唉,我这代码水平,怕是永远都逃不出"hello world"的魔咒咯。
代码仓库
Agent :https://gitee.com/impl/hello-agent
McpServer: https://gitee.com/impl/hello-mcp-server
MCP 传输模式
stdio (标准输入输出) ------ 最常用模式
这是本地 MCP 服务器的默认且性能最优的传输方式。
机制:Client(如 Claude Desktop 或 IDE)将 Server 作为一个子进程启动,通过进程的标准输入(stdin)发送 JSON-RPC 消息,通过标准输出(stdout)接收响应。
适用场景:本地运行的脚本、命令行工具或同一台机器上的集成。
优势:无需配置网络协议栈,延迟极低,安全性高(无需暴露网络端口)。
Streamable HTTP (可流化 HTTP) ------ 现代标准
这是 MCP 在 2025 年推出的现代远程传输标准,用于取代早期的纯 SSE 实现。
机制:基于 HTTP 协议。Client 使用 HTTP POST 发送请求,而 Server 使用一个单一的 HTTP 端点来处理双向消息流。
适用场景:跨网络、云端部署或多用户环境下的远程 MCP 服务器连接。
优势:支持标准 HTTP 认证(如 OAuth、API Key),且能够跨越复杂的网络架构。
SSE (Server-Sent Events) ------ 传统/兼容模式
在 2025 年的规范中,纯 SSE 传输已被视为过时(Deprecated),但在许多旧工具中仍有应用。
机制:一种单向的长连接模式。Server 通过一个长连接持续向 Client 推送数据(事件流),而 Client 若要回传数据,必须发起额外的 HTTP POST 请求。
适用场景:遗留系统的向后兼容。
核心特性对比总结
| 特性 | stdio | Streamable HTTP (2025新标) | SSE (传统) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 连接位置 | 本地 (Local) | 远程/本地均可 | 远程/Web |
| 通信方向 | 全双工 (双向) | 增强型双向流 | 伪双向 (推+传) |
| 开销 | 极低 | 较高 (HTTP 握手) | 中等 |
| 首选建议 | 本地开发首选 | 生产环境/远程连接首选 | 仅用于维护旧项目 |
开发建议:如果你正在编写一个新的 MCP Server,建议默认提供 stdio 支持以供本地测试,并根据需要实现 Streamable HTTP 以支持远程部署。所有传输层最终都必须将 MCP 语义封装在 JSON-RPC 2.0 格式中。
依赖
- TRAE IDE,参考:https://docs.trae.cn/ide/what-is-trae
- DeepSeek:参考:https://platform.deepseek.com/usage
- UV:参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_41120248/article/details/156125353
- Python:3.11
前置准备
- 注册DeepSeek账号,并创建创建 API key
- 同步代码,并切换至对应示例分支,例如:
feature-sse、feature-stdio、feature-http - 增加.env文件,在.env文件中增加
DEEPSEEK_API_KEY=sk-***** - 支持
uv sync同步环境
流程图
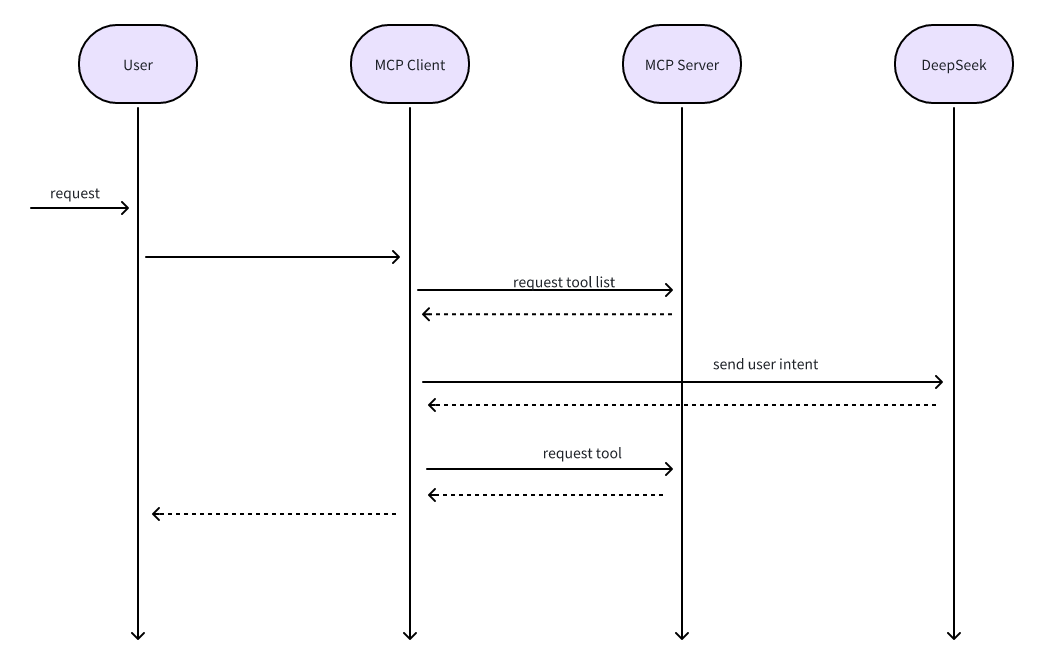
ps:我也是菜鸟,如有问题,请留下评论
SSE模式示例
hello-agent、hello-mcp-server 均需要切换至feature-sse
启动过程
优先启动hello-mcp-server,在启动hello-agent
hello-mcp-server
uv run --env-file .env main.pyhello-agent
uv run --env-file .env main.pystdio模式示例
本章节与hello-agent项目无关,hello-mcp-server 分支至feature-stdio即可
hello-mcp-server main.py代码调整
if __name__ == "__main__":
# mcp.run(transport="sse")
mcp.run(transport="stdio")流程
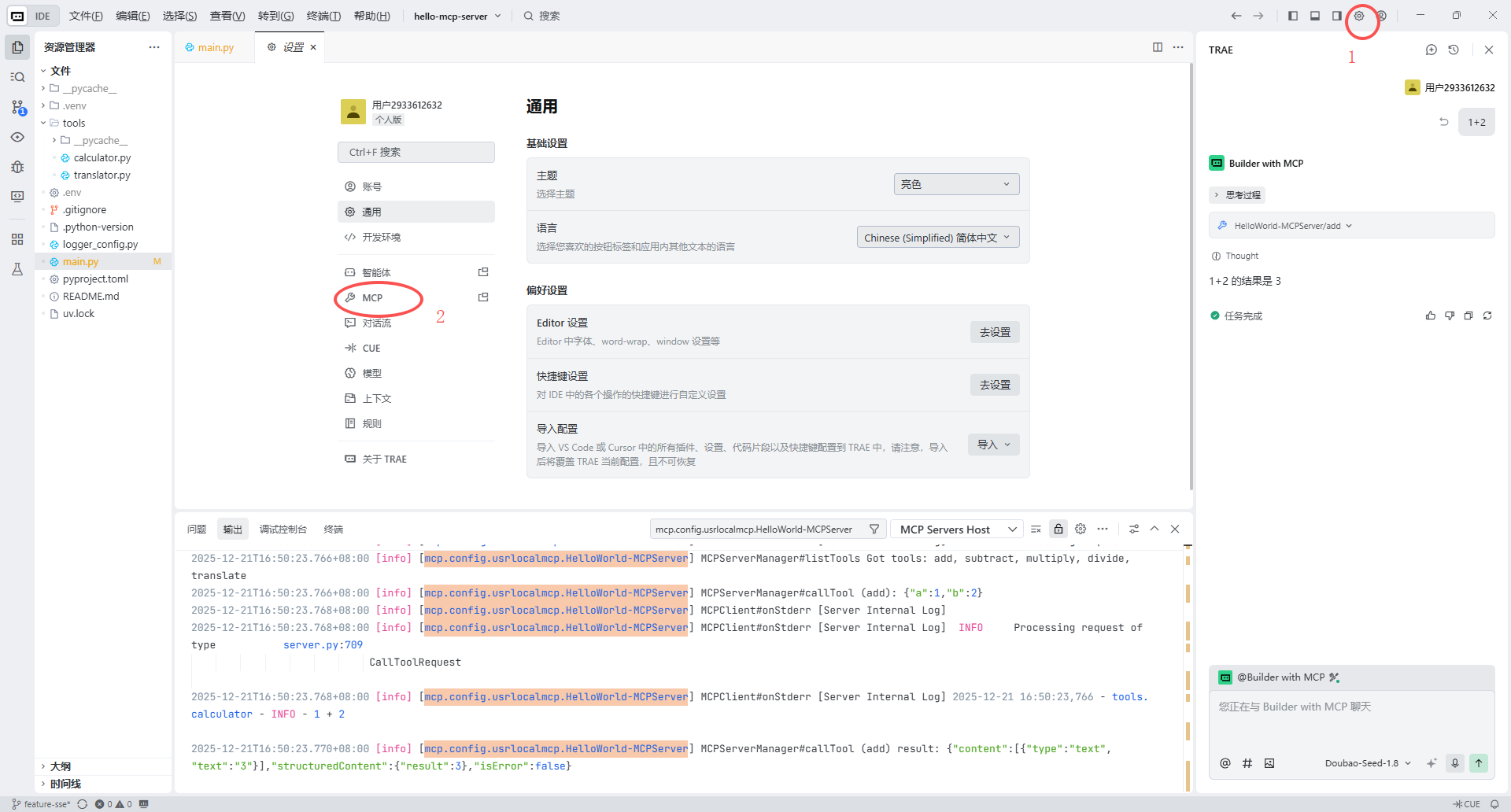
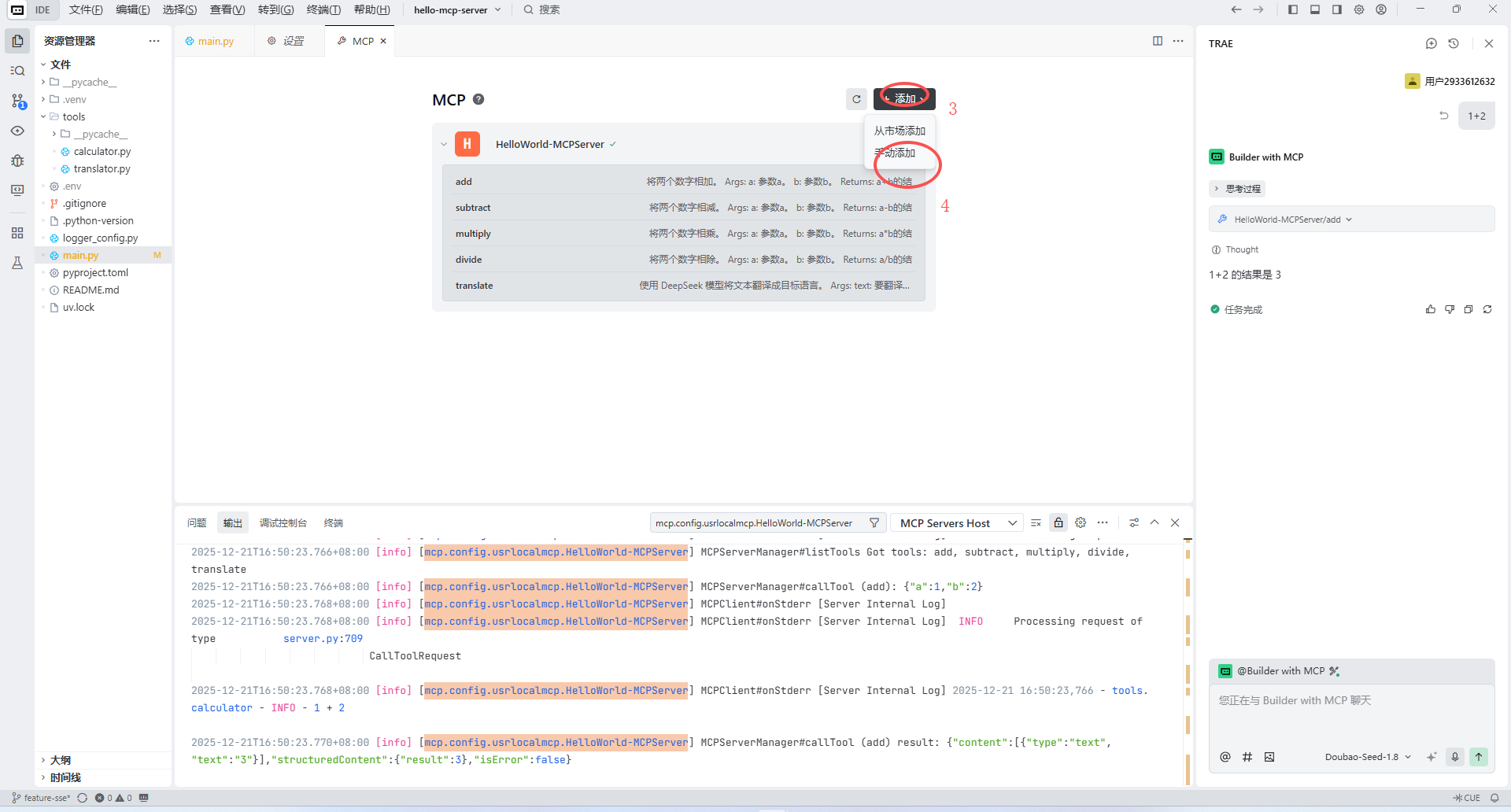
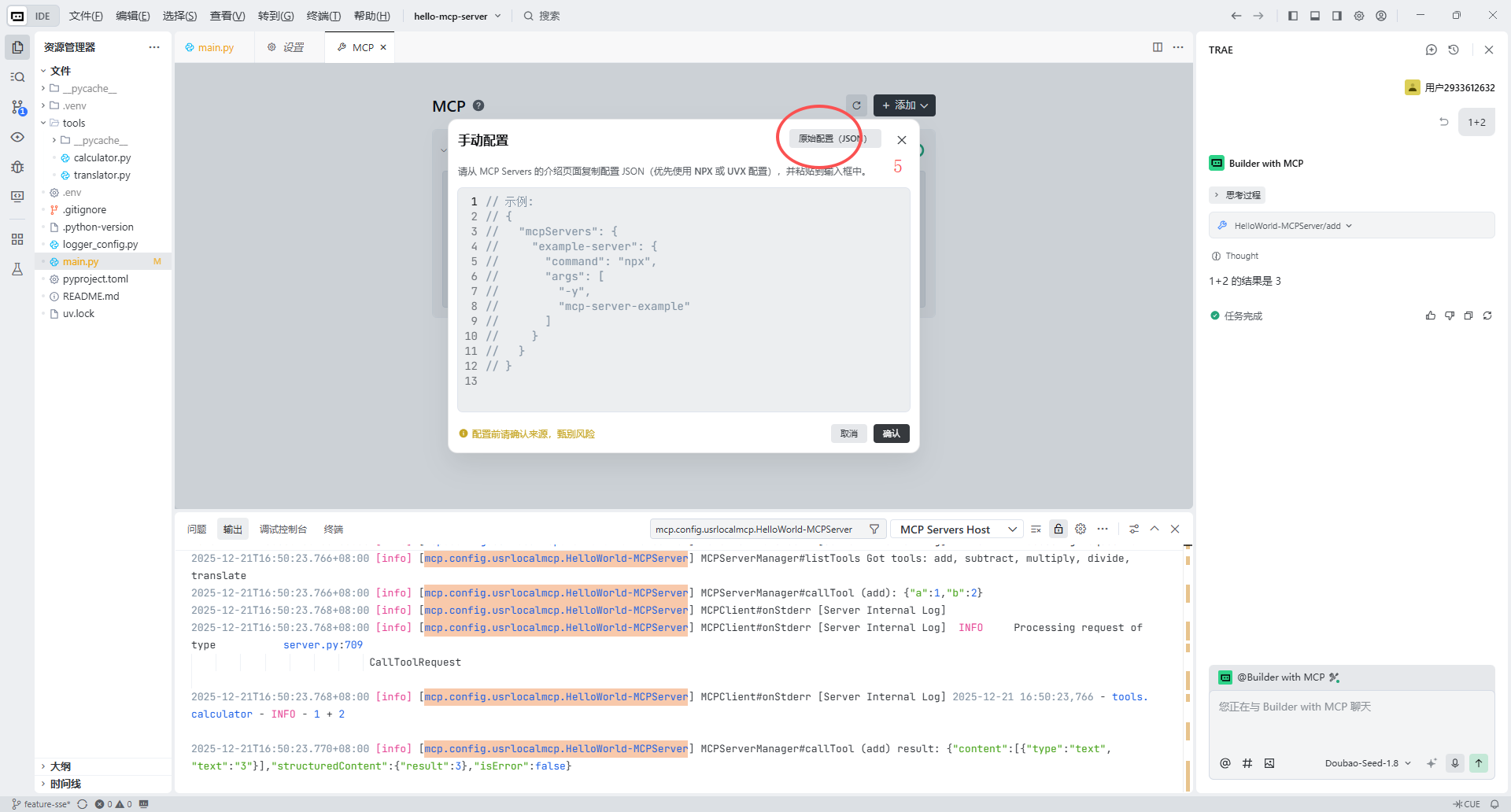
发起请求
HTTP模式示例
hello-agent、hello-mcp-server 均需要切换至feature-http
启动过程
参考:SSE模式启动过程
重要代码
hello-agent
async def run_agent(user_prompt: str):
# 1. 建立与远程 MCP Server 的连接
async with sse_client(url=url) as (read_stream, write_stream):
async with ClientSession(read_stream, write_stream) as session:
await session.initialize()
# 2. 列出 MCP Server 提供的所有工具
tools_response = await session.list_tools()
available_tools = []
for tool in tools_response.tools:
available_tools.append({
"type": "function",
"function": {
"name": tool.name,
"description": tool.description,
"parameters": tool.inputSchema
}
})
# 3. 第一次请求:将用户意图发送给 DeepSeek
messages = [{"role": "user", "content": user_prompt}]
response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat",
messages=messages,
tools=available_tools,
tool_choice="auto"
)
# 4. 处理 DeepSeek 的工具调用决策
response_message = response.choices[0].message
if response_message.tool_calls:
for tool_call in response_message.tool_calls:
function_name = tool_call.function.name
function_args = eval(tool_call.function.arguments)
# 远程调用 MCP Server 的工具
print(f"正在通过 MCP 调用远程工具: {function_name}...")
tool_result = await session.call_tool(function_name, function_args)
# 5. 将工具结果返回给 DeepSeek
messages.append(response_message)
messages.append({
"role": "tool",
"tool_call_id": tool_call.id,
"content": str(tool_result.content)
})
# 6. 获取 DeepSeek 结合工具结果后的最终回复
final_response = client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat",
messages=messages
)
print("DeepSeek Agent 回复:", final_response.choices[0].message.content)
else:
print("DeepSeek Agent 回复:", response_message.content)Hello-Server
# 创建服务器实例
mcp = FastMCP("HelloWorld-MCPServer")
# mcp_app = FastAPI(name="HelloWorld-MCPServer-Tools")
mcp.tool()(add)
mcp.tool()(subtract)
mcp.tool()(multiply)
mcp.tool()(divide)
mcp.tool()(translate)
if __name__ == "__main__":
mcp.run(transport="sse")加法计算器示例
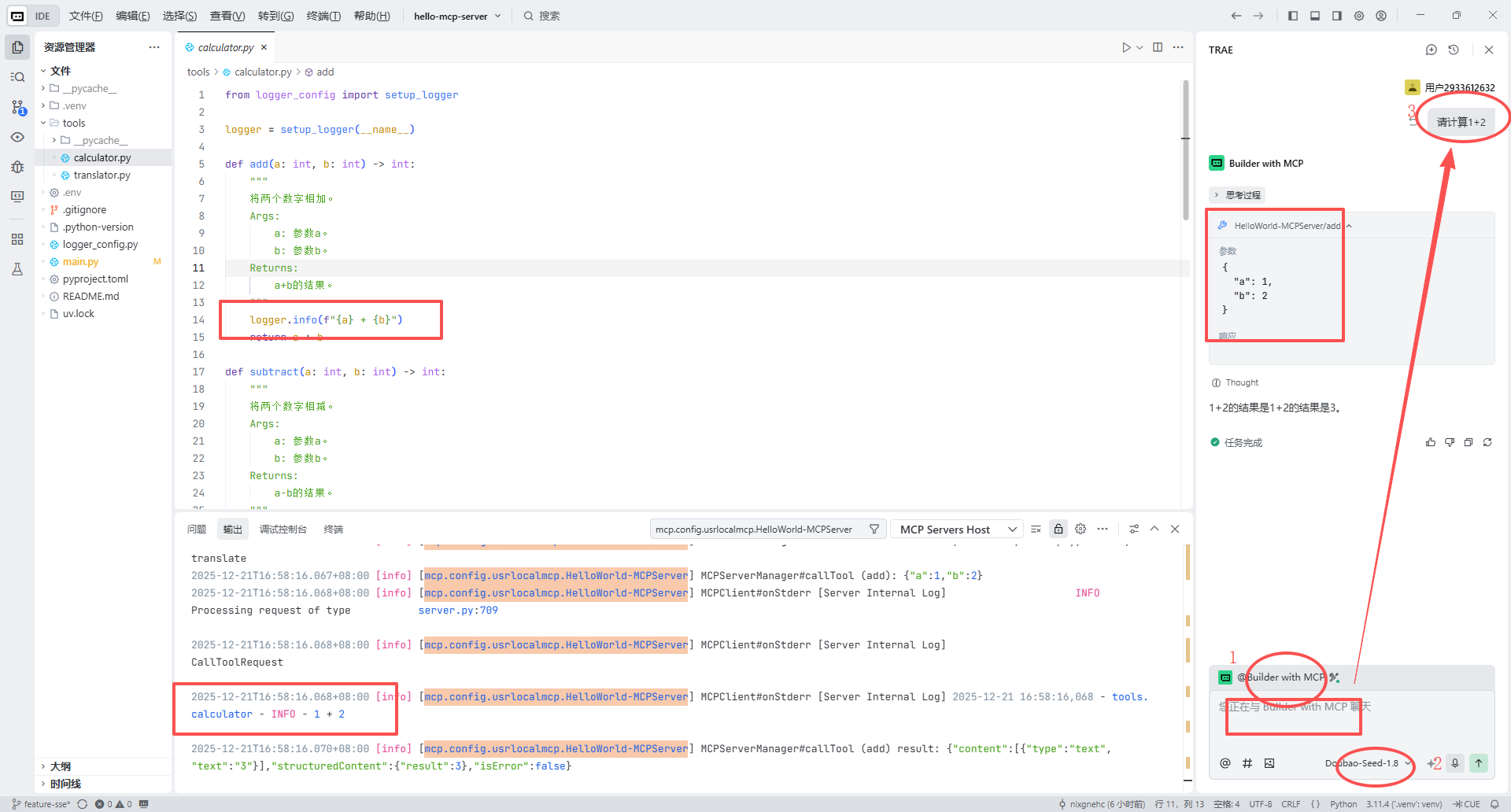
def add(a: int, b: int) -> int:
"""
将两个数字相加。
Args:
a: 参数a。
b: 参数b。
Returns:
a+b的结果。
"""
logger.info(f"{a} + {b}")
return a + b