ReLU Function and Leaky ReLU Function - Derivatives and Gradients {导数和梯度}
- [1. ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) Function](#1. ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) Function)
-
- [1.1. Parameters](#1.1. Parameters)
- [1.2. Shape](#1.2. Shape)
- [2. LeakyReLU (Leaky Rectified Linear Unit)](#2. LeakyReLU (Leaky Rectified Linear Unit))
-
- [2.1. Parameters](#2.1. Parameters)
- [2.2. Shape](#2.2. Shape)
- [3. ReLU Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度)](#3. ReLU Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度))
-
- [3.1. PyTorch `torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=False)`](#3.1. PyTorch
torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=False)) - [3.2. Python ReLU Function](#3.2. Python ReLU Function)
- [3.3. Python ReLU Function](#3.3. Python ReLU Function)
- [3.1. PyTorch `torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=False)`](#3.1. PyTorch
- [4. Leaky ReLU Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度)](#4. Leaky ReLU Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度))
-
- [4.1. PyTorch `torch.nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01, inplace=False)`](#4.1. PyTorch
torch.nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01, inplace=False)) - [4.2. Python Leaky ReLU Function](#4.2. Python Leaky ReLU Function)
- [4.3. Python Leaky ReLU Function](#4.3. Python Leaky ReLU Function)
- [4.1. PyTorch `torch.nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01, inplace=False)`](#4.1. PyTorch
- References
Activation functions decide whether a neuron should be activated or not by calculating the weighted sum and further adding bias to it. They are differentiable operators for transforming input signals to outputs, while most of them add nonlinearity.
激活函数 (activation function) 通过计算加权和并加上偏置来确定神经元是否应该被激活,它们将输入信号转换为输出的可微运算。大多数激活函数都是非线性的。
1. ReLU (Rectified Linear Unit) Function
class torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
https://docs.pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.ReLU.html
torch.nn.functional.relu(input, inplace=False) -> Tensor
https://docs.pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.relu.html
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/main/torch/nn/modules/activation.py
ReLU provides a very simple nonlinear transformation.
ReLU 提供了一种非常简单的非线性变换。
Applies the rectified linear unit function element-wise.
The definition of the ReLU function:
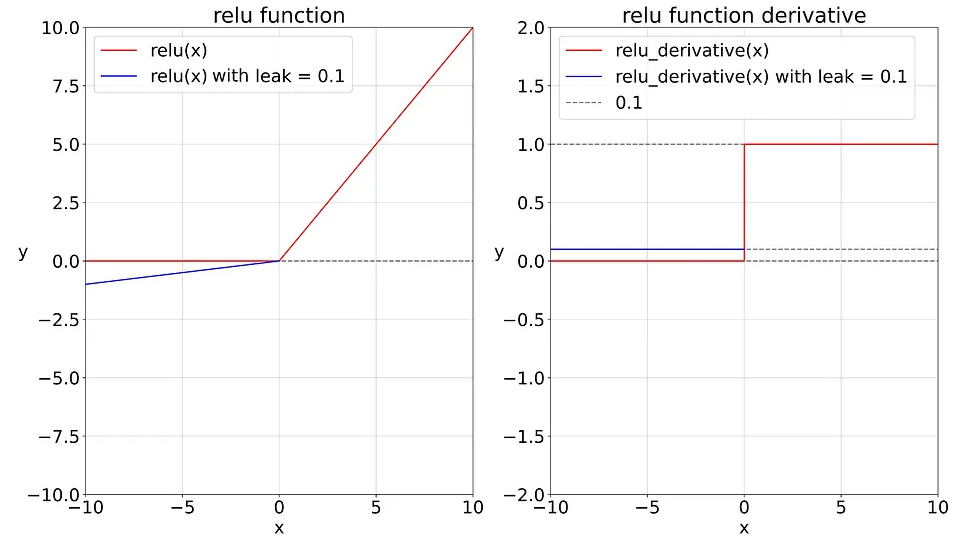
ReLU ( x ) = max ( 0 , x ) = x + ∣ x ∣ 2 = { x , x > 0 0 , x ≤ 0 \begin{aligned} \text{ReLU}(x) &= \max(0, x) = \frac{x+|x|}{2} \\ &= \begin{cases} x, & x > 0 \\ 0, & x \le 0 \\ \end{cases} \end{aligned} ReLU(x)=max(0,x)=2x+∣x∣={x,0,x>0x≤0
The ReLU function retains only positive elements and discards all negative elements by setting the corresponding activations to 0.
ReLU 函数通过将相应的活性值设为 0,仅保留正元素并丢弃所有负元素。
The derivative of the ReLU function:
d y d x = f ′ ( x ) = d ( { x , x > 0 0 , x ≤ 0 ) d x = { 1 , x > 0 0 , x ≤ 0 \begin{aligned} \frac{dy}{dx} &= f'(x) \\ &= \frac{d \left( {\begin{cases} x, & x > 0 \\ 0, & x \le 0 \\ \end{cases}} \right) }{dx} \\ &= \begin{cases} 1, & x > 0 \\ 0, & x \le 0 \\ \end{cases} \\ \end{aligned} dxdy=f′(x)=dxd({x,0,x>0x≤0)={1,0,x>0x≤0
When the input is negative, the derivative of the ReLU function is 0, and when the input is positive, the derivative of the ReLU function is 1. Note that the ReLU function is not differentiable when the input takes value precisely equal to 0. In these cases, we default to the left-hand-side derivative and say that the derivative is 0 when the input is 0. We can get away with this because the input may never actually be zero (mathematicians would say that it is nondifferentiable on a set of measure zero).
当输入为负时,ReLU 函数的导数为 0,而当输入为正时,ReLU 函数的导数为 1。注意,当输入值精确等于 0 时,ReLU 函数不可导。在此时,我们默认使用左侧的导数,即当输入为 0 时导数为 0。我们可以忽略这种情况,因为输入可能永远都不会是 0。
The reason for using ReLU is that its derivatives are particularly well behaved: either they vanish or they just let the argument through. This makes optimization better behaved and it mitigated the well-documented problem of vanishing gradients that plagued previous versions of neural networks.
使用 ReLU 的原因是,它求导表现得特别好:要么让参数消失,要么让参数通过。这使得优化表现得更好,并且 ReLU 减轻了困扰以往神经网络的梯度消失问题。
plague [pleɪɡ]
n. 瘟疫;死亡率高的传染病;祸患
v. 困扰;折磨;给...造成长时间的痛苦或麻烦;使受煎熬1.1. Parameters
- inplace (bool) - can optionally do the operation in-place. Default:
False
1.2. Shape
-
Input :
(*), where*means any number of dimensions. -
Output :
(*), same shape as the input.
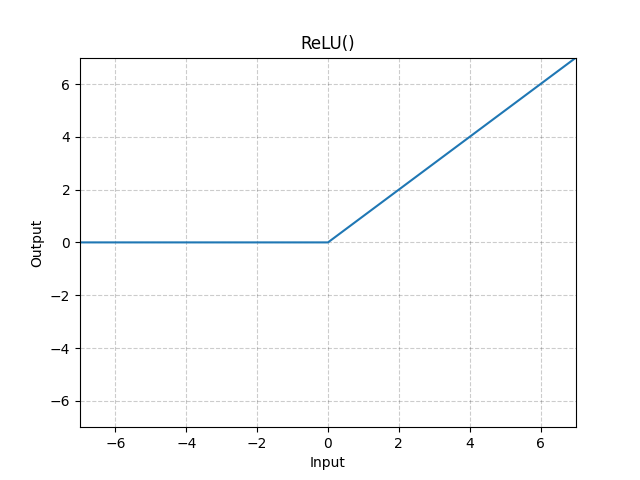
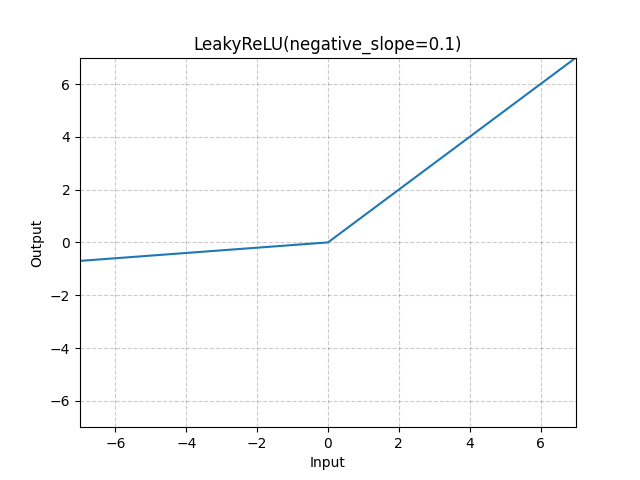
2. LeakyReLU (Leaky Rectified Linear Unit)
class torch.nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01, inplace=False)
https://docs.pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.LeakyReLU.html
torch.nn.functional.leaky_relu(input, negative_slope=0.01, inplace=False) -> Tensor
https://docs.pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.leaky_relu.html
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/main/torch/nn/modules/activation.py
Applies the LeakyReLU function element-wise.
The definition of the Leaky ReLU function:
LeakyReLU ( x ) = max ( 0 , x ) + negative_slope ∗ min ( 0 , x ) = { x , x ≥ 0 negative_slope ∗ x , otherwise \begin{aligned} \text{LeakyReLU}(x) &= \max(0, x) + \text{negative\_slope} * \min(0, x) \\ &= \begin{cases} x, & x \geq 0 \\ \text{negative\_slope} * x, & \text{ otherwise } \end{cases} \end{aligned} LeakyReLU(x)=max(0,x)+negative_slope∗min(0,x)={x,negative_slope∗x,x≥0 otherwise
The derivative of the Leaky ReLU function:
d y d x = f ′ ( x ) = d ( { x , x ≥ 0 negative_slope ∗ x , otherwise ) d x = { 1 , x ≥ 0 negative_slope , x < 0 \begin{aligned} \frac{dy}{dx} &= f'(x) \\ &= \frac{d \left( \begin{cases} x, & x \geq 0 \\ \text{negative\_slope} * x, & \text{ otherwise } \end{cases} \right) }{dx} \\ &= \begin{cases} 1, & x \geq 0 \\ \text{negative\_slope}, & x < 0 \\ \end{cases} \\ \end{aligned} dxdy=f′(x)=dxd({x,negative_slope∗x,x≥0 otherwise )={1,negative_slope,x≥0x<0
在 x = 0 x = 0 x=0 处,Leaky ReLU 函数的导数函数是不连续的。
2.1. Parameters
-
negative_slope (float) - Controls the angle of the negative slope (which is used for negative input values). Default:
1e-2 -
inplace (bool) - can optionally do the operation in-place. Default:
False
2.2. Shape
-
Input :
(*)where*means, any number of additional dimensions -
Output :
(*), same shape as the input
This is the graph for the ReLU and Leaky ReLU functions and their derivatives.
3. ReLU Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度)
3.1. PyTorch torch.nn.ReLU(inplace=False)
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6)
input = torch.tensor([[-1.5, 0.0, 1.5], [0.5, -2.0, 3.0]], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
print(f"input.requires_grad: {input.requires_grad}, input.shape: {input.shape}")
relu = nn.ReLU()
forward_output = relu(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/relu.py
input.requires_grad: True, input.shape: torch.Size([2, 3])
forward_output.shape: torch.Size([2, 3])
Forward Pass Output:
tensor([[0.000000, 0.000000, 1.500000],
[0.500000, 0.000000, 3.000000]], grad_fn=<ReluBackward0>)
Process finished with exit code 03.2. Python ReLU Function
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
# numpy.multiply:
# Multiply arguments element-wise
# Equivalent to x1 * x2 in terms of array broadcasting
class ReLULayer:
"""
Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation function layer
"""
def __init__(self):
# Cache the input for the backward pass (gradient calculation)
self.input = None
def forward(self, input):
"""
Performs the forward pass for the relu function: output = max(0, input)
f(x) = max(0, x)
"""
self.input = input
# Returns the input directly if positive, otherwise 0
self.output = np.maximum(0, input)
return self.output
def backward(self, upstream_gradient):
"""
Calculates the gradient of the ReLU function with respect to the input x
The derivative of the relu function is 1 for x > 0 and 0 for x <= 0
"""
# Create an array of the same shape as the input 'x', initialized to zeros
relu_derivative = np.zeros_like(self.input)
relu_derivative[self.input > 0] = 1
print(f"\nrelu_derivative.shape: {relu_derivative.shape}")
print(f"ReLU Derivative:\n{relu_derivative}")
# Apply the chain rule: multiply the derivative by the upstream gradient
downstream_gradient = upstream_gradient * relu_derivative
return downstream_gradient
relu_layer = ReLULayer()
input = np.array([-1.5, 0.0, 1.5, 0.5, -2.0, 3.0], dtype=np.float32)
# Forward pass
forward_output = relu_layer.forward(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
# Backward pass
upstream_gradient = np.ones(forward_output.shape) * 0.1
backward_output = relu_layer.backward(upstream_gradient)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {backward_output.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{backward_output}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/relu.py
forward_output.shape: (6,)
Forward Pass Output:
[0. 0. 1.5 0.5 0. 3. ]
relu_derivative.shape: (6,)
ReLU Derivative:
[0. 0. 1. 1. 0. 1.]
backward_output.shape: (6,)
Backward Pass Output:
[0. 0. 0.1 0.1 0. 0.1]
Process finished with exit code 03.3. Python ReLU Function
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
# numpy.multiply:
# Multiply arguments element-wise
# Equivalent to x1 * x2 in terms of array broadcasting
class ReLULayer:
"""
Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) activation function layer
"""
def __init__(self):
# Cache the input for the backward pass (gradient calculation)
self.input = None
def forward(self, input):
"""
Performs the forward pass for the relu function: output = max(0, input)
f(x) = max(0, x)
"""
self.input = input
# Returns the input directly if positive, otherwise 0
self.output = np.maximum(0, input)
return self.output
def backward(self, upstream_gradient):
"""
Calculates the gradient of the ReLU function with respect to the input x
The derivative of the relu function is 1 for x > 0 and 0 for x <= 0
"""
# Create an array of the same shape as the input 'x', initialized to zeros
relu_derivative = np.zeros_like(self.input)
relu_derivative[self.input > 0] = 1
print(f"\nrelu_derivative.shape: {relu_derivative.shape}")
print(f"ReLU Derivative:\n{relu_derivative}")
# Apply the chain rule: multiply the derivative by the upstream gradient
downstream_gradient = upstream_gradient * relu_derivative
return downstream_gradient
relu_layer = ReLULayer()
input = np.array([[-1.5, 0.0, 1.5], [0.5, -2.0, 3.0]], dtype=np.float32)
# Forward pass
forward_output = relu_layer.forward(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
# Backward pass
upstream_gradient = np.ones(forward_output.shape) * 0.1
backward_output = relu_layer.backward(upstream_gradient)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {backward_output.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{backward_output}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/relu.py
forward_output.shape: (2, 3)
Forward Pass Output:
[[0. 0. 1.5]
[0.5 0. 3. ]]
relu_derivative.shape: (2, 3)
ReLU Derivative:
[[0. 0. 1.]
[1. 0. 1.]]
backward_output.shape: (2, 3)
Backward Pass Output:
[[0. 0. 0.1]
[0.1 0. 0.1]]
Process finished with exit code 04. Leaky ReLU Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度)
4.1. PyTorch torch.nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.01, inplace=False)
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6)
input = torch.tensor([[-1.5, 0.0, 1.5], [0.5, -2.0, 3.0]], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
print(f"input.requires_grad: {input.requires_grad}, input.shape: {input.shape}")
leaky_relu = nn.LeakyReLU(negative_slope=0.1)
forward_output = leaky_relu(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/leaky_relu.py
input.requires_grad: True, input.shape: torch.Size([2, 3])
forward_output.shape: torch.Size([2, 3])
Forward Pass Output:
tensor([[-0.150000, 0.000000, 1.500000],
[ 0.500000, -0.200000, 3.000000]], grad_fn=<LeakyReluBackward0>)
Process finished with exit code 04.2. Python Leaky ReLU Function
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
# numpy.multiply:
# Multiply arguments element-wise
# Equivalent to x1 * x2 in terms of array broadcasting
class LeakyReLULayer:
"""
Leaky Rectified Linear Unit (Leaky ReLU) activation function
"""
def __init__(self, negative_slope=0.2):
# Cache the input for the backward pass (gradient calculation)
self.input = None
self.negative_slope = negative_slope
def forward(self, input):
"""
Applies the Leaky ReLU function: f(x) = x if x > 0, else negative_slope * x
"""
self.input = input
# Apply the Leaky ReLU function: x for positive values, negative_slope * x for negative values
self.output = np.where(input >= 0, input, self.negative_slope * input)
return self.output
def backward(self, upstream_gradient):
"""
Calculates the gradient of the Leaky ReLU function with respect to the input x
The derivative of the Leaky ReLU function is 1 if x > 0, else negative_slope
"""
# Create an array of the same shape as the input 'x', initialized to zeros
leaky_relu_derivative = np.ones_like(self.input)
leaky_relu_derivative[self.input < 0] = self.negative_slope
print(f"\nleaky_relu_derivative.shape: {leaky_relu_derivative.shape}")
print(f"Leaky ReLU Derivative:\n{leaky_relu_derivative}")
# Apply the chain rule: multiply the derivative by the upstream gradient
downstream_gradient = upstream_gradient * leaky_relu_derivative
return downstream_gradient
leaky_relu_layer = LeakyReLULayer()
input = np.array([-1.5, 0.0, 1.5, 0.5, -2.0, 3.0], dtype=np.float32)
# Forward pass
forward_output = leaky_relu_layer.forward(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
# Backward pass
upstream_gradient = np.ones(forward_output.shape) * 0.1
backward_output = leaky_relu_layer.backward(upstream_gradient)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {backward_output.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{backward_output}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/leaky_relu.py
forward_output.shape: (6,)
Forward Pass Output:
[-0.3 0. 1.5 0.5 -0.4 3. ]
leaky_relu_derivative.shape: (6,)
Leaky ReLU Derivative:
[0.2 1. 1. 1. 0.2 1. ]
backward_output.shape: (6,)
Backward Pass Output:
[0.02 0.1 0.1 0.1 0.02 0.1 ]
Process finished with exit code 04.3. Python Leaky ReLU Function
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
np.set_printoptions(threshold=np.inf)
# numpy.multiply:
# Multiply arguments element-wise
# Equivalent to x1 * x2 in terms of array broadcasting
class LeakyReLULayer:
"""
Leaky Rectified Linear Unit (Leaky ReLU) activation function
"""
def __init__(self, negative_slope=0.2):
# Cache the input for the backward pass (gradient calculation)
self.input = None
self.negative_slope = negative_slope
def forward(self, input):
"""
Applies the Leaky ReLU function: f(x) = x if x > 0, else negative_slope * x
"""
self.input = input
# Apply the Leaky ReLU function: x for positive values, negative_slope * x for negative values
self.output = np.where(input >= 0, input, self.negative_slope * input)
return self.output
def backward(self, upstream_gradient):
"""
Calculates the gradient of the Leaky ReLU function with respect to the input x
The derivative of the Leaky ReLU function is 1 if x > 0, else negative_slope
"""
# Create an array of the same shape as the input 'x', initialized to zeros
leaky_relu_derivative = np.ones_like(self.input)
leaky_relu_derivative[self.input < 0] = self.negative_slope
print(f"\nleaky_relu_derivative.shape: {leaky_relu_derivative.shape}")
print(f"Leaky ReLU Derivative:\n{leaky_relu_derivative}")
# Apply the chain rule: multiply the derivative by the upstream gradient
downstream_gradient = upstream_gradient * leaky_relu_derivative
return downstream_gradient
leaky_relu_layer = LeakyReLULayer()
input = np.array([[-1.5, 0.0, 1.5], [0.5, -2.0, 3.0]], dtype=np.float32)
# Forward pass
forward_output = leaky_relu_layer.forward(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
# Backward pass
upstream_gradient = np.ones(forward_output.shape) * 0.1
backward_output = leaky_relu_layer.backward(upstream_gradient)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {backward_output.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{backward_output}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/leaky_relu.py
forward_output.shape: (2, 3)
Forward Pass Output:
[[-0.3 0. 1.5]
[ 0.5 -0.4 3. ]]
leaky_relu_derivative.shape: (2, 3)
Leaky ReLU Derivative:
[[0.2 1. 1. ]
[1. 0.2 1. ]]
backward_output.shape: (2, 3)
Backward Pass Output:
[[0.02 0.1 0.1 ]
[0.1 0.02 0.1 ]]
Process finished with exit code 0References
1\] Yongqiang Cheng (程永强),