Basic statistics - 05. Confidence intervals
We have learned standard of mean in last notes, so how can we use it?
we can use it to calculate a confidence interval.
Example
We will pretend that we don't know the population mean in this example. Instead, we will here try to estimate it based on a sample from the population .
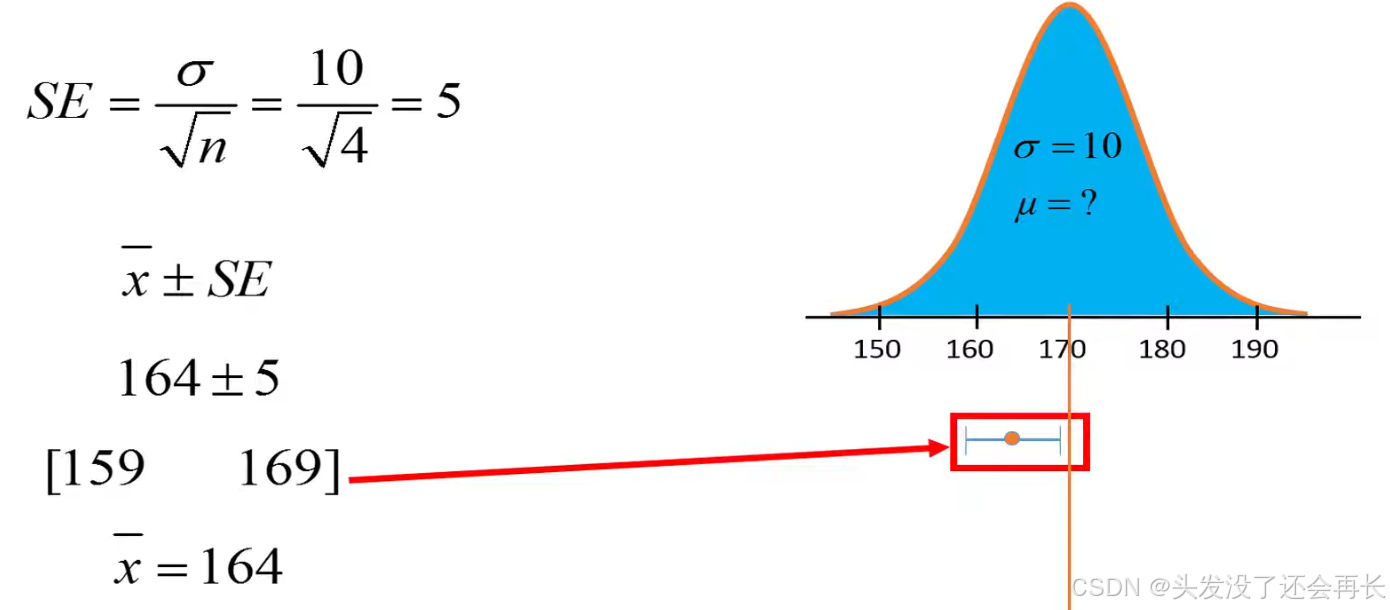
Here, we randomly select four individuals and measure their body heights.
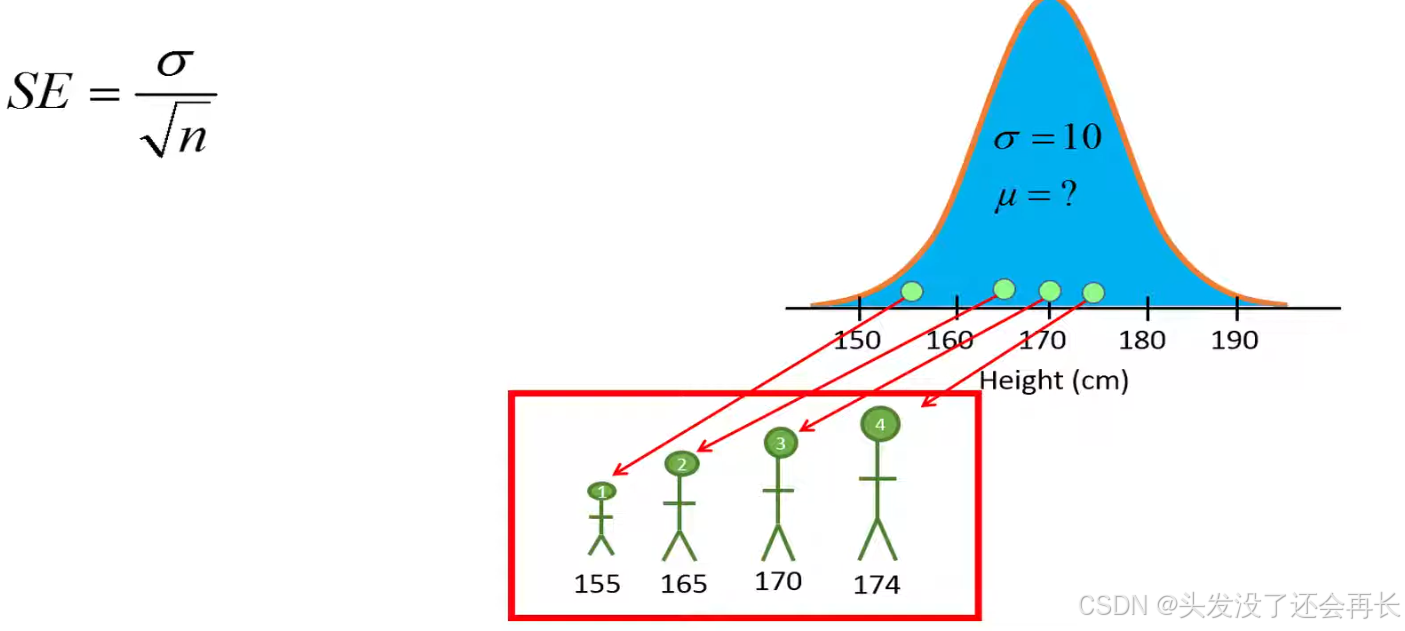
Then, we can calculate the SE and get interval [161 171]
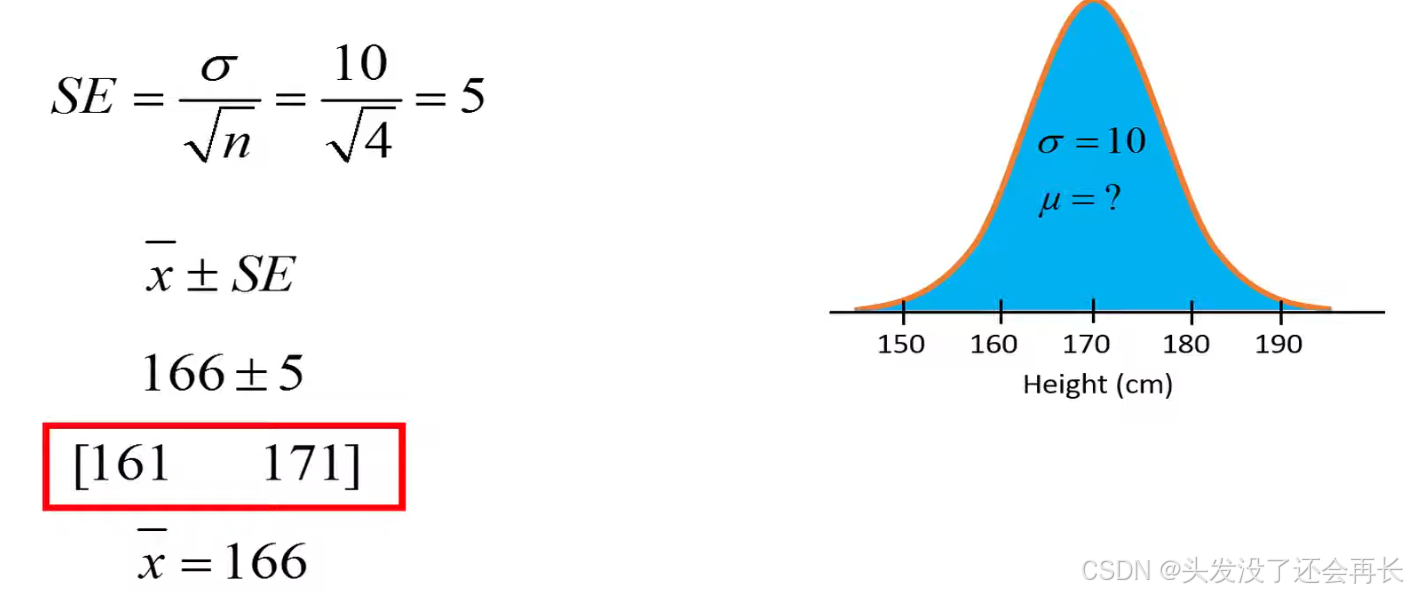
This interval calculated based on the estimated mean and the standard error, tells us that we are about 68% confident or certain that the true population mean is located inside this interval .
And the interval includes 170.
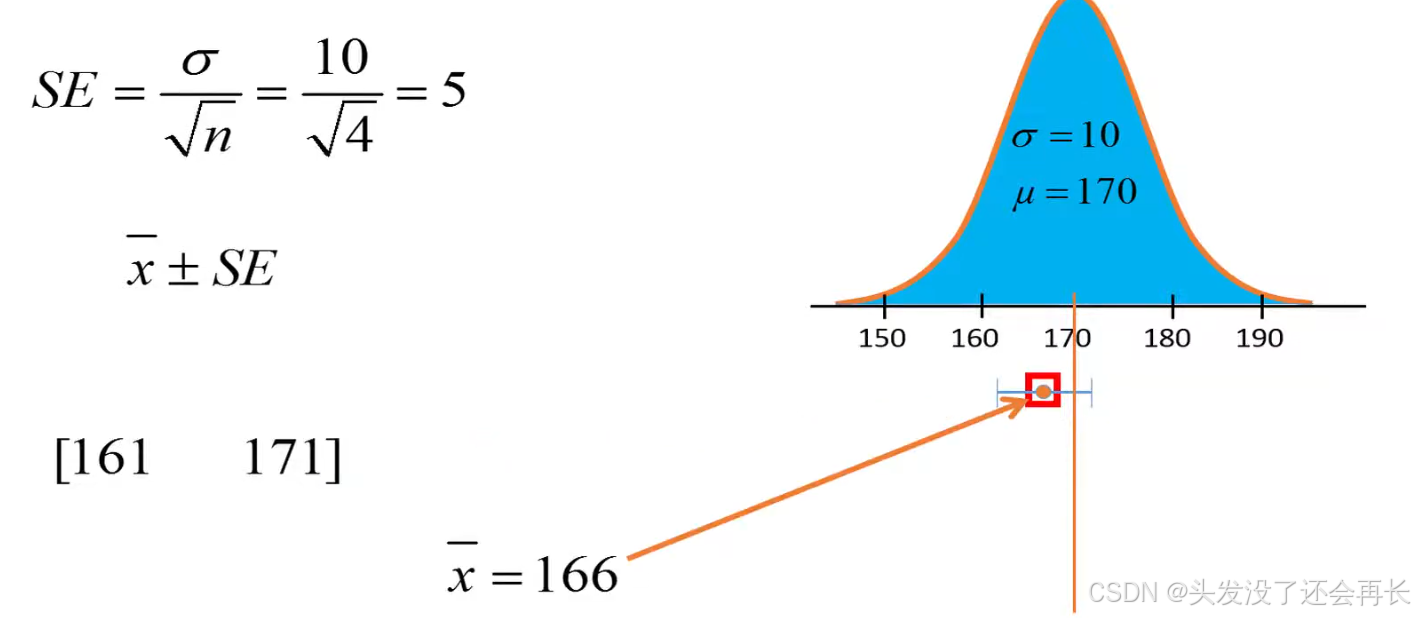
Another sample, the interval did not include the true population mean this time. because we only have 68% confidence, there is 32% risk that the interval does not include the population mean.
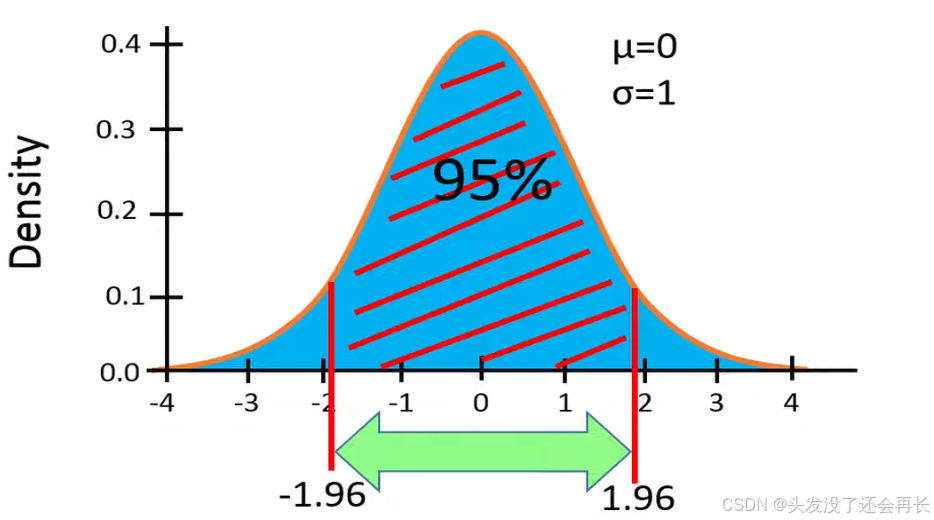
95% confidence interval
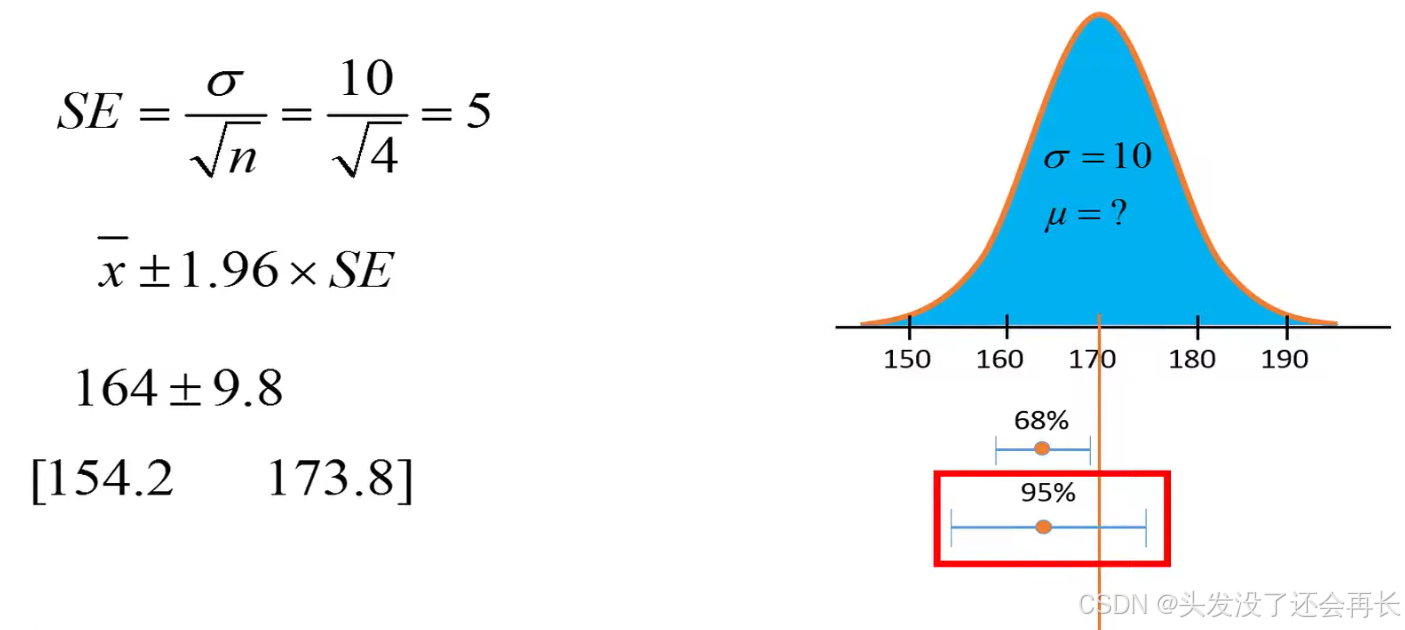
So, the last example mean is 164, if we use 95% confidence interval, it includes the true population mean.
Sample size
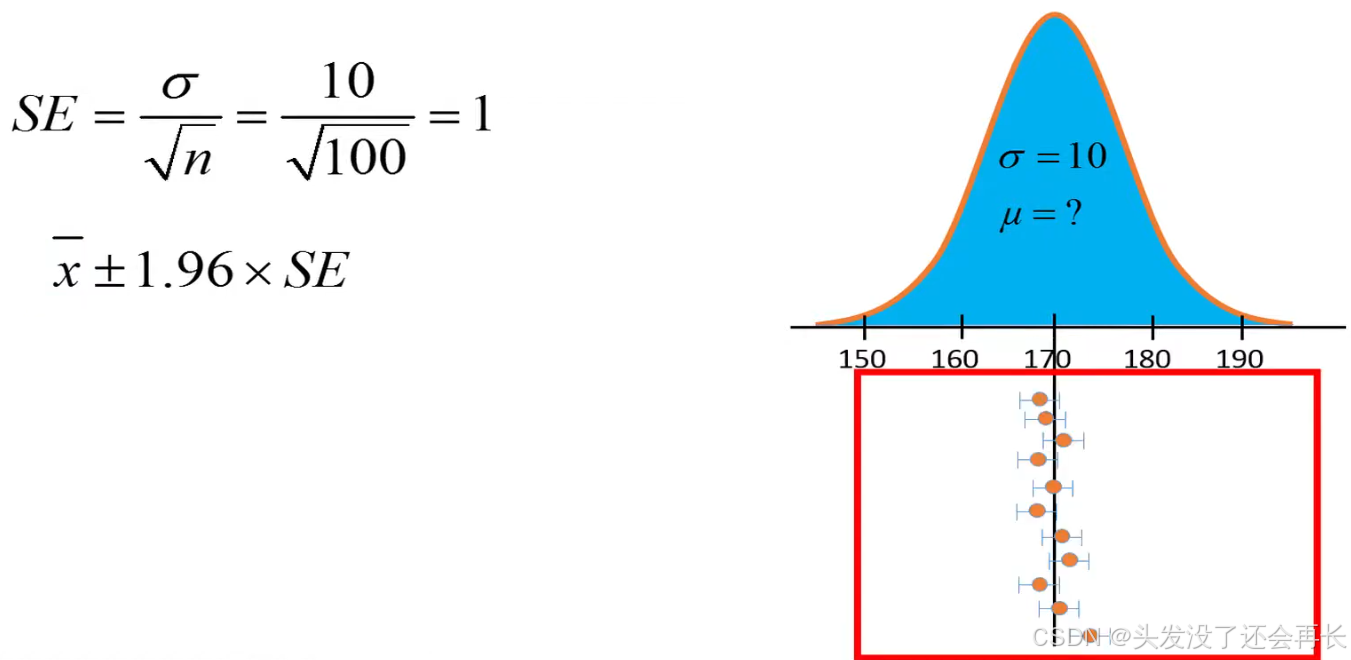
If we take a random sample of four individuals 100 times and compute 100 confidence intervals , we would expect that 95% of these confidence intervals include the true population mean.
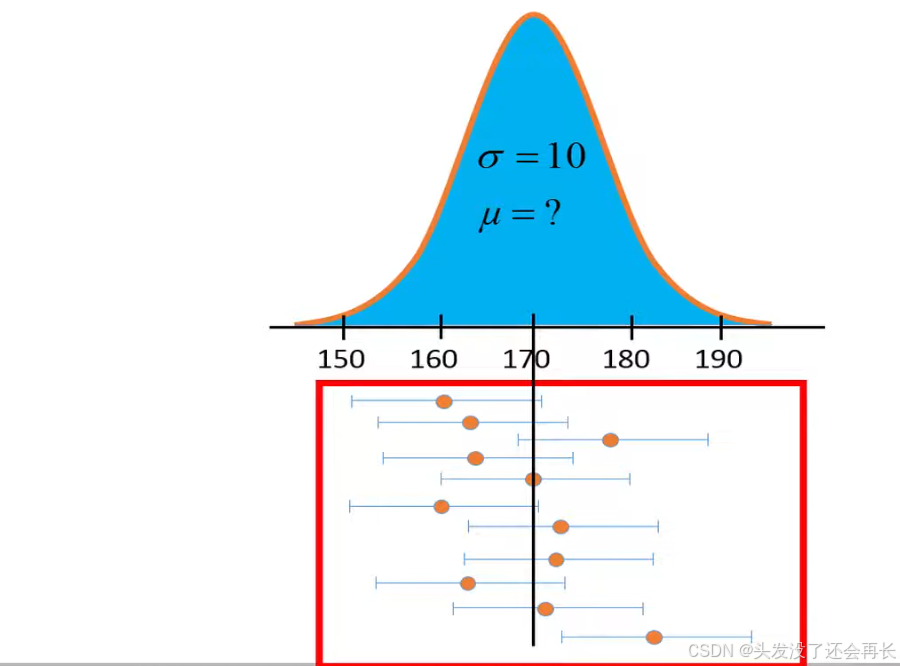
So the sample size = 100, we can get SE=1, the width of interval will be reduced from 9.8 to 1.96. the intervals will be narrower and more centered around population mean.
Which means we require a large sample size , which will reduce the standard error.
Standard error when sigma is unknown
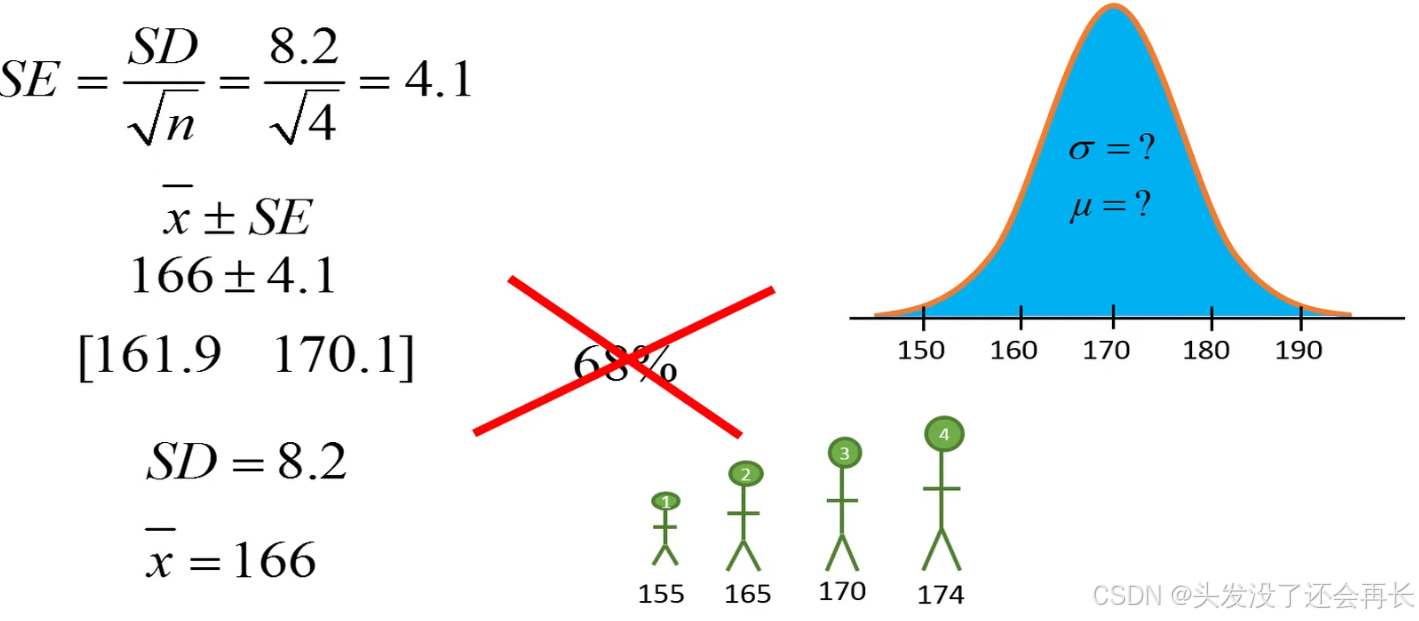
SD denotes that the standard deviation is an estimate of the true population standard deviation , sigma.
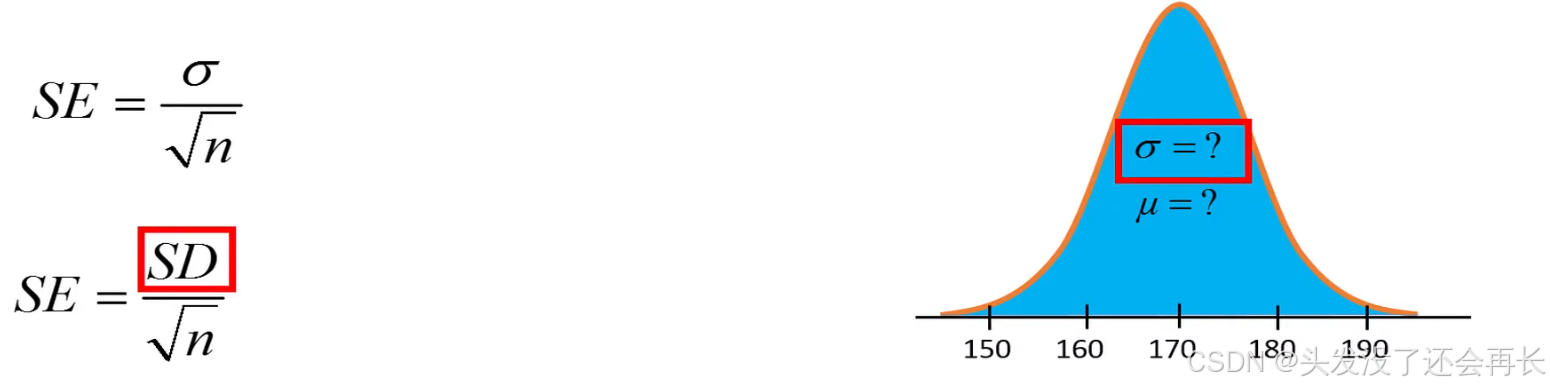
But, it is common to use these notations for the standard error of the mean based on the population standard deviation or based on the sample standard deviation .
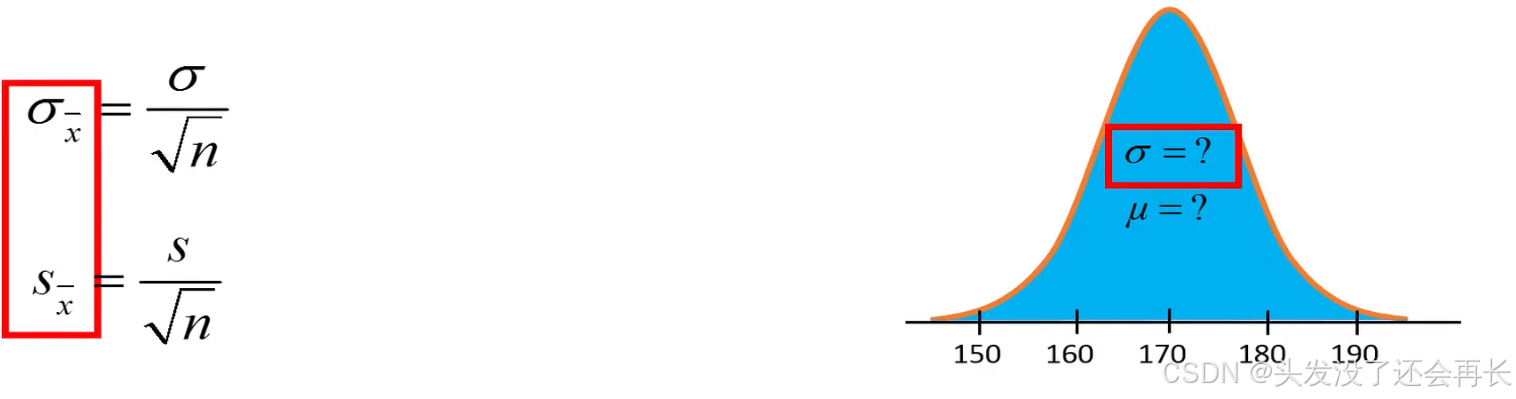
If we use sample SD=8.2, we can get interval [161.9, 170.1],
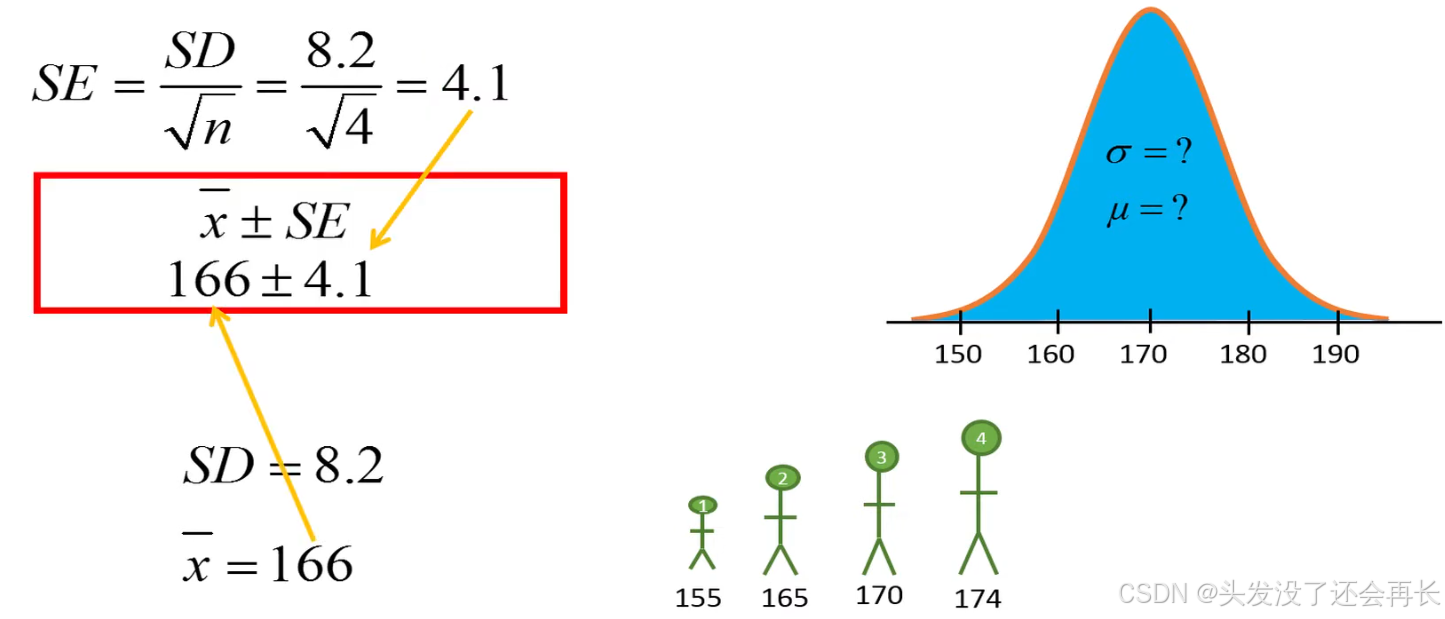
but since the SE is based a very small sample, we are no larger 68% certain that the interval includes the true population mean.