目录
- 一、第三大的数
- 二、将x减到0的最小操作数
- 三、删除有序数组中的重复项
- 四、破冰问题
- 五、分割链表
- 六、将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
- 七、合并区间
- 八、连续数组
- 九、用栈实现队列
- 十、数青蛙
- 十一、重排链表

一、第三大的数

只需要遍历数组,记录下前三大的数即可。我们使用两个标记,一个flag标记交换的次数,x标记Inums[ i ]是最小值导致不会发生交换,单独列出来给flag加一次。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
class Solution {
public int thirdMax(int[] nums) {
int one = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int two = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int three = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
int flag = 0;
boolean x = false;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] > one) {
int tmp = one;
three = two;
two = one;
one = nums[i];
flag++;
} else if(nums[i] < one && nums[i] > two) {
three = two;
two = nums[i];
flag++;
} else if(nums[i] < two && nums[i] >= three) {
three = nums[i];
flag++;
}
if(nums[i] == Integer.MIN_VALUE && !x) {
flag++;
x = true;
}
}
if(flag < 3) return one;
else return three;
}
}二、将x减到0的最小操作数
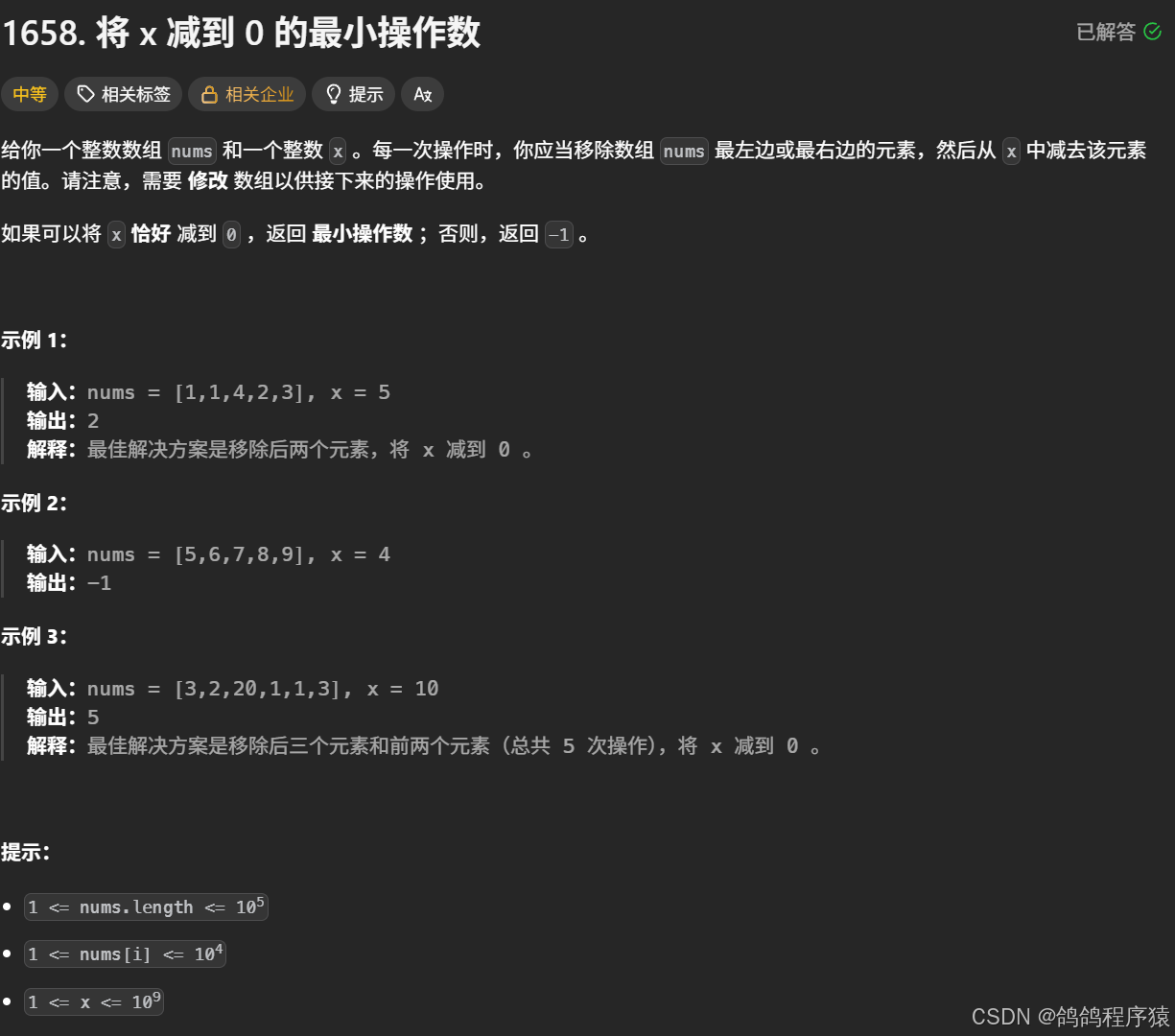
滑动窗口 + 正难则反 思路解决问题,我们直接去移除数组两头元素不好把控,只需要掌握不被移除的数组元素即可。
窗口,记录按照题目规则没有移除的中间元素的和,当数组元素和减去窗口元素和大于x的时候,就代表我们窗口中元素过多,删除窗口元素。
最后更新结果最小值,注意要使用取较小值函数,最好将结果初始值设为int最大值。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
class Solution {
public int minOperations(int[] nums, int x) {
int len = nums.length;
int ret = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int numsSum = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
numsSum += nums[i];
}
if(numsSum == x) return len;
//窗口,记录按照题目规则没有移除的中间元素的和
int sum = 0;
for(int left = 0, right = 0; right < len; right++) {
sum += nums[right];
//出窗口,
while(left < right && numsSum - sum < x) {
sum -= nums[left++];
}
//更新结果
if(numsSum - sum == x) {
ret = Math.min(ret, len - right + left -1);
}
}
return ret == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? -1 : ret;
}
}三、删除有序数组中的重复项
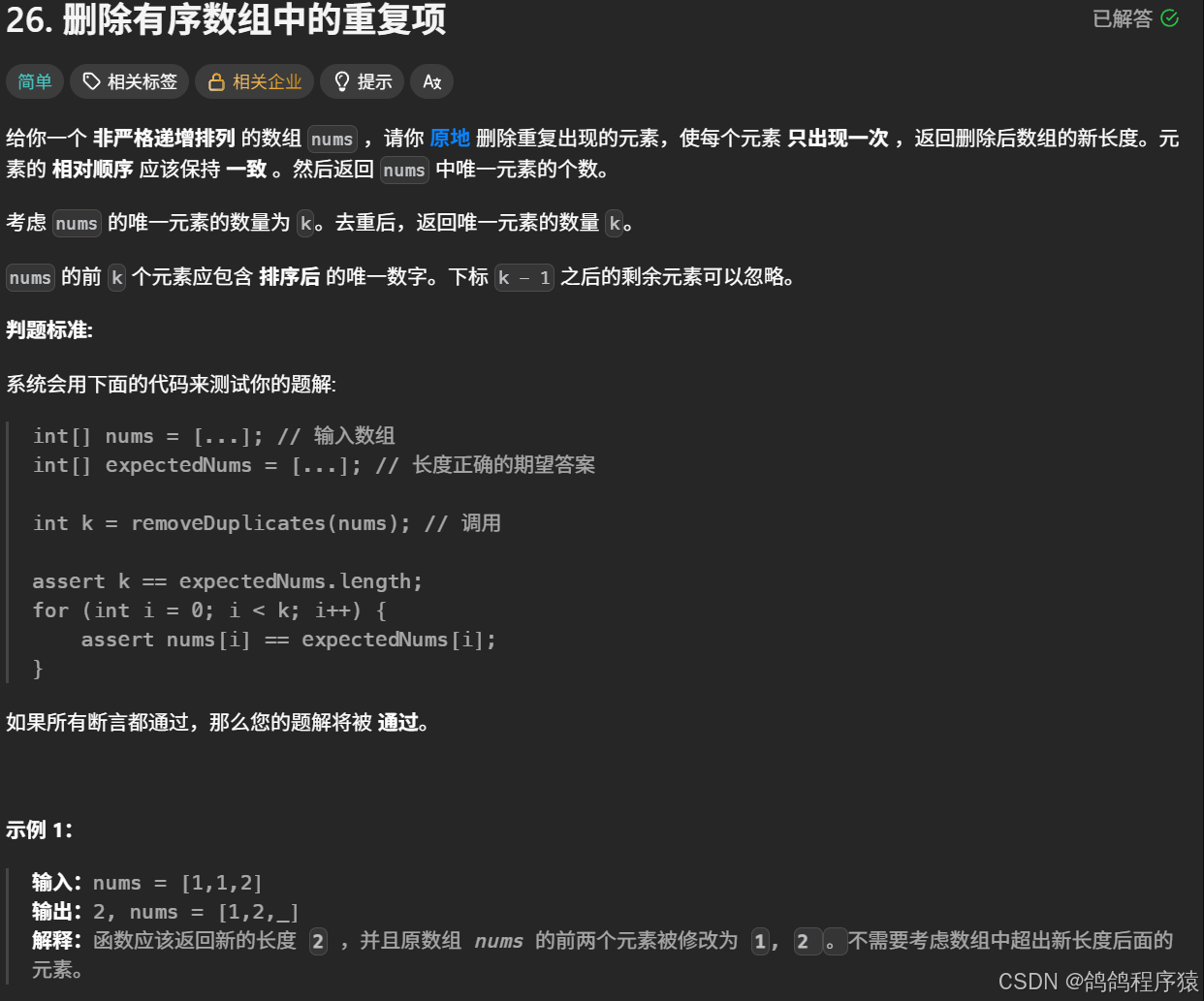
直接暴力遍历即可,将不是重复的元素往前提。
时间复杂度:O(N*N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
class Solution {
public int removeDuplicates(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
int ret = len;
for(int i = 1; i < len; i++) {
if(nums[i] == nums[i-1]) {
int tmp = 0;//记录重复元素个数-1
//覆盖
for(int j = i, k = i ; j < len; j++) {
if(nums[j] != nums[k-1]) {
nums[k++] = nums[j];
} else {
tmp++;
}
}
len -= tmp;
}
}
return len;
}
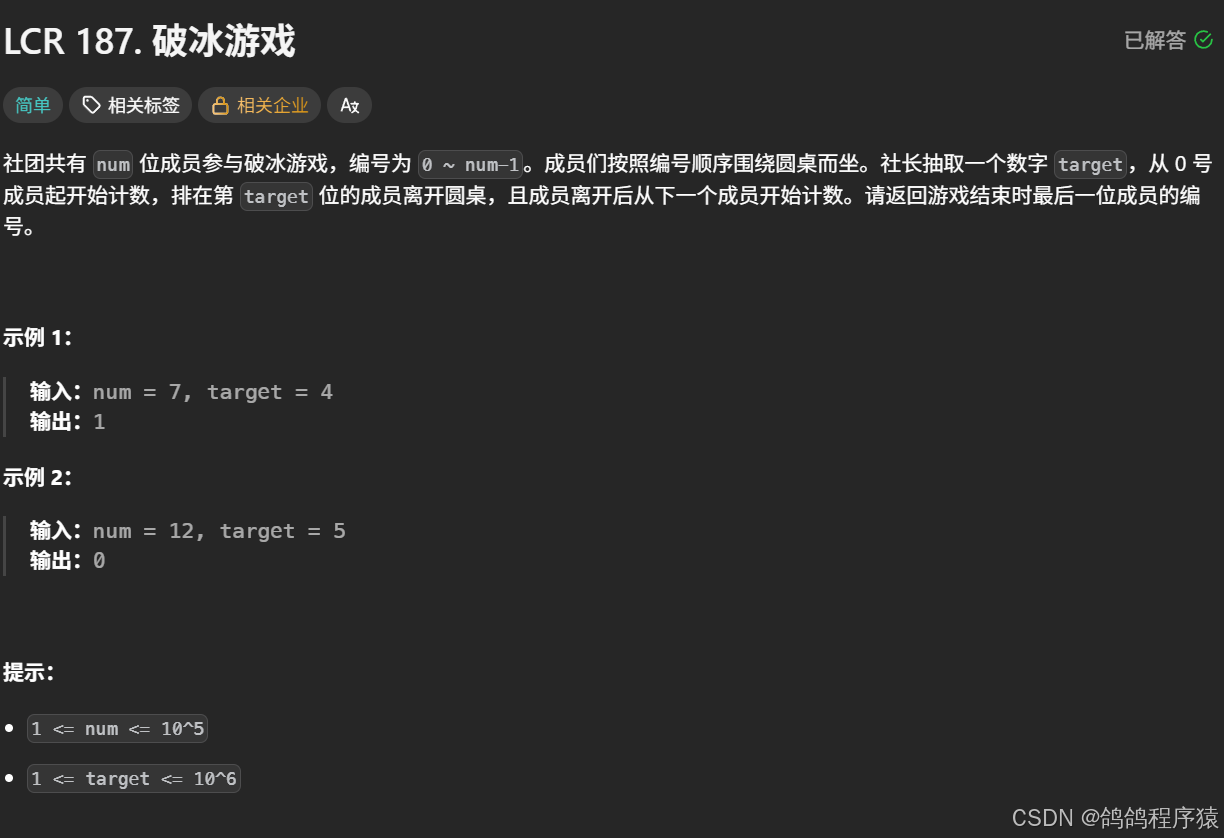
}四、破冰问题
一个约瑟夫环问题,两种思路,设计一个逻辑结构为环形链表的数组,一直遍历删除,直到只有一个元素为止。第二种直接使用数学思路,1 - n 个数字,对应的删除坐标为上一个存活的下标往下数 target ,再对数字个数取余。即(target + ret) % i
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
class Solution {
public int iceBreakingGame(int num, int target) {
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= num; i++) {
ret = (target + ret) % i;
}
return ret;
}
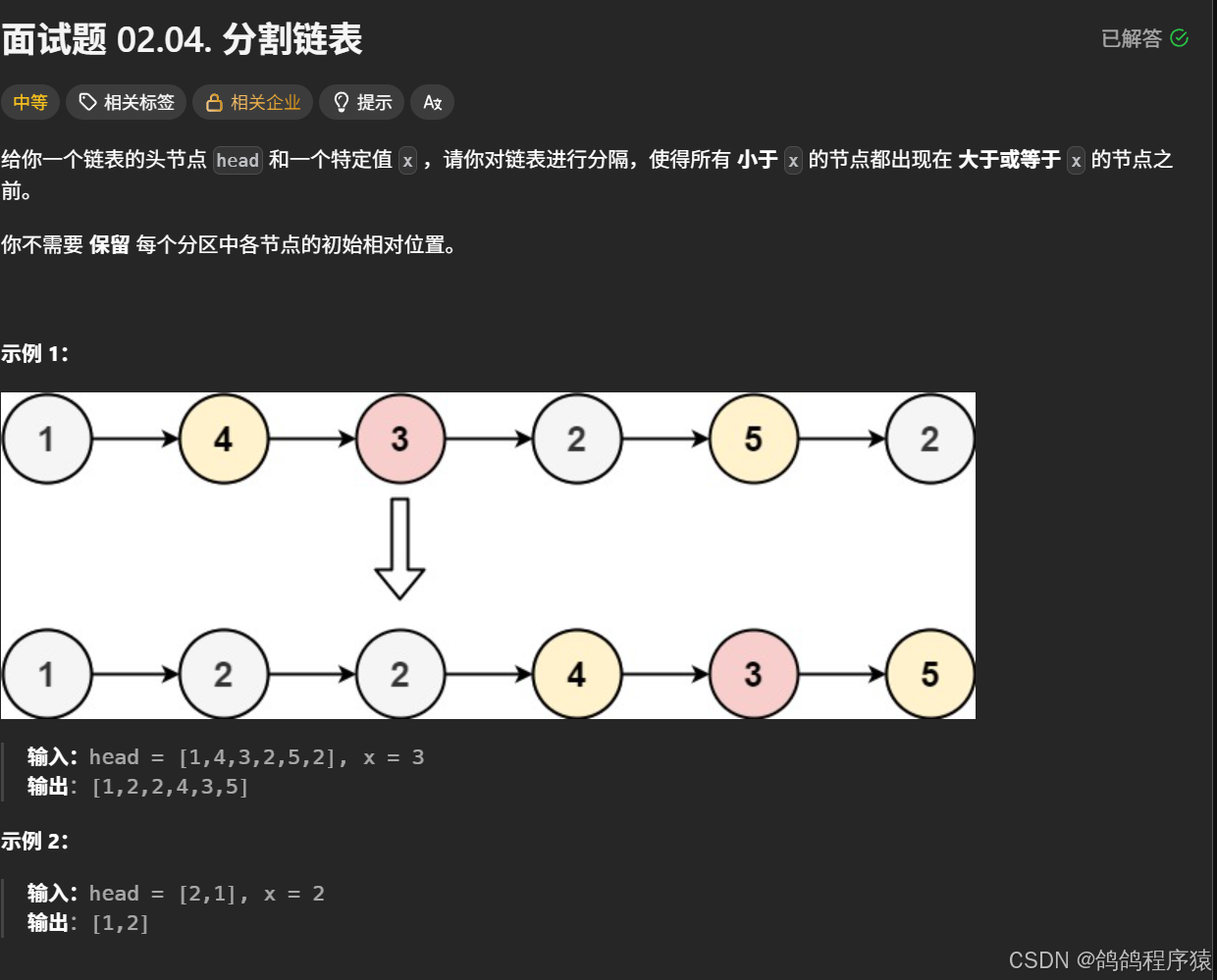
}五、分割链表
直接遍历链表,将比x小的节点头插一下即可。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode partition(ListNode head, int x) {
if(head == null) return head;
ListNode cur = head.next;
ListNode prev = head;
while(cur != null) {
if(cur.val < x) {
//头插
ListNode tmp = cur;
prev.next = cur.next;
tmp.next = head;
head = tmp;
cur = prev.next;
} else {
prev = cur;
cur = cur.next;
}
}
return head;
}
}六、将有序数组转换为二叉搜索树
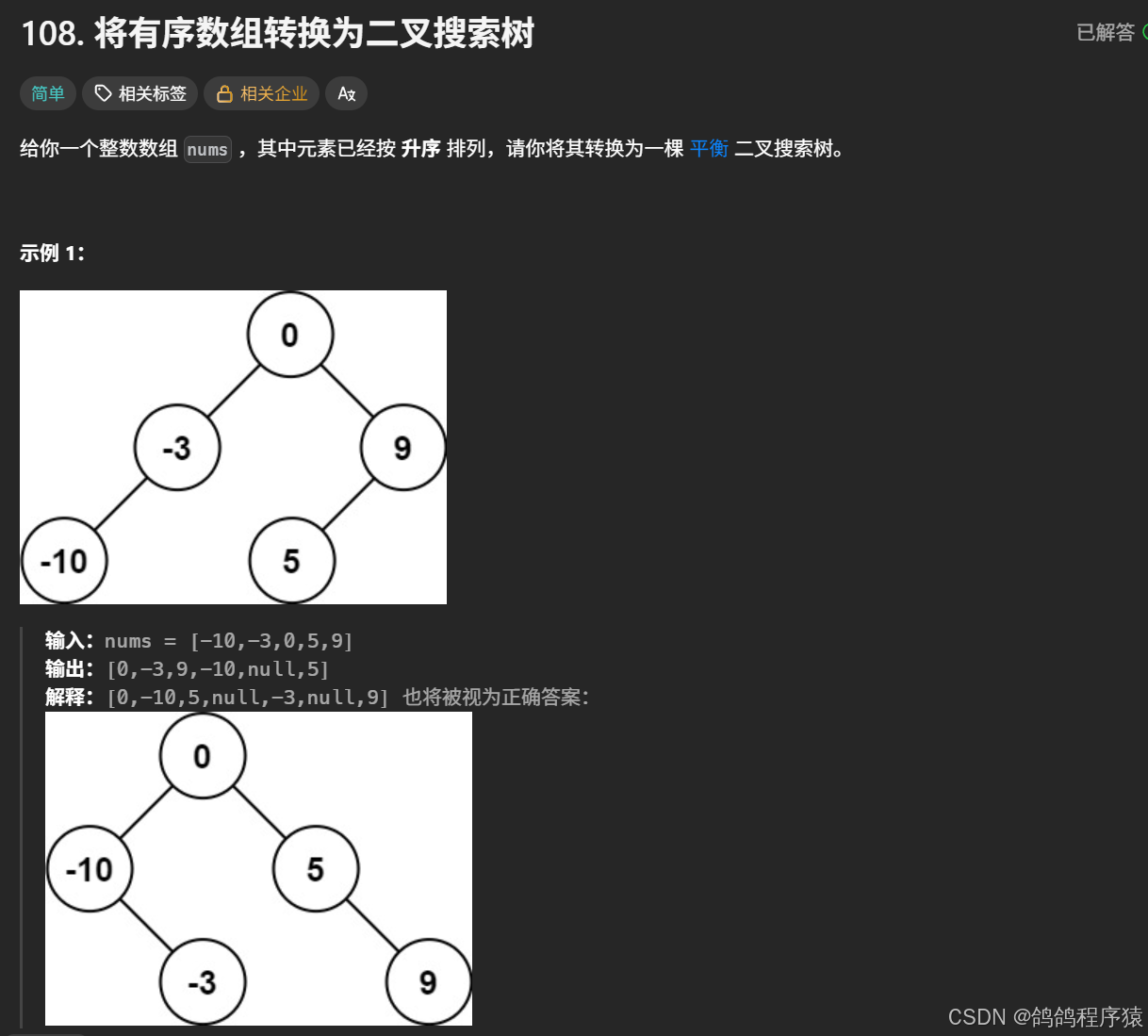
直接每次使用中间的数作为根节点,两边的数组递归即可。
时间复杂度:O(logN)
空间复杂度:O(N)
java
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode() {}
* TreeNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* TreeNode(int val, TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = left;
* this.right = right;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode sortedArrayToBST(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[len/2]);
root.left = bst(nums,0,len/2-1);
root.right = bst(nums,len/2 + 1,len-1);
return root;
}
public TreeNode bst(int[] nums,int left, int right) {
if(left > right) return null;
if(left == right) return new TreeNode(nums[left]);
int mid = (left + right) / 2;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(nums[mid]);
root.left = bst(nums,left,mid - 1);
root.right = bst(nums,mid + 1,right);
return root;
}
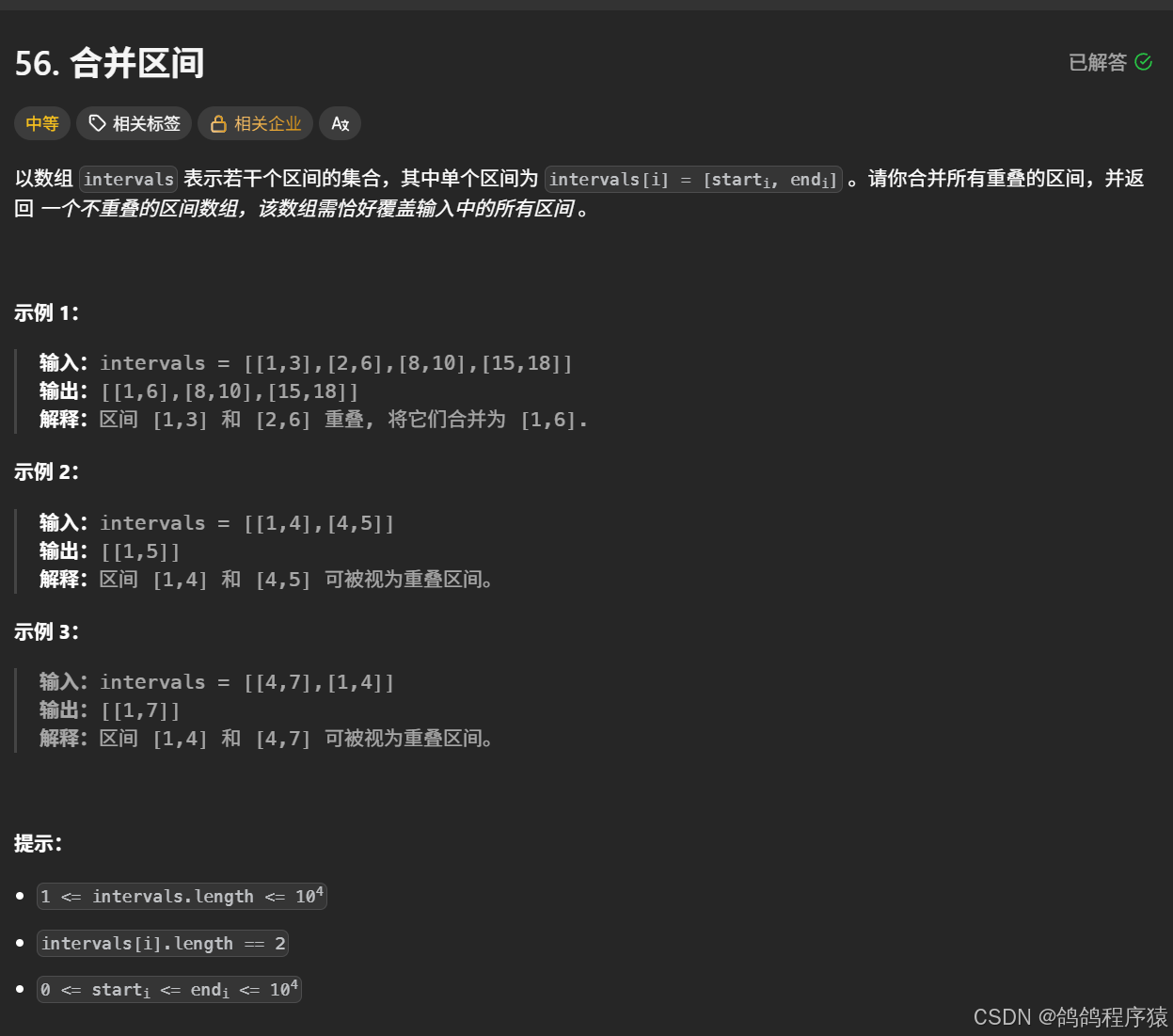
}七、合并区间
我们只需要将二维数组中每个一维数组的第一个元素进行排序,从小到大调整一维数组的位置,
这样就可以直接连续去比较前一个一维数组末尾元素和后一个一维数组第一个元素的大小,就可以判断是不是重叠的区间了。
如果是,就直接将两个一维数组末尾元素的较大值放入前一个一维数组即可。
如果不是,就将后一个一维数组入结果数组。
时间复杂度:O(N*logN)
空间复杂度:O(logN)
java
class Solution {
public int[][] merge(int[][] intervals) {
int len = intervals.length;
if(len == 0) {
return new int[0][2];
}
//按照左端点排序数组
Arrays.sort(intervals, new Comparator<int[]>() {
public int compare(int[] intervals1, int[] intervals2) {
return intervals1[0] - intervals2[0];
}
});
//跟结果最后一个数组最后值做对比
List<int[]> ret = new ArrayList<int[]>();
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
int left = intervals[i][0];
int right = intervals[i][1];
if(ret.size() == 0 || ret.get(ret.size() -1)[1] < left) {
ret.add(intervals[i]);
} else {
ret.get(ret.size() -1)[1] = Math.max(ret.get(ret.size() -1)[1], right);
}
}
return ret.toArray(new int[ret.size()][]);
}
}八、连续数组
hash + 前缀和
使用一个hash表,key记录子数组0、1个数差,value记录当前0到i构成的子数组的结束坐标。
使用一个标记记录子数组0、1个数差。
便利数组,当nums[ i ] 是0的时候标记-1,反之+1。当hash有当前标记值,证明只需要减去hash中的子数组,结果就是符合条件的数组,更新结果
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(N)
java
class Solution {
public int findMaxLength(int[] nums) {
int ret = 0;
int n = nums.length;
//key - 1和0个数之差, value - 0到子数组结束坐标
Map<Integer,Integer> hash = new HashMap<>();
hash.put(0,-1);
//前面1和0个数之差
int num = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if(nums[i] == 0) num--;
else num++;
if(hash.containsKey(num)) ret = Math.max(ret, i - hash.get(num));
else hash.put(num, i);
}
return ret;
}
}九、用栈实现队列
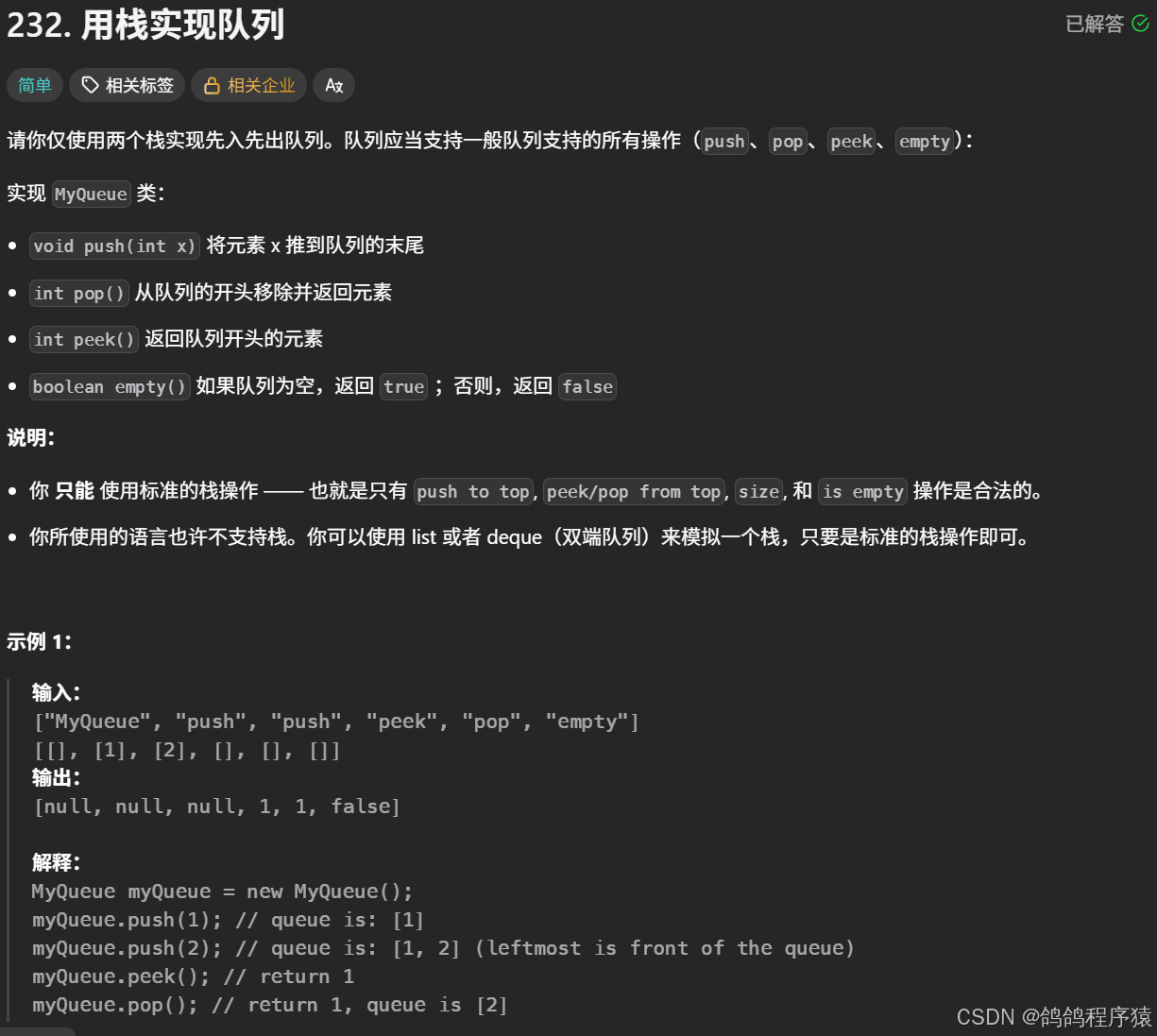
两个栈分工合作,栈1负责接收数据,栈2负责接收栈1的数据,数据经过两次的栈存储,对栈2里面的数据操作就相当于是队列操作了。
时间复杂度:O(logN)
空间复杂度:O(N)
java
class MyQueue {
private Stack<Integer> stack1;
private Stack<Integer> stack2;
public MyQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<>();
stack2 = new Stack<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
stack1.push(x);
}
public int pop() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()) {
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.pop();
}
public int peek() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()) {
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.peek();
}
public boolean empty() {
if(stack2.isEmpty()) {
while(!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
return stack2.isEmpty();
}
}
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = new MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* boolean param_4 = obj.empty();
*/十、数青蛙
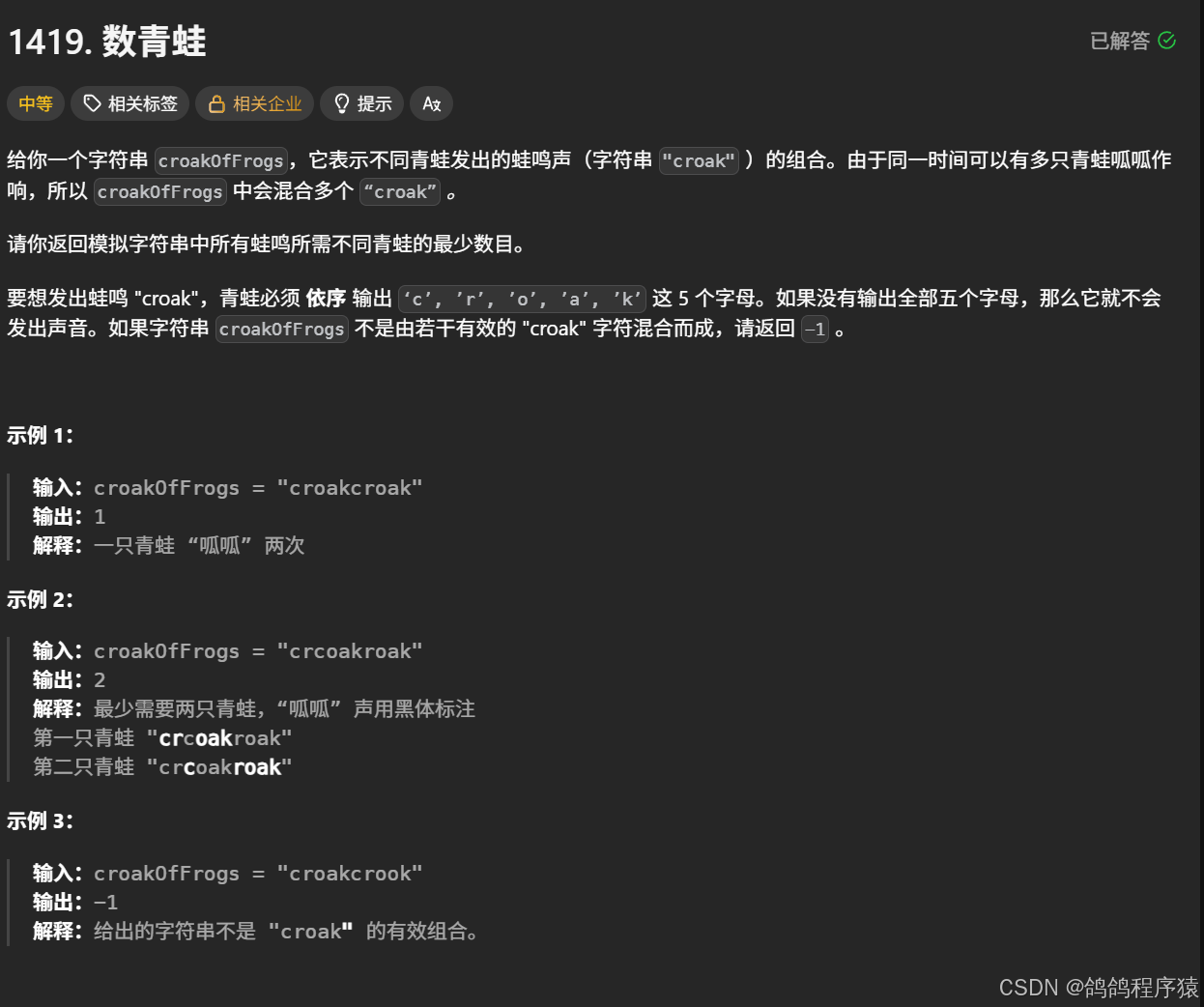
我们使用一个数组hash来表示正在叫哪个字母的青蛙数量,随后遍历字符串,当遇到第一个字母c的时候,就要在hash[0]加一个青蛙,如果hash[4]有青蛙就要减去一个,其余字母就对当前字母对应的下标数组值加1,前面一个减去1,如果前面减去小于0了就返回-1,最后返回hash[4]的值就行了。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
class Solution {
public int minNumberOfFrogs(String croakOfFrogs) {
if(croakOfFrogs.length() % 5 != 0) return -1;
int[] hash = new int[5];
String s = "croak";
Map<Character, Integer> index = new HashMap<>();
for(int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
index.put(s.charAt(i), i);
}
for(int i = 0; i < croakOfFrogs.length(); i++) {
if(croakOfFrogs.charAt(i) == s.charAt(0)) {
if(hash[4] > 0) hash[4]--;
hash[0]++;
} else {
int in = index.get(croakOfFrogs.charAt(i));
if(hash[in-1] == 0) return -1;
hash[in-1]--;
hash[in]++;
}
}
return hash[0] != 0 ? -1 : hash[4];
}
}十一、重排链表
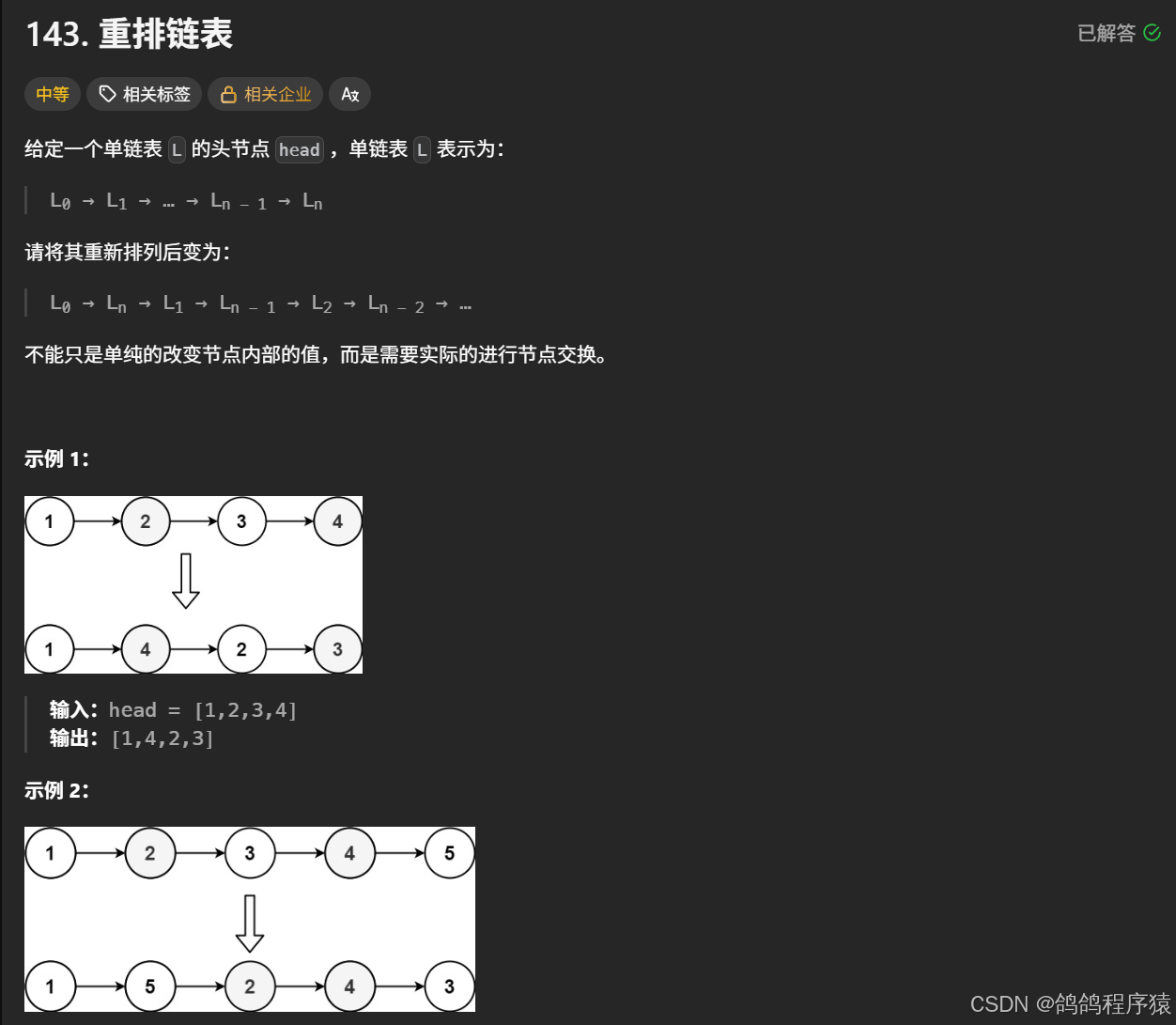
我们只需要从中间节点将给的链表一分为二(使用快慢指针找到中间节点),然后将后半段链表逆置(头插法),最后按要求合并两个链表即可。
时间复杂度:O(N)
空间复杂度:O(1)
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head;
//快慢双指针,找中间节点
while(fast != null && fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
//头插逆置后半段节点
ListNode head2 = null;
ListNode cur = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
while(cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = head2;
head2 = cur;
cur = next;
}
//合并两段链表
ListNode newHead = head;
ListNode cur1 = head;
ListNode cur2 = head2;
while(cur1 != null && cur2 != null) {
ListNode next1 = cur1.next;
ListNode next2 = cur2.next;
cur1.next = cur2;
cur2.next = next1;
cur1 = next1;
cur2 = next2;
}
}
}