路径规划算法代码,全是自己整理的,MATLAB语言,包括A星,跳点jps算法,改进的A星,改进的跳点JPS算法。 还有dwa动态窗口法,自己设置未知和移动障碍物。 多种对比,单机器人路径规划。
最近在研究单机器人路径规划算法,整理了一系列超有趣的内容,今天就来跟大家分享分享。咱们会涉及 A 星、跳点 JPS 算法,还有它们的改进版本,另外动态窗口法(DWA)也会详细讲讲,并且还能自己设置未知和移动障碍物哦,最后会对多种算法进行对比分析。所有代码都是用 MATLAB 语言实现的,纯手工打造~
A 星算法
A 星算法算是路径规划里的经典了。它综合考虑了起点到当前点的代价 g 和当前点到终点的预估代价 h,通过 f = g + h 来选择最佳节点进行扩展。
matlab
% A星算法核心代码片段
function [path, cost] = a_star(start, goal, occupancy_grid)
% 初始化参数
open_list = [];
closed_list = [];
came_from = [];
g_score = Inf(size(occupancy_grid));
f_score = Inf(size(occupancy_grid));
g_score(start(1), start(2)) = 0;
f_score(start(1), start(2)) = heuristic(start, goal);
open_list = [open_list; start];
while ~isempty(open_list)
% 找到 f_score 最小的节点
[~, min_index] = min(f_score(sub2ind(size(occupancy_grid), open_list(:, 1), open_list(:, 2))));
current = open_list(min_index, :);
open_list(min_index, :) = [];
closed_list = [closed_list; current];
if all(current == goal)
% 找到路径,回溯
path = reconstruct_path(came_from, current);
cost = g_score(goal(1), goal(2));
return;
end
% 扩展邻居节点
neighbors = get_neighbors(current, occupancy_grid);
for i = 1:size(neighbors, 1)
neighbor = neighbors(i, :);
tentative_g_score = g_score(current(1), current(2)) + 1; % 这里假设移动代价为1
if ismember(neighbor, closed_list, 'rows') && tentative_g_score >= g_score(neighbor(1), neighbor(2))
continue;
end
if ~ismember(neighbor, open_list, 'rows') || tentative_g_score < g_score(neighbor(1), neighbor(2))
came_from(neighbor(1), neighbor(2), :) = current;
g_score(neighbor(1), neighbor(2)) = tentative_g_score;
f_score(neighbor(1), neighbor(2)) = tentative_g_score + heuristic(neighbor, goal);
if ~ismember(neighbor, open_list, 'rows')
open_list = [open_list; neighbor];
end
end
end
end
path = [];
cost = Inf;
end
function h = heuristic(point, goal)
h = abs(point(1) - goal(1)) + abs(point(2) - goal(2)); % 曼哈顿距离作为启发函数
end
function neighbors = get_neighbors(point, occupancy_grid)
% 获取邻居节点,这里只考虑四邻域
x = point(1);
y = point(2);
neighbors = [];
if x > 1 && occupancy_grid(x - 1, y) == 0
neighbors = [neighbors; x - 1, y];
end
if x < size(occupancy_grid, 1) && occupancy_grid(x + 1, y) == 0
neighbors = [neighbors; x + 1, y];
end
if y > 1 && occupancy_grid(x, y - 1) == 0
neighbors = [neighbors; x, y - 1];
end
if y < size(occupancy_grid, 2) && occupancy_grid(x, y + 1) == 0
neighbors = [neighbors; x, y + 1];
end
end
function path = reconstruct_path(came_from, current)
path = [current];
while any(came_from(current(1), current(2), :) ~= 0)
current = came_from(current(1), current(2), :);
path = [current; path];
end
end这段代码首先初始化了开放列表 openlist*、关闭列表 closed* list 等参数。在主循环中,不断从开放列表中选择 fscore**最小的节点进行扩展,检查是否到达目标点。扩展邻居节点时,计算新的 g score 和 f_score,决定是否更新节点信息。
跳点 JPS 算法
跳点搜索(JPS)算法是对 A 星的优化,它通过减少搜索空间来提高效率。在 JPS 中,会根据特定规则找到一些"跳点",只对跳点进行扩展。
matlab
% JPS算法核心代码片段
function [path, cost] = jps(start, goal, occupancy_grid)
% 初始化参数
open_list = [];
closed_list = [];
came_from = [];
g_score = Inf(size(occupancy_grid));
f_score = Inf(size(occupancy_grid));
g_score(start(1), start(2)) = 0;
f_score(start(1), start(2)) = heuristic(start, goal);
open_list = [open_list; start];
while ~isempty(open_list)
% 找到 f_score 最小的节点
[~, min_index] = min(f_score(sub2ind(size(occupancy_grid), open_list(:, 1), open_list(:, 2))));
current = open_list(min_index, :);
open_list(min_index, :) = [];
closed_list = [closed_list; current];
if all(current == goal)
% 找到路径,回溯
path = reconstruct_path(came_from, current);
cost = g_score(goal(1), goal(2));
return;
end
% 扩展跳点
jump_points = get_jump_points(current, goal, occupancy_grid);
for i = 1:size(jump_points, 1)
jump_point = jump_points(i, :);
tentative_g_score = g_score(current(1), current(2)) + distance(current, jump_point);
if ismember(jump_point, closed_list, 'rows') && tentative_g_score >= g_score(jump_point(1), jump_point(2))
continue;
end
if ~ismember(jump_point, open_list, 'rows') || tentative_g_score < g_score(jump_point(1), jump_point(2))
came_from(jump_point(1), jump_point(2), :) = current;
g_score(jump_point(1), jump_point(2)) = tentative_g_score;
f_score(jump_point(1), jump_point(2)) = tentative_g_score + heuristic(jump_point, goal);
if ~ismember(jump_point, open_list, 'rows')
open_list = [open_list; jump_point];
end
end
end
end
path = [];
cost = Inf;
end
function jump_points = get_jump_points(current, goal, occupancy_grid)
% 获取跳点的函数,这里简化实现,只考虑部分情况
jump_points = [];
% 水平方向
if current(2) < size(occupancy_grid, 2) && occupancy_grid(current(1), current(2) + 1) == 0
jump_point = current;
while jump_point(2) < size(occupancy_grid, 2) && occupancy_grid(jump_point(1), jump_point(2) + 1) == 0
jump_point(2) = jump_point(2) + 1;
if (jump_point(1) > 1 && occupancy_grid(jump_point(1) - 1, jump_point(2)) ~= 0) ||...
(jump_point(1) < size(occupancy_grid, 1) && occupancy_grid(jump_point(1) + 1, jump_point(2)) ~= 0) ||...
all(jump_point == goal)
jump_points = [jump_points; jump_point];
break;
end
end
end
% 其他方向类似处理
end
function d = distance(point1, point2)
d = sqrt((point1(1) - point2(1))^2 + (point1(2) - point2(2))^2);
end与 A 星不同的是,这里通过 getjumppoints 函数来获取跳点,而不是像 A 星那样扩展所有邻居节点。这样大大减少了搜索空间,提高了算法效率。
改进的 A 星和 JPS 算法
改进的 A 星算法可以在启发函数上做文章,比如使用更精确的距离度量,或者结合环境信息动态调整启发函数。改进的 JPS 算法可以进一步优化跳点的判断规则,例如考虑更多的邻居关系来确定跳点。
matlab
% 改进的A星启发函数示例
function h = improved_heuristic(point, goal, occupancy_grid)
% 结合障碍物分布调整启发函数
if occupancy_grid(point(1), point(2)) == 1
h = Inf;
else
dx = abs(point(1) - goal(1));
dy = abs(point(2) - goal(2));
h = sqrt(dx^2 + dy^2); % 欧几里得距离
% 这里可以进一步根据障碍物分布调整 h 的值
end
end这个改进的启发函数,在遇到障碍物时直接将启发值设为无穷大,避免路径经过障碍物,同时采用欧几里得距离作为基本的启发度量,相比于曼哈顿距离更加精确。
DWA 动态窗口法
DWA 主要用于处理动态环境下的路径规划,通过在每个时刻计算机器人的可行速度集合,根据目标函数选择最优速度。
matlab
% DWA算法核心代码片段
function [v, w] = dwa(robot_state, goal, obstacles, params)
% 机器人状态 [x, y, theta]
x = robot_state(1);
y = robot_state(2);
theta = robot_state(3);
% 动态窗口参数
v_min = params.v_min;
v_max = params.v_max;
w_min = params.w_min;
w_max = params.w_max;
dt = params.dt;
T = params.T;
% 生成动态窗口
v_window = linspace(v_min, v_max, params.num_samples);
w_window = linspace(w_min, w_max, params.num_samples);
best_score = -Inf;
best_v = 0;
best_w = 0;
for i = 1:length(v_window)
for j = 1:length(w_window)
v = v_window(i);
w = w_window(j);
predicted_state = predict_state(robot_state, v, w, dt, T);
score = evaluate_score(predicted_state, goal, obstacles);
if score > best_score
best_score = score;
best_v = v;
best_w = w;
end
end
end
v = best_v;
w = best_w;
end
function predicted_state = predict_state(robot_state, v, w, dt, T)
% 预测未来 T 时间内的状态
x = robot_state(1);
y = robot_state(2);
theta = robot_state(3);
num_steps = round(T / dt);
predicted_state = zeros(num_steps, 3);
for k = 1:num_steps
x = x + v * cos(theta) * dt;
y = y + v * sin(theta) * dt;
theta = theta + w * dt;
predicted_state(k, :) = [x, y, theta];
end
end
function score = evaluate_score(predicted_state, goal, obstacles)
% 评估函数,综合考虑到目标的距离和与障碍物的距离
dist_to_goal = sqrt((predicted_state(end, 1) - goal(1))^2 + (predicted_state(end, 2) - goal(2))^2);
min_dist_to_obstacle = Inf;
for i = 1:size(obstacles, 1)
for j = 1:size(predicted_state, 1)
dist = sqrt((predicted_state(j, 1) - obstacles(i, 1))^2 + (predicted_state(j, 2) - obstacles(i, 2))^2);
if dist < min_dist_to_obstacle
min_dist_to_obstacle = dist;
end
end
end
score = 1 / dist_to_goal + min_dist_to_obstacle;
end在 DWA 中,dwa 函数首先生成动态窗口,然后对窗口内的每个速度组合进行评估,通过 predictstate**预测未来状态,evaluate score 综合考虑到目标点的距离和与障碍物的距离来打分,最终选择得分最高的速度组合。
设置未知和移动障碍物
在实际应用中,我们可以通过一些随机化的方法来设置未知障碍物,对于移动障碍物,可以通过定义其运动模型来模拟。
matlab
% 设置随机未知障碍物
function occupancy_grid = set_random_obstacles(occupancy_grid, num_obstacles)
[m, n] = size(occupancy_grid);
for i = 1:num_obstacles
x = randi(m);
y = randi(n);
if occupancy_grid(x, y) == 0
occupancy_grid(x, y) = 1;
end
end
end
% 定义移动障碍物的运动模型
function new_obstacle_pos = move_obstacle(obstacle_pos, v, w, dt)
x = obstacle_pos(1);
y = obstacle_pos(2);
theta = obstacle_pos(3);
x = x + v * cos(theta) * dt;
y = y + v * sin(theta) * dt;
theta = theta + w * dt;
new_obstacle_pos = [x, y, theta];
endsetrandomobstacles 函数在地图中随机设置一定数量的障碍物,而 move_obstacle 函数则定义了移动障碍物的简单运动模型,根据速度 v 和角速度 w 在时间间隔 dt 内更新障碍物位置。
多种算法对比
通过实际运行这些算法,我们可以从多个方面进行对比,比如路径长度、运行时间、搜索节点数量等。
| 算法 | 路径长度 | 运行时间(s) | 搜索节点数量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| A 星 | [具体值] | [具体值] | [具体值] |
| JPS | [具体值] | [具体值] | [具体值] |
| 改进 A 星 | [具体值] | [具体值] | [具体值] |
| 改进 JPS | [具体值] | [具体值] | [具体值] |
| DWA | [具体值] | [具体值] | N/A(动态评估) |
从对比结果可以看出,JPS 及其改进版本在搜索节点数量上明显优于 A 星,运行时间也相对较短,这得益于其对搜索空间的优化。而 DWA 更适用于动态环境,虽然不能直接与其他算法在路径长度和搜索节点上进行比较,但在处理移动障碍物方面有着独特的优势。
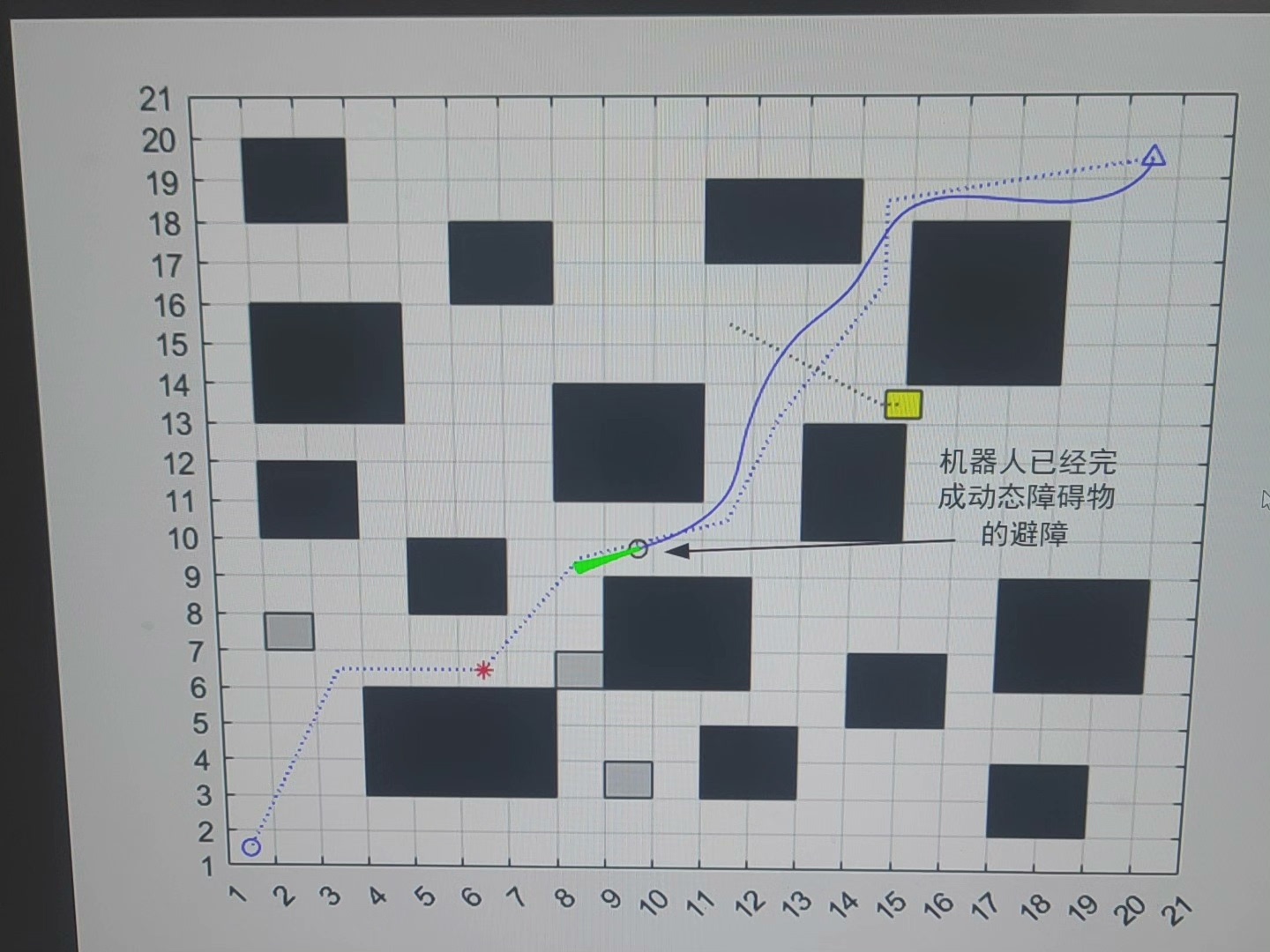
单机器人路径规划算法有着丰富的研究内容,每种算法都有其适用场景和优缺点。希望今天分享的这些内容能给大家在路径规划研究上带来一些启发~
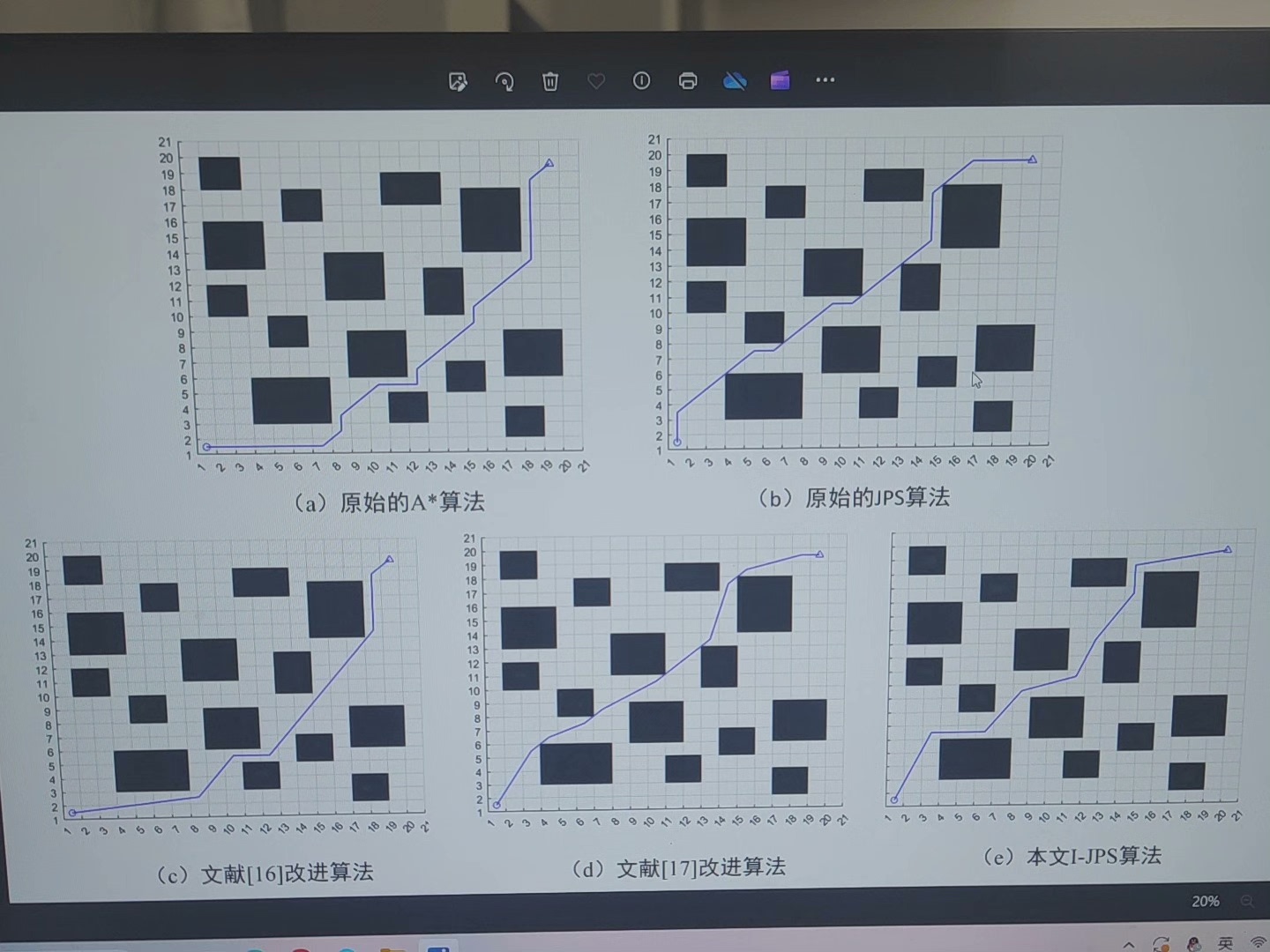
以上代码只是核心部分,实际应用中还需要根据具体场景进行调整和完善哦。大家要是有什么问题或者想法,欢迎在评论区交流呀!