写在开头的话
昨天学习了Rabin-Karp算法,今天让我们来学习一下数组与搜索的相关知识吧。
第一节
知识点:
(1)线性搜索(2)二分搜索
线性搜索
算法介绍
线性搜索(Linear Search)是一种最简单且直观的搜索算法,用于在列表或数组中查找特定元素。它的基本思想是从列表的第一个元素开始,逐个检查每个元素,直到找到目标元素或者到达列表的末尾。线性搜索适用于未排序的列表或数组。
算法步骤
- 从列表的第一个元素开始。
- 将当前元素与目标元素进行比较。
- 如果当前元素等于目标元素,搜索成功,返回当前元素的索引。
- 如果当前元素不等于目标元素,移动到下一个元素。
- 重复步骤 2 和 3,直到找到目标元素或到达列表的末尾。
- 如果遍历完整个列表仍未找到目标元素,搜索失败,返回 -1 或其他表示未找到的标志。
图示
线性搜索图示
公式表示
设列表为 a,目标元素为 x,列表长度为 n。
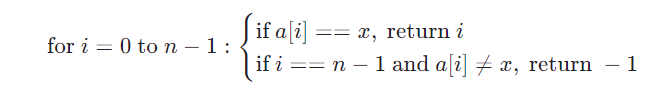
代码实现
C++代码实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int linear_search(vector<int>& arr, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.size(); ++i) {
if (arr[i] == target) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 示例用法
int main() {
vector<int> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int target = 3;
int index = linear_search(arr, target);
if (index != -1) {
cout << "目标元素 " << target << " 在数组中的索引为 " << index << endl;
} else {
cout << "数组中不存在目标元素 " << target << endl;
}
return 0;
}Java代码实现
java
public class LinearSearch {
public static int linearSearch(int[] arr, int target) {
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i] == target) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int target = 3;
int index = linearSearch(arr, target);
if (index != -1) {
System.out.println("目标元素 " + target + " 在数组中的索引为 " + index);
} else {
System.out.println("数组中不存在目标元素 " + target);
}
}
}Python代码实现
python
def linear_search(arr, target):
for i in range(len(arr)):
if arr[i] == target:
return i
return -1
# 示例用法
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
target = 3
index = linear_search(arr, target)
if index != -1:
print(f"目标元素 {target} 在数组中的索引为 {index}")
else:
print(f"数组中不存在目标元素 {target}")运行结果

复杂度分析
- 时间复杂度: 在最坏情况下,需要检查列表中的每一个元素,时间复杂度为 O(n)。
- 空间复杂度: 线性搜索仅需要常量级别的额外空间,空间复杂度为 O(1)。
线性搜索的主要优点是实现简单,并且不需要列表有序。然而,由于时间复杂度较高,它在处理大规模数据时可能效率较低。
二分搜索
算法介绍
二分搜索是一种用于在 有序数组 中查找特定元素的高效算法。它基于"分而治之"的策略,每次通过比较中间元素与目标元素,将搜索范围缩小一半,从而大大减少了所需的比较次数。
二分搜索的过程
假设我们在一个升序排列的数组 arr 中搜索目标元素 target,二分搜索的步骤如下:
- 初始化 :定义两个指针
low和high,分别指向数组的起始和末尾位置。 - 查找中间元素 :计算中间位置
mid = (low + high) / 2。 - 比较 :
- 如果
arr[mid]等于target,则搜索成功,返回mid位置。 - 如果
arr[mid]小于target,则将low更新为mid + 1,缩小搜索范围到右半部分。 - 如果
arr[mid]大于target,则将high更新为mid - 1,缩小搜索范围到左半部分。
- 如果
- 重复 :重复步骤 2 和步骤 3,直到
low大于high,表示搜索范围为空,目标元素不存在于数组中。
图示
二分搜索演示
二分搜索的时间复杂度
二分搜索每次将搜索范围缩小一半,时间复杂度为 O(logn),其中 n 是数组的大小。这使得它比线性搜索更高效,特别是在处理大型有序数组时。
代码实现
C++代码实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int binary_search(const vector<int>& arr, int target) {
int low = 0, high = arr.size() - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
// 示例用法
int main() {
vector<int> arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int target = 3;
int index = binary_search(arr, target);
if (index != -1) {
cout << "目标元素 " << target << " 在数组中的索引为 " << index << endl;
} else {
cout << "数组中不存在目标元素 " << target << endl;
}
return 0;
}Java代码实现
java
public class BinarySearch {
public static int binarySearch(int[] arr, int target) {
int low = 0, high = arr.length - 1;
while (low <= high) {
int mid = (low + high) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return mid;
} else if (arr[mid] < target) {
low = mid + 1;
} else {
high = mid - 1;
}
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int target = 3;
int index = binarySearch(arr, target);
if (index != -1) {
System.out.println("目标元素 " + target + " 在数组中的索引为 " + index);
} else {
System.out.println("数组中不存在目标元素 " + target);
}
}
}Python代码实现
python
def binary_search(arr, target):
low, high = 0, len(arr) - 1
while low <= high:
mid = (low + high) // 2
if arr[mid] == target:
return mid
elif arr[mid] < target:
low = mid + 1
else:
high = mid - 1
return -1
# 示例用法
arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
target = 3
index = binary_search(arr, target)
if index != -1:
print(f"目标元素 {target} 在数组中的索引为 {index}")
else:
print(f"数组中不存在目标元素 {target}")运行结果

二分搜索要求数组必须是有序的。如果数组未排序,则需要先进行排序,排序的时间复杂度为 O(nlogn)。
简单总结
在本节中,我们认识到了,线性搜索适合小规模数组,二分搜索效率高,适合大规模有序数据。
第二节
知识点:
(1)有序数组查找(2)数组的旋转搜索
有序数组查找
实现方式
有序数组查找通常使用二分查找法,这是在有序数组中高效查找某个元素的方法。二分查找的基本思想是:
-
定义区间 :设定初始搜索范围的起始位置(
left)和结束位置(right)。 -
计算中点 :计算当前区间的中点索引
(left + right) / 2。 -
比较元素:将中点索引的元素与目标元素比较。
-
如果中点元素等于目标元素,则查找成功,返回中点索引。
-
如果中点元素小于目标元素,则将搜索范围缩小到中点的右侧,即
left = mid + 1。 -
如果中点元素大于目标元素,则将搜索范围缩小到中点的左侧,即
right = mid - 1。
-
-
重复搜索:在缩小后的区间继续重复上述过程,直到找到目标元素或搜索范围为空。
二分查找的时间复杂度是 O(logn),比线性查找更高效,尤其适用于大规模的有序数组。
图示
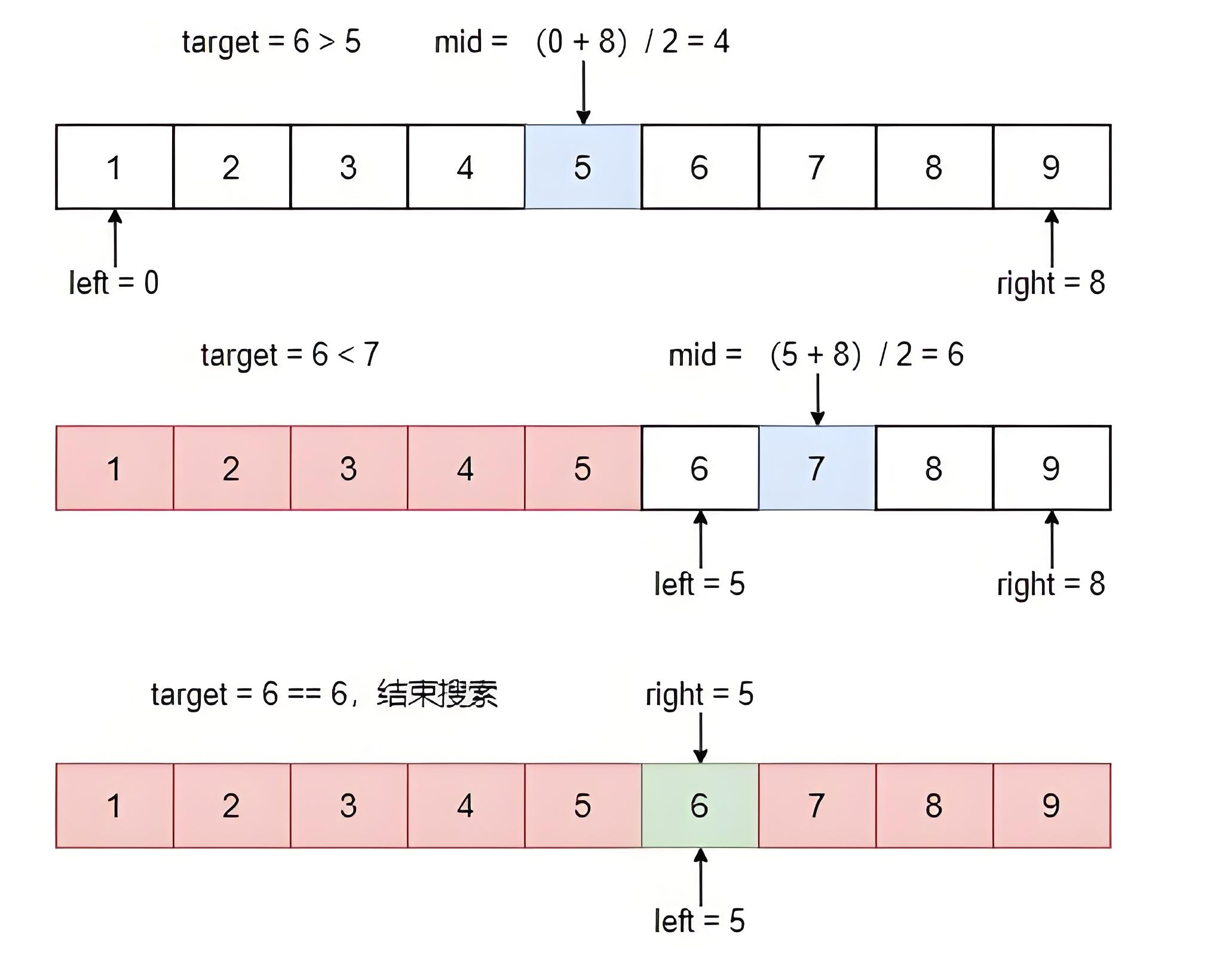
这个代码定义了一个 binarySearch 函数来执行二分查找。在 main 函数中,我们定义了一个有序数组 nums 和一个目标元素 target ,然后调用 binarySearch 函数进行查找,并输出结果。
代码实现
C++代码实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
// 二分查找函数
int binarySearch(const vector<int>& nums, int target) {
// 定义搜索范围的起始位置和结束位置
int left = 0, right = nums.size() - 1;
// 当搜索范围不为空时执行查找
while (left <= right) {
// 计算当前区间的中点索引
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 如果中点元素等于目标元素,则查找成功,返回中点索引
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
// 如果中点元素小于目标元素,则将搜索范围缩小到中点的右侧
else if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
// 如果中点元素大于目标元素,则将搜索范围缩小到中点的左侧
else
right = mid - 1;
}
// 若搜索范围为空仍未找到目标元素,返回 -1 表示查找失败
return -1;
}
int main() {
// 测试用例:有序数组
vector<int> nums = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13};
// 目标元素
int target = 7;
// 调用二分查找函数
int index = binarySearch(nums, target);
// 输出查找结果
if (index != -1)
cout << "目标元素 " << target << " 的索引为 " << index << endl;
else
cout << "未找到目标元素 " << target << endl;
return 0;
}Java代码实现
java
public class BinarySearch {
// 二分查找函数
public static int binarySearch(int[] nums, int target) {
// 定义搜索范围的起始位置和结束位置
int left = 0, right = nums.length - 1;
// 当搜索范围不为空时执行查找
while (left <= right) {
// 计算当前区间的中点索引
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 如果中点元素等于目标元素,则查找成功,返回中点索引
if (nums[mid] == target)
return mid;
// 如果中点元素小于目标元素,则将搜索范围缩小到中点的右侧
else if (nums[mid] < target)
left = mid + 1;
// 如果中点元素大于目标元素,则将搜索范围缩小到中点的左侧
else
right = mid - 1;
}
// 若搜索范围为空仍未找到目标元素,返回 -1 表示查找失败
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 测试用例:有序数组
int[] nums = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13};
// 目标元素
int target = 7;
// 调用二分查找函数
int index = binarySearch(nums, target);
// 输出查找结果
if (index != -1)
System.out.println("目标元素 " + target + " 的索引为 " + index);
else
System.out.println("未找到目标元素 " + target);
}
}Python代码实现
python
# 二分查找函数
def binary_search(nums, target):
# 定义搜索范围的起始位置和结束位置
left, right = 0, len(nums) - 1
# 当搜索范围不为空时执行查找
while left <= right:
# 计算当前区间的中点索引
mid = (left + right) // 2
# 如果中点元素等于目标元素,则查找成功,返回中点索引
if nums[mid] == target:
return mid
# 如果中点元素小于目标元素,则将搜索范围缩小到中点的右侧
elif nums[mid] < target:
left = mid + 1
# 如果中点元素大于目标元素,则将搜索范围缩小到中点的左侧
else:
right = mid - 1
# 若搜索范围为空仍未找到目标元素,返回 -1 表示查找失败
return -1
# 测试用例:有序数组
nums = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13]
# 目标元素
target = 7
# 调用二分查找函数
index = binary_search(nums, target)
# 输出查找结果
if index != -1:
print(f"目标元素 {target} 的索引为 {index}")
else:
print(f"未找到目标元素 {target}")运行结果
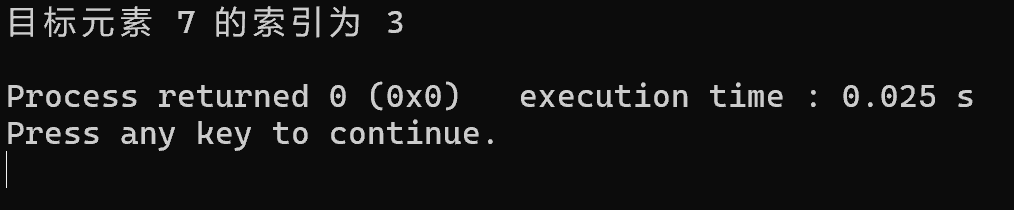
数组的旋转搜索
算法介绍
数组的旋转搜索是指在一个有序数组经过旋转后进行搜索指定元素的过程。通常情况下,有序数组是按照升序排列的,但在旋转搜索中,数组在某个位置发生了旋转,例如 [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2] 这样的数组就是一个被旋转过的有序数组。
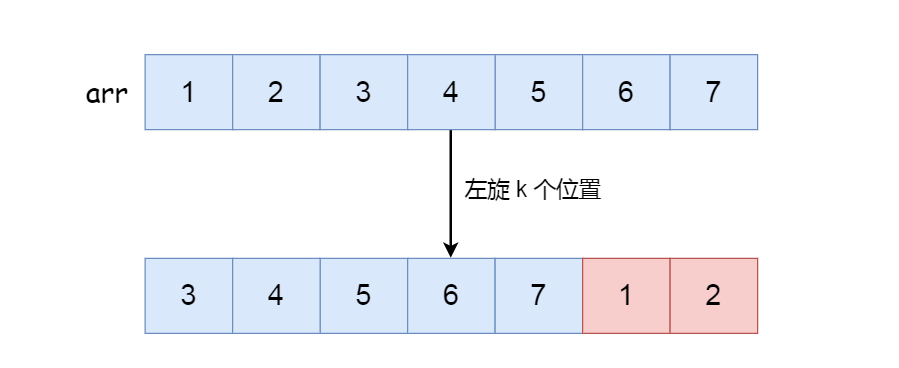
在这种情况下,传统的二分查找可能不再适用,因为数组不再是完全有序的。但仍然可以通过修改二分查找算法来处理这种情况。基本思路是根据当前区间的特点,决定是向左子数组还是向右子数组进行搜索。
例如,对于上述的数组 [3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 1, 2],我们可以观察到,数组被分成了两部分:前半部分是升序排列的,后半部分也是升序排列的。因此,我们可以根据目标元素与数组两端元素的关系,决定向左子数组还是向右子数组进行搜索。
数组的旋转搜索是一个常见的算法问题,其解法通常需要根据具体情况进行一些变化,但核心思想仍然是利用二分查找的思想在旋转后的有序数组中进行搜索。
旋转搜索的步骤
当你需要在一个被旋转过的有序数组中搜索目标元素时,可以采用修改后的二分查找算法来解决。下面是详细步骤:
-
初始化:
- 定义搜索范围的起始位置
left和结束位置right,初始时left = 0,right = len(nums) - 1。 - 开始时,整个数组都是候选的搜索区间。
- 定义搜索范围的起始位置
-
循环:
- 当
left <= right时,执行循环。 - 计算当前区间的中点索引
mid,使用mid = (left + right) / 2。
- 当
-
判断中点元素:
- 检查中点元素
nums[mid]与目标元素target的关系:- 如果
nums[mid] == target,则找到了目标元素,返回mid。 - 如果
nums[mid]小于target,说明中点元素在旋转点左侧,此时需要判断目标元素是否在右子数组中:- 如果
nums[mid] < nums[right],说明右半部分是有序的,且目标元素可能在右侧,更新left = mid + 1。 - 否则,目标元素在左侧,更新
right = mid - 1。
- 如果
- 如果
nums[mid]大于target,说明中点元素在旋转点右侧,此时需要判断目标元素是否在左子数组中:- 如果
nums[mid] > nums[left],说明左半部分是有序的,且目标元素可能在左侧,更新right = mid - 1。 - 否则,目标元素在右侧,更新
left = mid + 1。
- 如果
- 如果
- 检查中点元素
-
更新搜索范围:
- 根据判断结果更新搜索范围:
- 如果目标元素在左子数组中,更新
right = mid - 1; - 如果目标元素在右子数组中,更新
left = mid + 1。
- 如果目标元素在左子数组中,更新
- 根据判断结果更新搜索范围:
-
结束条件:
- 当
left > right时,表示搜索范围为空,说明未找到目标元素,返回-1表示查找失败。
- 当
这样,在循环过程中,根据中点元素与两端元素的关系,逐步缩小搜索范围,直到找到目标元素或者确定目标元素不存在为止。
图示

实例
我们来举一个例子详细说明在一个被旋转过的有序数组中搜索目标元素的过程。
假设有一个被旋转过的有序数组 nums = [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2],我们要在其中搜索目标元素 0。
-
初始化:
- 初始时,
left = 0,right = 6,整个数组[4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2]是候选的搜索范围。
- 初始时,
-
第一次循环:
- 计算中点索引
mid = (0 + 6) / 2 = 3,中点元素为nums[3] = 7。 - 检查
nums[mid]与目标元素0的关系:nums[mid] = 7 > 0,说明中点元素在旋转点的左侧,因此我们需要判断目标元素是否在右子数组中。
- 计算中点索引
-
更新搜索范围:
- 右半部分
[0, 1, 2]是有序的,且0可能在右侧,所以更新left = mid + 1 = 4。
- 右半部分
-
第二次循环:
- 计算新的中点索引
mid = (4 + 6) / 2 = 5,中点元素为nums[5] = 1。 - 检查
nums[mid]与目标元素0的关系:nums[mid] = 1 > 0,说明中点元素在旋转点的右侧,因此我们需要判断目标元素是否在左子数组中。
- 计算新的中点索引
-
更新搜索范围:
- 左半部分
[4, 5, 6, 7]是有序的,且0可能在左侧,所以更新right = mid - 1 = 4。
- 左半部分
-
第三次循环:
- 计算新的中点索引
mid = (4 + 4) / 2 = 4,中点元素为nums[4] = 0。 - 发现
nums[mid] == target,即找到了目标元素,返回mid = 4。
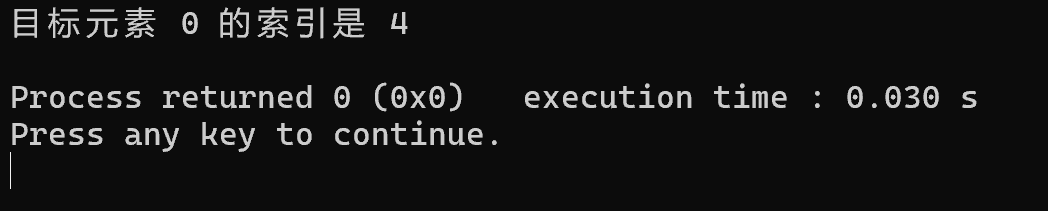
- 计算新的中点索引
通过以上步骤,我们成功地在被旋转过的有序数组中找到了目标元素 0 的索引为 4。
代码实现
C++代码实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int search(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.size() - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 找到目标元素,返回索引
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
// 左半部分有序
if (nums[left] <= nums[mid]) {
// 目标元素在左侧
if (nums[left] <= target && target < nums[mid]) {
right = mid - 1;
}
// 目标元素在右侧
else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
// 右半部分有序
else {
// 目标元素在右侧
if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[right]) {
left = mid + 1;
}
// 目标元素在左侧
else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
// 未找到目标元素,返回-1
return -1;
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums = {4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2};
int target = 0;
int index = search(nums, target);
if (index != -1) {
cout << "目标元素 " << target << " 的索引是 " << index << endl;
} else {
cout << "未找到目标元素 " << target << endl;
}
return 0;
}Java代码实现
java
import java.util.Arrays;
public class RotatedSortedArraySearch {
public static int search(int[] nums, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = nums.length - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
// 找到目标元素,返回索引
if (nums[mid] == target) {
return mid;
}
// 左半部分有序
if (nums[left] <= nums[mid]) {
// 目标元素在左侧
if (nums[left] <= target && target < nums[mid]) {
right = mid - 1;
}
// 目标元素在右侧
else {
left = mid + 1;
}
}
// 右半部分有序
else {
// 目标元素在右侧
if (nums[mid] < target && target <= nums[right]) {
left = mid + 1;
}
// 目标元素在左侧
else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
}
// 未找到目标元素,返回-1
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] nums = {4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2};
int target = 0;
int index = search(nums, target);
if (index != -1) {
System.out.println("目标元素 " + target + " 的索引是 " + index);
} else {
System.out.println("未找到目标元素 " + target);
}
}
}Python代码实现
python
def search(nums, target):
left = 0
right = len(nums) - 1
while left <= right:
mid = (left + right) // 2
# 找到目标元素,返回索引
if nums[mid] == target:
return mid
# 左半部分有序
if nums[left] <= nums[mid]:
# 目标元素在左侧
if nums[left] <= target < nums[mid]:
right = mid - 1
# 目标元素在右侧
else:
left = mid + 1
# 右半部分有序
else:
# 目标元素在右侧
if nums[mid] < target <= nums[right]:
left = mid + 1
# 目标元素在左侧
else:
right = mid - 1
# 未找到目标元素,返回-1
return -1
nums = [4, 5, 6, 7, 0, 1, 2]
target = 0
index = search(nums, target)
if index != -1:
print(f"目标元素 {target} 的索引是 {index}")
else:
print(f"未找到目标元素 {target}")运行结果
简单总结
在本节中,我们学习的这些算法是解决特定问题的有效工具,可以在较短的时间内找到目标元素,尤其对于大型数据集来说,效率更为突出。对于二分查找算法,它要求目标数组必须是有序的,然后通过每次将搜索范围缩小一半的方式来快速定位目标元素,效率极高。而在旋转数组中搜索的问题中,我们可以通过修改二分查找的条件来适应数组的特殊性,从而解决了这一类问题。
第三节
知识点:
(1)查找三数之和(2)时间旅行者的地图:跳表
查找三数之和
题目描述
给你一个整数数组 nums ,判断是否存在三元组 [nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]] 满足 i != j、i != k 且 j != k ,同时还满足 nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0 。请你返回所有和为 0 且不重复的三元组。
数据范围
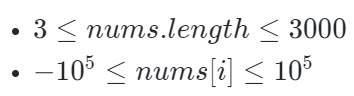
解法
我们考虑一种朴素的做法,也就是使用三重 for 循环,直接暴力搜索枚举到的三个数是否可以满足。这样的做法时间复杂度为 O() 显然不太行。我们考虑在此基础上进行优化。考虑只枚举其中两个数,因为总和是确定的,所以我们可以直接考虑判断第三个数是否存在。
于是我们得到一种优化的解法:先排序,然后枚举前两个数,二分查找最后的数中有没有我们要找的那个数即可。时间复杂度为 O() ,还是有点卡的。于是我们再看能不能优化。
我们注意到,先排序之后,枚举第二个数的时候,随着第二个数的增长,第三个数是单调递减的。于是我们想到将找第三个数的二分查找替换成双指针。这样的复杂度就是 O() 的了,比较充裕。
代码实现
C++代码实现
cpp
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> threeSum(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
vector<vector<int>> ans;
for (int first = 0; first < n; ++first) {
if (first > 0 && nums[first] == nums[first - 1]) {
continue;
}
int third = n - 1;
int target = -nums[first];
for (int second = first + 1; second < n; ++second) {
if (second > first + 1 && nums[second] == nums[second - 1]) {
continue;
}
while (second < third && nums[second] + nums[third] > target) {
--third;
}
if (second == third) {
break;
}
if (nums[second] + nums[third] == target) {
ans.push_back({nums[first], nums[second], nums[third]});
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};Java代码实现
java
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
Arrays.sort(nums);
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList<List<Integer>>();
for (int first = 0; first < n; ++first) {
if (first > 0 && nums[first] == nums[first - 1]) {
continue;
}
int third = n - 1;
int target = -nums[first];
for (int second = first + 1; second < n; ++second) {
if (second > first + 1 && nums[second] == nums[second - 1]) {
continue;
}
while (second < third && nums[second] + nums[third] > target) {
--third;
}
if (second == third) {
break;
}
if (nums[second] + nums[third] == target) {
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(nums[first]);
list.add(nums[second]);
list.add(nums[third]);
ans.add(list);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}Python代码实现
python
class Solution:
def threeSum(self, nums: List[int]) -> List[List[int]]:
n = len(nums)
nums.sort()
ans = list()
for first in range(n):
if first > 0 and nums[first] == nums[first - 1]:
continue
third = n - 1
target = -nums[first]
for second in range(first + 1, n):
if second > first + 1 and nums[second] == nums[second - 1]:
continue
while second < third and nums[second] + nums[third] > target:
third -= 1
if second == third:
break
if nums[second] + nums[third] == target:
ans.append([nums[first], nums[second], nums[third]])
return ans时间旅行者的地图:跳表
跳表(Skip List)是一种数据结构,类似于链表,但它通过添加一些额外的链接来提高查找的效率。跳表允许快速查找、插入和删除操作,其平均时间复杂度为 O(logn),与平衡二叉树相当,但实现上更简单。
结构和原理
跳表是由多层链表组成的,其中每一层都是原始链表的一个子集。最底层是原始链表,每一层向上都是原始链表的稀疏表达。每个节点都包含一个指向同一层中下一个节点的指针,以及一个指向下一层中相同位置节点的指针。
跳表的核心思想是使用"跳跃"来快速搜索。通过跳跃,算法可以直接跳到更远的节点,而不必遍历每个节点。跳表的高效性依赖于它的层数和每一层的节点数量。
为了更好地理解跳表的工作原理和操作过程,我们可以通过一个具体的例子来说明。在这个例子中,我们将插入一些元素到跳表中,并通过图示展示每一步的变化。
操作
-
查找: 从头节点开始,沿着每一层前进,直到找到目标值或者找到比目标值大的节点。如果目标值存在,则返回节点;如果不存在,则返回空。
-
插入: 首先执行查找操作,找到插入位置。然后在适当的层上插入新节点,并更新相应的指针。
-
删除: 同样,首先执行查找操作,找到要删除的节点。然后删除该节点,并更新相应的指针。
时间复杂度
- 查找: 平均情况下为 O(logn),最坏情况下为 O(n)。
- 插入和删除: 平均情况下为 O(logn),最坏情况下为 O(n)。这是因为在插入或删除时可能需要重新平衡跳表的结构。
优缺点
优点:
- 相对于平衡树来说,实现更简单。
- 在大部分操作(查找、插入、删除)的平均情况下具有较好的性能。
- 支持动态操作,插入和删除操作的时间复杂度相对较低。
缺点:
- 跳表需要额外的空间来存储指针,空间复杂度较高。
- 不如平衡树在最坏情况下的性能表现好,最坏情况下的时间复杂度为 O(n)。
- 实现稍微复杂一些,相对于链表来说。
应用场景
- 数据库中的索引结构。
- Redis 中的有序集合(Sorted Set)实现。
- 跳表可以用作一种替代数据结构,用于实现有序集合、有序映射等,尤其适用于需要高效插入、删除和查找操作的场景。
跳表示例
我们将插入以下元素到跳表中:3, 6, 7, 9, 12, 19, 17, 26, 21
初始状态
跳表为空,仅包含一个头节点。
Level 3: None
Level 2: None
Level 1: None
Level 0: None插入 3
生成的随机层级为 1。
Level 3: None
Level 2: None
Level 1: 3 -> None
Level 0: 3 -> None插入 6
生成的随机层级为 2。
Level 3: None
Level 2: 6 -> None
Level 1: 3 -> 6 -> None
Level 0: 3 -> 6 -> None插入 7
生成的随机层级为 1。
Level 3: None
Level 2: 6 -> None
Level 1: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> None
Level 0: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> None插入 9
生成的随机层级为 3。
Level 3: 9 -> None
Level 2: 6 -> 9 -> None
Level 1: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> None
Level 0: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> None插入 12
生成的随机层级为 2。
Level 3: 9 -> None
Level 2: 6 -> 9 -> 12 -> None
Level 1: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> 12 -> None
Level 0: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> 12 -> None插入 19
生成的随机层级为 1。
Level 3: 9 -> None
Level 2: 6 -> 9 -> 12 -> None
Level 1: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> 12 -> 19 -> None
Level 0: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> 12 -> 19 -> None插入 17
生成的随机层级为 1。
Level 3: 9 -> None
Level 2: 6 -> 9 -> 12 -> None
Level 1: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> 12 -> 17 -> 19 -> None
Level 0: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> 12 -> 17 -> 19 -> None插入 26
生成的随机层级为 2。
Level 3: 9 -> None
Level 2: 6 -> 9 -> 12 -> 26 -> None
Level 1: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> 12 -> 17 -> 19 -> 26 -> None
Level 0: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> 12 -> 17 -> 19 -> 26 -> None插入 21
生成的随机层级为 1。
Level 3: 9 -> None
Level 2: 6 -> 9 -> 12 -> 26 -> None
Level 1: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> 12 -> 17 -> 19 -> 21 -> 26 -> None
Level 0: 3 -> 6 -> 7 -> 9 -> 12 -> 17 -> 19 -> 21 -> 26 -> None代码实现
C++代码实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
const int MAX_LEVEL = 6;
struct Node {
int value;
vector<Node*> forward;
Node(int level, int value) : value(value) {
forward.resize(level, nullptr);
}
};
class SkipList {
private:
Node* header;
int level;
public:
SkipList() {
header = new Node(MAX_LEVEL, 0);
level = 0;
}
int randomLevel() {
int level = 1;
while (rand() % 2 == 0 && level < MAX_LEVEL)
level++;
return level;
}
void insert(int value) {
Node* update[MAX_LEVEL];
Node* current = header;
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current->forward[i] != nullptr && current->forward[i]->value < value)
current = current->forward[i];
update[i] = current;
}
int newLevel = randomLevel();
if (newLevel > level) {
for (int i = level; i < newLevel; i++)
update[i] = header;
level = newLevel;
}
Node* newNode = new Node(newLevel, value);
for (int i = 0; i < newLevel; i++) {
newNode->forward[i] = update[i]->forward[i];
update[i]->forward[i] = newNode;
}
}
bool search(int value) {
Node* current = header;
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current->forward[i] != nullptr && current->forward[i]->value < value)
current = current->forward[i];
}
current = current->forward[0];
return current != nullptr && current->value == value;
}
};
int main() {
SkipList skipList;
skipList.insert(3);
skipList.insert(6);
skipList.insert(9);
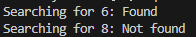
cout << "Searching for 6: " << (skipList.search(6) ? "Found" : "Not found") << endl;
cout << "Searching for 8: " << (skipList.search(8) ? "Found" : "Not found") << endl;
return 0;
}Java代码实现
java
import java.util.Random;
class Node {
int value;
Node[] forward;
Node(int level, int value) {
this.value = value;
this.forward = new Node[level];
}
}
public class SkipList {
private static final int MAX_LEVEL = 6;
private Node header;
private int level;
public SkipList() {
this.header = new Node(MAX_LEVEL, 0);
this.level = 0;
}
private int randomLevel() {
int level = 1;
Random rand = new Random();
while (rand.nextBoolean() && level < MAX_LEVEL)
level++;
return level;
}
public void insert(int value) {
Node[] update = new Node[MAX_LEVEL];
Node current = header;
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current.forward[i] != null && current.forward[i].value < value)
current = current.forward[i];
update[i] = current;
}
int newLevel = randomLevel();
if (newLevel > level) {
for (int i = level; i < newLevel; i++)
update[i] = header;
level = newLevel;
}
Node newNode = new Node(newLevel, value);
for (int i = 0; i < newLevel; i++) {
newNode.forward[i] = update[i].forward[i];
update[i].forward[i] = newNode;
}
}
public boolean search(int value) {
Node current = header;
for (int i = level - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
while (current.forward[i] != null && current.forward[i].value < value)
current = current.forward[i];
}
current = current.forward[0];
return current != null && current.value == value;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SkipList skipList = new SkipList();
skipList.insert(3);
skipList.insert(6);
skipList.insert(9);
System.out.println("Searching for 6: " + (skipList.search(6) ? "Found" : "Not found"));
System.out.println("Searching for 8: " + (skipList.search(8) ? "Found" : "Not found"));
}
}Python代码实现
python
import random
MAX_LEVEL = 6
class Node:
def __init__(self, level, value):
self.value = value
self.forward = [None] * level
class SkipList:
def __init__(self):
self.header = Node(MAX_LEVEL, 0)
self.level = 0
def random_level(self):
level = 1
while random.random() < 0.5 and level < MAX_LEVEL:
level += 1
return level
def insert(self, value):
update = [None] * MAX_LEVEL
current = self.header
for i in range(self.level - 1, -1, -1):
while current.forward[i] and current.forward[i].value < value:
current = current.forward[i]
update[i] = current
new_level = self.random_level()
if new_level > self.level:
for i in range(self.level, new_level):
update[i] = self.header
self.level = new_level
new_node = Node(new_level, value)
for i in range(new_level):
new_node.forward[i] = update[i].forward[i]
update[i].forward[i] = new_node
def search(self, value):
current = self.header
for i in range(self.level - 1, -1, -1):
while current.forward[i] and current.forward[i].value < value:
current = current.forward[i]
current = current.forward[0] if current.forward[0] else None
return current and current.value == value
if __name__ == "__main__":
skip_list = SkipList()
skip_list.insert(3)
skip_list.insert(6)
skip_list.insert(9)
print("Searching for 6:", "Found" if skip_list.search(6) else "Not found")
print("Searching for 8:", "Found" if skip_list.search(8) else "Not found")运行结果
简单总结
本节主要学习了一些高级的搜索技巧,其中跳表用的较少,读者们了解即可。但是"三数之和"这样经典的题目应该掌握。