Tanh Function - Derivatives and Gradients {导数和梯度}
- [1. Tanh Function](#1. Tanh Function)
-
- [1.1. Shape](#1.1. Shape)
- [2. Tanh Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度)](#2. Tanh Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度))
-
- [2.1. PyTorch `torch.nn.Tanh(*args, **kwargs)`](#2.1. PyTorch
torch.nn.Tanh(*args, **kwargs)) - [2.2. PyTorch `torch.nn.Tanh(*args, **kwargs)`](#2.2. PyTorch
torch.nn.Tanh(*args, **kwargs)) - [2.3. Python Tanh Function](#2.3. Python Tanh Function)
- [2.4. Python Tanh Function](#2.4. Python Tanh Function)
- [2.1. PyTorch `torch.nn.Tanh(*args, **kwargs)`](#2.1. PyTorch
- References
1. Tanh Function
class torch.nn.Tanh(*args, **kwargs)
https://docs.pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.Tanh.html
torch.nn.functional.tanh(input) -> Tensor
https://docs.pytorch.org/docs/stable/generated/torch.nn.functional.tanh.html
https://github.com/pytorch/pytorch/blob/v2.9.1/torch/nn/modules/activation.py
class torch.nn.Tanh(*args, **kwargs)
Applies the Hyperbolic Tangent (Tanh) function element-wise.
hyperbolic [ˌhaɪpə'bɒlɪk]
adj. 双曲线的;夸张的;夸张法的
tangent [ˈtændʒ(ə)nt]
n. 切线;正切
adj. 切线的;正切的;接触的;离题的The definition of the Tanh function:
tanh ( x ) = sinh ( x ) cosh ( x ) = exp ( x ) − exp ( − x ) exp ( x ) + exp ( − x ) = e x − e − x e x + e − x = e 2 x − 1 e 2 x + 1 = 1 − e − 2 x 1 + e − 2 x \begin{aligned} \tanh(x) = \frac{\sinh(x)}{\cosh(x)} &= \frac{\exp(x) - \exp(-x)} {\exp(x) + \exp(-x)} \\ &= \frac{e^{x} - e^{-x}}{e^{x} + e^{-x}} \\ &= \frac{e^{2x} - 1} {e^{2x} + 1} \\ &= \frac{1 - e^{-2x}} {1 + e^{-2x}} \\ \end{aligned} tanh(x)=cosh(x)sinh(x)=exp(x)+exp(−x)exp(x)−exp(−x)=ex+e−xex−e−x=e2x+1e2x−1=1+e−2x1−e−2x
若已知两个可导函数 g g g, h h h 及其导数 g ′ g' g′, h ′ h' h′,且 h ( x ) ≠ 0 h(x)\neq 0 h(x)=0,则它们的商
f ( x ) = g ( x ) h ( x ) \begin{aligned} f(x) = \frac{g(x)}{h(x)} \end{aligned} f(x)=h(x)g(x)
的导数为:
f ′ ( x ) = d d x ( g ( x ) h ( x ) ) = d d x g ( x ) ∗ h ( x ) − g ( x ) ∗ d d x h ( x ) ( h ( x ) ) 2 = g ′ ( x ) ∗ h ( x ) − g ( x ) ∗ h ′ ( x ) ( h ( x ) ) 2 \begin{aligned} f'(x) &= \frac{d}{dx} \left( {\frac{{g\left( x \right)}}{{h\left( x \right)}}} \right) \\ &= \frac{{\frac{d}{dx} g\left( x \right) * h\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right) * \frac{d}{dx}h\left( x \right)}}{(h \left( x \right))^2} \\ &= \frac{g'(x) * h(x) - g(x) * h'(x)}{(h(x))^2} \end{aligned} f′(x)=dxd(h(x)g(x))=(h(x))2dxdg(x)∗h(x)−g(x)∗dxdh(x)=(h(x))2g′(x)∗h(x)−g(x)∗h′(x)
The derivative of the Tanh function:
d d x tanh ( x ) = d d x ( e x − e − x e x + e − x ) = d d x ( e x − e − x ) ∗ ( e x + e − x ) − ( e x − e − x ) ∗ d d x ( e x + e − x ) ( e x + e − x ) 2 = ( e x + e − x ) ∗ ( e x + e − x ) − ( e x − e − x ) ∗ ( e x − e − x ) ( e x + e − x ) 2 = ( e x + e − x ) 2 − ( e x − e − x ) 2 ( e x + e − x ) 2 = 1 − ( e x − e − x ) 2 ( e x + e − x ) 2 = 1 − ( tanh ( x ) ) 2 \begin{aligned} \frac{d}{dx} \tanh(x) &= \frac{d}{dx} \left( \frac{e^{x} - e^{-x}}{e^{x} + e^{-x}} \right) \\[1ex] &= \frac{ \frac{d}{dx} \left( e^{x} - e^{-x} \right) * \left( e^{x} + e^{-x} \right) - \left( e^{x} - e^{-x} \right) * \frac{d}{dx} \left( e^{x} + e^{-x} \right) }{{\left( e^{x} + e^{-x} \right)}^2} \\[1ex] &= \frac{ \left( e^{x} + e^{-x} \right) * \left( e^{x} + e^{-x} \right) - \left( e^{x} - e^{-x} \right) * \left( e^{x} - e^{-x} \right) }{{\left( e^{x} + e^{-x} \right)}^2} \\[1ex] &= \frac{ \left( e^{x} + e^{-x} \right)^{2} - \left( e^{x} - e^{-x} \right)^{2} }{{\left( e^{x} + e^{-x} \right)}^2} \\[1.2ex] &= 1 - \frac{\left( e^{x} - e^{-x} \right)^{2} }{{\left( e^{x} + e^{-x} \right)}^2} \\[1.2ex] &= 1 - \left( \tanh(x) \right)^2 \\ \end{aligned} dxdtanh(x)=dxd(ex+e−xex−e−x)=(ex+e−x)2dxd(ex−e−x)∗(ex+e−x)−(ex−e−x)∗dxd(ex+e−x)=(ex+e−x)2(ex+e−x)∗(ex+e−x)−(ex−e−x)∗(ex−e−x)=(ex+e−x)2(ex+e−x)2−(ex−e−x)2=1−(ex+e−x)2(ex−e−x)2=1−(tanh(x))2
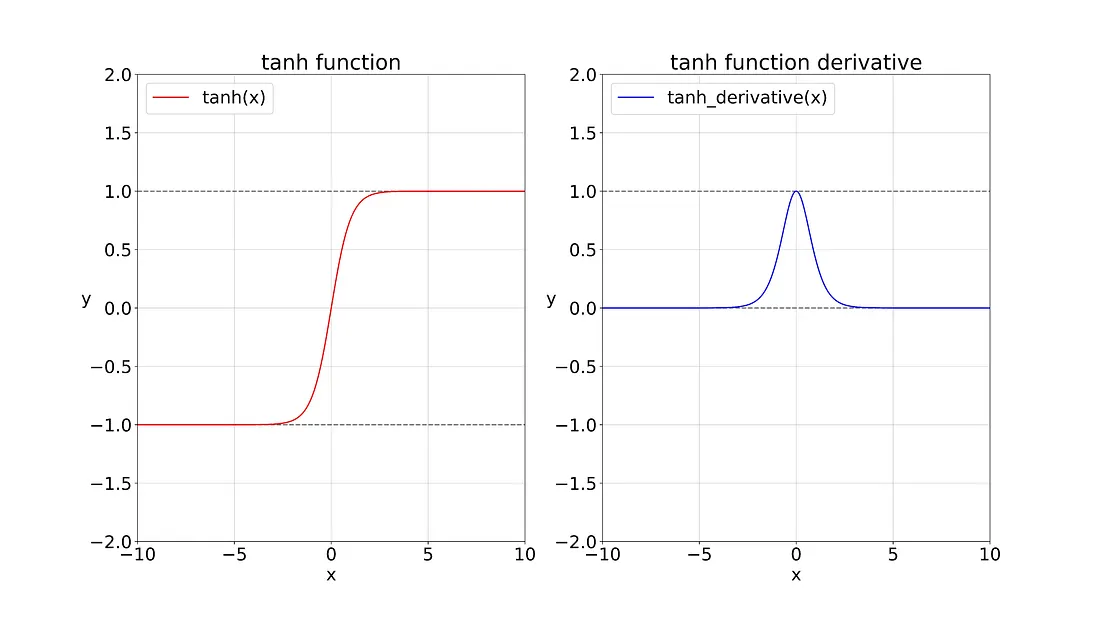
This is the graph for the Tanh function and its derivative.
1.1. Shape
-
Input : (
*), where*means any number of dimensions. -
Output : (
*), same shape as the input.
Note that as input nears 0, the Tanh function approaches a linear transformation. Although the shape of the function is similar to that of the Sigmoid function, the Tanh function exhibits point symmetry about the origin of the coordinate system.
注意,当输入在 0 附近时,Tanh 函数接近线性变换。函数的形状类似于 Sigmoid 函数,不同的是 Tanh 函数关于坐标系原点中心对称。
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import torch
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
def plot(X, Y=None, xlabel=None, ylabel=None, legend=[], xlim=None, ylim=None, xscale='linear', yscale='linear',
fmts=('-', 'm--', 'g-.', 'r:'), figsize=(3.5, 2.5), axes=None):
"""
https://github.com/d2l-ai/d2l-en/blob/master/d2l/torch.py
"""
def has_one_axis(X): # True if X (tensor or list) has 1 axis
return ((hasattr(X, "ndim") and (X.ndim == 1)) or (isinstance(X, list) and (not hasattr(X[0], "__len__"))))
if has_one_axis(X): X = [X]
if Y is None:
X, Y = [[]] * len(X), X
elif has_one_axis(Y):
Y = [Y]
if len(X) != len(Y):
X = X * len(Y)
# Set the default width and height of figures globally, in inches.
plt.rcParams['figure.figsize'] = figsize
if axes is None:
axes = plt.gca() # Get the current Axes
# Clear the Axes
axes.cla()
for x, y, fmt in zip(X, Y, fmts):
axes.plot(x, y, fmt) if len(x) else axes.plot(y, fmt)
axes.set_xlabel(xlabel), axes.set_ylabel(ylabel) # Set the label for the x/y-axis
axes.set_xscale(xscale), axes.set_yscale(yscale) # Set the x/y-axis scale
axes.set_xlim(xlim), axes.set_ylim(ylim) # Set the x/y-axis view limits
if legend:
axes.legend(legend) # Place a legend on the Axes
# Configure the grid lines
axes.grid()
plt.show()
plt.savefig("yongqiang.png", transparent=True) # Save the current figure
x = torch.arange(-8.0, 8.0, 0.1, requires_grad=True)
y = torch.tanh(x)
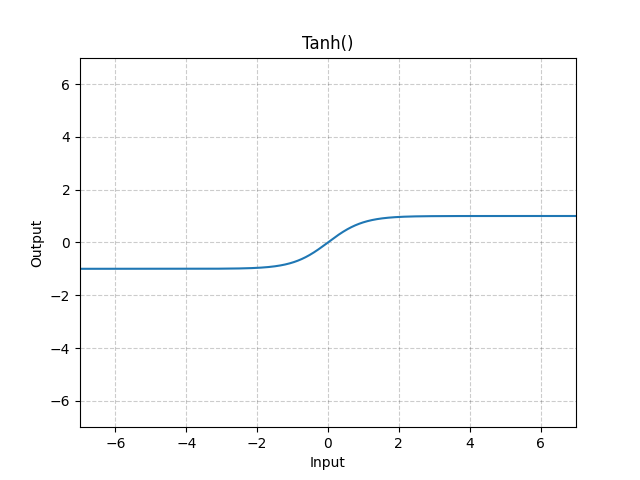
plot(x.detach(), y.detach(), 'x', 'Tanh(x)', figsize=(5, 2.5))
# Clear out previous gradients
# x.grad.data.zero_()
y.backward(torch.ones_like(x), retain_graph=True)
plot(x.detach(), x.grad, 'x', 'gradient of Tanh', figsize=(5, 2.5))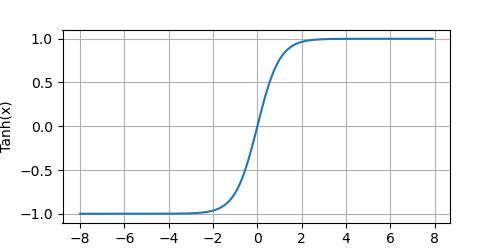
The derivative of the Tanh function:
d d x tanh ( x ) = 1 − tanh 2 ( x ) . \frac{d}{dx} \operatorname{tanh}(x) = 1 - \operatorname{tanh}^2(x). dxdtanh(x)=1−tanh2(x).
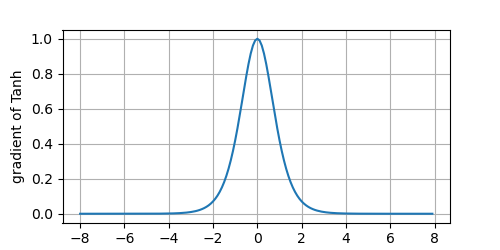
As the input nears 0, the derivative of the Tanh function approaches a maximum of 1. And as we saw with the Sigmoid function, as input moves away from 0 in either direction, the derivative of the Tanh function approaches 0.
当输入接近 0 时,Tanh 函数的导数接近最大值 1。与我们在 Sigmoid 函数图像中看到的类似,输入在任一方向上越远离 0 点,导数越接近 0。
2. Tanh Function - Derivatives and Gradients (导数和梯度)
Notes
- Element-wise Multiplication (Hadamard Product) (
*operator ornumpy.multiply()): Multiplies corresponding elements of two arrays that must have the same shape (or be broadcastable to a common shape). - Matrix Multiplication (Dot Product) (
@operator ornumpy.matmul()ornumpy.dot()): Performs the standard linear algebra operation that requires specific dimension compatibility rules. (e.g., the number of columns in the first array must match the number of rows in the second).
2.1. PyTorch torch.nn.Tanh(*args, **kwargs)
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6)
input = torch.tensor([[-1.5, 0.0, 1.5], [0.5, -2.0, 3.0]], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
print(f"input.requires_grad: {input.requires_grad}, input.shape: {input.shape}")
tanh = nn.Tanh()
forward_output = tanh(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
forward_output.backward(torch.ones_like(input), retain_graph=True)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {input.grad.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{input.grad}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/tanh.py
input.requires_grad: True, input.shape: torch.Size([2, 3])
forward_output.shape: torch.Size([2, 3])
Forward Pass Output:
tensor([[-0.905148, 0.000000, 0.905148],
[ 0.462117, -0.964028, 0.995055]], grad_fn=<TanhBackward0>)
backward_output.shape: torch.Size([2, 3])
Backward Pass Output:
tensor([[0.180707, 1.000000, 0.180707],
[0.786448, 0.070651, 0.009866]])
Process finished with exit code 02.2. PyTorch torch.nn.Tanh(*args, **kwargs)
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
torch.set_printoptions(precision=6)
input = torch.tensor([-1.5, 0.0, 1.5, 0.5, -2.0, 3.0], dtype=torch.float, requires_grad=True)
print(f"input.requires_grad: {input.requires_grad}, input.shape: {input.shape}")
tanh = nn.Tanh()
forward_output = tanh(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
forward_output.backward(torch.ones_like(input), retain_graph=True)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {input.grad.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{input.grad}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/tanh.py
input.requires_grad: True, input.shape: torch.Size([6])
forward_output.shape: torch.Size([6])
Forward Pass Output:
tensor([-0.905148, 0.000000, 0.905148, 0.462117, -0.964028, 0.995055],
grad_fn=<TanhBackward0>)
backward_output.shape: torch.Size([6])
Backward Pass Output:
tensor([0.180707, 1.000000, 0.180707, 0.786448, 0.070651, 0.009866])
Process finished with exit code 02.3. Python Tanh Function
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
# numpy.multiply:
# Multiply arguments element-wise
# Equivalent to x1 * x2 in terms of array broadcasting
class TanhLayer:
"""
A class to represent a Tanh activation layer for a neural network.
"""
def __init__(self):
# Cache the output for the backward pass
self.output = None
def forward(self, input):
"""
Compute tanh(x) and store it for the backward pass
"""
self.output = np.tanh(input)
return self.output
def backward(self, upstream_gradient):
"""
The derivative of tanh(x) is (1 - tanh(x)^2)
The total gradient is the element-wise product of the upstream
gradient and the derivative of the Tanh.
"""
tanh_derivative = 1 - self.output ** 2
print(f"\ntanh_derivative.shape: {tanh_derivative.shape}")
print(f"Tanh Derivative:\n{tanh_derivative}")
# Computes the gradient of the loss with respect to the input (dL/dx)
# Apply the chain rule: multiply the derivative by the upstream gradient
# dL/dx = dL/dy * dy/dx = upstream_gradient * (1 - tanh(x)^2)
downstream_gradient = upstream_gradient * tanh_derivative
return downstream_gradient
tanh_layer = TanhLayer()
input = np.array([[-1.5, 0.0, 1.5], [0.5, -2.0, 3.0]], dtype=np.float32)
# Forward pass
forward_output = tanh_layer.forward(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
# Backward pass
upstream_gradient = np.ones(forward_output.shape) * 0.1
backward_output = tanh_layer.backward(upstream_gradient)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {backward_output.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{backward_output}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/tanh.py
forward_output.shape: (2, 3)
Forward Pass Output:
[[-0.9051482 0. 0.9051482]
[ 0.4621172 -0.9640276 0.9950548]]
tanh_derivative.shape: (2, 3)
Tanh Derivative:
[[0.18070674 1. 0.18070674]
[0.7864477 0.07065082 0.009866 ]]
backward_output.shape: (2, 3)
Backward Pass Output:
[[0.01807067 0.1 0.01807067]
[0.07864477 0.00706508 0.0009866 ]]
Process finished with exit code 02.4. Python Tanh Function
# !/usr/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
import numpy as np
# numpy.multiply:
# Multiply arguments element-wise
# Equivalent to x1 * x2 in terms of array broadcasting
class TanhLayer:
"""
A class to represent a Tanh activation layer for a neural network.
"""
def __init__(self):
# Cache the output for the backward pass
self.output = None
def forward(self, input):
"""
Compute tanh(x) and store it for the backward pass
"""
self.output = np.tanh(input)
return self.output
def backward(self, upstream_gradient):
"""
The derivative of tanh(x) is (1 - tanh(x)^2)
The total gradient is the element-wise product of the upstream
gradient and the derivative of the Tanh.
"""
tanh_derivative = 1 - self.output ** 2
print(f"\ntanh_derivative.shape: {tanh_derivative.shape}")
print(f"Tanh Derivative:\n{tanh_derivative}")
# Computes the gradient of the loss with respect to the input (dL/dx)
# Apply the chain rule: multiply the derivative by the upstream gradient
# dL/dx = dL/dy * dy/dx = upstream_gradient * (1 - tanh(x)^2)
downstream_gradient = upstream_gradient * tanh_derivative
return downstream_gradient
tanh_layer = TanhLayer()
input = np.array([-1.5, 0.0, 1.5, 0.5, -2.0, 3.0], dtype=np.float32)
# Forward pass
forward_output = tanh_layer.forward(input)
print(f"\nforward_output.shape: {forward_output.shape}")
print(f"Forward Pass Output:\n{forward_output}")
# Backward pass
upstream_gradient = np.ones(forward_output.shape) * 0.1
backward_output = tanh_layer.backward(upstream_gradient)
print(f"\nbackward_output.shape: {backward_output.shape}")
print(f"Backward Pass Output:\n{backward_output}")
/home/yongqiang/miniconda3/bin/python /home/yongqiang/quantitative_analysis/tanh.py
forward_output.shape: (6,)
Forward Pass Output:
[-0.9051482 0. 0.9051482 0.4621172 -0.9640276 0.9950548]
tanh_derivative.shape: (6,)
Tanh Derivative:
[0.18070674 1. 0.18070674 0.7864477 0.07065082 0.009866 ]
backward_output.shape: (6,)
Backward Pass Output:
[0.01807067 0.1 0.01807067 0.07864477 0.00706508 0.0009866 ]
Process finished with exit code 0References
1\] Yongqiang Cheng (程永强),