目录
1.priority_queue介绍
内置类型创建堆:
- priority_queue在queue头文件中,除了具有了顺序排列特性以外,常用函数有pop、push、top、empty与size函数,函数用法与其他数据结构大致一样
- priority_queue<int> heap; 表示创建出一个大根堆(默认为大根堆)
- priority_queue<int,vector,less<int>> heap; 创建大根堆的完整格式
- priority_queue<int,vector,greater<int>> heap; 创建小根堆的完整格式
- 记忆方式:不同于sort函数中使用less、greater模板,堆的创建当中小根堆用大于(greater),大根堆用小于(less)
结构体类型创建堆:
要求:结构体中有a、b、c三个变量,要求根据b的大小来创建堆
方法:通过运算符重载(给运算符一个新定义)的方式来完成
代码1(根据b的大小建立起来的大根堆):
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef struct node{
int a,b,c;
bool operator < (const node& x)const
{
return b<x.b;
}
}node;
int main()
{
priority_queue<node> heap;
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
{
heap.push({i-1,i+1,i-1});
}
while(heap.size())
{
node t = heap.top();heap.pop();
cout<<t.a<<" "<<t.b<<" "<<t.c<<endl;
}
return 0;
}代码2(根据b的大小建立起来的小根堆):
cpp
typedef struct node{
int a,b,c;
bool operator < (const node& x)const
{
return b>x.b;
}
}node;2.洛谷---【模板】堆

代码:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
priority_queue<int,vector<int>,greater<int>> heap;
int n;cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
int in;cin>>in;
if(in==1)
{
int input;cin>>input;
heap.push(input);
}
if(in==2) cout<<heap.top()<<endl;
if(in==3) heap.pop();
}
return 0;
}3.牛客---第k小

存放所有的数在堆中会比较麻烦,所以只存k个于k中并使用大根堆,那么头部的元素即为第k小的元素
代码:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
priority_queue<int> heap;
int n,m,k;cin>>n>>m>>k;
while(n--)
{
int in;cin>>in;
heap.push(in);
if(heap.size()>k)heap.pop();
}
while(m--)
{
int in;cin>>in;
if(in==1)
{
int input;cin>>input;
heap.push(input);
if(heap.size()>k)heap.pop();
}
if(in==2)
{
if(heap.size()==k)cout<<heap.top()<<endl;
else cout<<-1<<endl;
}
}
}4.牛客---除2!

代码:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
signed main()
{
int n,k;cin>>n>>k;
int ret=0;
priority_queue<int> heap;
while(n--)
{
int input;cin>>input;
if(input%2)ret+=input;
else heap.push(input);
}
while(heap.size()&&k--)
{
int cur = heap.top();heap.pop();
cur/=2;
if(cur%2) ret+=cur;
else heap.push(cur);
}
while(heap.size())
{
int val = heap.top();heap.pop();
ret+=val;
}
cout<<ret;
return 0;
}代码易错点:
当堆中没有元素时,k可能还不为0,所以在进行除2操作时还需注意,堆里有元素可以用来除2操作
5.洛谷---最小函数值
在所有函数的函数值当中,挑选出最小的m个(如有重复的函数值,则有几个算几个)
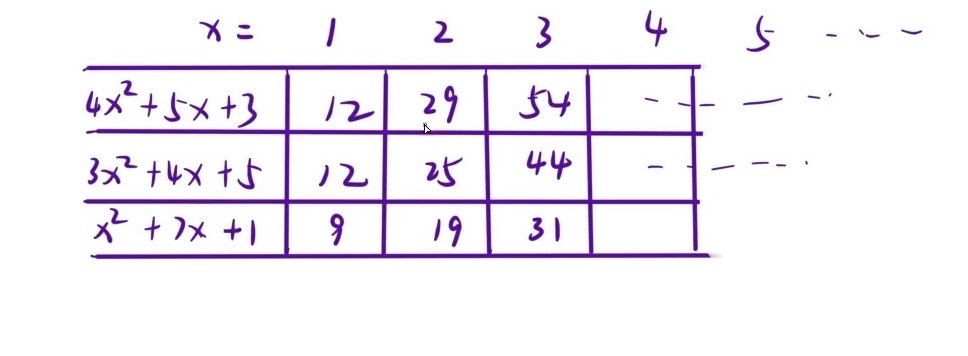
如下图所示,每个不同函数因为x不同,值也会跟着变
由于函数值全都可以保证是单调递增的,所以 x == 1 中函数值最小的,到了 x == 2 时也只会是所有函数值中最小的,所以可以先对x为1时函数值最小的函数计算x为2时的情况,如果还是比x==1时除自身以外的任意一个函数值小,那么继续计算其x==3的情况,这就可以用到小根堆的特性来保存函数值;给每个函数一个编号,每个函数值对应一个x,所以可以搞出一个结构体,其中有<函数值,函数编号,函数值对应的x>;然后根据函数值创建出一个小根堆,该小根堆保持着只有n个值,直到打印完m个值结束循环即可
代码:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
struct function{
int A,B,C;
}fun[N];
typedef struct node{
int val,num,num_x;
bool operator < (const node& x) const
{
return val>x.val;
}
}node;
int add(int x,int i)
{
return fun[i].A*x*x + fun[i].B*x + fun[i].C;
}
int main()
{
int n,m;cin>>n>>m;
priority_queue<node> heap;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>fun[i].A>>fun[i].B>>fun[i].C;
int e = add(1,i);//返回x为1时,当前编号函数的函数值
heap.push({e,i,1});
}
while(m--)
{
node t = heap.top();heap.pop();
cout<<t.val<<" ";
int e = add(t.num_x+1,t.num);
heap.push({e,t.num,t.num_x+1});
}
return 0;
}6.洛谷---序列合并
如下图所示,结构体保存a值的下标,b值的下标,已经a值b值相加的结果,小根堆比较a值b值相加的结果
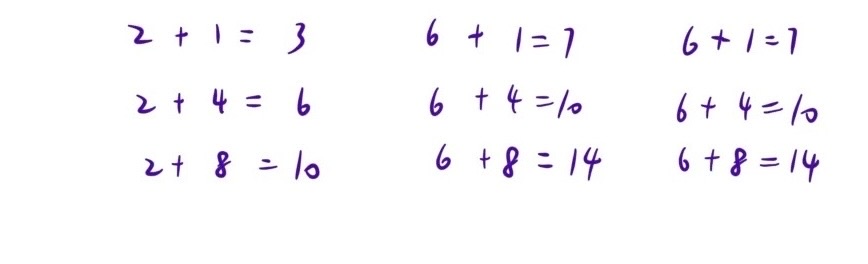
代码:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int a[N],b[N];
typedef struct node{
int i_a,i_b,val;
bool operator < (const node& x) const
{
return val>x.val;
}
}node;
int add(int x,int y)
{
return a[x]+b[y];
}
int main()
{
int n;cin>>n;
priority_queue<node> heap;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>a[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)cin>>b[i];
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int in = add(1,i);
heap.push({1,i,in});
}
while(n--)
{
node t = heap.top();heap.pop();
cout<<t.val<<" ";
int in = add(t.i_a+1,t.i_b);
heap.push({t.i_a+1,t.i_b,in});
}
return 0;
}7.洛谷---舞蹈课(难题)

本题难点:
- 取出相邻的一对异性以后,他们的左右有可能变为新的一对(B++GB++G -> BG)
- 堆中可能存在已经出列的人(一开始BGBG,堆中存了3对BG的差值,出了一队BG后,还剩下2对BG的差值,但实际情况是只剩下一对可以出队的异性了)
- 堆中应该存什么?
代码思路:
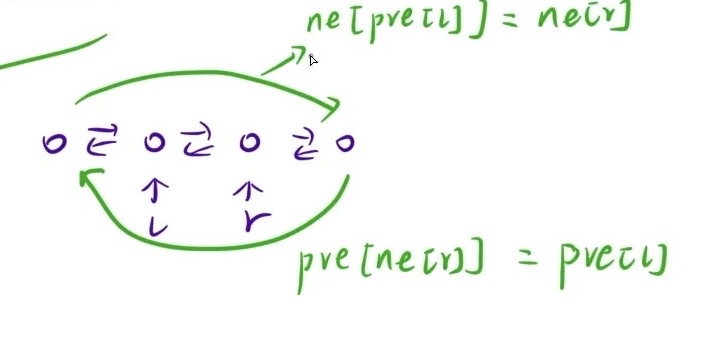
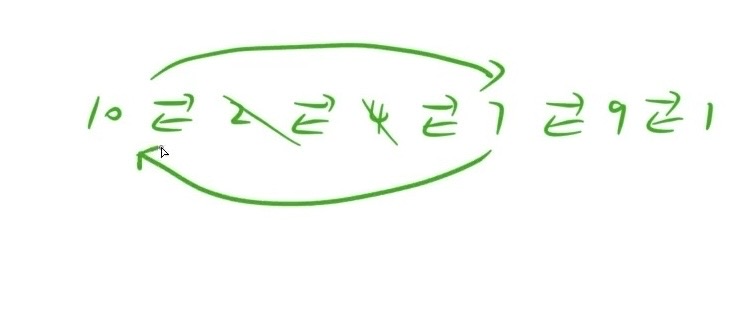
对于取出异性以后,左右可能成为新的一对,可以用双向链表来解决(如下图所示,当中2个结点被删除以后,左边删除结点的前一个结点连向右边删除结点的后一个结点)
为了判断某人是否已经出列,就像判断一个无根树的结点是否遍历过一样,可以通过一个bool数组来标记
堆中存3个内容,分别是<技术差,左编号,右编号>,堆为小根堆比较对象是技术差
代码:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<cmath>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6;
//创建出一个双向链表
int e[N];
int ne[N],pre[N];
int sex[N];//标记男女,男1女0
bool st[N];
typedef struct node{
int d;//差
int left,right;//左编号、右编号
bool operator < (const node& x)const
{
if(d!=x.d) return d>x.d;
else return left>x.left;
}
}node;
int main()
{
int n;cin>>n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
char in;cin>>in;
if(in=='B')sex[i]=1;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
cin>>e[i];
ne[i]=i+1;
pre[i]=i-1;
}
ne[n]=0;
//开始存差值
priority_queue<node> heap;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)
{
if(sex[i]!=sex[i-1]) heap.push({abs(e[i]-e[i-1]),i-1,i});
}
//存完差值开始出人
vector<node> ret;
while(heap.size())
{
node t = heap.top();heap.pop();
int d=t.d,l=t.left,r=t.right;
//判断其中是否已经出队的人
if(st[l]||st[r]) continue;
//如果没有,开始存结果+改变链表+更新堆
ret.push_back(t);
st[l]=st[r]=true;
ne[pre[l]] = ne[r];
pre[ne[r]] = pre[l];
int left = pre[l],right = ne[r];//获取被删除结点的左右结点
if(left&&right&&sex[left]!=sex[right])
heap.push({abs(e[right]-e[left]),left,right});
}
cout<<ret.size()<<endl;
for(auto& x:ret)
cout<<x.left<<" "<<x.right<<endl;
return 0;
} 代码讲解:
- 可以用 0/1 来模拟表示 G/B ,这个方法也是很常用的一个办法(例如把 */ 转换为 @ 或者直接转换为数字)
- 因为会存在2对相邻异性的技术差相等的情况,这个时候按照题目要求先输出前面一对,因此在运算符重载时需要考虑 差值相等、差值不相等 2种情况,差值相等时需要根据左编号的大小来进行小根堆存储
- 双向链表创建时,无需id与p了来标记头结点与新节点的存放位置了,由于静态链表的存放顺序与输入顺序一致,所以直接一边输入一遍存储即可,然后把下标为0处视为头结点
- 双向链表建立以后,需要把最后一个结点的next指针指向无效结点,要不然链表中会出现一个不该存在的有效节点
- 因为需要统计完共有几对相邻异性输出以后,再进行是哪两队匹配上的输出,所以可以搞一个vector数组来预先保存结果,最终的size即为共有几对
- 如下图那样进行双向链表的修改
- 修改完链表更新堆以前,需要先判断新的左右两个相邻节点是否为异性,同时需要判断左右两个结点是否为无效结点(当删除的是头结点或最后一个结点时,则会出现这种状况)