相关内容来自腾讯元宝, 作者也属于入门,仅做参考
我们学习了异常, 除了具体业务里针对不同的异常, 我们还可以统一拦截异常
创建自定义异常
前面我们学习了异常类的知识, 有个知识点叫抛出自定义异常, 如何定义呢, 我们定义一个粗略的业务异常
java
public class BusinessException extends Exception {
public BusinessException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}这个自定义的异常就是要继承Exception或其他Exception的子类, 我们这个类就继承了异常类的特性.
比如订单,金额,是否为空等, 写到不满足业务条件 我们就可以throw
java
throw new BusinessException("这是一个自定义的异常")Throwable
├── Exception
│ ├── RuntimeException
│ │ ├── DataAccessException (Spring)
│ │ │ ├── DuplicateKeyException
│ │ │ ├── DataIntegrityViolationException
│ │ │ └── ...
│ │ ├── IllegalArgumentException
│ │ └── ...
│ ├── IOException
│ └── ...
└── Error
下面是继承的Exception
自定义一个异常类来 处理运行时的异常
java
package com.example.demo.autil;
import lombok.Data;
/*
@Data相当于以下注解的组合:
@Getter:生成所有字段的 getter 方法
@Setter:生成所有字段的 setter 方法(final 字段除外)
@ToString:生成 toString() 方法
@EqualsAndHashCode:生成 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法
@RequiredArgsConstructor:生成包含 final 字段和 @NonNull 字段的构造方法
*/
@Data
public class AppBusinessException extends Exception{
private int code;
private String message;
public AppBusinessException(int code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public AppBusinessException(int code, String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
}下面是继承的RuntimeException
java
package com.example.demo.autil;
/**
* 自定义异常类 需要继承 RuntimeException 然后需要构造函数
*/
public class AppException extends RuntimeException {
private int code;
private String message;
public AppException(int code, String message) {
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public AppException(int code, String message, Throwable cause) {
super(message, cause);
this.code = code;
this.message = message;
}
public int getCode() {
return code;
}
public void setCode(int code) {
this.code = code;
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}下面是个通用的统一拦截异常
@RestControllerAdvice 注解
java
package com.example.demo.autil;
import com.example.demo.aenum.ResultCode;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.springframework.dao.DataAccessException;
import org.springframework.http.HttpStatus;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.MissingServletRequestParameterException;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ControllerAdvice;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ExceptionHandler;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import com.example.demo.autil.ResultUtil;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestControllerAdvice;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
/**
* 全局捕获异常, 这个类可以监听服务器,数据库操作,自定义异常等
*/
@RestControllerAdvice
public class GlobalExceptionHandler {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(GlobalExceptionHandler.class);
/**
* 处理所有传参异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(MissingServletRequestParameterException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> handleException(MissingServletRequestParameterException e) {
String message = String.format("缺少必需参数: %s (类型: %s)",
e.getParameterName(), e.getParameterType());
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(ResultUtil.failed(message));
}
/**
* 处理所有业务的异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(value = AppBusinessException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> handleException(AppBusinessException e) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(ResultUtil.failed(e.getMessage()));
}
/**
* 处理所有SQL异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> handleException(Exception e) {
logger.error("系统异常---: ", e);
// 自定义异常--
if (e instanceof AppException) {
AppException appException = (AppException) e;
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(ResultUtil.failed(appException.getCode(), appException.getMessage()));
}
// 根据异常类型返回不同的错误信息
if (e instanceof DataAccessException) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(ResultUtil.failed("数据库操作失败,请稍后重试"));
}
if (e instanceof RuntimeException) {
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(ResultUtil.failed("系统运行异常"));
}
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(ResultUtil.failed("系统内部错误"));
}
/**
* 专门处理数据访问异常
*/
@ExceptionHandler(DataAccessException.class)
public ResponseEntity<?> handleDataAccessException(DataAccessException e) {
logger.error("数据库访问异常: ", e);
// 获取根异常信息
Throwable rootCause = getRootCause(e);
String errorMessage = "数据库操作失败";
if (rootCause != null) {
// 根据具体的SQL异常类型返回更详细的错误信息
// 这个提示是根据唯一索引提示的
if (rootCause.getMessage().contains("Duplicate entry")) {
errorMessage = "数据已存在,请勿重复添加";
} else if (rootCause.getMessage().contains("Data too long")) {
errorMessage = "数据长度超过限制";
} else if (rootCause.getMessage().contains("cannot be null")) {
errorMessage = "必填字段不能为空";
} else if (rootCause.getMessage().contains("foreign key constraint")) {
errorMessage = "存在关联数据,无法删除";
}
}
return ResponseEntity.status(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR)
.body(ResultUtil.failed(errorMessage));
}
private Throwable getRootCause(Throwable throwable) {
Throwable cause = throwable;
while (cause.getCause() != null) {
cause = cause.getCause();
}
return cause;
}
}注意到: @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) 和 @ExceptionHandler(DataAccessException.class) 冲突么?
不会冲突! Spring 会按照最精确匹配的原则执行异常处理。
@ExceptionHandler 注解的执行顺序和冲突处理
核心原则:精确匹配优先
下面例子写一个几种捕获异常的情况
java
@GetMapping("getSystemError")
public Result<?> getSystemError(@RequestParam String type, @RequestParam Integer id) throws AppBusinessException{
if (type.equals("appBusiness")) {
throw new AppBusinessException("业务异常");
}
// 如果我们接口就没有 ?type= 会怎么样呢
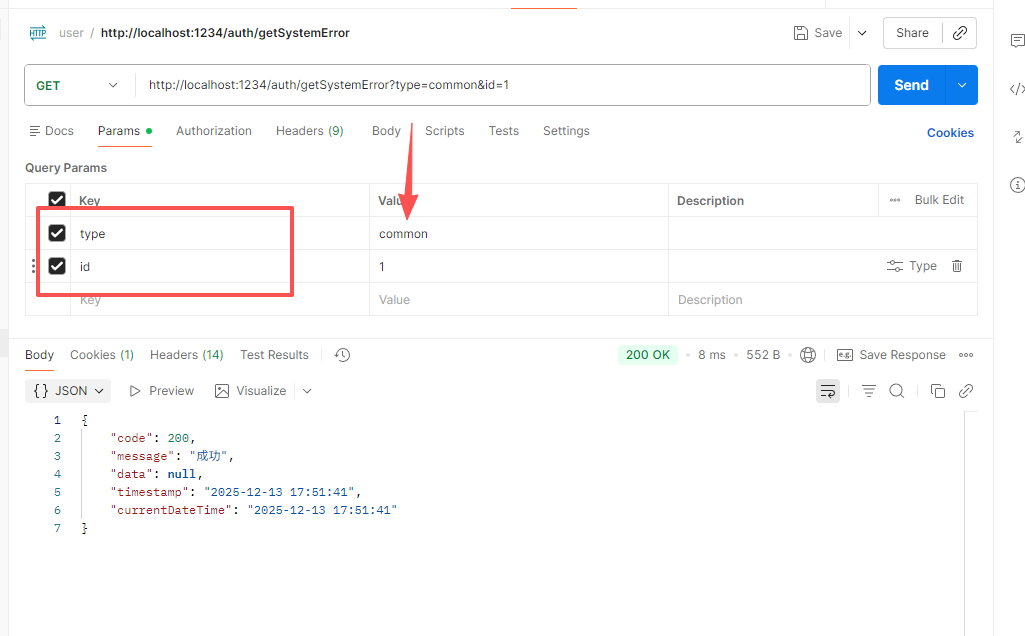
return ResultUtil.success("成功");
}- 没有传参 ,统一拦截MissingServletRequestParameterException
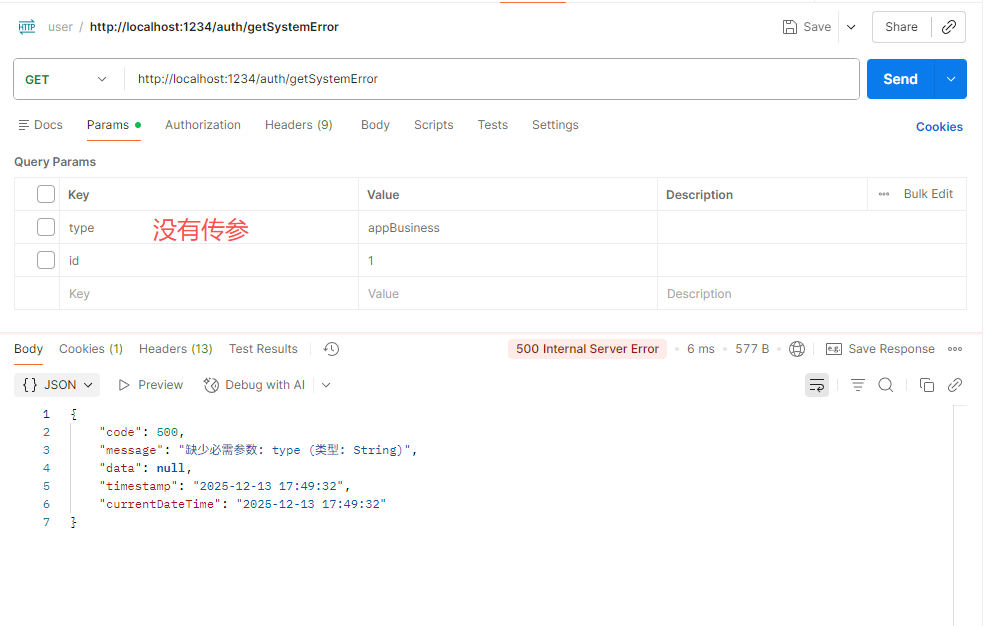
2.捕获业务的异常
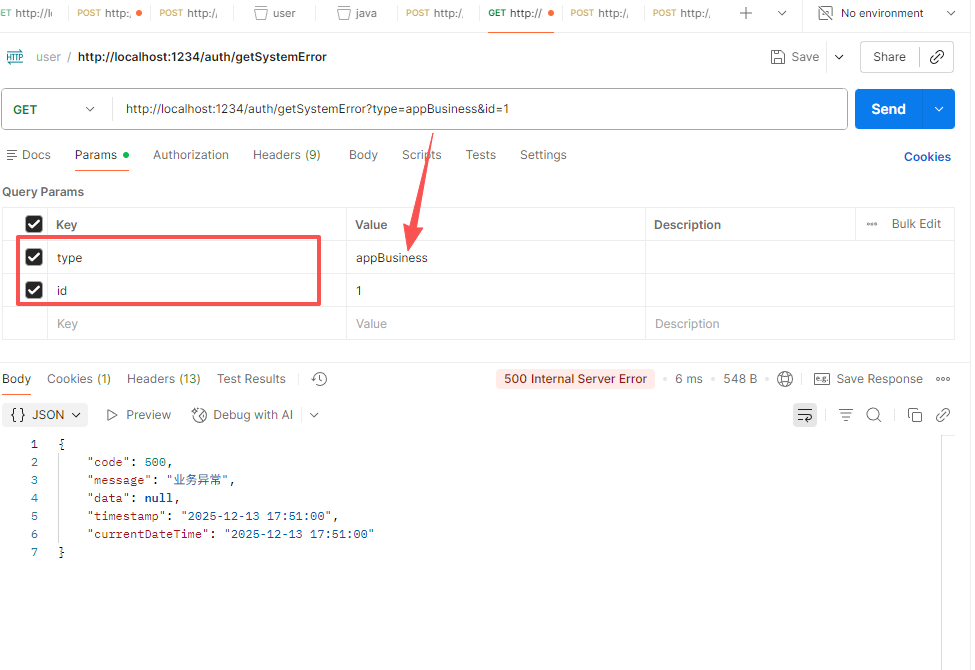
- 正常情况