六、Mybatis
6.1 之前的 JDBC 的使用缺点?
- 大量的代码重复
- 加载驱动,获得连接,获得执行语句,执行 sql, 关闭连接
- 手动加载驱动,创建连接 (Connection), 关连接
- 封装数据麻烦 (ORM)
- 效率不高 (没有缓存)
6.2 Mybatis 的介绍

MyBatis 本是 apache 的一个开源项目
iBatis,2010 年这个项目由 apache software foundation 迁移到了 google code,并且改名为**MyBatis** 。2013 年 11 月迁移到Github。iBATIS 一词来源于 "internet" 和 "abatis" 的组合,是一个基于 Java 的持久层 (Dao)框架。用于操作数据库。
MyBatis 是一款优秀的持久层框架,它支持定制化 SQL 、存储过程以及高级映射。MyBatis 避免了几乎所有的 JDBC 代码和手动设置参数以及获取结果集 。MyBatis 可以使用简单的 XML 或注解来配置和映射原生信息,将接口和 Java 的 POJOs (Plain Ordinary Java Object, 普通的 Java 对象) 映射成数据库中的记录。且有缓存机制,可以提高查询效率。
Mybatis 是一个**
半ORM框架** ,可以消除 JDBC 的代码和步骤,让开发者**只关注SQL**本身。
- ORM 是对象关系映射,是指数据库表和 java 实体类一一对应.
- 半 ORM 框架,还是需要写 SQL, 由框架帮你完成映射
- 完全 ORM 框架,连 SQL 都不需要写,只需要遵循 ORM 的要求,就会自动生成 SQL 完成映射 (Hibernate,JPA,MybatisPlus 等)
6.3 xml 方式整合 Mybatis [重点]
xml 方式在编写复杂 SQL 时,更适合
6.3.1 环境
mybatis 和 druid 的 springboot 环境下的依赖 (别忘了 web 依赖)
xml
XML
<!-- 小辣椒 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!-- mysql驱动 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<!-- druid 数据库连接池 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.1.10</version>
</dependency>
<!-- mybatis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>准备数据库
sql
sql
CREATE TABLE `tb_user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT COMMENT '用户编号',
`username` varchar(10) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '用户名',
`password` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '密码',
`phone` varchar(11) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '手机号',
`create_time` date DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '注册时间',
`money` double(10,2) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '账户余额',
`sex` int(1) DEFAULT NULL COMMENT '性别 1男2女',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=15 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8实体类
java
@Data
public class User {
private int id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String phone;
private Date createTime;
private double money;
private int sex;
}6.3.2 编写接口和映射文件
接口就是我们之前的 Dao 层接口,Mybatis 习惯叫做 Mapper, 所以先创建 mapper 包,然后再在其中创建接口文件
java
public interface UserMapper {
User findUserById(int id);
}以前是写接口的实现类,现在 mybatis 的接口实现功能由 xml 文件来实现了在 resources / 下创建 m
XML
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<!DOCTYPE mapper
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN"
"https://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd">
<!--namespace名称空间,根据接口的全限定名,来关联接口和xml文件-->
<mapper namespace="com.qf.day34mybatis.mapper.UserMapper">
<!--前面接口中定义的方法,这里要写标签,然后写sql-->
<!--根据需求,写不同的标签,
查询 <select>
更新 <update>
删除 <delete>
插入 <insert>
-->
<!--根据id查询用户-->
<!--
id: 是前面接口的方法名
resultType: 结果类型,即语句的返回值类型,查询的结果会封装到这个类型的对象中
-->
<!--resultType,是要封装的类型的路径,比较长,如果配置type-aliases-package,可以省略包名-->
<select id="getUserById" resultType="User">
<!--原来?的地方,现在mybatis写的#{},内部写变量名-->
select * from tb_user where id = #{id}
</select>
</mapper>6.3.3 yml 文件
SpringBoot 项目,默认配置文件类型是 properties 改成后缀为 yml 的文件
yaml
XML
server:
port: 8080
# 连接数据库的信息
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb5?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&characterEncoding=utf8&useUnicode=true
username: root
password: root
# 数据库连接池
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
# mybatis配置
mybatis:
# 扫描映射文件
mapper-locations: classpath:mapper/*.xml
# 配置别名扫描的包
type-aliases-package: com.example.entity
configuration:
# 开启驼峰映射配置
map-underscore-to-camel-case: true
# 打印执行过程的sql信息
logging:
level:
com.com.example.dao: DEBUG6.3.4 扫描 mapper
主类扫描 mapper
java
@SpringBootApplication
@MapperScan("com.qf.mapper") // 扫描mapper接口,创建代理对象
public class TestSpringbootApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(TestSpringbootApplication.class, args);
}
}6.3.5 测试
创建 controller,service , 按以前三层架构,依次调用即可// Controller
java
package com.qf.day34mybatis.controller;
import com.qf.day34mybatis.entity.User;
import com.qf.day34mybatis.service.UserService;
import com.qf.day34mybatis.utils.R;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
// 根据id查询用户
@GetMapping("/{id}")
public R getUserById(@PathVariable Integer id) {
User user = userService.getUserById(id);
if (user == null) {
return R.fail("用户不存在");
}
return R.ok(user);
}
}// 业务层 (接口 + 实现类)
java
public interface UserService {
User getUserById(Integer id);
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public User getUserById(Integer id) {
return userMapper.getUserById(id);
}
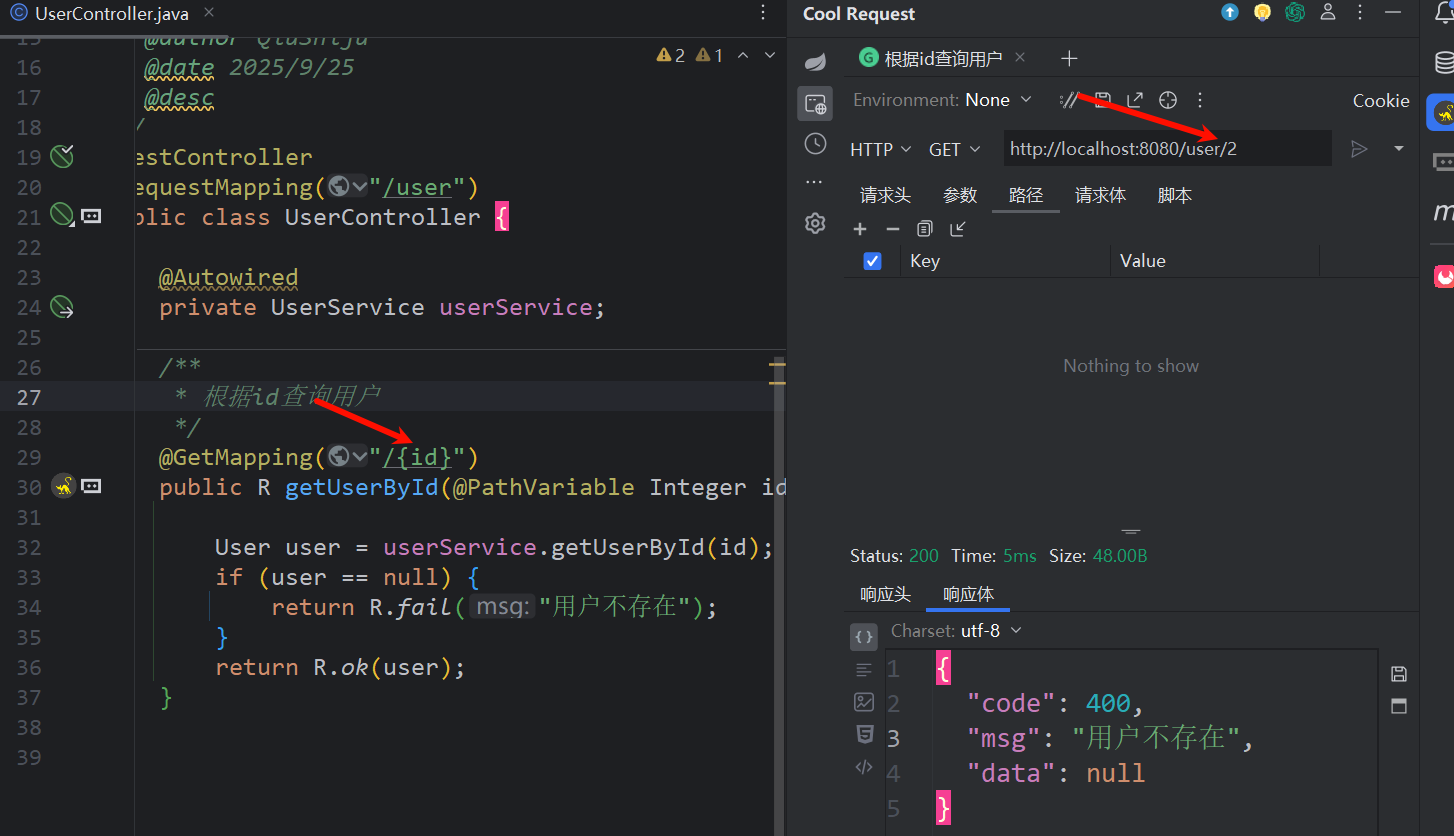
}启动项目,发出请求localhost:8080/user/1即可
完整项目结构
6.3.6 接口工具测试
idea 下载 Cool Request 插件
6.4 CRUD [核心]
6.4.1 查询
6.4.1.1 单条件查询
详情看入门演示【特别注意:ORM 时字段名要和实体类属性一致,否则封装失败】
对象关系映射(Object Relational Mapping)
6.4.1.2 查询全部
设计查询接口方法
java
public interface UserMapper {
User findUserById(int id);
List<User> findAll();
}映射文件xml
XML
<!-- 一个标签,就是一个SQL执行的语句 -->
<!-- 【注意】虽然查询返回集合,但是返回类型此处还要写集合中存储的类型 -->
<!-- 【或者这样理解】虽然返回集合,此处定义的是查询返回要封装的实体类类型 -->
<select id="findAll" resultType="User">
select * from tb_user
</select>一样的设计 Controller,Service 调用即可,启动项目测试
java
// Server
public interface UserServer {
List<User> findAll();
}
// ServerImpl
@Service
public class UserServerImpl implements UserServer {
@Autowired
private UserDao userDao;
public List<User> findAll(){
return (List<User>) userDao.findAll();
}
}
// Controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@Autowired
private UserServer userServer;
@RequestMapping("/findAll")
public List<User> findAll(){
return userServer.findAll();
}
}6.4.1.3 多参数查询
需求: 通过用户名和密码查询接口方法
java
public interface UserMapper {
User findUserByLogin(String username,String password);
}映射文件xml
XML
<select id="findUserByLogin" resultType="com.qf.model.User">
<!-- 默认是不支持传多个参数,传入多个参数时,需要如下操作 -->
<!--
方案1: #{}内按顺序写param1,param2,....或者agr0,arg1
但是此种方式不建议
-->
select * from tb_user
where username = #{param1} and password = #{param2}
</select>(解决方案 2)(推荐) 接口方法(参数加注解)
java
public interface UserMapper {
User findUserByLogin(
@Param("username") String username,
@Param("password") String password);
}映射文件xml
XML
<select id="findUserByLogin" resultType="User">
<!-- 默认是不支持传多个参数,传入多个参数时,需要如下操作(2选1) -->
<!--
方案2: 1)在接口方法参数前添加注解@Param并设置注解参数
2)在#{}内写注解中的值
-->
select * from tb_user
where username = #{username} and password = #{password}
</select>6.4.1.4 Map 参数查询
需求:查询时,就要传递分页数据,又要传递模糊查询关键词,此时就可以使用 Map 来封装参数 (即请求中参数有点多....)接口方法
java
public interface UserMapper {
// Mapper接口传递map参数
List<User> search(HashMap<String, String> map);
}映射文件xml
XML
<!--接口虽然返回的List,但是此处resultType写的是User-->
<!--此处是模拟搜索,先固定查询条件(查询用户名和密码都包含指定字符串的用户)-->
<select id="search" resultType="User">
select * from tb_user
where username like '%${username}%' and password like '%${password}%'
<!--传递是map,${}或者#{} 写的是map的key-->
</select>强调:前面使用 map 传递参数,${} #{} 内部需要根据 map 的 key 来取值:::
#{}vs${}的区别:
#{}:预编译参数,会自动转义 ,能防止 SQL 注入,推荐使用 (需配合CONCAT函数拼接通配符)。${}:直接字符串替换 ,有 SQL 注入风险,仅适用于确定无注入风险的场景(比如固定参数)。
java
// 搜索,模拟传递Map参数
@GetMapping("/search")
public R search(@RequestParam HashMap<String,String> map) {
List<User> list = userService.search(map);
return R.ok(list);
}6.4.1.5 对象参数
比如登录,前端传递 (用户名 + 密码)(手机号 + 验证码) 等等
- 可以会传递多个参数,上面讲过可以在 Mapper 接口的方法中设计注解来解决或者使用 Map 封装数据
- 但是,常见的方案是用对象接收前端数据,向业务层 / 持久层传递对象!接口方法
java
public interface UserMapper {
User loginV2(User user);
}映射文件
XML
<select id="loginV2" resultType="com.qf.day34mybatis.entity.User">
select * from tb_user
where username = #{username} and password = #{password}
<!--#{}是对象的属性名-->
</select>controller
java
/**登录,使用对象接收
* 前端发送json格式数据
*/
@PostMapping("/loginv2")
public R loginV2(@RequestBody User user){
User user2 = userService.loginV2(user);
if (user2 == null) {
return R.fail("登录失败");
}
return R.ok(user2);
}6.4.2 增加
需求:如下场景
前端使用 JSON 发送,后端使用对象接收还得使用 @RequestBody 配合
controller
java
/**
* 添加用户
* 添加/更新/登录 发post请求
* 前端的数据格式是json
*/
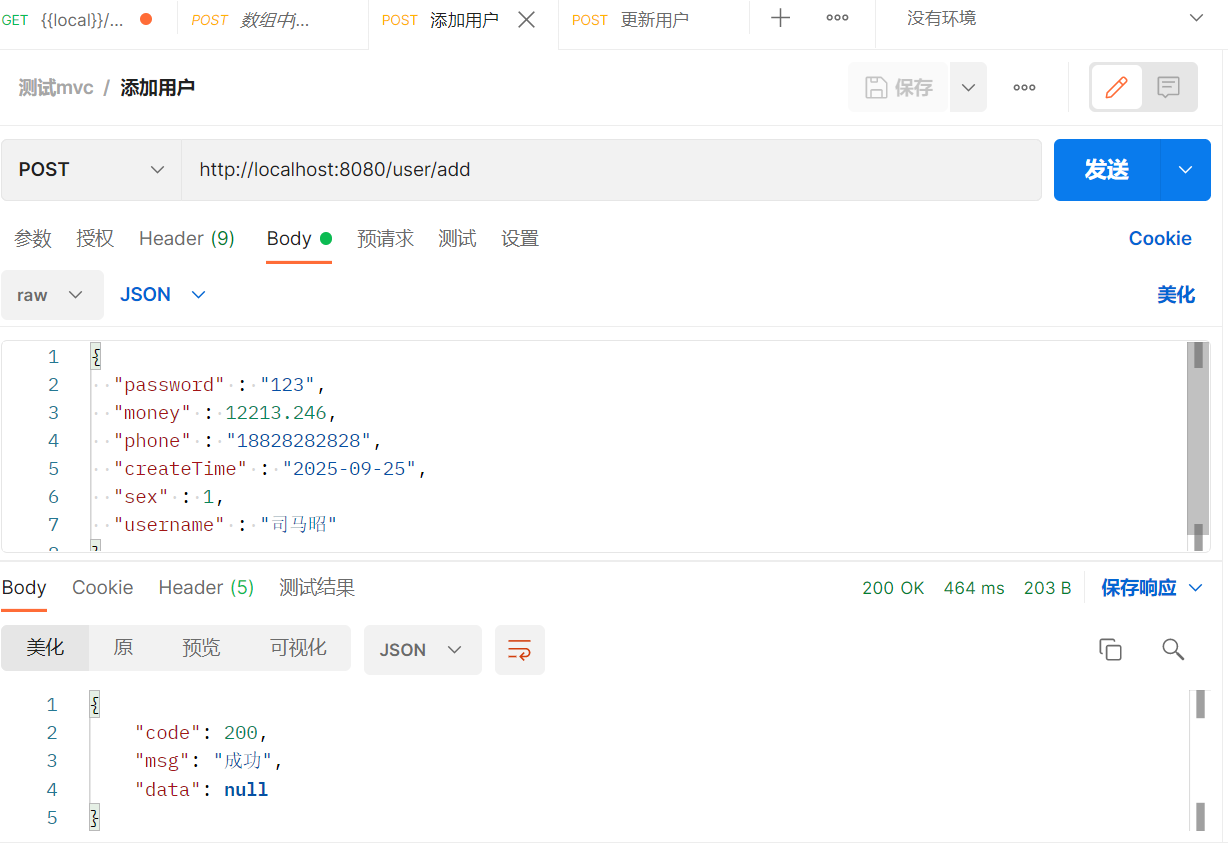
@PostMapping("/add")
public R addUser(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("UserController.addUser收到数据,user"+user);
// 调用业务层
// 增删改,可以不要返回值
// 也可以要返回值---> int / boolean
userService.addUser(user);
return R.ok();
}service
java
public interface UserService {
void addUser(User user);
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Override
public void addUser(User user) {
userMapper.addUser(user);
}
}Mapper 接口方法
java
public interface UserMapper {
void addUser(User user);
}Mapper 映射文件
xml
XML
<!--插入,增删改标签内不需要定义返回值类型,但是想返回只需要接口的方法定义返回值类int boolean-->
<insert id="addUser">
insert into tb_user
(username , password,phone,create_time,money,sex)
values (#{username},#{password},#{phone},#{createTime},#{money},#{sex})
</insert>测试
6.4.3 修改
6.4.3 修改
需求场景:如下暂定:需求就是只要是传递过来的数据都会修改 (全量更新)
java
// 更新
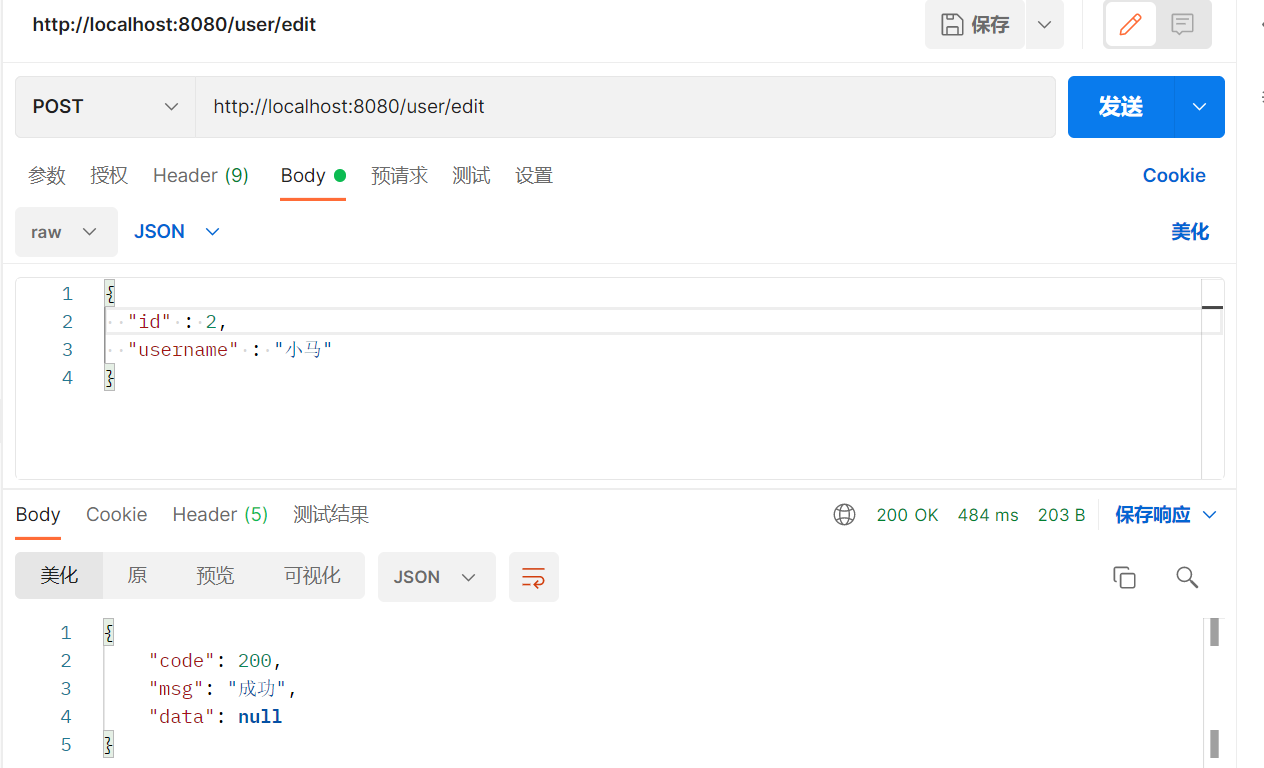
@PostMapping("/edit")
public R editUser(@RequestBody User user){
userService.updateById(user);
return R.ok();
}service....接口方法
java
public interface UserMapper {
void updateById(User user); // 修改方法的参数是对象
}映射文件
xml
XML
<update id="updateById">
<!-- 对象参数,#{}内属性名 -->
update tb_user set username=#{username},password=#{password},
phone= #{phone},create_time=#{createTime},money=#{money},sex=#{sex}
where id = #{id}
</update>测试
6.4.4 删除 (自学)
需求:场景如下
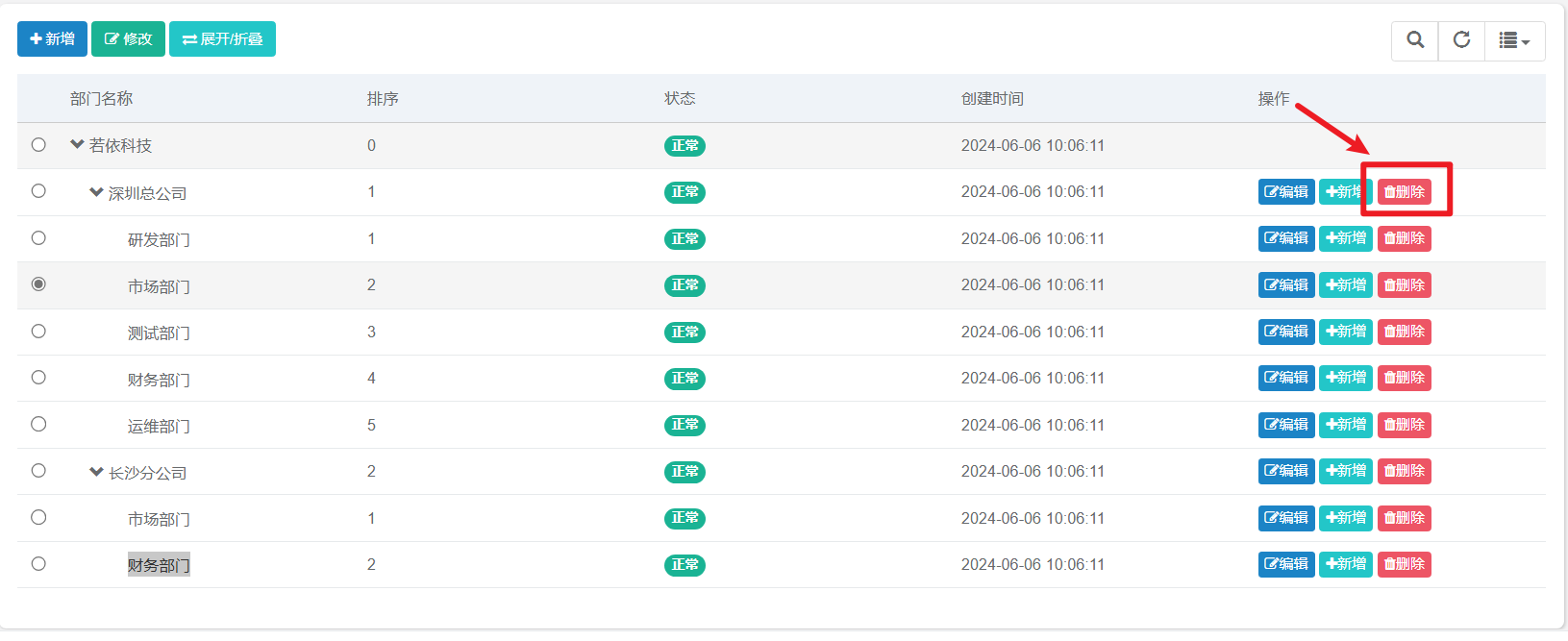
在前端,设置删除按钮,点击发出请求,请求中携带这条数据的 id
接口方法
java
int deleteById (int id);映射文件 xml
XML
<delete id="deleteById">
delete from tb_user where id = #{id}
</delete>6.5 动态 SQL【重要!!!】
帮助我们拼接 SQL
MyBatis 动态 SQL 是一个模板适配所有查询场景 ,替代上面 4 条原生 SQL,核心靠
<where>和<if>标签实现「条件动态拼接」
XML
// 所有查询场景
select * from tb_user where username = ? and sex = ?
select * from tb_user
select * from tb_user where username= ?
select * from tb_user where sex = ?
// 该模板会根据传入的参数(用户名 / 性别)自动拼接条件,适配所有查询场景
<select id="findUserByCondition" resultType="User">
select * from tb_user
<where>
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
and username = #{username} <!-- 建议用#{参数名},比?更直观,MyBatis自动转? -->
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
and sex = #{sex}
</if>
</where>
</select>常见的动态 SQL 语法
- sql 片段
- where+if
- set+if
- foreach
- trim
- choose-when-otherwise
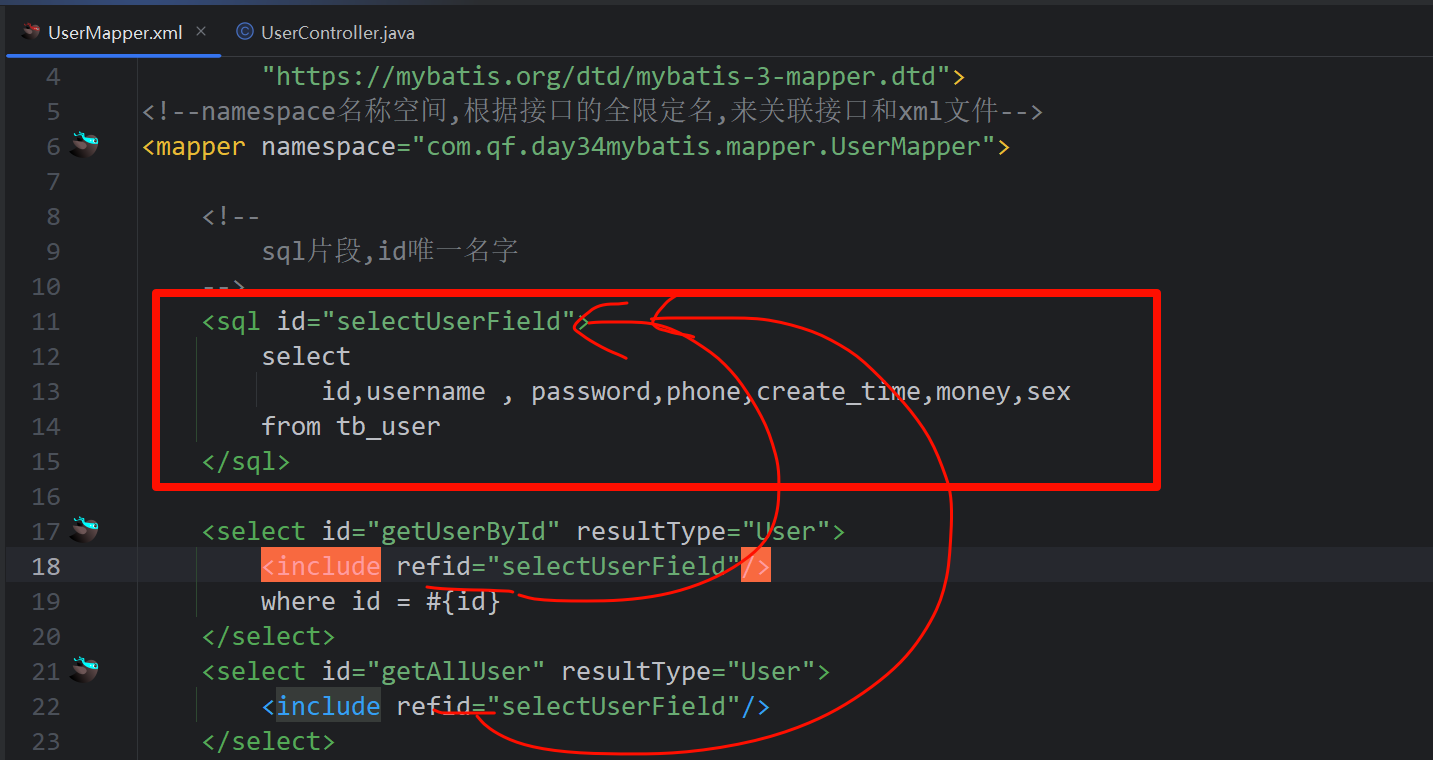
6.5.1 sql 片段
抽取重复 sql 语句
使用<sql id="">标签定义重复的 sql 语句
在下方的 sql 语句中使用 **<include refid="">**将其引入
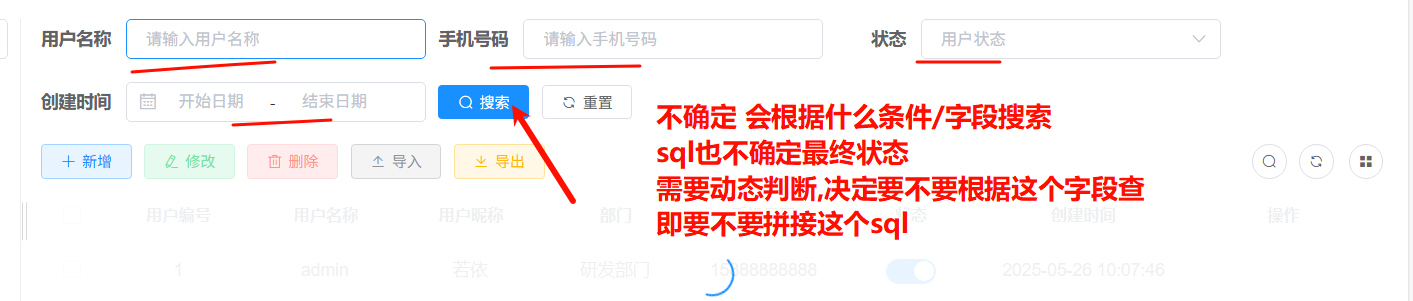
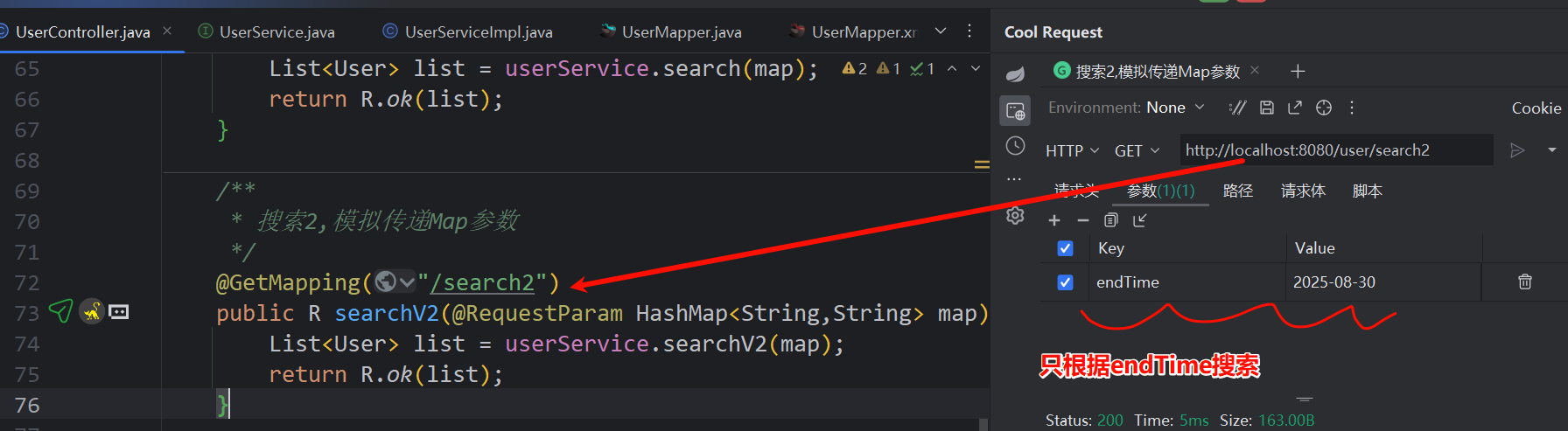
6.5.2 where+if [重点]
场景:搜索
测试
Controller
java
// 搜索2,模拟传递Map参数
@GetMapping("/search2")
public R searchV2(@RequestParam HashMap<String,String> map) {
List<User> list = userService.searchV2(map);
return R.ok(list);
}service ...
java
public interface UserService {
List<User> searchV2(HashMap<String, String> map);
}
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
@Override
public List<User> searchV2(HashMap<String, String> map) {
return userMapper.searchV2(map);
}
}mapper
java
public interface UserMapper {
List<User> searchV2(HashMap<String, String> map);
}模拟的效果是
- 根据用户名,密码,手机号 模糊搜索
- 根据注册时间 范围搜索
xml
XML
<!--
sql片段,id唯一名字
-->
<sql id="selectUserField">
select
id,username , password,phone,create_time,money,sex
from tb_user
</sql>
<!--模糊搜索,演示动态sql where + if-->
<select id="searchV2" resultType="User">
<include refid="selectUserField"/>
<!--where标签,如果下方有条件,会自动产出where关键词,如果没有任何条件,where就消失-->
<!--where会自动去掉多于的and-->
<where>
<!--取出map的键所对应值,判断有无数据-->
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
and username like '%${username}%'
</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone != ''">
and phone like '%${phone}%'
</if>
<if test="password != null and password != ''">
and password like '%${password}%'
</if>
<if test="beginTime != null">
<!-- 大于>运算不能使用,需要写成 >-->
and create_time > #{beginTime}
</if>
<if test="endTime != null">
<!--小于< 运算,需要写成 <-->
and create_time < #{endTime}
</if>
</where>
</select>特别注意: xml 文件中,
大于 > 运算不能使用,需要写成 >
小于 < 运算,需要写成**<**
6.5.3 set+if
场景:动态更新 (部分更新)
之前更新是全量更新,只要没有传递数据,即认为要置为 null
其实我们认为,不传递数据是不修改,保持原样!
controller
java
/**
* 更新2 动态更新,即没有传递的数据,即不更新保持原样
*/
@PostMapping("/edit2")
public R editUser2(@RequestBody User user){
userService.updateById2(user);
return R.ok();
}动态更新 mapper xml
| 传入参数情况 | 最终拼接的 SQL(简化版) | 效果说明 |
|---|---|---|
| 仅传 id=1、username="zhangsan" | update tb_user set username = ? where id = ? |
只更新用户名,其他字段不变 |
| 传 id=1、password="123456"、sex=1 | update tb_user set password = ?, sex = ? where id = ? |
只更新密码和性别 |
| 传 id=1、所有字段都有值 | update tb_user set username=?, password=?, phone=?, create_time=?, sex=?, money=? where id=? |
所有字段都更新,无多余逗号 |
| 仅传 id=1、无其他字段 | 拼接为 update tb_user where id = ?(语法错误) |
XML
<!--动态更新-->
<update id="updateById2">
update tb_user
<!--set标签, 1)会产生set关键词, 2) 取出多于最后一个,逗号-->
<set>
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
username = #{username},
</if>
<if test="password != null and password != ''">
password = #{password},
</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone != ''">
phone = #{phone},
</if>
<!--createTime是Date类型,不能和 字符串'' 判断-->
<if test="createTime != null">
create_time = #{createTime},
</if>
<!--sex是Integer类型,不能和 字符串'' 判断-->
<if test="sex != null">
sex = #{sex},
</if>
<if test="money != null">
money = #{money},
</if>
</set>
where id = #{id}
</update>6.5.4 foreach
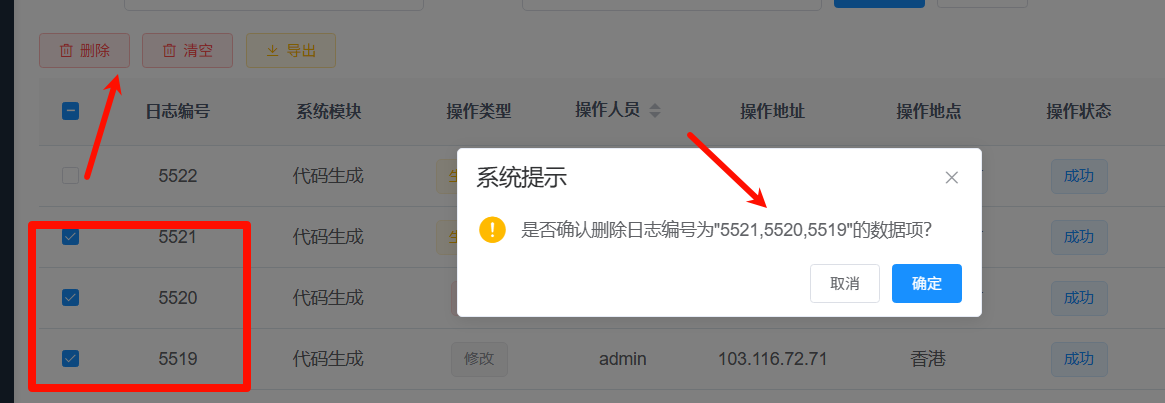
场景
- 批量删除
- delete from tb_user where id in (1,2,3);
- 批量插入 (自学)
测试
Controller
java
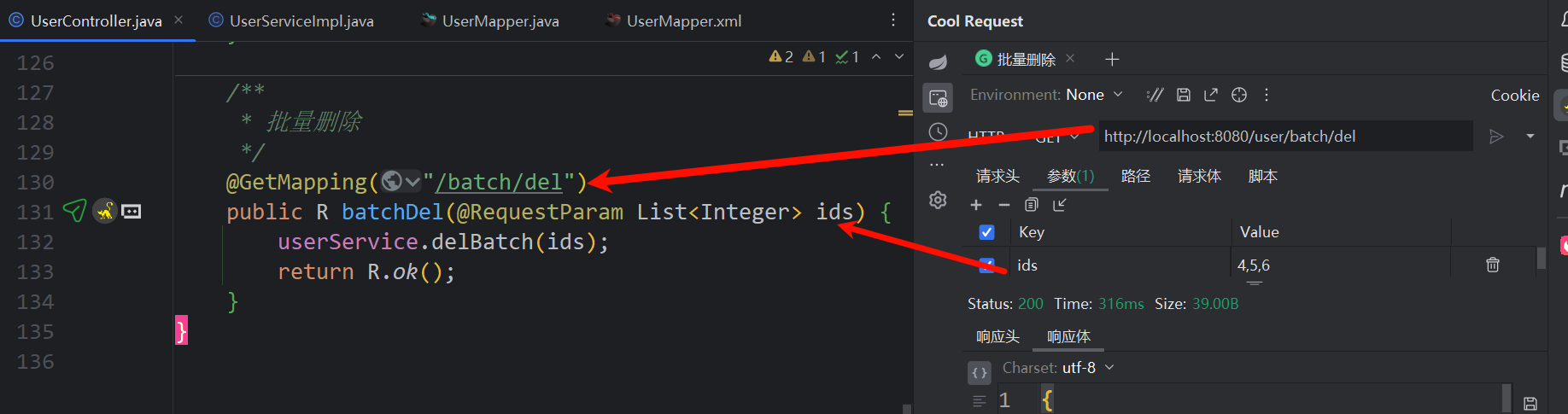
// 批量删除
@GetMapping("/batch/del")
public R batchDel(@RequestParam List<Integer> ids) {
userService.delBatch(ids);
return R.ok();
}service.....
批量删除
--> mapper xml
XML
<!--批量删除-->
<delete id="delBatch">
delete from tb_user where id in
<!--collection是要遍历的集合,此处必须叫list
item 就是遍历得到的数据 -->
<foreach collection="list" item="id" open="(" separator="," close=")">
#{id}
</foreach>
</delete>6.5.6 动态插入
MyBatis 实现
tb_user表的动态插入功能,核心价值是:根据传入
User对象的非空字段,动态拼接插入的「字段列表」和「值列表」,只插入有值的字段,替代固定字段的原生插入 SQL(如**
insert into tb_user (username, sex) values(#{username}, #{sex})),**适配多场景插入需求。
标签:
<trim>(通用动态拼接标签)
<trim>是 MyBatis 最灵活的动态标签,通过 3 个属性解决拼接语法问题,这里用了两个<trim>分别处理「字段列表」和「值列表」:
| 属性 | 作用 | 示例(第一个 <trim>) |
|---|---|---|
prefix |
给拼接后的片段加「前缀」 | prefix="(" → 字段列表开头加左括号 ( |
suffix |
给拼接后的片段加「后缀」 | suffix=")" → 字段列表结尾加右括号 ) |
suffixOverrides |
剔除片段最后多余的指定字符(这里是 ,) |
自动删掉最后一个字段后的逗号,避免 (username, sex,) 语法错误 |
XML
insert into tb_user (username, sex) values(#{username}, #{sex})
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="com.example.entity.User">
INSERT INTO tb_user
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
username,
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
sex,
</if>
<if test="age != null">
age,
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
email,
</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone != ''">
phone,
</if>
<if test="createTime != null">
create_time,
</if>
</trim>
<trim prefix="VALUES (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
#{username},
</if>
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
#{sex},
</if>
<if test="age != null">
#{age},
</if>
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
#{email},
</if>
<if test="phone != null and phone != ''">
#{phone},
</if>
<if test="createTime != null">
#{createTime},
</if>
</trim>
</insert>xml
XML
<!-- 1. 定义插入语句,id 为方法名,parameterType 指定参数类型 -->
<insert id="insertUser" parameterType="com.example.entity.User">
<!-- 2. 固定的 INSERT INTO 表名部分 -->
INSERT INTO tb_user
<!-- 3. 第一个 <trim> 标签:处理字段列表 -->
<!--
prefix="(" :在内容前添加左括号
suffix=")" :在内容后添加右括号
suffixOverrides=",":移除末尾多余的逗号
-->
<trim prefix="(" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<!-- 4. 判断 username 字段是否非空且非空字符串 -->
<!-- 如果条件成立,添加 "username," 到字段列表 -->
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
username,
</if>
<!-- 5. 判断 sex 字段是否非空且非空字符串 -->
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
sex,
</if>
<!-- 6. 判断 age 字段是否非空(age 可能是 Integer/Long 类型) -->
<if test="age != null">
age,
</if>
<!-- 7. 判断 email 字段是否非空且非空字符串 -->
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
email,
</if>
<!-- 8. 判断 phone 字段是否非空且非空字符串 -->
<if test="phone != null and phone != ''">
phone,
</if>
<!-- 9. 判断 createTime 字段是否非空 -->
<if test="createTime != null">
create_time, <!-- 注意:数据库字段名是蛇形命名 create_time -->
</if>
</trim> <!-- 第一个 <trim> 结束,此时会生成类似 (username, sex, age) 的字段列表 -->
<!-- 10. 第二个 <trim> 标签:处理 VALUES 部分 -->
<trim prefix="VALUES (" suffix=")" suffixOverrides=",">
<!-- 11. 对应 username 字段的值 -->
<!-- 判断条件与字段列表的 username 判断保持一致 -->
<if test="username != null and username != ''">
#{username}, <!-- MyBatis 参数占位符 -->
</if>
<!-- 12. 对应 sex 字段的值 -->
<if test="sex != null and sex != ''">
#{sex},
</if>
<!-- 13. 对应 age 字段的值 -->
<if test="age != null">
#{age},
</if>
<!-- 14. 对应 email 字段的值 -->
<if test="email != null and email != ''">
#{email},
</if>
<!-- 15. 对应 phone 字段的值 -->
<if test="phone != null and phone != ''">
#{phone},
</if>
<!-- 16. 对应 create_time 字段的值 -->
<if test="createTime != null">
#{createTime}, <!-- Java 对象属性名是驼峰命名 createTime -->
</if>
</trim> <!-- 第二个 <trim> 结束,此时会生成类似 (?, ?, ?) 的值列表 -->
</insert> <!-- 整个插入语句结束 -->