【实验2.1】字段查询
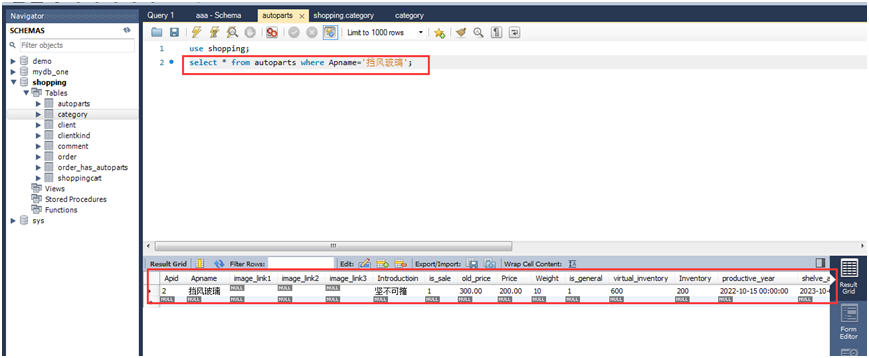
(1)查询商品名称为"挡风玻璃"的商品信息。
(2)查询ID为1的订单。
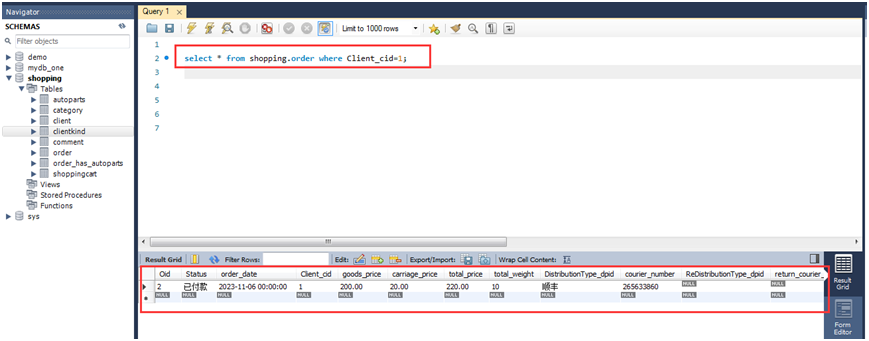
1.查询用户ID为1的订单:
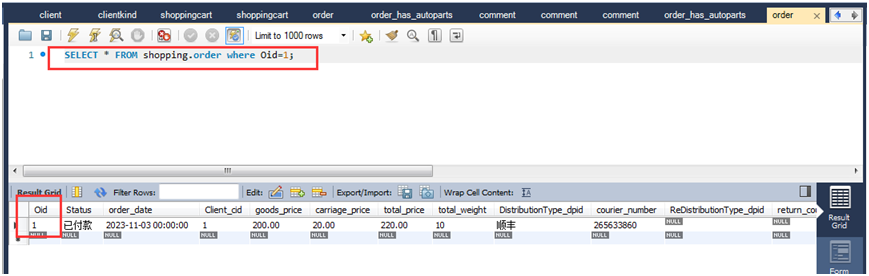
2.查询订单ID为1的订单:
【实验2.2】多条件查询
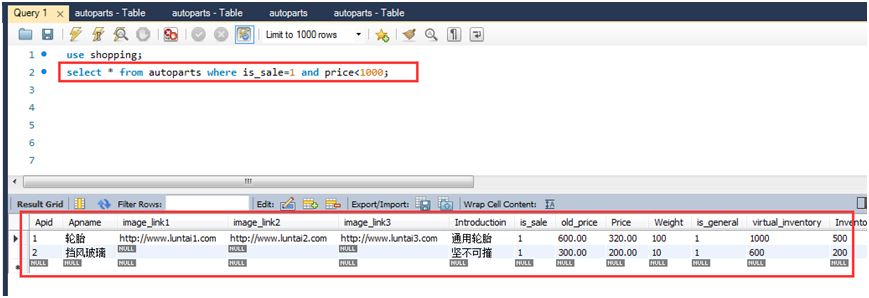
查询所有促销的价格小于1000的商品信息。
【实验2.3】DISTINCT
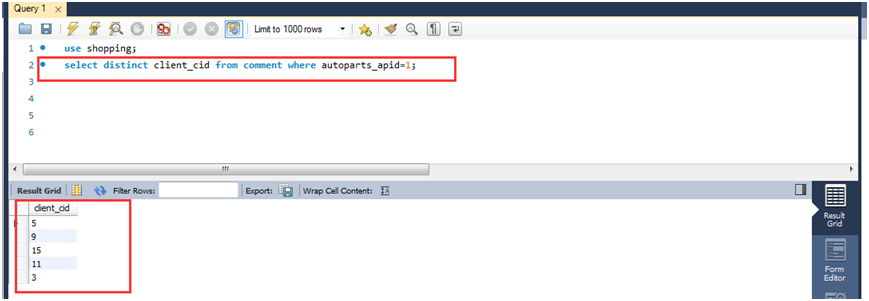
(1)查询所有对商品ID为1的商品发表过评论的用户ID。
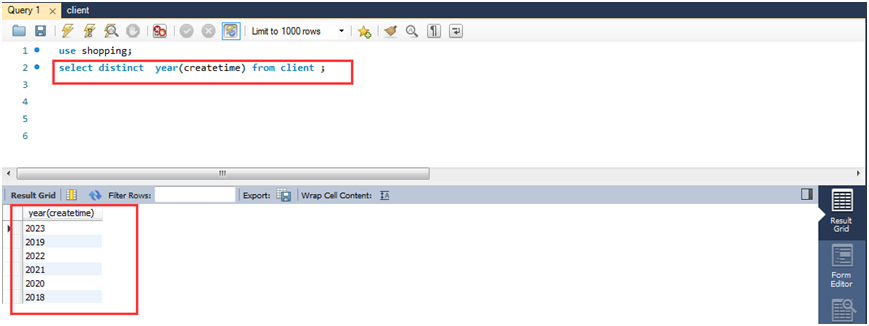
(2)查询此汽车用品网上商城会员的创建时间段,1年为一段。
【实验2.4】ORDER BY
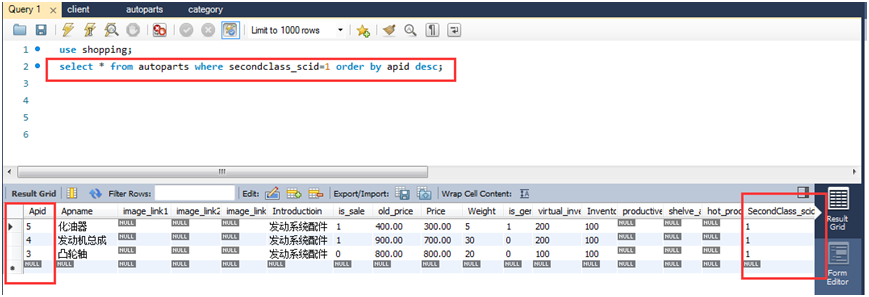
(1)查询类别ID为1的所有商品,结果按照商品ID降序排列。
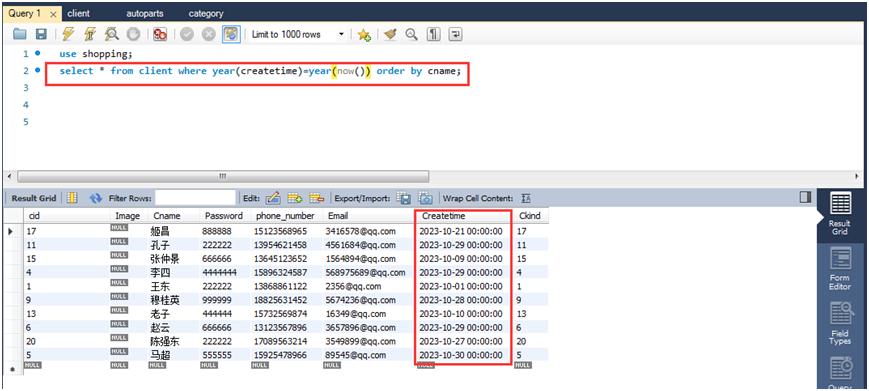
(2)查询今年新增的所有会员,结果按照用户名字排序。
【实验2.5】GROUP BY
(1)查询每个用户的消费总金额(所有订单)。
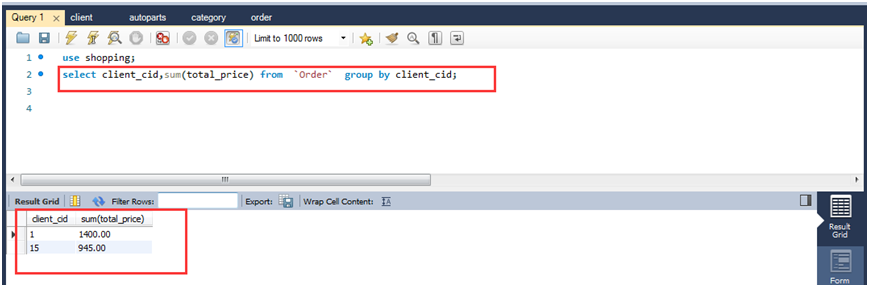
注:由于order表名与关键字order冲突,所以要用``框起来(ESC下面那个键)。
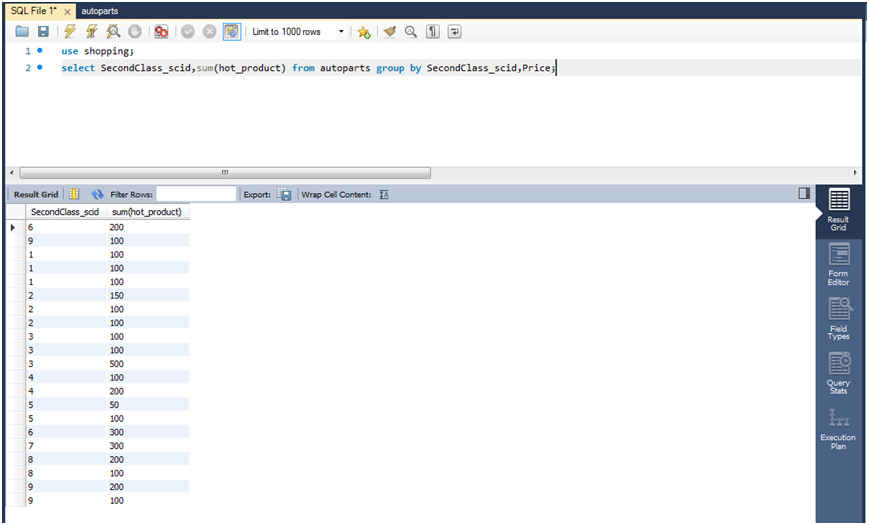
(2)查询类别价格一样的各种商品数量总和。
【实验2.6】COUNT()
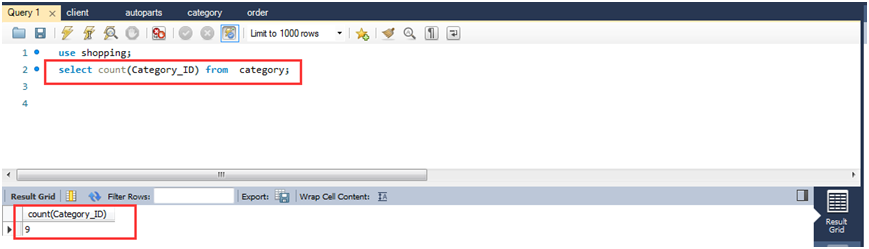
(1)查询类别的数量。
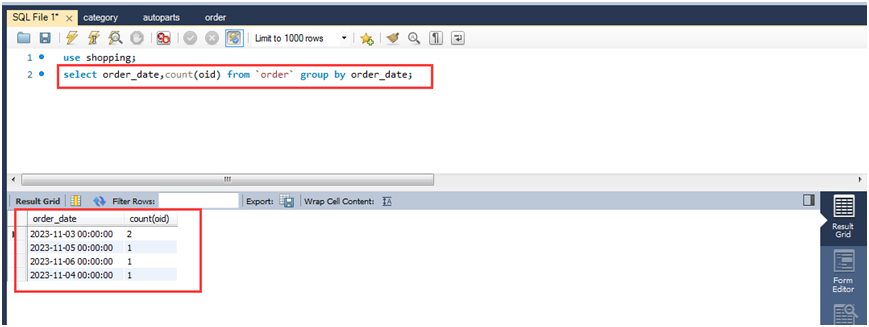
(2)查询汽车用品网上商城的每天的接单数。
【实验2.7】 SUM()
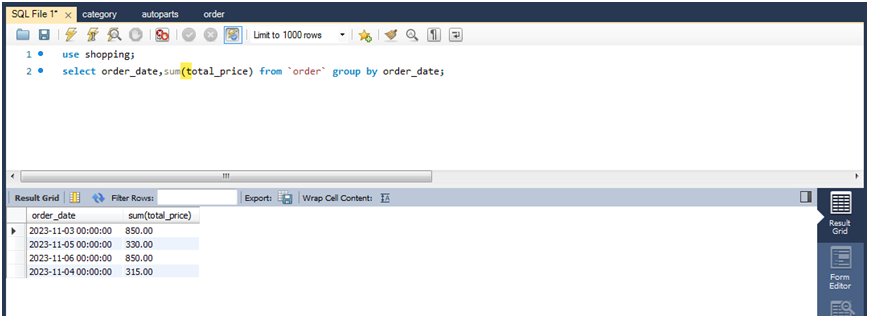
查询该商城每天的销售额。
【实验 2.8 】 AVG()
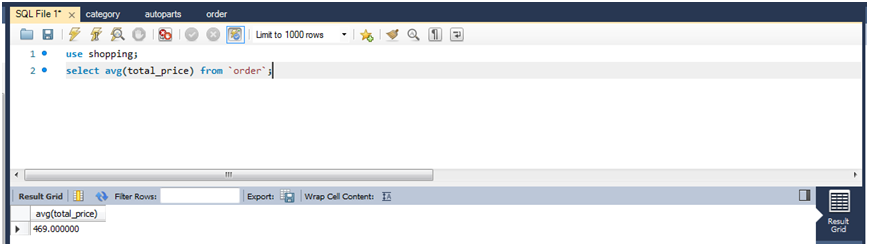
(1)查询所有订单的平均销售金额。
【实验 2.9 】 MAX()
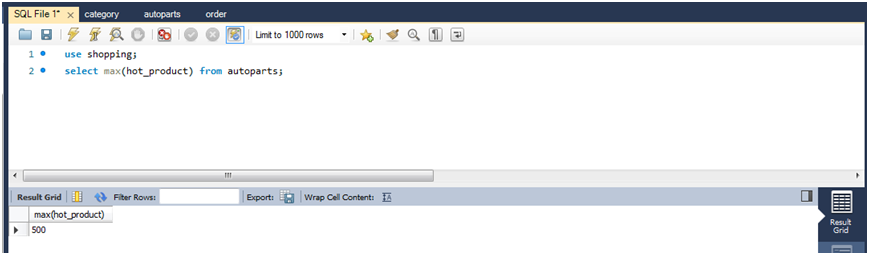
(1)查询所有商品中的数量最大者。
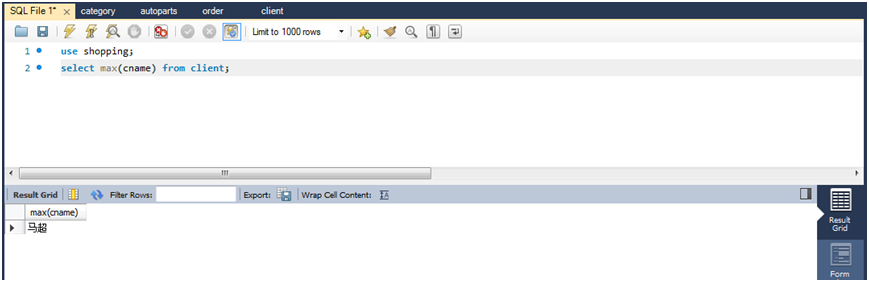
(2)查询所有用户按字母排序中名字最靠前者。
【实验 2.10 】 MIN()
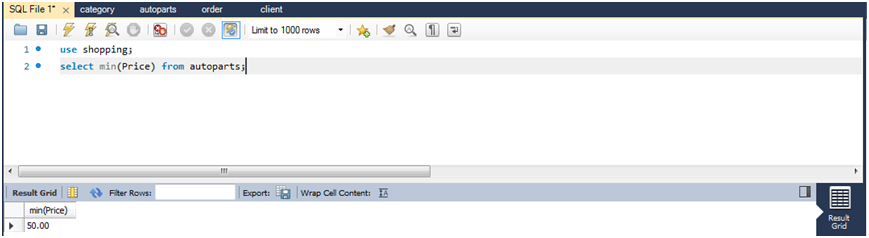
(1)查询所有商品中价格最低者。
【实验 2.11 】内连接查询
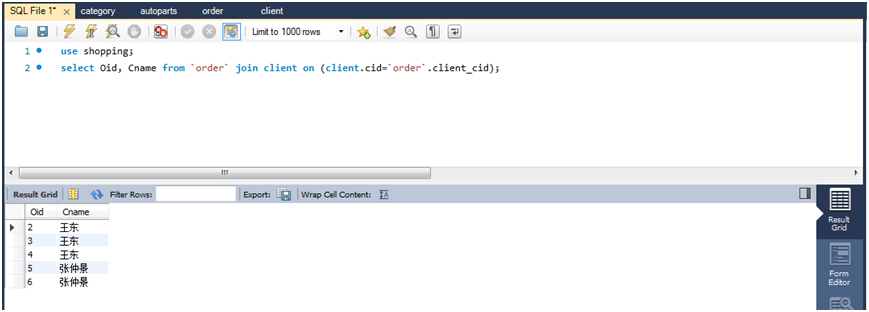
(1)查询所有订单的发出者名字。
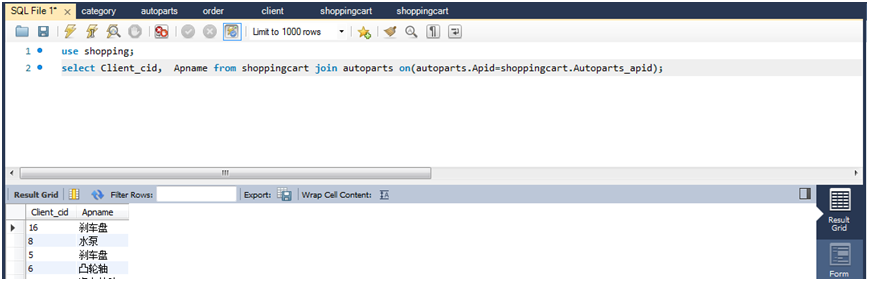
(2)查询每个用户购物车中的商品名称。
【实验 2.12 】外连接查询
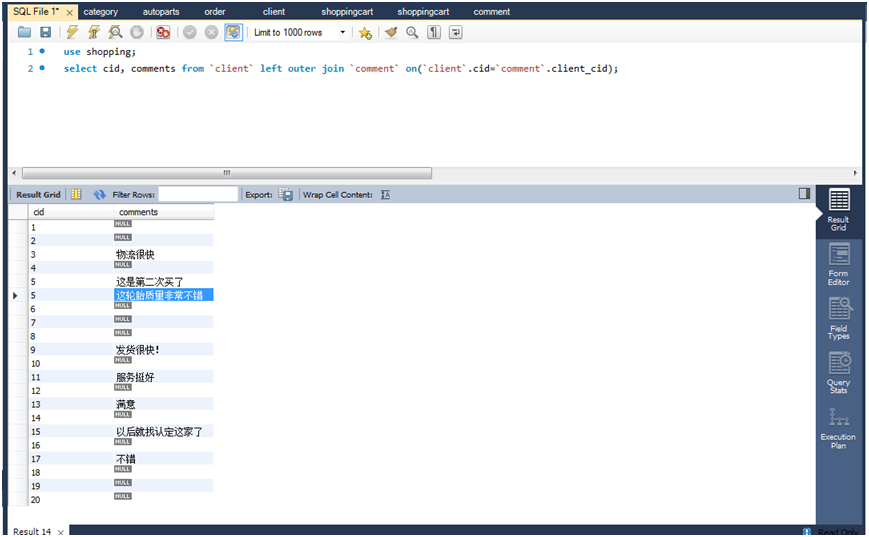
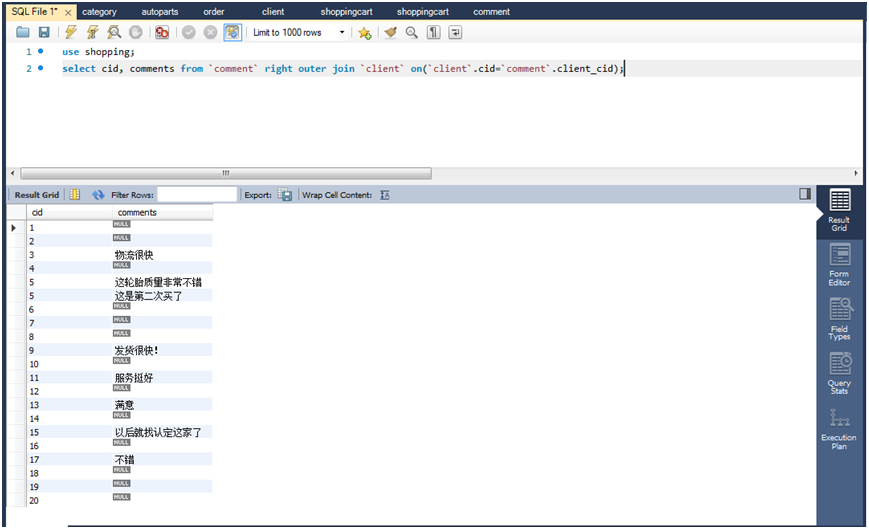
(1)查询列出所有用户ID,以及他们的评论,如果有的话。(left outer join)
(2)查询列出所有用户ID,以及他们的评论,如果有的话。(right outer join)
【实验 2.13 】复合条件连接查询
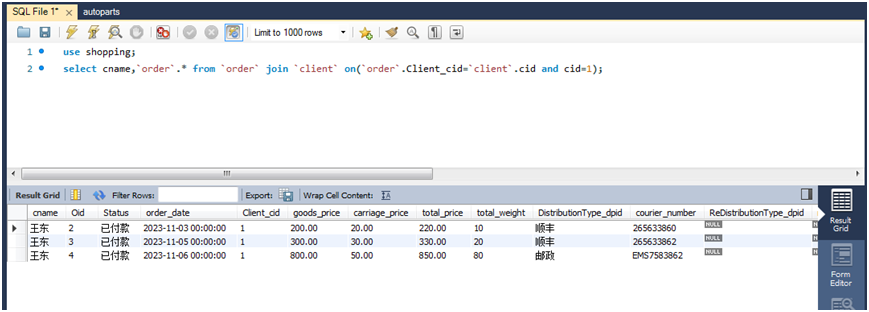
(1)查询用户ID为1的客户的订单信息和客户名。
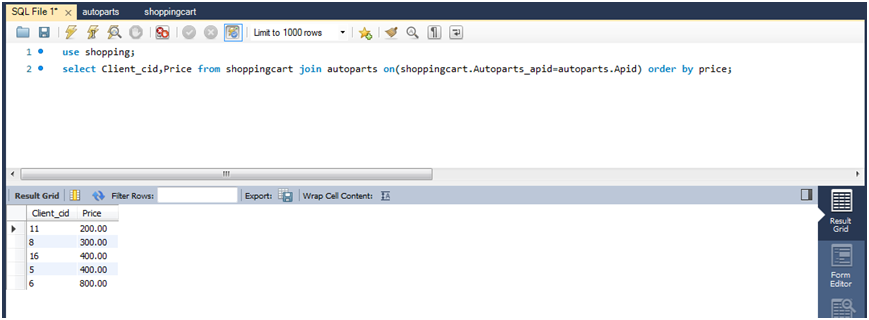
(2)查询每个用户的购物车中的商品价格,并且按照价格顺序排列。
【实验 2.14 】 IN
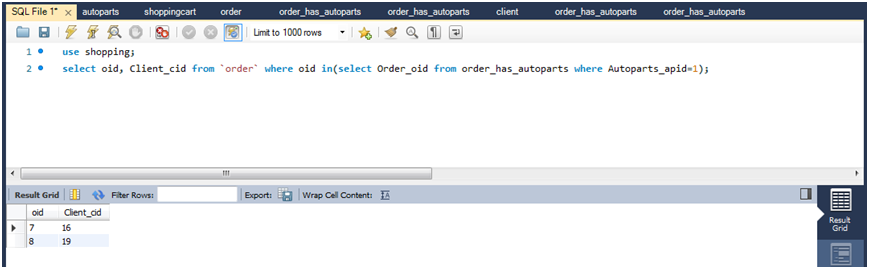
(1)查询订购商品ID为1的订单ID,并根据订单ID查询发出此订单的用户ID。
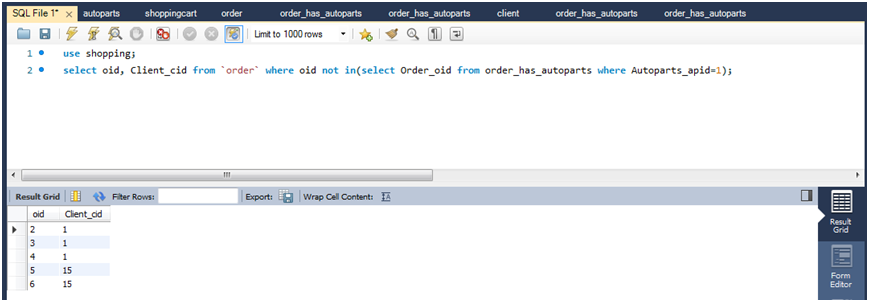
(2)查询订购商品ID为1的订单ID,并根据订单ID查询未发出此订单的用户ID。
【实验 2.15 】比较运算符
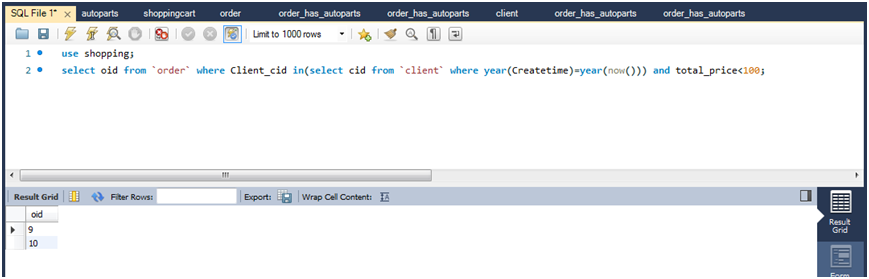
(1)查询今年新增会员的订单,并且列出所有订单总价小于100的订单ID。
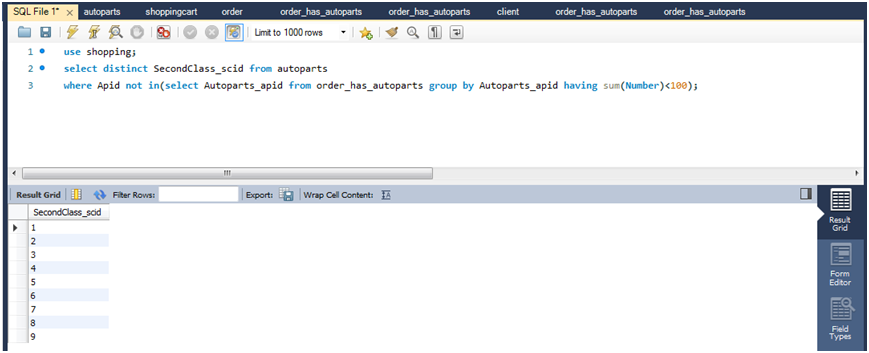
(2)查询所有订单商品数量总和小于100的商品ID,并将不在此商品所在类别的其他类别的ID列出来。
【实验 2.16 】 EXISTS
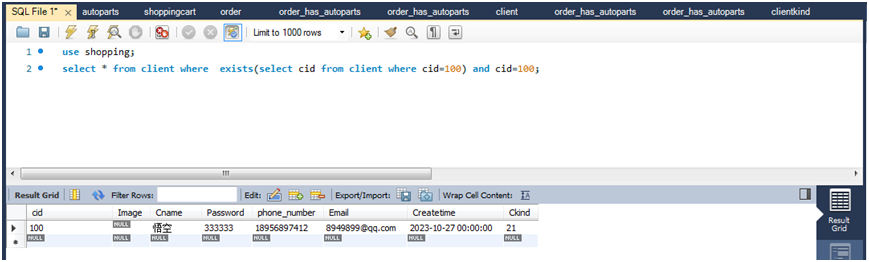
(1)查询表中是否存在用户ID为100的用户,如果存在,列出此用户的信息。
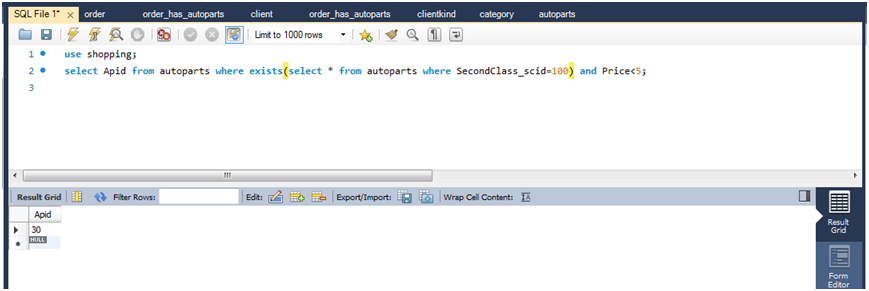
(2)查询表中是否存在类别ID为100的商品类别,如果存在,列出此类别中商品价格小于5的商品ID。
【实验 2.17 】 ANY
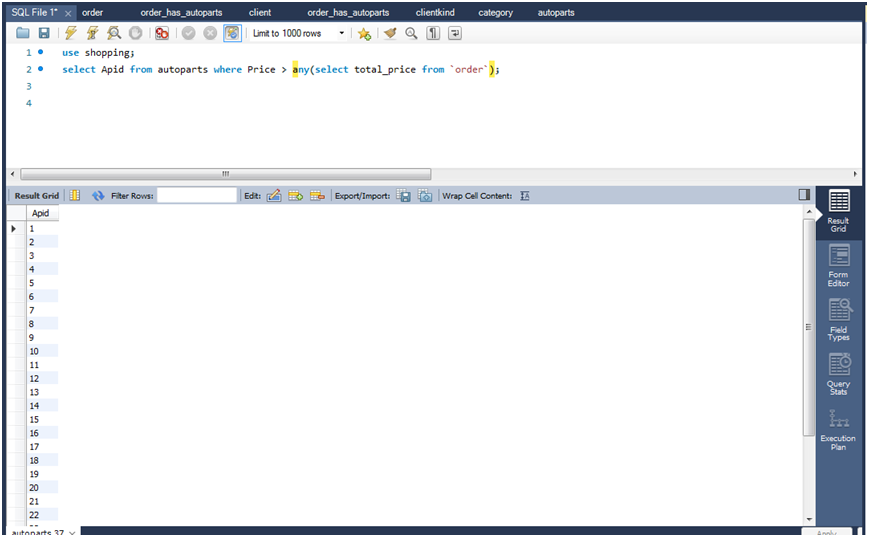
查询所有商品表中价格比订单表中商品ID对应的价格大的商品ID。
【实验 2.18 】 ALL
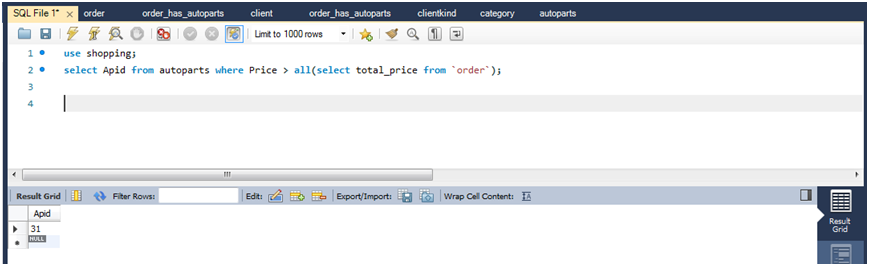
查询所有商品表中价格比订单表中所有商品ID对应的价格大的商品ID。
【实验 2.19 】集合查询
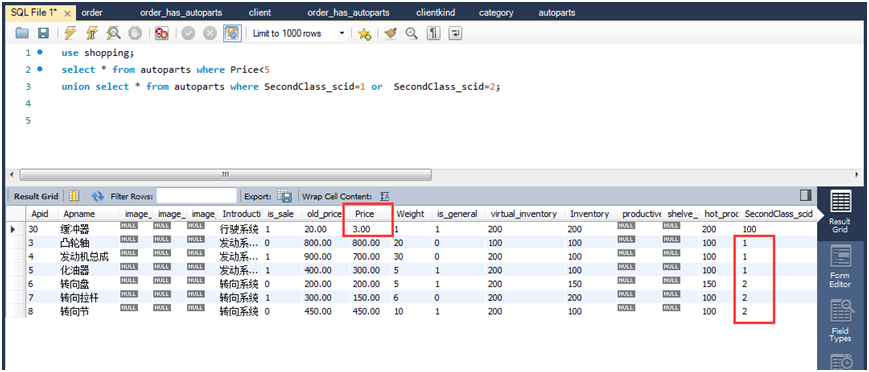
(1)查询所有价格小于5的商品,查询类别ID为1和2的所有商品,使用UNION连接查询结果。
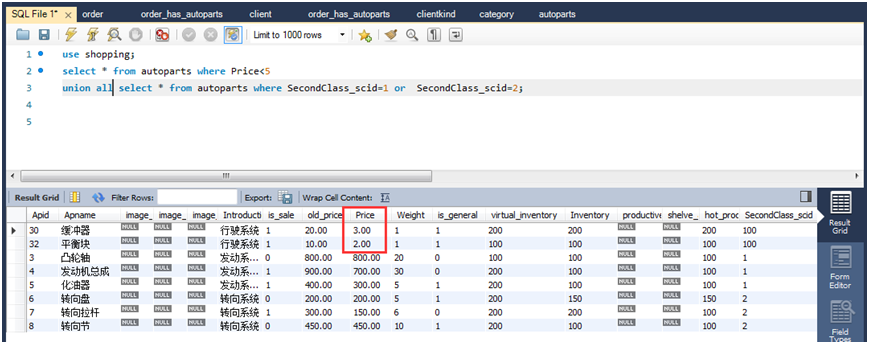
(2)查询所有价格小于5的商品,查询类别ID为1和2的所有商品,使用UNION ALL连接查询结果。
以下为代码:
sql
【实验2.1】字段查询
(1)查询商品名称为"挡风玻璃"的商品信息。
select * from autoparts where apname="挡风玻璃";
(2)查询ID为1的订单。
1.查询用户ID为1的订单:
select * from shopping.order where client_cid=1;
2.查询订单ID为1的订单:
select * from shopping.order where oid=1;
【实验2.2】多条件查询
查询所有促销的价格小于1000的商品信息。
select * from autoparts where is_sale=1 and price<1000;
【实验2.3】DISTINCT
(1)查询所有对商品ID为1的商品发表过评论的用户ID。
select distinct client_cid from comment where autoparts_apid=1;
(2)查询此汽车用品网上商城会员的创建时间段,1年为一段。
select distinct year(createtime) from client;
【实验2.4】ORDER BY
(1)查询类别ID为1的所有商品,结果按照商品ID降序排列。
select * from autoparts where secondclass_scid=1 order by apid desc;
(2)查询今年新增的所有会员,结果按照用户名字排序。
select * from client where year(createtime)=year(now()) order by cname;
【实验2.5】GROUP BY
(1)查询每个用户的消费总金额(所有订单)。
select client_cid,sum(total_price) from`order`group by client_cid;
注:由于order表名与关键字order冲突,所以要用``框起来(ESC下面那个键)。
(2)查询类别价格一样的各种商品数量总和。
select secondclass_scid,sum(hot_product) from autoparts group by secondcalss_scid,price;
【实验2.6】COUNT()
(1)查询类别的数量。
select count(category_id) from category;
(2)查询汽车用品网上商城的每天的接单数。
select order_date,count(oid) from `order` group by order_date;
【实验2.7】 SUM()
查询该商城每天的销售额。
select order_date,sum(total_price) from `order` group by order_date;
【实验2.8】AVG()
(1)查询所有订单的平均销售金额。
select avg(total_price) from `order`;
【实验2.9】MAX()
(1)查询所有商品中的数量最大者。
select max(hot_product) from autoparts;
(2)查询所有用户按字母排序中名字最靠前者。
select max(cname) from client;
【实验2.10】MIN()
(1)查询所有商品中价格最低者。
select min(price) from autoparts;
【实验2.11】内连接查询
(1)查询所有订单的发出者名字。
select oid,cname from `order` join client on(client.cid=`order`.client_cid);
(2)查询每个用户购物车中的商品名称。
select client_cid,apname from shoppingcart join autoparts on(autoparts.apid=shoppingcart.autoparts_apid);
【实验2.12】外连接查询
(1)查询列出所有用户ID,以及他们的评论,如果有的话。(left outer join)
select cid,comments from client left outer join comment on(client.cid=comment.client_cid);
(2)查询列出所有用户ID,以及他们的评论,如果有的话。(right outer join)
select cid,comments from comment right outer join client on(client.cid=comment.client_cid);
【实验2.13】复合条件连接查询
(1)查询用户ID为1的客户的订单信息和客户名。
select cname `order`.* from `order` join client on(`order`.client_cid=client.cid and cid=1);
(2)查询每个用户的购物车中的商品价格,并且按照价格顺序排列。
select client_cid,price from shoppingcart join autoparts on(shoppingcart.autoparts_apid=autoparts.apid) order by price;
【实验2.14】 IN
(1)查询订购商品ID为1的订单ID,并根据订单ID查询发出此订单的用户ID。
select oid,client_cid from `order` where oid in(select order_oid from order_has_autoparts where autoparts_apid=1);
(2)查询订购商品ID为1的订单ID,并根据订单ID查询未发出此订单的用户ID。
select oid,client_cid from `order` where oid not in(select order_oid fromorder_has_autoparts where autoparts_apid=1)
【实验2.15】比较运算符
(1)查询今年新增会员的订单,并且列出所有订单总价小于100的订单ID。
select oid from `order` where clinet_cid in(select cid from client where year(createtime)=year(now())) and total_price<100;
(2)查询所有订单商品数量总和小于100的商品ID,并将不在此商品所在类别的其他类别的ID列出来。
select distinct secondclass_scid from autoparts where apid notin(select autoparts_apid from order_has_autoparts group by autoparts_apid having sum(number)<100);
【实验2.16】EXISTS
(1)查询表中是否存在用户ID为100的用户,如果存在,列出此用户的信息。
select * from client where exists(select cid from client where cid=100) and cid=100;
(2)查询表中是否存在类别ID为100的商品类别,如果存在,列出此类别中商品价格小于5的商品ID。
select apid from autoparts where exists(select * from autoparts where secondclass_scid=100) and price<5;
【实验2.17】ANY
查询所有商品表中价格比订单表中商品ID对应的价格大的商品ID。
select apid from autoparts where price >any(select total_price from `order`);
【实验2.18】ALL
查询所有商品表中价格比订单表中所有商品ID对应的价格大的商品ID。
select apid from autoparts where price >all(select total_price from `order`);
【实验2.19】集合查询
(1)查询所有价格小于5的商品,查询类别ID为1和2的所有商品,使用UNION连接查询结果。
select * from autoparts where price<5 unionselect * from autoparts where secondclass_scid=1 or secondclass_scid=2;
(2)查询所有价格小于5的商品,查询类别ID为1和2的所有商品,使用UNION ALL连接查询结果。
select * from autoparts where price<5 unionallselect * from autoparts where secondclass_scid=1 or secondclass_scid=2;