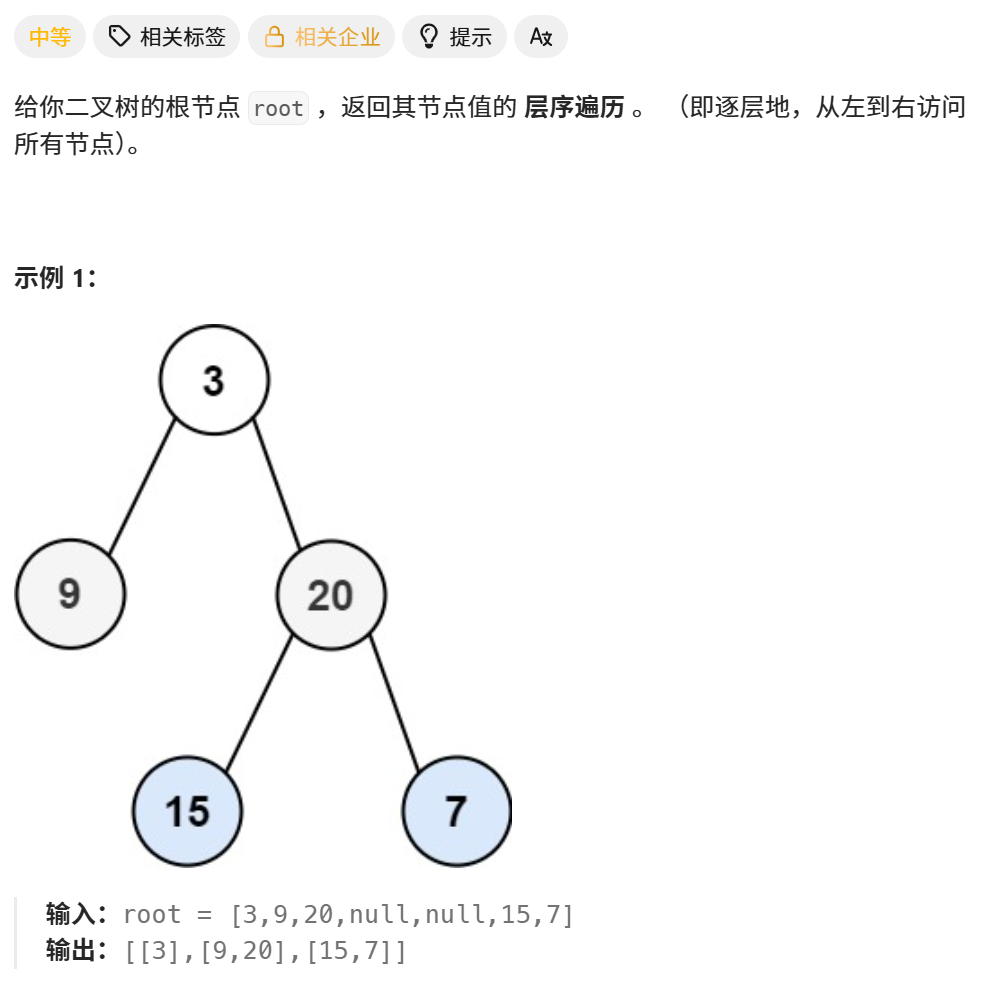
2、分析
使用队列,初始根节点入队。后续每层循环(队列为空停止):取当前层 size,出队队首、访问、入队左右孩子,size 减为 0,进入下一个循环。
时间复杂度:O(n)。
空间复杂度:额外队列 O(n),队列元素不超过n。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> list = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) { // 空树
return list;
}
// 初始,根节点入队
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); // 下一层队列
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()) { // 直到下一层为空
List<Integer> curLevel = new ArrayList<>(); // 当前层
int size = queue.size(); // 当前层大小
while(size-- != 0) { // 遍历当前层
TreeNode node = queue.poll(); // 弹出一个结点
curLevel.add(node.val); // 包装到当前层中
if(node.left != null) { // 左孩子放入下一层
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if(node.right != null) { // 右孩子放入下一层
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
list.add(curLevel);
}
return list;
}
}三、从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
1、题目
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
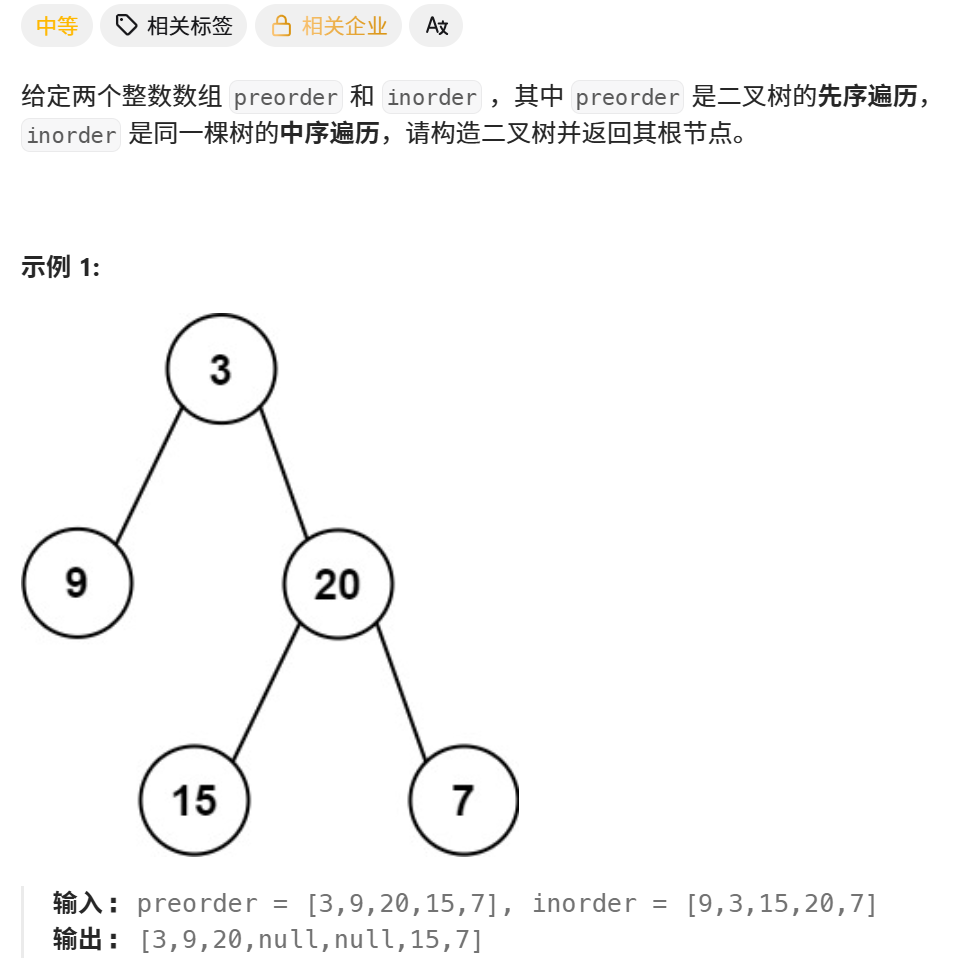

2、分析
(1)子问题:preorder 第一个是根节点。从 inorder 中找到根节点位置 rootIndex,划分出左右子树节点个数大小。根据这个大小,在 preorder 中划分出左右子树范围。构建根节点,构建左、右子树,返回整棵树。

(2)时间复杂度:构造 inorder 每个节点下标的哈希表 O(n),查找每个子树中根节点在 inorder 中的下标 O(1),构建树的每个节点 O(n)。共 O(n)。
空间复杂度:哈希表O(n),递归深度是树高,最高 O(n),共 O(n)。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
int n = preorder.length;
// 构造 inorder 中每个元素的下标的哈希表
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) map.put(inorder[i], i);
// 构造二叉树,需要每棵子树在 preorder 中的范围,每棵子树在 inorder 中左边界
return buildTree(preorder, inorder, 0, n-1, 0);
}
private TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder, int preStart, int preEnd, int inStart) {
if (preStart > preEnd) return null; // 子树为空
int rootVal = preorder[preStart]; // 前序序列的第一个,是根节点
int rootIndex = map.get(rootVal); // 在中序序列中,找到根节点的下标
int leftTreeNum = rootIndex - inStart; // 计算左子树的节点个数
// 构建左右子树
TreeNode leftRoot = buildTree(preorder, inorder, preStart+1, preStart+leftTreeNum, inStart);
TreeNode rightRoot = buildTree(preorder, inorder, preStart+leftTreeNum+1, preEnd, rootIndex+1);
return new TreeNode(rootVal, leftRoot, rightRoot); // 构造树
}
}四、二叉树的最近公共祖先
1、题目
236. 二叉树的最近公共祖先 - 力扣(LeetCode)
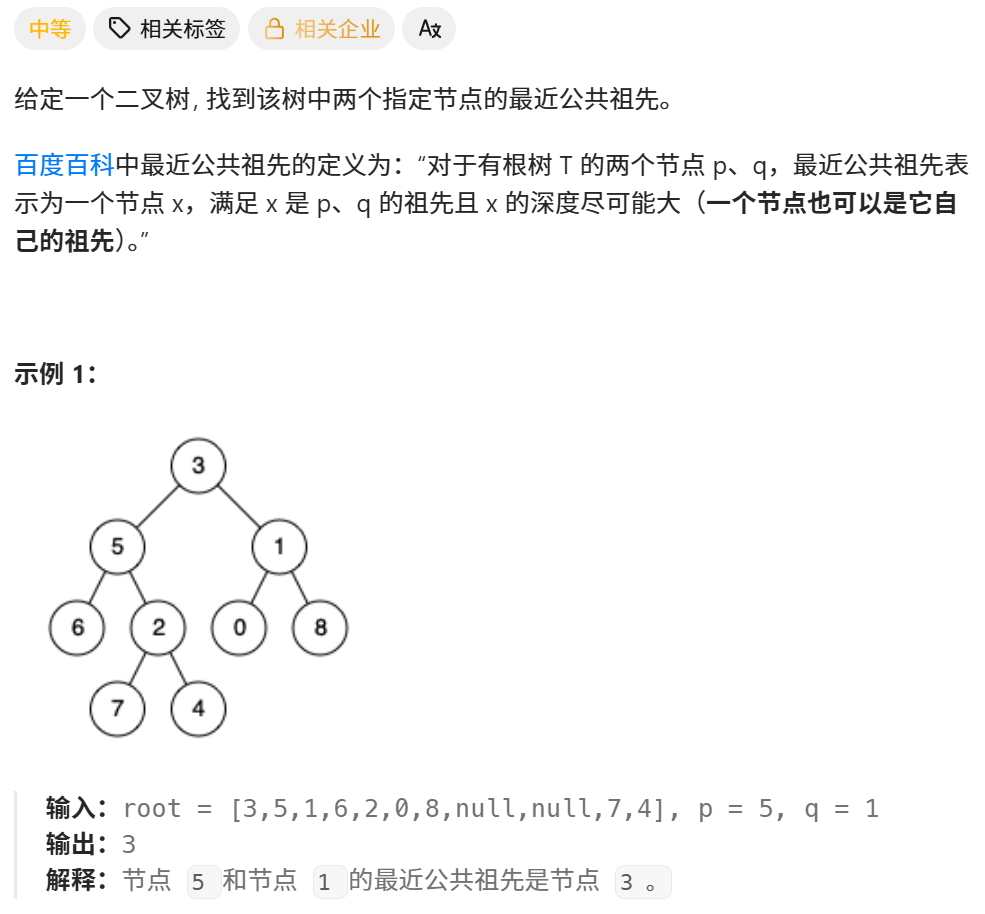
2、分析
x 的深度尽可能大,就表示最近的公共祖先。
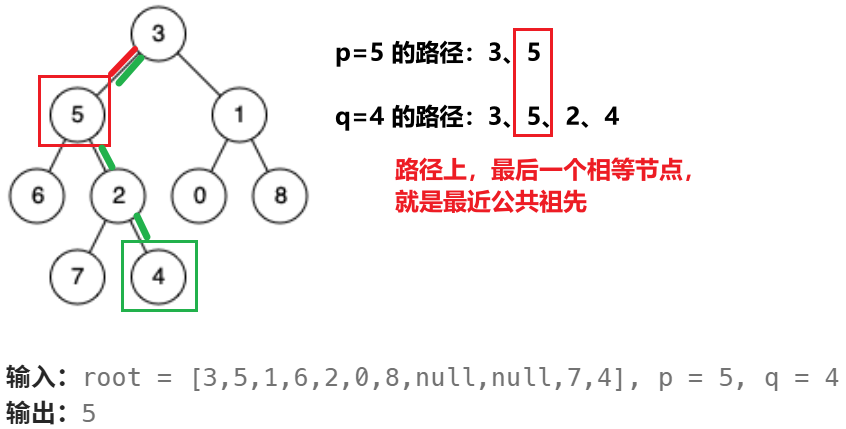
先深度遍历,找出 root 到 p、q 的路径。再对比两条路径,找出最后相等的节点。
可能深度遍历一条路径时,没有中找全 p、q,就需要回退到父节点,遍历另一个分支,path 需要弹出节点。(不弹出,path 包含的就是所有节点的遍历)
时间复杂度:深度遍历O(n),遍历路径比较,树高,最高 O(n)。共 O(n)。
空间复杂度:保存两条路径,深度遍历递归,都是树高大小,O(n)。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private Stack<Integer> pathP = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> pathQ = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Integer> path = new Stack<>();
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
// 深度遍历树,找到 p、q 的路径
dfs(root, p, q);
// 路径长的,弹出多余的长度
int size = Math.abs(pathP.size()-pathQ.size());
Stack<Integer> stack = pathP.size() > pathQ.size() ? pathP : pathQ;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) stack.pop();
// 找到第一个相等的节点,就是最近公共祖先
while (pathP.peek() != pathQ.peek()) {
pathP.pop();
pathQ.pop();
}
return new TreeNode(pathP.peek());
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if (root == null) return; // 树为空,停止遍历
path.push(root.val); // 节点入栈
if (root.val == p.val) pathP = (Stack<Integer>)path.clone(); // 找到 p 的路径
if (root.val == q.val) pathQ = (Stack<Integer>)path.clone(); // 找到 q 的路径
if (!pathP.isEmpty() && !pathQ.isEmpty()) return; // 找到所有路径,结束遍历
// 遍历左右子树
dfs(root.left, p, q);
dfs(root.right, p, q);
path.pop(); // 该 root 子树没有找全 p、q,回溯,遍历其它分支的子树
}
}五、二叉树的直径
1、题目
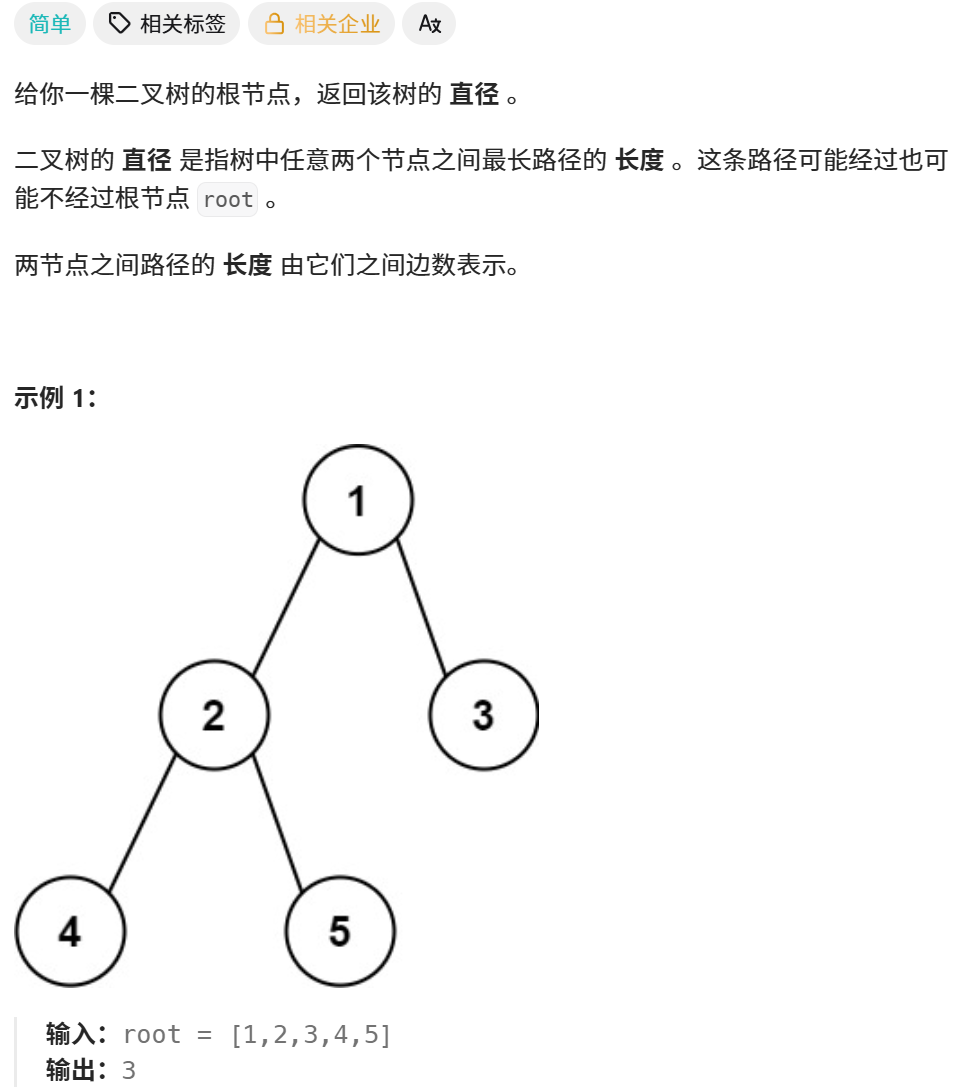
2、分析
(1)两个节点之间的最长直径,就是经过最高点的直径。
(2)求以每个节点为最高点的直径=左子树高度+右子树高度,结果是其中的最大直径。
(3)递归,深度优先搜索,求子树 root 高=max(左子树高度,右子树高度)+1。结束条件:子树为空,返回高度 0。
(4)时间复杂度:遍历每个节点,O(n)。
(5)空间复杂度:递归深度,树高,最高为 n,O(n)。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int maxLen = 0;
public int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
dfp(root); // 计算 root 子树的高度
return maxLen; // 返回最大高度
}
private int dfp(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0; // 子树为空,高度为 0
// 求左、右子树高度
int leftHeight = dfp(root.left);
int rightHeight = dfp(root.right);
maxLen = Math.max(maxLen, leftHeight+rightHeight); // 以 root 为高点的,最大子树路径长度
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1; // 返回子树高
}
}六、将有序数组转为二叉搜索树
1、题目
108. 将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树 - 力扣(LeetCode)
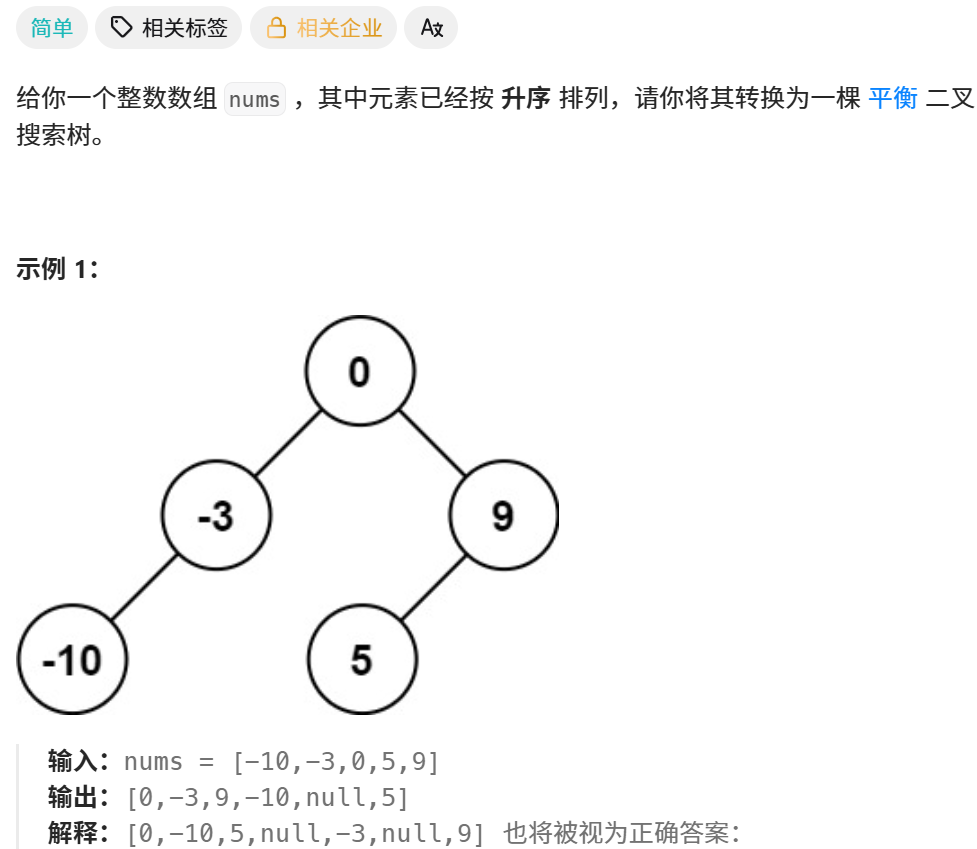
2、分析
(1)升序序列,本身就是一棵中序遍历的二叉搜索树。我们只需要找出每棵子树的根节点,就能确定其左、右子树。
(2)平衡二叉树指,左右子树高度差不超过 1,那么左右子树节点数应该尽量平衡。子树根节点取升序子序列的中部 rootIndex = (left+right)/2。
(3)求出升序子序列根节点,递归构造左右子树。
(4)时间复杂度:遍历每个节点构造根节点,O(n)。
(5)空间复杂度:递归深度,平衡树高,O(logn)。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
// 1.升序的数组,本身就是中序遍历的二叉搜索树,我们只需要确定到根节点,然后递归构造左、右子树
// 2.根节点要满足:左、右子树的结点数尽量相等。(平衡二叉树,左右子树高度差不超过1)
// 构造平衡二叉搜索树
return build(nums, 0, nums.length-1);
}
private TreeNode build(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) return null; // 树为空
int root = left+(right-left)/2; // 计算根节点位置
// 构建左右子树
TreeNode leftTree = build(nums, left, root-1);
TreeNode rightTree = build(nums, root+1, right);
return new TreeNode(nums[root], leftTree, rightTree); // 返回平衡二叉搜索树
}
}七、验证二叉搜索树
1、题目
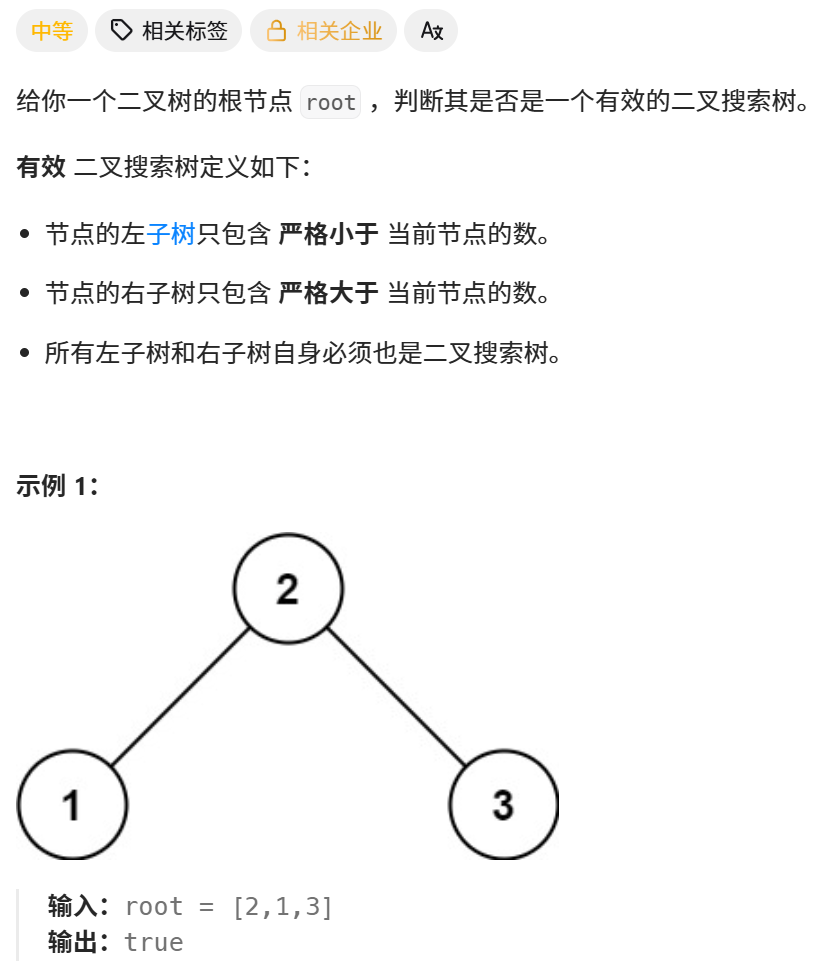
2、分析
(1)二叉搜索树,中序遍历的结果是严格递增数组。
(2)中序遍历二叉搜索树,比较上一个节点 pre 和当前节点 cur,pre < cur,满足要求,pre >= cur,不满足要求。左子树、根节点、右子树,任意一个不满足,这棵子树就不满足。
(3)时间复杂度:遍历每个结点,O(n)。
(4)空间复杂度:递归深度,树高,最高为 O(n)。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private TreeNode pre;
public boolean isValidBST(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true; // 空树,特殊的二叉搜索树
if (!isValidBST(root.left)) return false; // 遍历左子树,不是则返回 false
if (pre != null && pre.val >= root.val) return false; // pre 和 cur,需要满足递增要求
pre = root;
if(!isValidBST(root.right)) return false; // 遍历右子树
return true; // 该子树是二叉搜索树
}
}八、二叉搜索树中第 k 小的元素
1、题目
230. 二叉搜索树中第 K 小的元素 - 力扣(LeetCode)
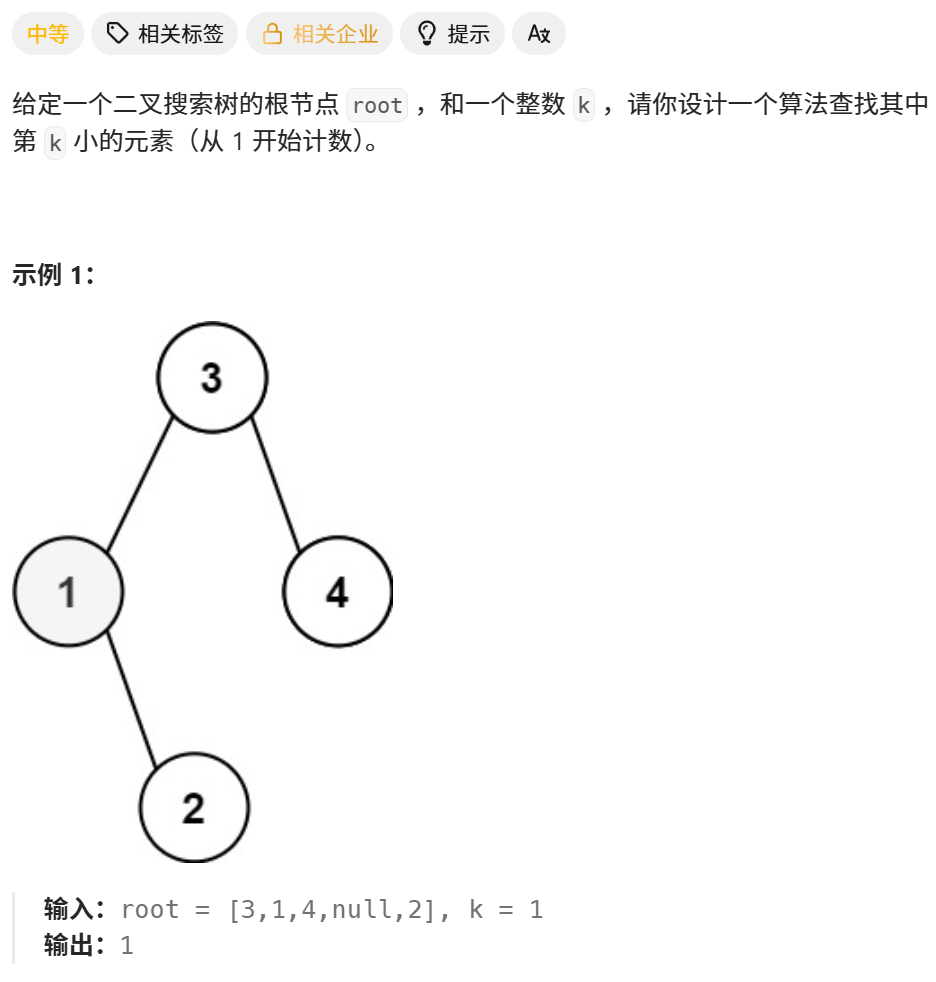
2、分析
(1)二叉搜索树中序遍历,是递增序列。
(2)中序遍历二叉搜索树,找到遍历的第 k 个元素。
(3)时间复杂度:遍历, O(n)。
(4)空间复杂度:递归栈深度 O(n)。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int count;
public int kthSmallest(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null) return -1; // 空树,没有第 k 小,返回-1
int leftRet = kthSmallest(root.left, k); // 遍历左子树
if (leftRet != -1) return leftRet; // 左子树找到
if (++count == k) return root.val; // 根节点找到第 k 小
int rightRet = kthSmallest(root.right, k); // 遍历右子树
if (rightRet != -1) return rightRet; // 右子树找到
return -1; // 当前子树没找到
}
}九、二叉树的右视图
1、题目
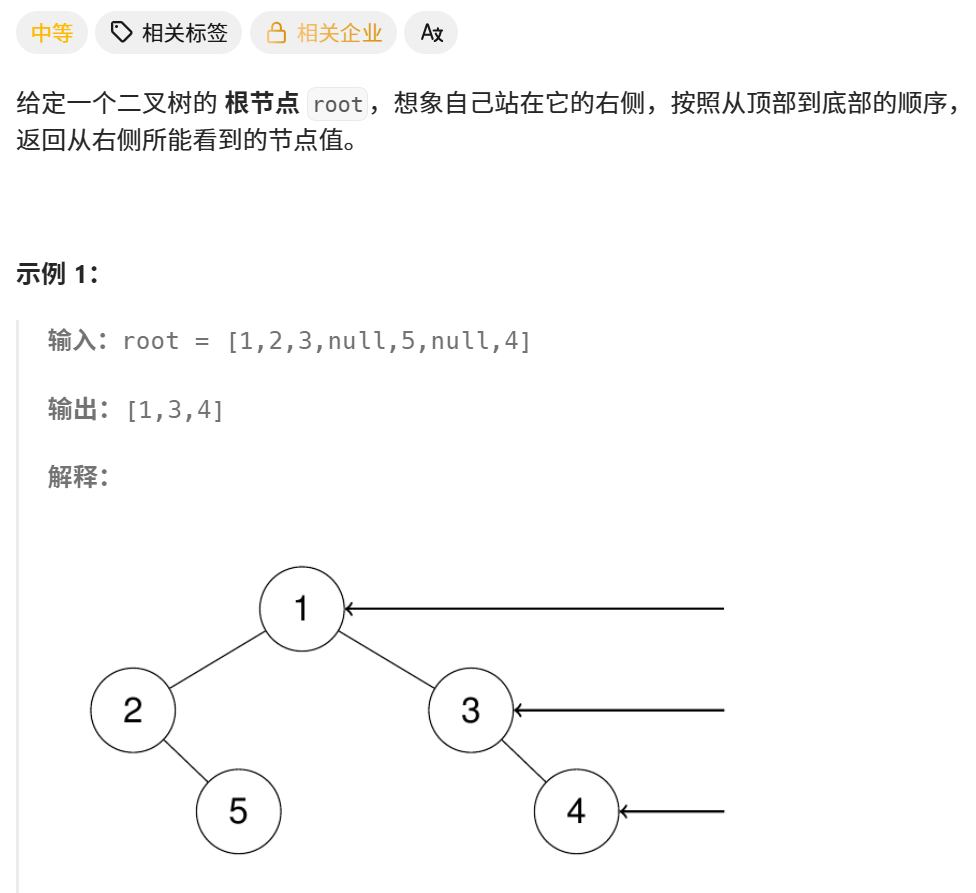
2、分析
(1)层序遍历,将每层的最后一个节点放入结果列表。
(2)时间复杂度 :层序遍历,O(n),空间复杂度 :队列长度,O(n)。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> rightSideView(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ret = new ArrayList<>();
if (root == null) return ret; // 空树返回空结果
Deque<TreeNode> tmp = new LinkedList<>();
tmp.add(root);
int size;
TreeNode node;
while (!tmp.isEmpty()) {
size = tmp.size(); // 每层的长度
while(size-- != 0) {
node = tmp.poll();
if (node.left != null) tmp.add(node.left);
if (node.right != null) tmp.add(node.right);
if (size == 0) ret.add(node.val); // 把每层的最后一个节点放入列表
}
}
return ret;
}
}十、二叉树展开为链表
1、题目
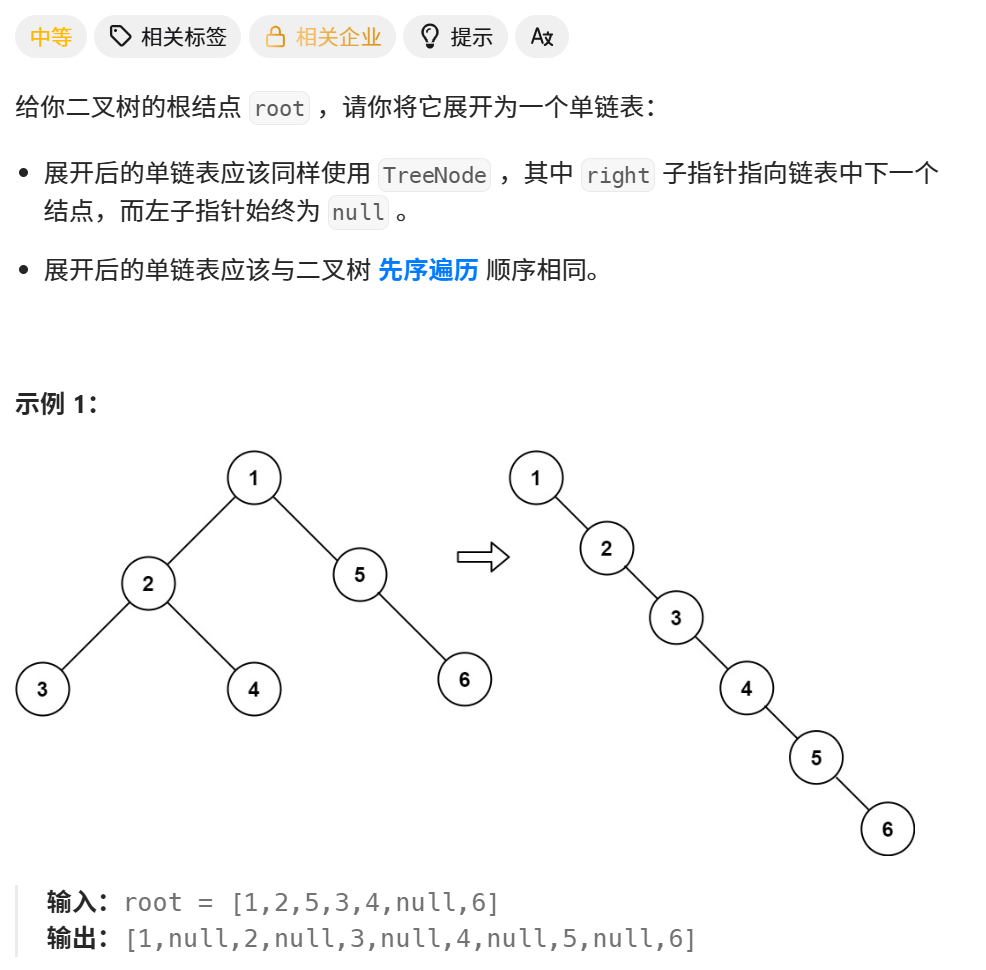
2、分析
法一:
(1)递归,先序遍历,把遍历的节点放入列表。再遍历列表,构建新的root。
(2)时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(n)。
法二:
(1)如图:
原树:
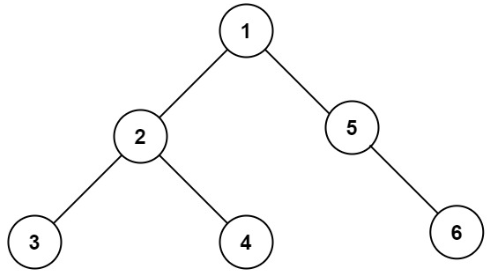
展开的左子树、右子树:
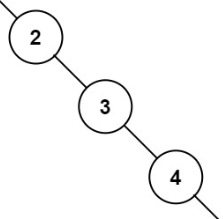
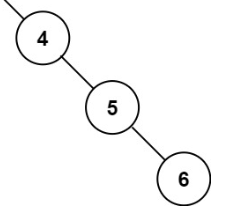
展开的左子树接在 root.right,展开的右子树接在 root.right 的最后一个节点的 right。
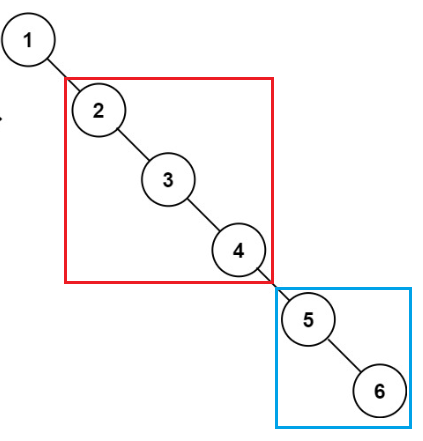
递归构建。
(2)时间复杂度 O(n),空间复杂度 O(1)。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void flatten(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return; // 树为空,不需要展开
flatten(root.left); // 展开左子树
flatten(root.right); // 展开右子树
TreeNode rightTree = root.right;
root.right = root.left; // 展开后的左子树,作为根节点的新右子树
root.left = null; // 根节点的新左子树为空
TreeNode cur = root;
while(cur.right != null) cur = cur.right; // 找到右子树的最后一个节点
cur.right = rightTree; // 把原右子树接在后面
}
}十一、路径总和Ⅲ
1、题目


2、分析
法一:暴力枚举。
(1)先层序遍历每个节点,再对每个节点为根的子树进行深度优先遍历,计数总和为 targetSum 的路径。
(2)时间复杂度:O(N^2)。空间复杂度:递归深度,树高,O(N)。
法二:前缀和。
(1)深度优先搜索,把遍历过的每个节点到 root 的路径和存在哈希map中,key-前缀和,value-前缀和的个数。
(2)计数当前node的前缀和-targetSum的个数。比如:当前前缀和(10+5+3)-targetSum(8)=前缀和(10),就能统计路径和为 targetSum 的条数。
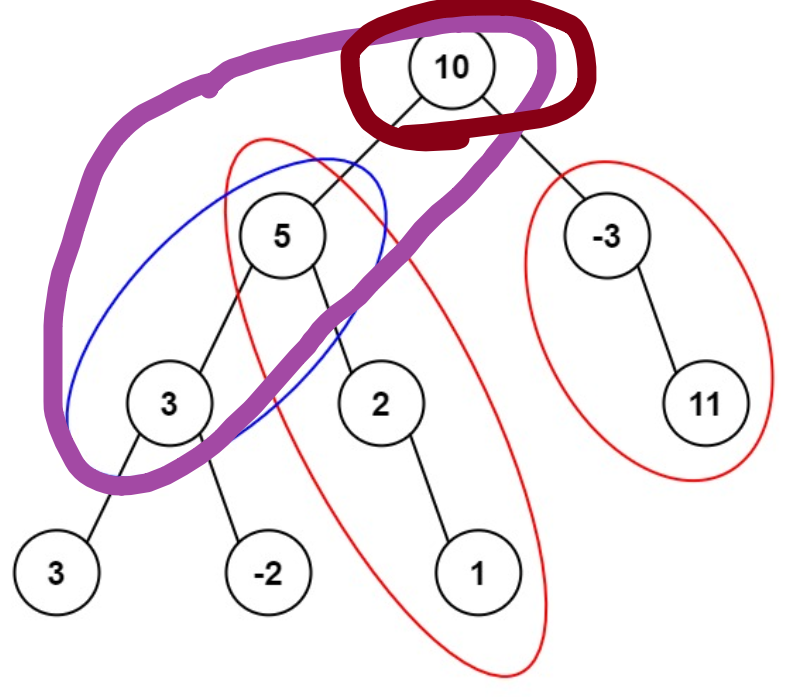
(3)时间复杂度:深搜一次O(n);空间复杂度:递归深度+map大小,O(n)。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int count;
private long tmp; // root->node的路径和
private Map<Long, Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // root->node的路径上,前缀和为key的路径有value条
public int pathSum(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
map.put(0L, 1); // 有可能 root->node 刚好是 targetSum,那么tmp-targetSum为0,计数1
dfs(root, targetSum);
return count;
}
private void dfs(TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
if (root == null) return; // 树空,停止深搜
tmp += root.val; // 根节点->子树根root的路径和
// 不能先把当前前缀和放入map,再计数。考虑这种情况:树只有一个节点1,targetSum=0,错误计数为1
count += map.getOrDefault(tmp-targetSum, 0); // 先前缀和计数
map.put(tmp, map.getOrDefault(tmp, 0)+1); // 再把当前的前缀和放入map
dfs(root.left, targetSum);
dfs(root.right, targetSum);
map.put(tmp, map.get(tmp)-1); // 回溯,把当前前缀和去掉,返回父节点
tmp -= root.val; // 回溯
}
}十二、二叉树中的最大路径和
1、题目
124. 二叉树中的最大路径和 - 力扣(LeetCode)
2、分析
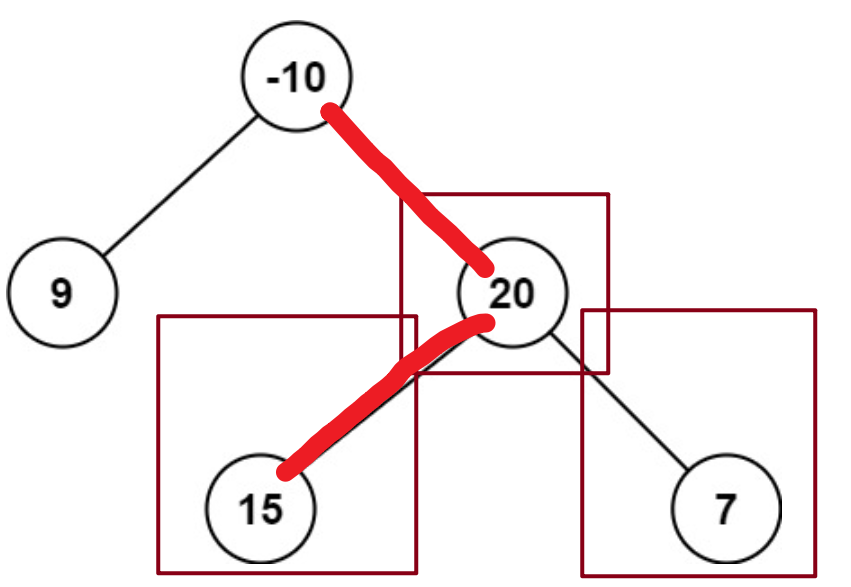
(1)求左、右子树的最大路径和(要大于0,否则加上反而变小了),与当前子树根节点相加,求得当前子树的最大路径和(至少包含一个节点,所以不管根节点是不是负数,都要包含)。
(2)返回给父节点(图中为-10)的最大路径和,只能走左子树、或者右子树,不然20会被重复走,因此返回20+较大子树路径。
(3)时间复杂度:遍历,O(N)。空间复杂度:递归深度,树高,O(N)。
3、代码
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
private int ret = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
public int maxPathSum(TreeNode root) {
dfs(root);
return ret;
}
private int dfs(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0; // 空树,最大路径和为0
int maxL = Math.max(dfs(root.left), 0); // 左子树中的做大路径和
int maxR = Math.max(dfs(root.right), 0); // 右子树中的最大路径和
ret = Math.max(ret, root.val+maxL+maxR); // 当前的最大路径和,与当前子树的最大路径和,比较
return root.val+Math.max(maxL, maxR); // root的父节点,左子树、右子树只能选一条路走,否则root会走两次
}
}