命令模式(Command)大白话讲解
一句话概括
就像餐厅点餐:你(客户)告诉服务员(调用者)要什么菜,服务员把订单(命令)交给厨师(接收者),厨师按订单做菜
现实生活比喻
场景1:餐厅点餐
- 你:顾客(客户端)
- 服务员:调用者(Invoker)
- 菜单/订单:命令(Command)
- 厨师:接收者(Receiver)
- 过程:你告诉服务员要什么菜 → 服务员写下订单 → 厨师按订单做菜
场景2:遥控器
- 你:使用者
- 遥控器按钮:调用者
- 按钮命令:命令对象
- 电视/空调:接收者
- 过程:你按遥控器按钮 → 遥控器执行对应命令 → 电视/空调响应
完整代码示例
场景1:智能家居遥控器
java
/**
* 命令模式 - 智能家居示例
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=== 智能家居控制系统 ===");
// 创建接收者(家电设备)
Light livingRoomLight = new Light("客厅灯");
Light bedroomLight = new Light("卧室灯");
Fan ceilingFan = new Fan("吊扇");
Door garageDoor = new Door("车库门");
Stereo stereo = new Stereo("音响");
// 创建具体命令
Command lightOnCommand = new LightOnCommand(livingRoomLight);
Command lightOffCommand = new LightOffCommand(livingRoomLight);
Command fanOnCommand = new FanOnCommand(ceilingFan);
Command fanOffCommand = new FanOffCommand(ceilingFan);
Command doorOpenCommand = new DoorOpenCommand(garageDoor);
Command doorCloseCommand = new DoorCloseCommand(garageDoor);
Command stereoOnCommand = new StereoOnCommand(stereo);
Command stereoOffCommand = new StereoOffCommand(stereo);
// 创建宏命令(一键执行多个命令)
Command[] partyOnCommands = {lightOnCommand, stereoOnCommand, fanOnCommand};
Command[] partyOffCommands = {lightOffCommand, stereoOffCommand, fanOffCommand};
Command partyModeOnCommand = new MacroCommand(partyOnCommands);
Command partyModeOffCommand = new MacroCommand(partyOffCommands);
// 创建调用者(遥控器)
RemoteControl remote = new RemoteControl();
// 设置遥控器按钮
remote.setCommand(0, lightOnCommand, lightOffCommand);
remote.setCommand(1, fanOnCommand, fanOffCommand);
remote.setCommand(2, doorOpenCommand, doorCloseCommand);
remote.setCommand(3, stereoOnCommand, stereoOffCommand);
remote.setCommand(4, partyModeOnCommand, partyModeOffCommand);
// 使用遥控器
System.out.println("\n--- 测试遥控器按钮 ---");
remote.onButtonPressed(0); // 打开客厅灯
remote.offButtonPressed(0); // 关闭客厅灯
remote.onButtonPressed(1); // 打开吊扇
remote.offButtonPressed(1); // 关闭吊扇
System.out.println("\n--- 测试一键派对模式 ---");
remote.onButtonPressed(4); // 开启派对模式
System.out.println("\n--- 测试撤销功能 ---");
remote.onButtonPressed(0); // 打开客厅灯
remote.onButtonPressed(1); // 打开吊扇
remote.undoButtonPressed(); // 撤销上一个命令(关闭吊扇)
remote.undoButtonPressed(); // 撤销上上个命令(关闭客厅灯)
System.out.println("\n--- 测试宏命令 ---");
remote.onButtonPressed(4); // 开启派对模式(同时打开灯、音响、风扇)
remote.offButtonPressed(4); // 关闭派对模式(同时关闭灯、音响、风扇)
}
}
/**
* 命令接口
*/
interface Command {
void execute();
void undo();
}
/**
* 接收者 - 电灯
*/
class Light {
private String location;
private boolean isOn = false;
public Light(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public void on() {
isOn = true;
System.out.println(location + " 打开");
}
public void off() {
isOn = false;
System.out.println(location + " 关闭");
}
public boolean isOn() {
return isOn;
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 开灯命令
*/
class LightOnCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public LightOnCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.on();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
light.off();
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 关灯命令
*/
class LightOffCommand implements Command {
private Light light;
public LightOffCommand(Light light) {
this.light = light;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
light.off();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
light.on();
}
}
/**
* 接收者 - 吊扇
*/
class Fan {
private String location;
private boolean isOn = false;
public Fan(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public void on() {
isOn = true;
System.out.println(location + " 打开");
}
public void off() {
isOn = false;
System.out.println(location + " 关闭");
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 开风扇命令
*/
class FanOnCommand implements Command {
private Fan fan;
public FanOnCommand(Fan fan) {
this.fan = fan;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
fan.on();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
fan.off();
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 关风扇命令
*/
class FanOffCommand implements Command {
private Fan fan;
public FanOffCommand(Fan fan) {
this.fan = fan;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
fan.off();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
fan.on();
}
}
/**
* 接收者 - 门
*/
class Door {
private String location;
public Door(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public void open() {
System.out.println(location + " 打开");
}
public void close() {
System.out.println(location + " 关闭");
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 开门命令
*/
class DoorOpenCommand implements Command {
private Door door;
public DoorOpenCommand(Door door) {
this.door = door;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
door.open();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
door.close();
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 关门命令
*/
class DoorCloseCommand implements Command {
private Door door;
public DoorCloseCommand(Door door) {
this.door = door;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
door.close();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
door.open();
}
}
/**
* 接收者 - 音响
*/
class Stereo {
private String location;
public Stereo(String location) {
this.location = location;
}
public void on() {
System.out.println(location + " 打开");
}
public void off() {
System.out.println(location + " 关闭");
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 开音响命令
*/
class StereoOnCommand implements Command {
private Stereo stereo;
public StereoOnCommand(Stereo stereo) {
this.stereo = stereo;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
stereo.on();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
stereo.off();
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 关音响命令
*/
class StereoOffCommand implements Command {
private Stereo stereo;
public StereoOffCommand(Stereo stereo) {
this.stereo = stereo;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
stereo.off();
}
@Override
public void undo() {
stereo.on();
}
}
/**
* 宏命令 - 一次执行多个命令
*/
class MacroCommand implements Command {
private Command[] commands;
public MacroCommand(Command[] commands) {
this.commands = commands;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
for (Command command : commands) {
command.execute();
}
}
@Override
public void undo() {
// 反序执行撤销
for (int i = commands.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
commands[i].undo();
}
}
}
/**
* 调用者 - 遥控器
*/
class RemoteControl {
private Command[] onCommands;
private Command[] offCommands;
private Command undoCommand;
public RemoteControl() {
onCommands = new Command[5];
offCommands = new Command[5];
// 初始化所有按钮为空命令
Command noCommand = new NoCommand();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
onCommands[i] = noCommand;
offCommands[i] = noCommand;
}
undoCommand = noCommand;
}
public void setCommand(int slot, Command onCommand, Command offCommand) {
onCommands[slot] = onCommand;
offCommands[slot] = offCommand;
}
public void onButtonPressed(int slot) {
onCommands[slot].execute();
undoCommand = onCommands[slot]; // 记录最后执行的命令用于撤销
}
public void offButtonPressed(int slot) {
offCommands[slot].execute();
undoCommand = offCommands[slot]; // 记录最后执行的命令用于撤销
}
public void undoButtonPressed() {
System.out.println("--- 撤销上一个操作 ---");
undoCommand.undo();
}
}
/**
* 空命令(用于初始化)
*/
class NoCommand implements Command {
@Override
public void execute() {
System.out.println("该按钮未设置命令");
}
@Override
public void undo() {
System.out.println("没有可撤销的操作");
}
}运行结果
=== 智能家居控制系统 ===
--- 测试遥控器按钮 ---
客厅灯 打开
客厅灯 关闭
吊扇 打开
吊扇 关闭
--- 测试一键派对模式 ---
客厅灯 打开
音响 打开
吊扇 打开
--- 测试撤销功能 ---
客厅灯 打开
吊扇 打开
--- 撤销上一个操作 ---
吊扇 关闭
--- 撤销上一个操作 ---
客厅灯 关闭
--- 测试宏命令 ---
客厅灯 打开
音响 打开
吊扇 打开
客厅灯 关闭
音响 关闭
吊扇 关闭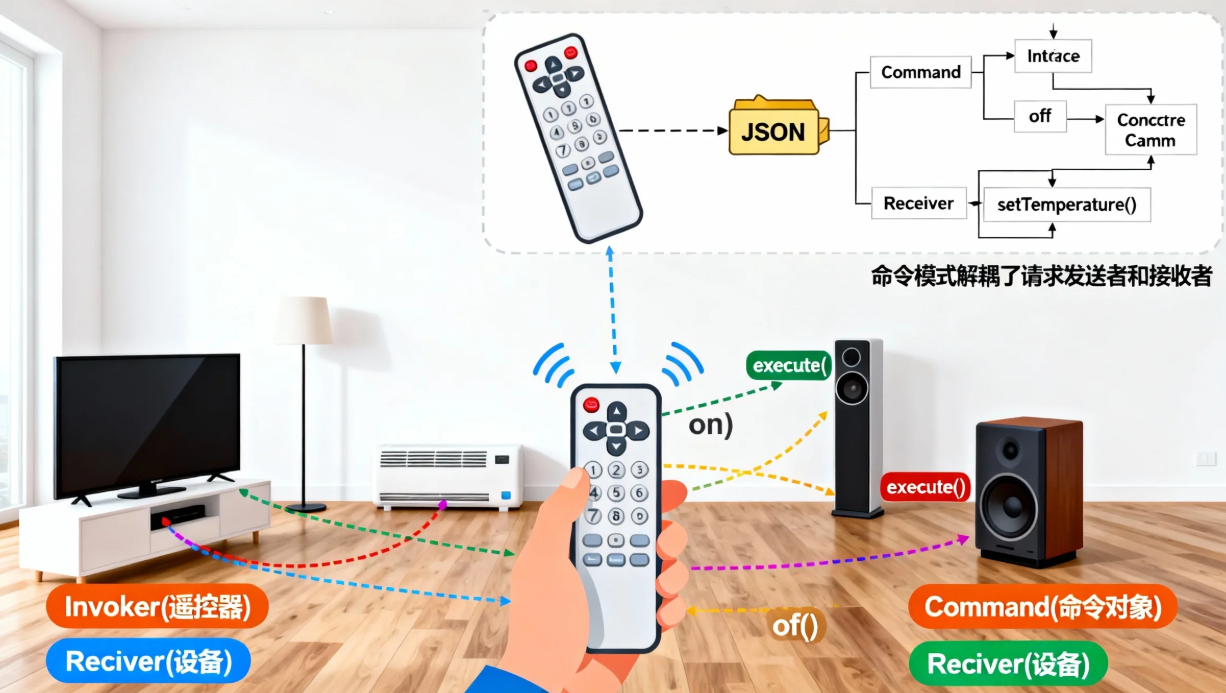
场景2:文本编辑器(支持撤销/重做)
java
/**
* 命令模式 - 文本编辑器示例(支持撤销/重做)
*/
public class TextEditorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("=== 文本编辑器(支持撤销/重做) ===");
// 创建接收者(文档)
Document document = new Document();
// 创建命令历史记录
CommandHistory history = new CommandHistory();
// 创建命令
Command insertCommand1 = new InsertTextCommand(document, "Hello, ", 0);
Command insertCommand2 = new InsertTextCommand(document, "World!", 7);
Command deleteCommand = new DeleteTextCommand(document, 5, 2);
Command updateCommand = new UpdateTextCommand(document, "Design Patterns", 7, 6);
// 执行命令
System.out.println("\n--- 执行命令 ---");
executeCommand(insertCommand1, history);
System.out.println("文档内容: " + document.getContent());
executeCommand(insertCommand2, history);
System.out.println("文档内容: " + document.getContent());
executeCommand(deleteCommand, history);
System.out.println("文档内容: " + document.getContent());
executeCommand(updateCommand, history);
System.out.println("文档内容: " + document.getContent());
// 撤销操作
System.out.println("\n--- 撤销操作 ---");
undoLastCommand(history);
System.out.println("文档内容: " + document.getContent());
undoLastCommand(history);
System.out.println("文档内容: " + document.getContent());
// 重做操作
System.out.println("\n--- 重做操作 ---");
redoLastCommand(history);
System.out.println("文档内容: " + document.getContent());
redoLastCommand(history);
System.out.println("文档内容: " + document.getContent());
// 显示历史记录
history.showHistory();
}
private static void executeCommand(Command command, CommandHistory history) {
command.execute();
history.add(command);
}
private static void undoLastCommand(CommandHistory history) {
history.undo();
}
private static void redoLastCommand(CommandHistory history) {
history.redo();
}
}
/**
* 接收者 - 文档
*/
class Document {
private StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
public void insert(String text, int position) {
content.insert(position, text);
}
public void delete(int position, int length) {
content.delete(position, position + length);
}
public void update(String newText, int position, int length) {
content.replace(position, position + length, newText);
}
public String getContent() {
return content.toString();
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 插入文本命令
*/
class InsertTextCommand implements Command {
private Document document;
private String text;
private int position;
public InsertTextCommand(Document document, String text, int position) {
this.document = document;
this.text = text;
this.position = position;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
document.insert(text, position);
System.out.println("执行: 在位置 " + position + " 插入文本 \"" + text + "\"");
}
@Override
public void undo() {
document.delete(position, text.length());
System.out.println("撤销: 删除在位置 " + position + " 插入的文本 \"" + text + "\"");
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 删除文本命令
*/
class DeleteTextCommand implements Command {
private Document document;
private int position;
private int length;
private String deletedText; // 用于撤销时恢复
public DeleteTextCommand(Document document, int position, int length) {
this.document = document;
this.position = position;
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
// 注意:这里需要先保存被删除的文本,但为了简化我们只记录位置和长度
System.out.println("执行: 从位置 " + position + " 删除 " + length + " 个字符");
document.delete(position, length);
}
@Override
public void undo() {
// 注意:实际实现中需要保存被删除的文本才能恢复
System.out.println("撤销: 无法恢复已删除的文本(简化实现)");
}
}
/**
* 具体命令 - 更新文本命令
*/
class UpdateTextCommand implements Command {
private Document document;
private String newText;
private int position;
private int length;
private String oldText; // 用于撤销时恢复
public UpdateTextCommand(Document document, String newText, int position, int length) {
this.document = document;
this.newText = newText;
this.position = position;
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public void execute() {
System.out.println("执行: 从位置 " + position + " 更新 " + length + " 个字符为 \"" + newText + "\"");
document.update(newText, position, length);
}
@Override
public void undo() {
System.out.println("撤销: 恢复更新的文本(简化实现)");
}
}
/**
* 命令历史记录(支持撤销/重做)
*/
class CommandHistory {
private Stack<Command> undoStack = new Stack<>();
private Stack<Command> redoStack = new Stack<>();
public void add(Command command) {
undoStack.push(command);
redoStack.clear(); // 执行新命令时清空重做栈
}
public void undo() {
if (!undoStack.isEmpty()) {
Command command = undoStack.pop();
command.undo();
redoStack.push(command);
} else {
System.out.println("没有可撤销的命令");
}
}
public void redo() {
if (!redoStack.isEmpty()) {
Command command = redoStack.pop();
command.execute();
undoStack.push(command);
} else {
System.out.println("没有可重做的命令");
}
}
public void showHistory() {
System.out.println("\n=== 命令历史 ===");
System.out.println("撤销栈大小: " + undoStack.size());
System.out.println("重做栈大小: " + redoStack.size());
}
}运行结果
=== 文本编辑器(支持撤销/重做) ===
--- 执行命令 ---
执行: 在位置 0 插入文本 "Hello, "
文档内容: Hello,
执行: 在位置 7 插入文本 "World!"
文档内容: Hello, World!
执行: 从位置 5 删除 2 个字符
文档内容: Hello World!
执行: 从位置 7 更新 6 个字符为 "Design Patterns"
文档内容: Hello Design Patterns
--- 撤销操作 ---
撤销: 恢复更新的文本(简化实现)
文档内容: Hello Design Patterns
撤销: 无法恢复已删除的文本(简化实现)
文档内容: Hello Design Patterns
--- 重做操作 ---
执行: 从位置 5 删除 2 个字符
文档内容: Hello Design Patterns
执行: 从位置 7 更新 6 个字符为 "Design Patterns"
文档内容: Hello Design Patterns
=== 命令历史 ===
撤销栈大小: 2
重做栈大小: 0命令模式的核心结构
Client(客户端)
↓ 创建
Command(命令接口) ← Invoker(调用者)
↑ 实现 ↓ 执行
ConcreteCommand(具体命令) → Receiver(接收者)关键特征:
- 命令对象:封装请求的所有信息(接收者、方法、参数)
- 调用者:触发命令执行,不知道具体实现
- 接收者:真正执行操作的对象
- 解耦:调用者和接收者完全解耦
命令模式的核心优势
1. 解耦调用者和接收者
java
// 遥控器(调用者)不知道具体设备(接收者)
remote.onButtonPressed(0); // 只知道执行命令,不知道是开灯还是开风扇2. 支持撤销/重做
java
// 命令对象可以记录状态,支持撤销
command.execute(); // 执行
command.undo(); // 撤销3. 支持命令队列和日志
java
// 命令可以排队执行
queue.add(command1);
queue.add(command2);
queue.processAll();
// 可以记录命令日志用于恢复
log.add(command);4. 支持宏命令(组合命令)
java
// 多个命令组合成一个命令
Command macro = new MacroCommand(command1, command2, command3);
macro.execute(); // 一次执行所有命令适用场景(大白话版)
✅ 适合用命令模式的场景:
-
需要撤销/重做功能
java// 文本编辑器、绘图软件、IDE等 // 每个操作都是一个命令对象 -
需要将操作排队或记录日志
java// 任务调度系统、事务系统 // 命令可以序列化、持久化 -
需要支持宏命令
java// 批处理操作、一键执行多个操作 // 游戏中的宏按键、IDE的宏录制 -
需要解耦调用者和接收者
java// GUI按钮点击事件 // 菜单项点击事件 // 遥控器按键
❌ 不适合的场景:
- 简单操作:如果操作很简单,直接调用方法即可
- 性能敏感:命令对象创建有开销
- 不需要撤销/队列功能:如果不需要这些高级功能
优缺点
优点:
- 解耦:调用者和接收者完全解耦
- 灵活:可以轻松添加新命令
- 支持撤销/重做:天然支持操作历史
- 支持组合命令:可以实现宏命令
- 支持命令队列:可以排队执行命令
缺点:
- 复杂度增加:每个命令都需要一个类
- 性能开销:创建大量命令对象有开销
- 可能过度设计:简单场景下显得复杂
实际应用案例
1. GUI事件处理
java
// Java Swing/AWT中的ActionListener
button.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
// 这就是一个命令
saveDocument();
}
});2. 线程池/任务队列
java
// Java的Runnable就是命令模式
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
executor.execute(new Runnable() { // 命令对象
public void run() {
// 执行任务
}
});3. 数据库事务
java
// 事务中的每个操作都是一个命令
Transaction tx = database.beginTransaction();
tx.execute(new InsertCommand(data1));
tx.execute(new UpdateCommand(data2));
tx.execute(new DeleteCommand(data3));
tx.commit(); // 一次执行所有命令
tx.rollback(); // 撤销所有命令4. 游戏开发
java
// 游戏中的输入处理
InputHandler handler = new InputHandler();
handler.bind(KeyEvent.VK_SPACE, new JumpCommand(player));
handler.bind(KeyEvent.VK_A, new MoveLeftCommand(player));
handler.bind(KeyEvent.VK_D, new MoveRightCommand(player));与其它模式对比
| 模式 | 目的 | 关键区别 |
|---|---|---|
| 命令模式 | 封装请求 | 将请求封装为对象,支持撤销/队列 |
| 策略模式 | 封装算法 | 封装算法,可以相互替换 |
| 责任链模式 | 传递请求 | 请求在链中传递,直到被处理 |
| 备忘录模式 | 保存状态 | 保存对象状态,用于恢复 |
总结
命令模式就是:
- 订单系统:顾客下单 → 厨房做菜
- 遥控器:你按按钮 → 设备响应
- 军事命令:将军下令 → 士兵执行
- 编程接口:API调用 → 系统执行
核心口诀:
请求需要封装好,
调用执行要解耦。
撤销重做是强项,
队列日志都能搞!
就像现实中的:
- 🍽️ 餐厅点餐:菜单(命令)连接顾客(客户端)和厨师(接收者)
- 🎮 游戏手柄:按键(命令)连接玩家(客户端)和游戏角色(接收者)
- 📝 办公流程:申请表(命令)连接申请人(客户端)和审批人(接收者)
- 🏦 银行交易:交易指令(命令)连接客户(客户端)和银行系统(接收者)
记住:当你需要将请求封装为对象,并支持撤销、排队、日志或事务功能时,考虑使用命令模式!