目录
[A. Maximize the Last Element](#A. Maximize the Last Element)
[B. AND Reconstruction](#B. AND Reconstruction)
[C. Absolute Zero](#C. Absolute Zero)
[D. Prime XOR Coloring](#D. Prime XOR Coloring)
引言:
昨天打了Round2,今天来打Pinely Round 4
A. Maximize the Last Element
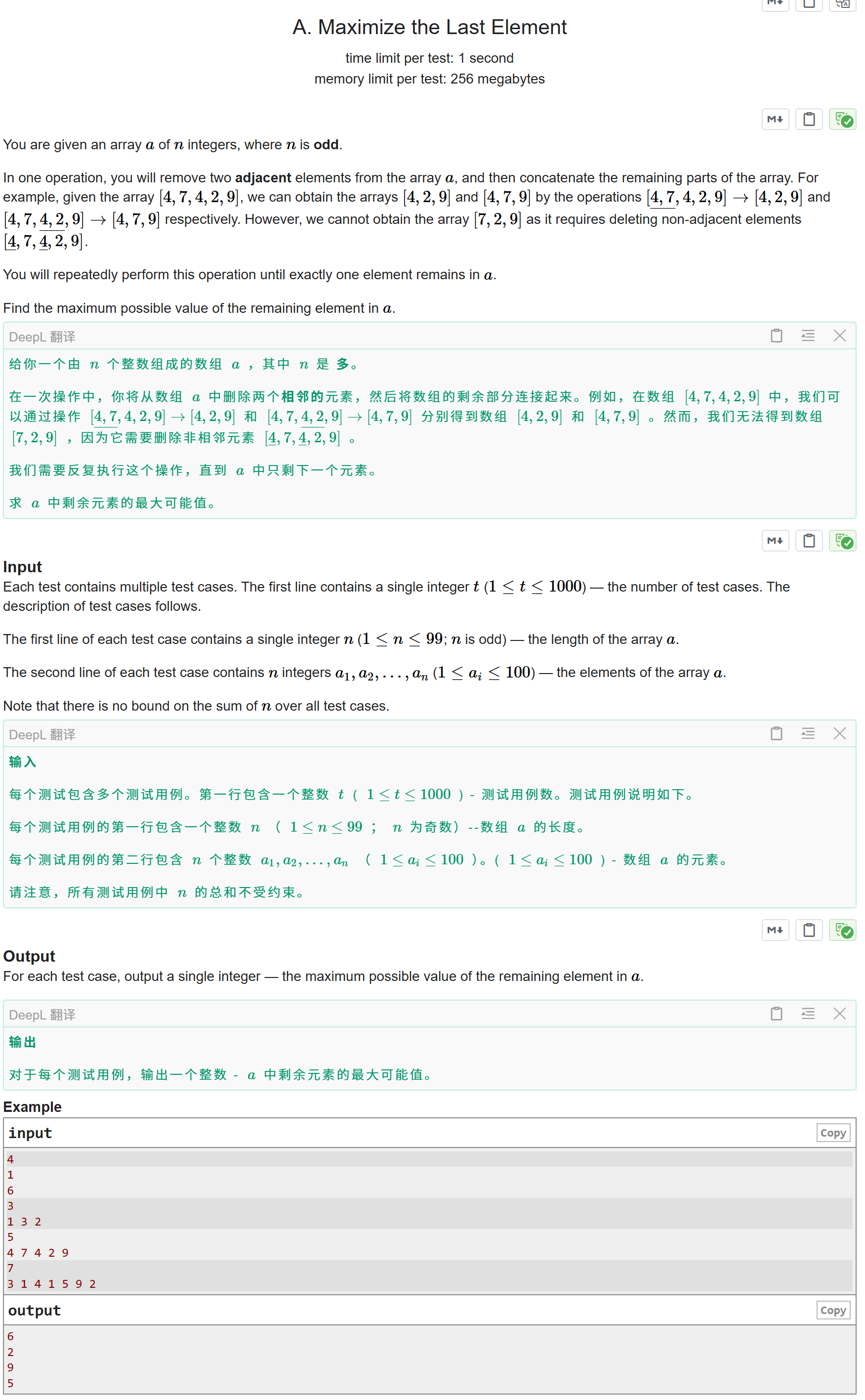
题目大意:
给定一个长度为奇数的数组,每次可以删除两个相邻的元素,直到剩下一个元素为止,求该元素的最大值。
算法分析:
我们进行模拟发现,最后总是会保留奇数位的值。
源码实现:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<numeric>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 2)
{
ans = max(ans, a[i]);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}B. AND Reconstruction
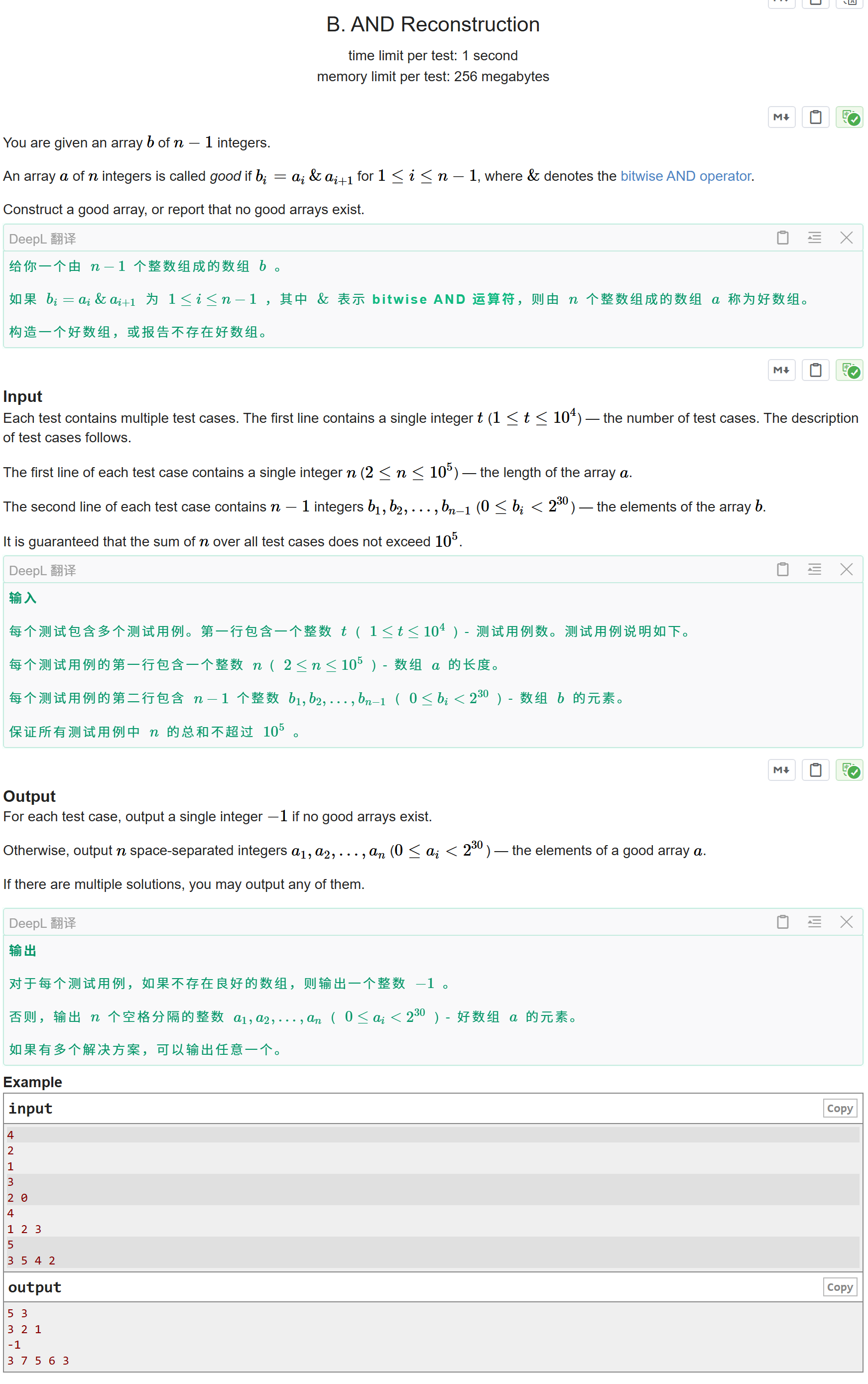
题目大意:
给定一个长为n-1的数组b,构造一个长度为n的数组a,满足ai&ai+1 == bi;,否则输出-1。
算法分析:
我们令a1== b1,。然后我们发现ai会影响bi与bi-1,那么a包含最少的1时,必须为bi-1 | bi,最后我们令an == bn-1。
源码实现:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<numeric>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve() {
int n;
cin>> n;
vector<int> a(n), b(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
cin >> b[i];
}
a[0] = b[0];
for (int i = 1; i < n - 1; i++)
{
a[i] = b[i] | b[i - 1];
}
a[n - 1] = b[n - 2];
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
if (b[i] != (a[i] & a[i+1]))
{
cout << -1 << endl;
return;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}C. Absolute Zero

题目大意:
给定一个长度为n的数组,每次操作可以选定一个x,将ai更新为|ai-x|。构造一个操作序列不操作40次,使数组a全为0.
算法分析:
进行模拟几组样例发现,数组中所有元素的奇偶性必须相同,否则当一个数变为奇数,另一个数会变成偶数。(开始时这两个数奇偶性不同)。
我们只需要每次减去(r+l)/2,逐渐缩小上界即可。
源码实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<numeric>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
vector<int> a(n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++)
{
if ((a[i] - a[i - 1]) & 1)
{
cout << -1 << endl;
return;
}
}
if (a[0] == a[n - 1])
{
if (a[0] == 0)
{
cout << 0 << endl<<endl;
return;
}
cout << 1 << endl;
cout << a[0] << endl;
return;
}
vector<int> ans;
while (a[0] != a[n - 1])
{
int op = (a[0] + a[n - 1]) / 2;
ans.push_back(op);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
a[i] = abs(a[i] - op);
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
}
if (a[0] != 0)
{
ans.push_back(a[0]);
}
cout << ans.size() << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++)
{
cout << ans[i] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}D. Prime XOR Coloring

题目大意:
有n个顶点,编号从1到n,当uXOR v为质数时,u和v之间有一条边。用最少的颜色给所有顶点
染色,要求相邻顶点的颜色不能相同。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<numeric>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
if (n == 1)
{
cout << 1 << endl << 1 << endl;
}
else if (n == 2)
{
cout << 2 << endl;
cout << 1 << " " << 2 << endl;
}
else if (n == 3)
{
cout << 2 << endl;
cout << "1 2 2\n";
}
else if (n == 4)
{
cout << 3 << endl;
cout << "1 2 2 3\n";
}
else if (n == 5)
{
cout << 3 << endl;
cout << "1 2 2 3 3\n";
}
else {
cout << 4 << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cout << (i % 4) + 1 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}算法分析:
在这里给大家普及一下四色定理:"将平面任意地细分为不相重叠的区域,每一个区域总可以用1234这四个数字之一来标记而不会使相邻的两个区域得到相同的数字。"这里所指的相邻区域是指有一整段边界是公共的。如果两个区域只相遇于一点或有限多点就不叫相邻的。
我们先考虑哪些点之间连边难,考虑哪些点之间不连边。根据四色定理知,当n>=6时,一定需要四种颜色。考虑所有质数,发现除了2都是奇数。2的二进制01,3的二进制10,4的二进制00。那么我们对4取余,mod4相同的数异或之后一定不是质数。然后特判n<=5。
源码实现:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<numeric>
#include <map>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#include<unordered_set>
#include<unordered_map>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
void solve() {
int n;
cin >> n;
if (n == 1)
{
cout << 1 << endl << 1 << endl;
}
else if (n == 2)
{
cout << 2 << endl;
cout << 1 << " " << 2 << endl;
}
else if (n == 3)
{
cout << 2 << endl;
cout << "1 2 2\n";
}
else if (n == 4)
{
cout << 3 << endl;
cout << "1 2 2 3\n";
}
else if (n == 5)
{
cout << 3 << endl;
cout << "1 2 2 3 3\n";
}
else {
cout << 4 << endl;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cout << (i % 4) + 1 << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int t = 1;
cin >> t;
while (t--)
{
solve();
}
return 0;
}结语:
以上就是Pinely Round 4 的四道题的题解,希望对你们有帮助,谢谢观看呀,如果有什么问题欢迎在评论取指出,我会继续努力哒!
