动态线程池+kafka自定义拒绝策略,做到任务不丢失
前言
开发环境为 jdk8 本文用到了 nacos、kafka 这两个第三方中间件,文章分为两个部分
第一部分:动态线程池 (nacos 必须要,kafka 不强求)(拒绝策略为默认报错)
第二部分:动态线程池 + kafka 自定义拒绝策略(nacos和kafka都需要,kafka是保证任务不丢失的关键)
项目地址:dynamic-thread-pool: 动态线程池+kafka自定义拒绝策略,做到任务不丢失
线程池执行过程(也是我的文章,这对后面测试用例有指导意义):线程池详解与线程池调优
技术实现选型
第三方中间件
| 工具 | 版本 | jdk版本 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|
| nacos | nacos-server-2.0.4 | 8 | 不能比这个低 |
| kafka | kafka_2.13-4.1.1 | 17 | 主要是4以上的版本不需要zookeeper,其他也行 |
maven 主要版本(开发环境jdk8)
| jar包 | 版本 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|
| spring-cloud-alibaba | 2021.0.6.2 | 不能比这个低 |
| spring-cloud | 2021.0.8 | 根据 spring-cloud-alibaba 版本选配 |
| spring-boot | 2.6.13 | 根据 spring-cloud-alibaba 版本选配 |
maven
xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.zhao</groupId>
<artifactId>dynamicPool</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>dynamicPool</name>
<description>dynamicPool</description>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.6.13</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<spring-boot.version>2.6.13</spring-boot.version>
<!-- 对应 Spring Boot 2.6.x -->
<spring-cloud.version>2021.0.8</spring-cloud.version>
<!-- 这里注意 2021.0.6.2 才能使用 @NacosConfigKeysListener 或 @NacosConfigListener 注解 参考链接如下 -->
<!-- https://nacos.io/en/blog/nacos-gvr7dx_awbbpb_mmufdmayp5dfozci/?spm=5238cd80.cff869d.0.0.237f7e849GXM35&source=blog#nacosconfiglistener%E6%B3%A8%E8%A7%A3%E7%94%A8%E6%B3%95%E4%BB%8B%E7%BB%8D -->
<!-- 请配合 nacos-server-2.0.4 使用(2以上) -->
<spring-cloud-alibaba.version>2021.0.6.2</spring-cloud-alibaba.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Cloud Alibaba -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-alibaba.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>fastjson</artifactId>
<version>2.0.42</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>cn.hutool</groupId>
<artifactId>hutool-all</artifactId>
<version>5.8.26</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-lang3</artifactId>
<version>3.18.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.google.guava</groupId>
<artifactId>guava</artifactId>
<version>32.0.1-android</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Actuator (必须) -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- nacos -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-config</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-alibaba-nacos-discovery</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-bootstrap</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>dynamicPool</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot.version}</version>
<configuration>
<mainClass>com.zhao.dynamicPool.DynamicPoolApplication</mainClass>
<!-- 移除 <skip>true</skip> 这一行 -->
<!-- 添加 excludes 排除不需要打包的依赖 -->
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>repackage</id>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>一、nacos配置(默认测试配置,测试完后归位)
bootstrap.yaml
yaml
spring:
application:
name: dynamic-pool-service # 应用名称,也是Nacos中的服务名
cloud:
nacos:
discovery:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 # Nacos Config Server地址
# 配置中心配置
config:
server-addr: 127.0.0.1:8848 # Nacos Config Server地址
file-extension: yaml # 配置文件扩展名(yaml, yml, properties等)
refresh-enabled: true # 必须为true配置如下
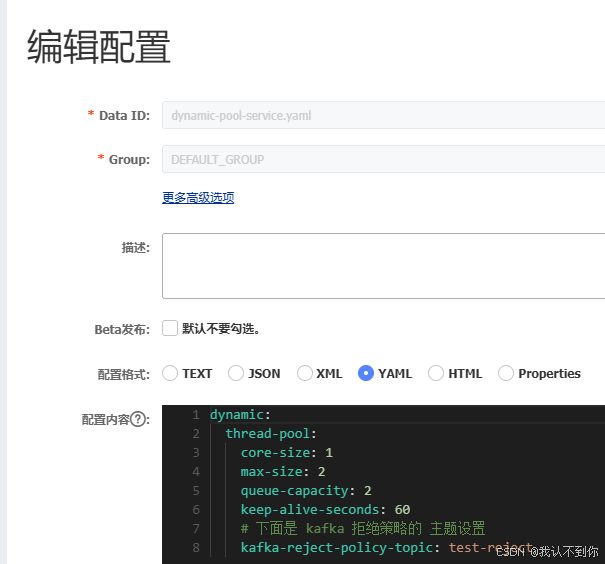
核心线程数:1,最大线程数:2,队列最大容量:2
二、动态线程池
spring 提供了 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 线程池
他可以通过编码实现动态的改变线程池的核心线程数、最大线程数、超时时间,但是不能动态的调整阻塞队列的队列长度
因为 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 使用的是 LinkedBlockingQueue 的阻塞队列
LinkedBlockingQueue 的 capacity 参数是 final 字段的,不可以修改
所以本章的核心是实现拥有可变的 capacity 参数的阻塞队列 VariableLinkedBlockingQueue + @NacosConfigKeysListener 注解实现 nacos 参数监听,通过配置文件修改线程池
可变阻塞队列:VariableLinkedBlockingQueue.java(不需要修改)
该 VariableLinkedBlockingQueue 队列是 dromara 团队的代码,dromara 团队是参考 rabbitmq 团队的代码,并实现了 LinkedBlockingQueue 的方法
dromara 团队代码如下:VariableLinkedBlockingQueue.java
rabbitmq 团队的代码如下:VariableLinkedBlockingQueue.java
java
public class VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<E> extends AbstractQueue<E>
implements BlockingQueue<E>, java.io.Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -6903933977591709194L;
static class Node<E> {
E item;
Node<E> next;
Node(E x) {
item = x;
}
}
private int capacity;
private final AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger();
transient Node<E> head;
private transient Node<E> last;
private final ReentrantLock takeLock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition notEmpty = takeLock.newCondition();
private final ReentrantLock putLock = new ReentrantLock();
private final Condition notFull = putLock.newCondition();
private void signalNotEmpty() {
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
notEmpty.signal();
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
}
private void signalNotFull() {
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
notFull.signal();
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
}
private void enqueue(Node<E> node) {
// assert putLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// assert last.next == null;
last = last.next = node;
}
private E dequeue() {
// assert takeLock.isHeldByCurrentThread();
// assert head.item == null;
Node<E> h = head;
Node<E> first = h.next;
h.next = h; // help GC
head = first;
E x = first.item;
first.item = null;
return x;
}
void fullyLock() {
putLock.lock();
takeLock.lock();
}
void fullyUnlock() {
takeLock.unlock();
putLock.unlock();
}
public VariableLinkedBlockingQueue() {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
public VariableLinkedBlockingQueue(int capacity) {
if (capacity <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
this.capacity = capacity;
last = head = new Node<E>(null);
}
public VariableLinkedBlockingQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) {
this(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock(); // Never contended, but necessary for visibility
try {
int n = 0;
for (E e : c) {
if (e == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (n == capacity) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Queue full");
}
enqueue(new Node<E>(e));
++n;
}
count.set(n);
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
}
@Override
public int size() {
return count.get();
}
public void setCapacity(int capacity) {
final int oldCapacity = this.capacity;
this.capacity = capacity;
final int size = count.get();
if (capacity > size && size >= oldCapacity) {
signalNotFull();
}
}
@Override
public int remainingCapacity() {
return capacity - count.get();
}
@Override
public void put(E e) throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() >= capacity) {
notFull.await();
}
enqueue(node);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
if (c + 1 < capacity) {
notFull.signal();
}
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0) {
signalNotEmpty();
}
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E e, long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException {
if (e == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
putLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() >= capacity) {
if (nanos <= 0) {
return false;
}
nanos = notFull.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
enqueue(new Node<E>(e));
c = count.getAndIncrement();
if (c + 1 < capacity) {
notFull.signal();
}
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0) {
signalNotEmpty();
}
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean offer(E e) {
if (e == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() >= capacity) {
return false;
}
int c = -1;
Node<E> node = new Node<E>(e);
final ReentrantLock putLock = this.putLock;
putLock.lock();
try {
if (count.get() < capacity) {
enqueue(node);
c = count.getAndIncrement();
if (c + 1 < capacity) {
notFull.signal();
}
}
} finally {
putLock.unlock();
}
if (c == 0) {
signalNotEmpty();
}
return c >= 0;
}
@Override
public E take() throws InterruptedException {
E x;
int c = -1;
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == 0) {
notEmpty.await();
}
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1) {
notEmpty.signal();
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c >= capacity) {
signalNotFull();
}
return x;
}
@Override
public E poll(long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
E x = null;
int c = -1;
long nanos = unit.toNanos(timeout);
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
while (count.get() == 0) {
if (nanos <= 0) {
return null;
}
nanos = notEmpty.awaitNanos(nanos);
}
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1) {
notEmpty.signal();
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c >= capacity) {
signalNotFull();
}
return x;
}
@Override
public E poll() {
final AtomicInteger count = this.count;
if (count.get() == 0) {
return null;
}
E x = null;
int c = -1;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
if (count.get() > 0) {
x = dequeue();
c = count.getAndDecrement();
if (c > 1) {
notEmpty.signal();
}
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
if (c >= capacity) {
signalNotFull();
}
return x;
}
@Override
public E peek() {
if (count.get() == 0) {
return null;
}
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
Node<E> first = head.next;
if (first == null) {
return null;
} else {
return first.item;
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
}
}
void unlink(Node<E> p, Node<E> trail) {
// assert isFullyLocked();
// p.next is not changed, to allow iterators that are
// traversing p to maintain their weak-consistency guarantee.
p.item = null;
trail.next = p.next;
if (last == p) {
last = trail;
}
if (count.getAndDecrement() >= capacity) {
notFull.signal();
}
}
@Override
public boolean remove(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
return false;
}
fullyLock();
try {
for (Node<E> trail = head, p = trail.next;
p != null;
trail = p, p = p.next) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
unlink(p, trail);
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
@Override
public boolean contains(Object o) {
if (o == null) {
return false;
}
fullyLock();
try {
for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
if (o.equals(p.item)) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
@Override
public Object[] toArray() {
fullyLock();
try {
int size = count.get();
Object[] a = new Object[size];
int k = 0;
for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
a[k++] = p.item;
}
return a;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
@Override
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T[] toArray(T[] a) {
fullyLock();
try {
int size = count.get();
if (a.length < size) {
a = (T[]) java.lang.reflect.Array.newInstance(a.getClass().getComponentType(), size);
}
int k = 0;
for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
a[k++] = (T) p.item;
}
if (a.length > k) {
a[k] = null;
}
return a;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
@Override
public String toString() {
fullyLock();
try {
Node<E> p = head.next;
if (p == null) {
return "[]";
}
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append('[');
for (;;) {
E e = p.item;
sb.append(e == this ? "(this Collection)" : e);
p = p.next;
if (p == null) {
return sb.append(']').toString();
}
sb.append(',').append(' ');
}
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
@Override
public void clear() {
fullyLock();
try {
for (Node<E> p, h = head; (p = h.next) != null; h = p) {
h.next = h;
p.item = null;
}
head = last;
// assert head.item == null && head.next == null;
if (count.getAndSet(0) >= capacity) {
notFull.signal();
}
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
@Override
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c) {
return drainTo(c, Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
@Override
public int drainTo(Collection<? super E> c, int maxElements) {
if (c == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
if (c == this) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if (maxElements <= 0) {
return 0;
}
boolean signalNotFull = false;
final ReentrantLock takeLock = this.takeLock;
takeLock.lock();
try {
int n = Math.min(maxElements, count.get());
// count.get provides visibility to first n Nodes
Node<E> h = head;
int i = 0;
try {
while (i < n) {
Node<E> p = h.next;
c.add(p.item);
p.item = null;
h.next = h;
h = p;
++i;
}
return n;
} finally {
// Restore invariants even if c.add() threw
if (i > 0) {
// assert h.item == null;
head = h;
signalNotFull = (count.getAndAdd(-i) >= capacity);
}
}
} finally {
takeLock.unlock();
if (signalNotFull) {
signalNotFull();
}
}
}
@Override
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
private Node<E> current;
private Node<E> lastRet;
private E currentElement;
Itr() {
fullyLock();
try {
current = head.next;
if (current != null) {
currentElement = current.item;
}
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return current != null;
}
private Node<E> nextNode(Node<E> p) {
for (;;) {
Node<E> s = p.next;
if (s == p) {
return head.next;
}
if (s == null || s.item != null) {
return s;
}
p = s;
}
}
@Override
public E next() {
fullyLock();
try {
if (current == null) {
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
E x = currentElement;
lastRet = current;
current = nextNode(current);
currentElement = (current == null) ? null : current.item;
return x;
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
@Override
public void remove() {
if (lastRet == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
}
fullyLock();
try {
Node<E> node = lastRet;
lastRet = null;
for (Node<E> trail = head, p = trail.next;
p != null;
trail = p, p = p.next) {
if (p == node) {
unlink(p, trail);
break;
}
}
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
}
static final class LBQSpliterator<E> implements Spliterator<E> {
static final int MAX_BATCH = 1 << 25; // max batch array size;
final VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<E> queue;
Node<E> current; // current node; null until initialized
int batch; // batch size for splits
boolean exhausted; // true when no more nodes
long est; // size estimate
LBQSpliterator(VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<E> queue) {
this.queue = queue;
this.est = queue.size();
}
@Override
public long estimateSize() {
return est;
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> trySplit() {
Node<E> h;
final VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<E> q = this.queue;
int b = batch;
int n = (b <= 0) ? 1 : (b >= MAX_BATCH) ? MAX_BATCH : b + 1;
if (!exhausted &&
((h = current) != null || (h = q.head.next) != null) &&
h.next != null) {
Object[] a = new Object[n];
int i = 0;
Node<E> p = current;
q.fullyLock();
try {
if (p != null || (p = q.head.next) != null) {
do {
if ((a[i] = p.item) != null) {
++i;
}
} while ((p = p.next) != null && i < n);
}
} finally {
q.fullyUnlock();
}
if ((current = p) == null) {
est = 0L;
exhausted = true;
} else if ((est -= i) < 0L) {
est = 0L;
}
if (i > 0) {
batch = i;
return Spliterators.spliterator(a, 0, i, Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.NONNULL |
Spliterator.CONCURRENT);
}
}
return null;
}
@Override
public void forEachRemaining(Consumer<? super E> action) {
if (action == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
final VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<E> q = this.queue;
if (!exhausted) {
exhausted = true;
Node<E> p = current;
do {
E e = null;
q.fullyLock();
try {
if (p == null) {
p = q.head.next;
}
while (p != null) {
e = p.item;
p = p.next;
if (e != null) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
q.fullyUnlock();
}
if (e != null) {
action.accept(e);
}
} while (p != null);
}
}
@Override
public boolean tryAdvance(Consumer<? super E> action) {
if (action == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
final VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<E> q = this.queue;
if (!exhausted) {
E e = null;
q.fullyLock();
try {
if (current == null) {
current = q.head.next;
}
while (current != null) {
e = current.item;
current = current.next;
if (e != null) {
break;
}
}
} finally {
q.fullyUnlock();
}
if (current == null) {
exhausted = true;
}
if (e != null) {
action.accept(e);
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int characteristics() {
return Spliterator.ORDERED | Spliterator.NONNULL |
Spliterator.CONCURRENT;
}
}
@Override
public Spliterator<E> spliterator() {
return new LBQSpliterator<E>(this);
}
private void writeObject(java.io.ObjectOutputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException {
fullyLock();
try {
// Write out any hidden stuff, plus capacity
s.defaultWriteObject();
// Write out all elements in the proper order.
for (Node<E> p = head.next; p != null; p = p.next) {
s.writeObject(p.item);
}
// Use trailing null as sentinel
s.writeObject(null);
} finally {
fullyUnlock();
}
}
private void readObject(java.io.ObjectInputStream s)
throws java.io.IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
// Read in capacity, and any hidden stuff
s.defaultReadObject();
count.set(0);
last = head = new Node<E>(null);
// Read in all elements and place in queue
for (;;) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
E item = (E) s.readObject();
if (item == null) {
break;
}
add(item);
}
}
}线程池配置:DynamicThreadPoolConfig.java(需要根据自己业务把使用参数名进行修改即可(我用todo标记了))
该类重点有三个
第一个是,实现 DynamicThreadPoolTaskExecutor 类用于继承 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor,重写 createQueue 方法,让该线程池使用容量可变的阻塞队列
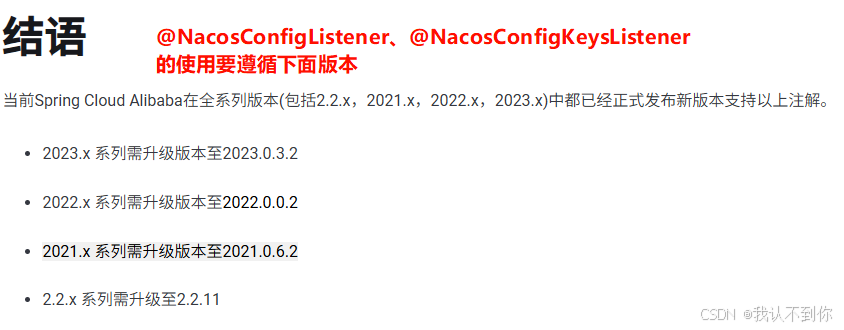
第二个是,使用 @NacosConfigKeysListener 注解监听配置中心的线程池参数,实现线程池的动态修改,这里注意要使用 spring-cloud-alibaba 2021.0.6.2 及以上的版本,说明如下版本说明
第三个是,使用 getThreadPoolStatus 方法,获取到线程池运行参数作为监控
java
/**
* 动态线程池
*
* 加 todo 的 就是可以选择性修改的
*/
@Configuration
@RefreshScope // 支持配置热更新
@EnableAsync // 启用异步支持
@Slf4j
public class DynamicThreadPoolConfig {
/**
* 核心参数 默认使用io密集型
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改
*/
@Value("${dynamic.thread-pool.core-size:0}")
private int coreSize;
/**
* 最大参数 默认使用io密集型
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改
*/
@Value("${dynamic.thread-pool.max-size:0}")
private int maxSize;
/**
* 队列容量 默认 1w 的队列
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改
*/
@Value("${dynamic.thread-pool.queue-capacity:10000}")
private int queueCapacity;
/**
* 超时时间 默认 60s 超时
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改
*/
@Value("${dynamic.thread-pool.keep-alive-seconds:60}")
private int keepAliveSeconds;
/**
* 动态线程池
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改 Bean 的值
*/
@Bean("dynamicThreadPool")
DynamicThreadPoolTaskExecutor dynamicThreadPool() {
int cpuCores = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
if (coreSize <= 0) {
coreSize = cpuCores * 2;
}
if (maxSize <= 0) {
maxSize = cpuCores * 4;
}
DynamicThreadPoolTaskExecutor executor = new DynamicThreadPoolTaskExecutor();
// 核心线程数(默认线程数)
executor.setCorePoolSize(coreSize);
// 最大线程数(队列满后扩容的最大值)
executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxSize);
// 线程空闲时间(秒)
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);
// 队列容量(超过核心线程数时,任务进入队列)
executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
// 线程名前缀
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("dynamic-thread-");
// 拒绝策略(此处使用报错执行)
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
// 初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
/**
* 动态线程池
* todo 如果你改了 Bean 的值 记得改 Qualifier 中的值
*/
@Autowired
@Qualifier("dynamicThreadPool")
@Lazy
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor dynamicThreadPool;
/**
* 公平读写锁
*/
private final static ReentrantReadWriteLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(true);
/**
* 动态调整线程池参数
*
* @param corePoolSize 核心线程数
* @param maxPoolSize 最大线程数
* @param keepAliveSeconds 超时时间(秒)
* @param queueCapacity 队列容量
*/
public void adjustThreadPool(Integer corePoolSize, Integer maxPoolSize, Integer keepAliveSeconds, Integer queueCapacity) {
ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock = reentrantLock.writeLock();
try {
writeLock.lock();
// 调整核心线程数
if (corePoolSize != null && corePoolSize != dynamicThreadPool.getCorePoolSize()) {
dynamicThreadPool.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
}
// 调整最大线程数
if (maxPoolSize != null && maxPoolSize != dynamicThreadPool.getMaxPoolSize()) {
dynamicThreadPool.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
}
// 调整超时时间
if (keepAliveSeconds != null && keepAliveSeconds != dynamicThreadPool.getKeepAliveSeconds()) {
dynamicThreadPool.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);
}
// 调整队列容量(需重置队列)
if (queueCapacity != null && queueCapacity != dynamicThreadPool.getQueueCapacity()) {
VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable> queue =
(VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>) dynamicThreadPool.getThreadPoolExecutor().getQueue();
if (queueCapacity < queue.remainingCapacity() + queue.size()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("线程池 不支持缩容");
}
// 需要自定义可调整队列容量
queue.setCapacity(queueCapacity);
// 重置线程池容量参数(这里只是改参数,用于查询时与队列保持同步,并不能调整队列大小)
dynamicThreadPool.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
}
} finally {
writeLock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取线程池状态
*/
public ThreadPoolStatus getThreadPoolStatus() {
ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock = reentrantLock.readLock();
try {
readLock.lock();
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = dynamicThreadPool.getThreadPoolExecutor();
BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = threadPoolExecutor.getQueue();
int useQueueCapacity = queue.size();
int remainingCapacity = queue.remainingCapacity();
return new ThreadPoolStatus()
.setCorePoolSize(dynamicThreadPool.getCorePoolSize())
.setMaxPoolSize(dynamicThreadPool.getMaxPoolSize())
.setActiveThreads(dynamicThreadPool.getActiveCount())
.setKeepAliveSeconds(dynamicThreadPool.getKeepAliveSeconds())
.setQueueMaxCapacity(useQueueCapacity + remainingCapacity)
.setQueueUseCapacity(useQueueCapacity)
.setQueueRemainingCapacity(remainingCapacity);
} finally {
readLock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 监听配置文件变更
* todo 监听配置文件变更
*/
@NacosConfigKeysListener(dataId = "dynamic-pool-service.yaml",
group = "DEFAULT_GROUP", interestedKeyPrefixes = "dynamic.thread-pool.")
private void onConfigChanged(ConfigChangeEvent changeEvent) {
log.info("onConfigChanged 监听到配置变化:{}", JSONObject.toJSONString(changeEvent));
DynamicPoolConfig config = new DynamicPoolConfig();
try {
Class<? extends DynamicPoolConfig> aClass = config.getClass();
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
if (declaredField.isAnnotationPresent(ConfigChangeEventToBean.class)) {
ConfigChangeEventToBean annotation = declaredField.getAnnotation(ConfigChangeEventToBean.class);
String value = annotation.value();
ConfigChangeItem changeItem = changeEvent.getChangeItem(value);
// 处理配置变更
if (changeItem != null && PropertyChangeType.MODIFIED.equals(changeItem.getType())){
declaredField.set(config, changeItem.getNewValue());
}
}
}
log.info("onConfigChanged 配置转换结果:{}", config);
this.adjustThreadPool(
Optional.ofNullable(config.getCoreSize()).map(Integer::parseInt).orElse(null),
Optional.ofNullable(config.getMaxSize()).map(Integer::parseInt).orElse(null),
Optional.ofNullable(config.getKeepAliveSeconds()).map(Integer::parseInt).orElse(null),
Optional.ofNullable(config.getQueueCapacity()).map(Integer::parseInt).orElse(null)
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("onConfigChanged 配置转换异常", e);
}
}
/**
* 线程池状态
*/
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public static class ThreadPoolStatus {
/**
* 核心线程数
*/
private int corePoolSize;
/**
* 最大线程数
*/
private int maxPoolSize;
/**
* 线程使用数
*/
private int activeThreads;
/**
* 线程空闲时间(秒)
*/
private int keepAliveSeconds;
/**
* 队列最大容量
*/
private int queueMaxCapacity;
/**
* 队列使用容量
*/
private int queueUseCapacity;
/**
* 队列剩余
*/
private int queueRemainingCapacity;
}
/**
* 用于解决配置转换问题
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
private @interface ConfigChangeEventToBean{
String value();
}
/**
* 动态线程池配置
* todo 需要自己改一下 注解的 value 属性
*/
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
static class DynamicPoolConfig {
/**
* 核心线程数
*/
@ConfigChangeEventToBean("dynamic.thread-pool.core-size")
private String coreSize;
/**
* 最大线程数
*/
@ConfigChangeEventToBean("dynamic.thread-pool.max-size")
private String maxSize;
/**
* 队列容量
*/
@ConfigChangeEventToBean("dynamic.thread-pool.queue-capacity")
private String queueCapacity;
/**
* 超时时间(秒)
*/
@ConfigChangeEventToBean("dynamic.thread-pool.keep-alive-seconds")
private String keepAliveSeconds;
}
/**
* 自定义线程池 实现自定义可变队列
*/
private static class DynamicThreadPoolTaskExecutor extends ThreadPoolTaskExecutor {
@Override
@NonNull
protected BlockingQueue<Runnable> createQueue(int queueCapacity) {
return queueCapacity > 0 ? new VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<>(queueCapacity) : new VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<>();
}
}
}测试案例:PoolTestController.java
java
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/poolTest")
public class PoolTestController {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("dynamicThreadPool")
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor dynamicThreadPool;
@Autowired
private DynamicThreadPoolConfig dynamicThreadPoolConfig;
/**
* 添加任务 测试 就让他等着 看拒绝情况
*/
@GetMapping("/addTask")
public Results<String> addTask() {
dynamicThreadPool.submit(() -> {
log.info("addTask 线程开始执行 {}", Thread.currentThread().getName());
while (true) {
try {
Thread.sleep(10000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
log.error("addTask 线程执行异常", e);
}
}
});
return Results.success();
}
/**
* 获取参数
*/
@GetMapping("/getParameter")
public Results<DynamicThreadPoolConfig.ThreadPoolStatus> getParameter() {
DynamicThreadPoolConfig.ThreadPoolStatus threadPoolStatus = dynamicThreadPoolConfig.getThreadPoolStatus();
return Results.success(threadPoolStatus);
}
}测试结果:
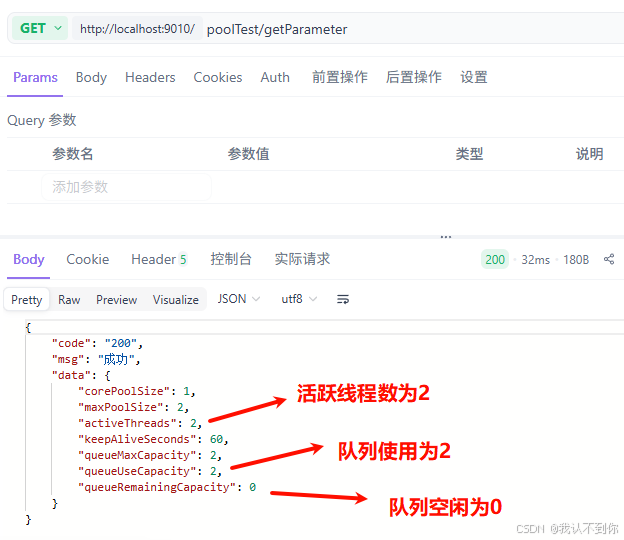
1、默认配置
根据默认配置的 核心线程数:1,最大线程数:2,队列长度:2
那么一共可以执行 4 个任务
按照理论,第五次调用 /poolTest/addTask 接口就会报错
控制台会显示两个任务执行,一个任务被拒绝,我们试一下
下面可以看见我们调用了五次接口,有一个报错
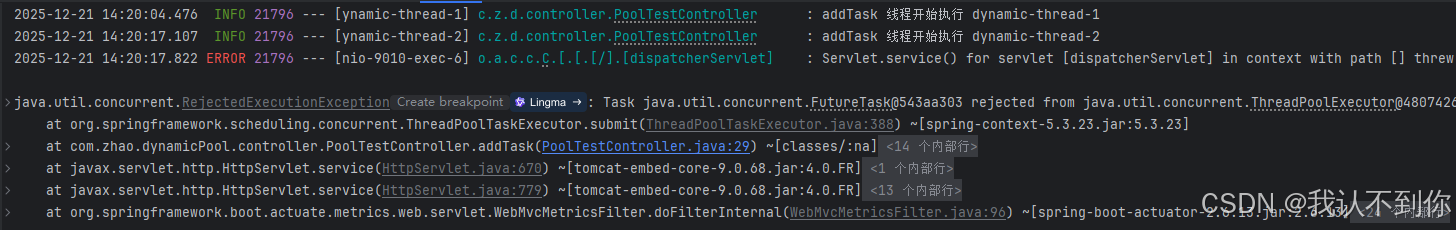
我们查一下线程池状态
有两个任务交由两个线程执行,有两个任务在队列里面,所以第五次请求失败
2、修改配置
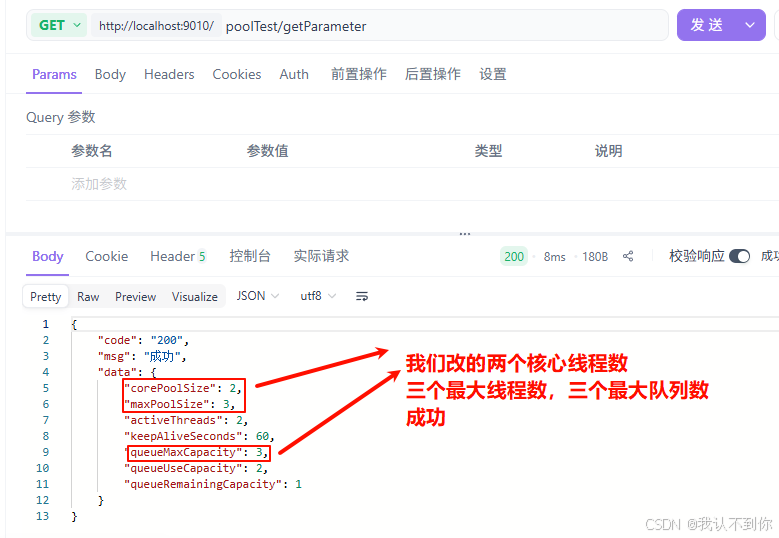
修改配置为 核心线程数:2,最大线程数:3,队列长度:3
那么一共可以执行的任务数量为 6,修改为后看下线程池配置
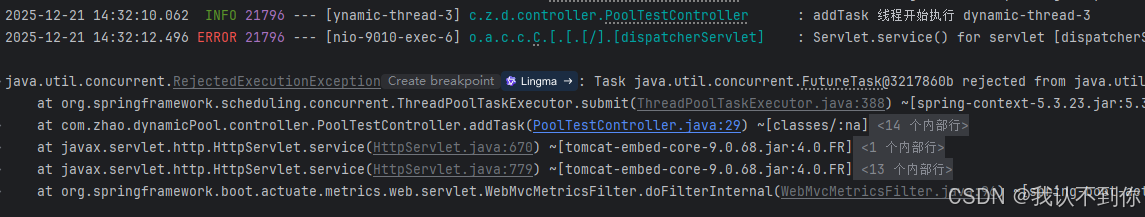
我们之前使用了 2 个线程 2 个队列
按照理论,我们再调用 /poolTest/addTask 接口三次会报错
我们会在控制台看见,有一个新线程开始任务,有一个新的报错,我们试一下
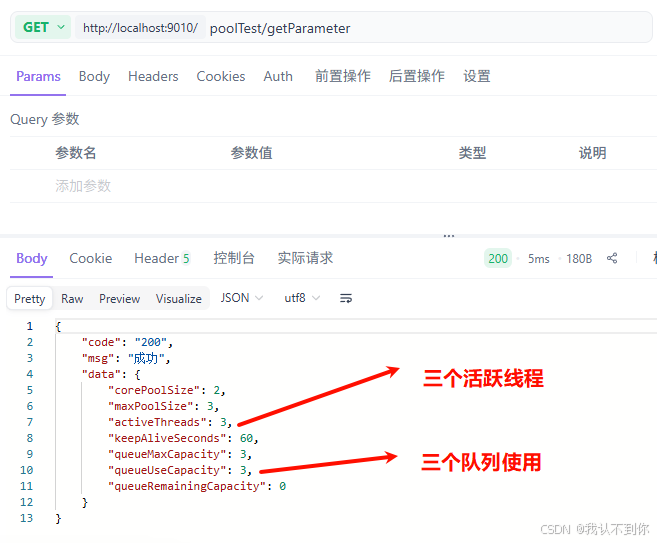
我们查线程状态时,队列里面也会多一个任务
三、动态线程池+kafka自定义拒绝策略
这里就不讲动态线程池的部分了,主要将 kafka 自定义拒绝策略的实现
因为这里也用到了动态线程池(有部分差异),所以得和上面二章节理论一起看
但测试时我就不展示动态线程部分了,就使用默认的 核心线程数:1,最大线程数:2,最大队列容量:2
kafka 配置:application.yaml(也可以放到nacos里面)
yaml
spring:
kafka:
bootstrap-servers: localhost:9092
consumer:
group-id: ${spring.application.name}
enable-auto-commit: false # 关闭自动提交
auto-offset-reset: earliest
key-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
value-deserializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringDeserializer
producer:
acks: -1
key-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
value-serializer: org.apache.kafka.common.serialization.StringSerializer
template:
default-topic: test-topic
listener:
ack-mode: manual # 监听,手动提交工具类:SpringBootBeanUtil.java
主要用于下面 kafka 拒绝策略获取到配置的应用名称
java
@Component
@SuppressWarnings("unused")
public class SpringBootBeanUtil implements ApplicationContextAware, EnvironmentAware {
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SpringBootBeanUtil.class);
private static ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private static Environment environment;
@Override
public void setEnvironment(final Environment environment) {
if (SpringBootBeanUtil.applicationContext == null) {
SpringBootBeanUtil.environment = environment;
}
}
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(final ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
if (SpringBootBeanUtil.applicationContext == null) {
SpringBootBeanUtil.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
}
/**
* 获取applicationContext
*/
public static ApplicationContext getApplicationContext() {
return applicationContext;
}
/**
* 获取applicationContext
*/
public static Environment getEnvironment() {
return environment;
}
/**
* 通过name获取 Bean.
*/
public static Object getBean(String name) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(name);
}
/**
* 通过class获取Bean.
*/
public static <T> T getBean(Class<T> clazz) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(clazz);
}
/**
* 通过name,以及Clazz返回指定的Bean
*/
public static <T> T getBean(String name, Class<T> clazz) {
return getApplicationContext().getBean(name, clazz);
}
}启动器:DynamicPoolApplication.java
优先把 SpringBootBeanUtil 注入到容器里面,不然后面初始化 kafka 的拒绝策略会报错(因为我们需要从配置里面获取应用名(spring.application.name))
java
@SpringBootApplication
public class DynamicPoolApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(DynamicPoolApplication.class);
app.addInitializers(new PriorityRegistrationClass());
app.run(args);
}
/**
* 优先注册
*/
static class PriorityRegistrationClass implements ApplicationContextInitializer<GenericApplicationContext> {
@Override
public void initialize(GenericApplicationContext applicationContext) {
// 你可以注册多个Bean
applicationContext.registerBean(SpringBootBeanUtil.class);
}
}
}kafka 生产者:KafkaProducerService.java
java
/**
* kafka 生产者
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class KafkaProducerService {
@Autowired
private KafkaTemplate<String, Object> kafkaTemplate;
/**
* 同步发送消息
* @param topic 主体
* @param msg 消息
*/
public void sendMessageSync(String topic, Object msg) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
try {
kafkaTemplate.send(topic, msg).get();
log.info("sendMessageSync 同步消息发送 成功 topic={} msg={}", topic, msg);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("sendMessageSync 同步消息发送 失败", e);
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 异步发送消息
* @param topic 主体
* @param msg 消息
*/
public void sendMessageAsync(String topic, Object msg) {
kafkaTemplate.send(topic, msg).addCallback(success -> {
log.info("sendMessageAsync 异步消息发送 成功 topic={} msg={}", topic, msg);
}, failure -> {
log.error("sendMessageAsync 异步消息发送 失败", failure);
});
}
}kafka 消费者:KafkaConsumerService.java
java
/**
* kafka 消费者
*/
@Service
@Slf4j
public class KafkaConsumerService {
/**
* 监听Kafka消息 手动提交
* todo 测试topic 需修改
*
* @param msg 消息内容
*/
@KafkaListener(topics = "test-reject", groupId = "dynamic-pool-service")
public void consume(String msg, Acknowledgment ack) {
log.info("kafka 开始消费 msg: {}", msg);
try {
// 这里是通过反射 进行任务执行
KafkaRejectPolicy.RejectedTaskMessage.taskStart(msg);
ack.acknowledge();
} catch (Exception e) {
log.info("kafka 消费异常", e);
}
}
}kafka 拒绝策略
这里面重要的就是 KafkaTaskInfoRunnable 这个抽象类
我们的任务都需要继承这个类来实现 kafka 异步任务来做到任务不丢失
逻辑是这样的(后面测试案例会讲到,这里只是给大家理一下逻辑)
我们先实现一个 A 类继承 KafkaTaskInfoRunnable 这个抽象类(A.java extends KafkaTaskInfoRunnable.java)
KafkaTaskInfoRunnable 实现了 Runnable 接口,所以 A 类需要实现 run 方法,这样就可以通过线程池进行异步任务
我们线程池满了之后,任务被拒绝了,会给 kafka 发送一个消息(json字符串)
json 里面包括了实现任务的类(A.java)(Class)、入参(具体值)、入参类型(Class)等(这三个比较关键)
kafka 监听后会从消息(json)里面获取到任务的类(Class)、入参(具体值)、入参类型(Class)
然后通过反射同步的调用 A.java 的 run 方法,达到消峰(因为kafka会一个任务执行完再接着执行)和任务不丢失
由于要使用反射获取 A.java 的具体数据,所以 A.java 是不能使用匿名内部类的
ps:发送警告我没有处理,有兴趣大家可以实现以下,这个也简单,如果警告频繁,说明 QPS 过大,我们就需要自己调整线程池或者就是加机器了
java
/**
* Kafka拒绝策略 - 将被拒绝的任务发送到Kafka队列
*/
@Slf4j
public class KafkaRejectPolicy implements RejectedExecutionHandler {
private static final AtomicLong rejectCount = new AtomicLong(0);
private final String topic;
/**
* 应用名称(用于消息标识)
*/
private final String applicationName;
/**
* 构造函数
*
* @param topic 目标主题
*/
public KafkaRejectPolicy(String topic) {
this.topic = topic;
// 这里得先在启动器配置优先加载 SpringBootBeanUtil 的 bean 对象
String applicationName = SpringBootBeanUtil.getEnvironment().getProperty("spring.application.name");
if (applicationName == null || applicationName.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("配置项 spring.application.name 不能为空");
}
this.applicationName = applicationName;
}
/**
* 获取ip 地址
*/
private static String getIpAddress() throws UnknownHostException {
InetAddress localHost = InetAddress.getLocalHost();
return localHost.getHostAddress();
}
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
try {
// 检查任务类型
if (!(r instanceof KafkaTaskInfoRunnable)) {
// 使用 submit 方法时会走到 AbstractExecutorService 的 submit 方法,会封装一层 FutureTask
// 如果是 FutureTask,尝试提取内部的 Runnable
if (r instanceof FutureTask) {
try {
// 通过反射获取 FutureTask 内部的 callable
Field callableField = FutureTask.class.getDeclaredField("callable");
callableField.setAccessible(true);
Object callable = callableField.get(r);
// 如果是 RunnableAdapter(Executor.callable 返回的内部类)
if (callable != null && callable.getClass().getName().contains("RunnableAdapter")) {
Field taskField = callable.getClass().getDeclaredField("task");
taskField.setAccessible(true);
Object originalTask = taskField.get(callable);
if (originalTask instanceof KafkaTaskInfoRunnable) {
r = (Runnable) originalTask;
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("提取 FutureTask 内部任务失败", e);
}
}
}
// 最终检查
if (!(r instanceof KafkaTaskInfoRunnable)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("该任务无法由 Kafka 执行,必须使用 KafkaTaskInfoRunnable 类型");
}
KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<?> KafkaTaskInfoRunnable = (KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<?>) r;
long count = rejectCount.incrementAndGet();
// 获取线程池状态信息
String poolInfo = getThreadPoolInfo(executor);
// 构建拒绝任务的消息
RejectedTaskMessage taskMessage = new RejectedTaskMessage()
.setTaskId(generateTaskId())
.setApplicationName(applicationName)
.setIpAddress(getIpAddress())
.setThreadPoolInfo(poolInfo)
.setRejectTime(System.currentTimeMillis())
.setRejectCount(count)
.setTaskDataJson(KafkaTaskInfoRunnable.getTaskDataJson())
.setTaskClass(KafkaTaskInfoRunnable.getTaskClass())
.setTaskInputParameterClass(KafkaTaskInfoRunnable.getTaskInputParameterClass());
// 发送到Kafka
String msg = JSONObject.toJSONString(taskMessage);
// 使用 kafka 生产者发送消息
KafkaProducerService kafkaProducer = SpringBootBeanUtil.getBean(KafkaProducerService.class);
// 同步发送并处理回调
kafkaProducer.sendMessageSync(topic, msg);
log.info("拒绝任务已发送到Kafka队列。拒绝次数: {}, 线程池状态: {}", count, poolInfo);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(" kafka 拒绝策略 发送消息异常", e);
// 降级处理(让当前线程自己处理)
if (!executor.isShutdown()) {
r.run();
}
}
}
/**
* 获取线程池状态信息
* <p>
* 包含以下关键指标:
* - 活跃线程数:当前正在执行任务的线程数量
* - 线程池大小:线程池中当前的线程数量(包括空闲线程)
* - 核心线程数:线程池保持的最小线程数量
* - 最大线程数:线程池允许创建的最大线程数量
* - 队列大小:任务队列中等待执行的任务数量
* - 队列容量:任务队列的最大容量
*/
private String getThreadPoolInfo(ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = executor.getQueue();
return String.format(
"活跃线程: %d, 池中线程: %d, 核心线程: %d, 最大线程: %d, 队列大小/队列容量: %d/%d",
// 正在执行任务的线程数
executor.getActiveCount(),
// 线程池中当前的线程总数
executor.getPoolSize(),
// 核心线程数
executor.getCorePoolSize(),
// 最大线程数
executor.getMaximumPoolSize(),
// 队列中等待的任务数
queue.size(),
// 队列总容量
queue.size() + queue.remainingCapacity()
);
}
/**
* 生成任务ID
*/
private String generateTaskId() {
return UUID.randomUUID().toString();
}
/**
* 发送告警
*/
private void sendAlert(RejectedTaskMessage message) {
// 实现告警逻辑(邮件、短信、钉钉等)
log.error("任务处理失败!任务ID: {}", message.getTaskId());
}
/**
* 任务信息接口(不能使用匿名内部类)
* 实现此接口的任务可以传递更多信息到拒绝策略
*/
public static abstract class KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<T> implements Runnable {
private final T taskData;
public KafkaTaskInfoRunnable(T taskData) {
// 运行时检查
if (this.getClass().isAnonymousClass()) {
throw new IllegalStateException("TaskInfoRunnable 类 不能使用匿名内部类");
}
this.taskData = taskData;
}
protected String getTaskDataJson() {
return JSONObject.toJSONString(taskData);
}
protected T getTaskData() {
return this.taskData;
}
/**
* 任务执行类名(全类名)
*/
protected Class<KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<T>> getTaskClass() {
return (Class<KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<T>>) this.getClass();
}
/**
* 任务入参类名(全类名)
*/
protected Class<T> getTaskInputParameterClass() {
return (Class<T>) taskData.getClass();
}
}
/**
* 拒绝任务消息实体
*/
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public static class RejectedTaskMessage implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* 任务ID(唯一ID)
*/
private String taskId;
/**
* 应用名称
*/
private String applicationName;
/**
* ip地址
*/
private String ipAddress;
/**
* 线程池状态信息
*/
private String threadPoolInfo;
/**
* 拒绝时间戳
*/
private long rejectTime;
/**
* 拒绝计数
*/
private long rejectCount;
/**
* 任务执行类名(全类名)
*/
private Class<? extends KafkaTaskInfoRunnable> taskClass;
/**
* 任务入参类名(全类名)
*/
private Class<?> taskInputParameterClass;
/**
* 任务入参数据(json)
*/
private String taskDataJson;
public static void taskStart(String msgJson) throws Exception {
JSON.config(JSONReader.Feature.SupportClassForName);
KafkaRejectPolicy.RejectedTaskMessage message = JSONObject.parseObject(
msgJson,
KafkaRejectPolicy.RejectedTaskMessage.class
);
String dataJson = message.getTaskDataJson();
Class<?> inputParameterClass = message.getTaskInputParameterClass();
Class<KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<?>> taskClass = (Class<KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<?>>) message.getTaskClass();
Object o = JSONObject.parseObject(dataJson, inputParameterClass);
Constructor<KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<?>> constructor = taskClass.getDeclaredConstructor(inputParameterClass);
constructor.setAccessible(true);
KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<?> infoRunnable = constructor.newInstance(o);
infoRunnable.run();
}
}
}动态线程池:DynamicKafkaRejectThreadPoolConfig.java
跟上面的动态线程池类似,但有细微差距
最主要的是 ThreadPoolKafkaTaskExecutor 类
该类也继承了 ThreadPoolTaskExecutor 类,用于可以动态改变线程池的参数(核心、最大线程、队列容量(也是通过VariableLinkedBlockingQueue 实现的))
这里比较重要的就是重写线程池的 execute 和 submit 方法,只允许继承了 KafkaTaskInfoRunnable 的任务入队
java
/**
* 动态线程池 (kafka 拒绝策略版本)
* <p>
* 加 todo 的 就是可以选择性修改的
*/
@Configuration
@RefreshScope // 支持配置热更新
@EnableAsync // 启用异步支持
@Slf4j
@Lazy
public class DynamicKafkaRejectThreadPoolConfig {
/**
* 核心参数 默认使用io密集型
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改
*/
@Value("${dynamic.thread-pool.core-size:0}")
private int coreSize;
/**
* 最大参数 默认使用io密集型
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改
*/
@Value("${dynamic.thread-pool.max-size:0}")
private int maxSize;
/**
* 队列容量 默认 1w 的队列
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改
*/
@Value("${dynamic.thread-pool.queue-capacity:10000}")
private int queueCapacity;
/**
* 超时时间 默认 60s 超时
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改
*/
@Value("${dynamic.thread-pool.keep-alive-seconds:60}")
private int keepAliveSeconds;
/**
* 超时时间 默认 60s 超时
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改
*/
@Value("${dynamic.thread-pool.kafka-reject-policy-topic:test-reject}")
private String kafkaRejectPolicyTopic;
/**
* 动态线程池
* todo 根据业务情况自行修改 Bean 的值
*/
@Bean("dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool")
ThreadPoolKafkaTaskExecutor dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool() {
int cpuCores = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
if (coreSize <= 0) {
coreSize = cpuCores * 2;
}
if (maxSize <= 0) {
maxSize = cpuCores * 4;
}
ThreadPoolKafkaTaskExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolKafkaTaskExecutor();
// 核心线程数(默认线程数)
executor.setCorePoolSize(coreSize);
// 最大线程数(队列满后扩容的最大值)
executor.setMaxPoolSize(maxSize);
// 线程空闲时间(秒)
executor.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);
// 队列容量(超过核心线程数时,任务进入队列)
executor.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
// 线程名前缀
executor.setThreadNamePrefix("dynamic-thread-");
// 拒绝策略(此处使用报错执行)
executor.setRejectedExecutionHandler(new KafkaRejectPolicy(kafkaRejectPolicyTopic));
// 初始化
executor.initialize();
return executor;
}
/**
* 动态线程池
* todo 如果你改了 Bean 的值 记得改 Qualifier 中的值
*/
@Autowired
@Qualifier("dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool")
@Lazy
private ThreadPoolTaskExecutor dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool;
/**
* 公平读写锁
*/
private final static ReentrantReadWriteLock reentrantLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock(true);
/**
* 动态调整线程池参数
*
* @param corePoolSize 核心线程数
* @param maxPoolSize 最大线程数
* @param keepAliveSeconds 超时时间(秒)
* @param queueCapacity 队列容量
*/
public void adjustThreadPool(Integer corePoolSize, Integer maxPoolSize, Integer keepAliveSeconds, Integer queueCapacity) {
ReentrantReadWriteLock.WriteLock writeLock = reentrantLock.writeLock();
try {
writeLock.lock();
// 调整核心线程数
if (corePoolSize != null && corePoolSize != dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.getCorePoolSize()) {
dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.setCorePoolSize(corePoolSize);
}
// 调整最大线程数
if (maxPoolSize != null && maxPoolSize != dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.getMaxPoolSize()) {
dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.setMaxPoolSize(maxPoolSize);
}
// 调整超时时间
if (keepAliveSeconds != null && keepAliveSeconds != dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.getKeepAliveSeconds()) {
dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.setKeepAliveSeconds(keepAliveSeconds);
}
// 调整队列容量(需重置队列)
if (queueCapacity != null && queueCapacity != dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.getQueueCapacity()) {
VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable> queue =
(VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable>) dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.getThreadPoolExecutor().getQueue();
if (queueCapacity < queue.remainingCapacity() + queue.size()) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("线程池 不支持缩容");
}
// 需要自定义可调整队列容量
queue.setCapacity(queueCapacity);
// 重置线程池容量参数(这里只是改参数,用于查询时与队列保持同步,并不能调整队列大小)
dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.setQueueCapacity(queueCapacity);
}
} finally {
writeLock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 获取线程池状态
*/
public ThreadPoolStatus getThreadPoolStatus() {
ReentrantReadWriteLock.ReadLock readLock = reentrantLock.readLock();
try {
readLock.lock();
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.getThreadPoolExecutor();
BlockingQueue<Runnable> queue = threadPoolExecutor.getQueue();
int useQueueCapacity = queue.size();
int remainingCapacity = queue.remainingCapacity();
return new ThreadPoolStatus()
.setCorePoolSize(dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.getCorePoolSize())
.setMaxPoolSize(dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.getMaxPoolSize())
.setActiveThreads(dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.getActiveCount())
.setKeepAliveSeconds(dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool.getKeepAliveSeconds())
.setQueueMaxCapacity(useQueueCapacity + remainingCapacity)
.setQueueUseCapacity(useQueueCapacity)
.setQueueRemainingCapacity(remainingCapacity);
} finally {
readLock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 监听配置文件变更
* todo 监听配置文件变更
*/
@NacosConfigKeysListener(dataId = "dynamic-pool-service.yaml",
group = "DEFAULT_GROUP", interestedKeyPrefixes = "dynamic.thread-pool.")
private void onConfigChanged(ConfigChangeEvent changeEvent) {
log.info("onConfigChanged 监听到配置变化:{}", JSONObject.toJSONString(changeEvent));
DynamicPoolConfig config = new DynamicPoolConfig();
try {
Class<? extends DynamicPoolConfig> aClass = config.getClass();
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
declaredField.setAccessible(true);
if (declaredField.isAnnotationPresent(ConfigChangeEventToBean.class)) {
ConfigChangeEventToBean annotation = declaredField.getAnnotation(ConfigChangeEventToBean.class);
String value = annotation.value();
ConfigChangeItem changeItem = changeEvent.getChangeItem(value);
// 处理配置变更
if (changeItem != null && PropertyChangeType.MODIFIED.equals(changeItem.getType())) {
declaredField.set(config, changeItem.getNewValue());
}
}
}
log.info("onConfigChanged 配置转换结果:{}", config);
this.adjustThreadPool(
Optional.ofNullable(config.getCoreSize()).map(Integer::parseInt).orElse(null),
Optional.ofNullable(config.getMaxSize()).map(Integer::parseInt).orElse(null),
Optional.ofNullable(config.getKeepAliveSeconds()).map(Integer::parseInt).orElse(null),
Optional.ofNullable(config.getQueueCapacity()).map(Integer::parseInt).orElse(null)
);
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error("onConfigChanged 配置转换异常", e);
}
}
/**
* 线程池状态
*/
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
public static class ThreadPoolStatus {
/**
* 核心线程数
*/
private int corePoolSize;
/**
* 最大线程数
*/
private int maxPoolSize;
/**
* 线程使用数
*/
private int activeThreads;
/**
* 线程空闲时间(秒)
*/
private int keepAliveSeconds;
/**
* 队列最大容量
*/
private int queueMaxCapacity;
/**
* 队列使用容量
*/
private int queueUseCapacity;
/**
* 队列剩余
*/
private int queueRemainingCapacity;
}
/**
* 用于解决配置转换问题
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.FIELD})
private @interface ConfigChangeEventToBean {
String value();
}
/**
* 动态线程池配置
* todo 需要自己改一下 注解的 value 属性
*/
@Data
@Accessors(chain = true)
static class DynamicPoolConfig {
/**
* 核心线程数
*/
@ConfigChangeEventToBean("dynamic.thread-pool.core-size")
private String coreSize;
/**
* 最大线程数
*/
@ConfigChangeEventToBean("dynamic.thread-pool.max-size")
private String maxSize;
/**
* 队列容量
*/
@ConfigChangeEventToBean("dynamic.thread-pool.queue-capacity")
private String queueCapacity;
/**
* 超时时间(秒)
*/
@ConfigChangeEventToBean("dynamic.thread-pool.keep-alive-seconds")
private String keepAliveSeconds;
}
/**
* 自定义线程池 实现自定义可变队列
*/
public static class ThreadPoolKafkaTaskExecutor extends ThreadPoolTaskExecutor {
public <T extends KafkaRejectPolicy.KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<?>> void execute(T task) {
super.execute(task);
}
public <T extends KafkaRejectPolicy.KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<?>> Future<?> submit(T task) {
return super.submit(task);
}
@Override
@NonNull
protected BlockingQueue<Runnable> createQueue(int queueCapacity) {
return queueCapacity > 0 ? new VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<>(queueCapacity) : new VariableLinkedBlockingQueue<>();
}
}
}任务执行:UserModifyNameHandler.java
这个方法就是用于执行异步任务(不能是匿名内部类,不然反射获取不到对应的类就执行 kafka 的任务了)
User.java 就是有两个成员变量 name 和 age 用于测试,这里就不展示了,可以看我 gitee 中的代码(链接再最上面的前言部分)
java
@Slf4j
public class UserModifyNameHandler extends KafkaRejectPolicy.KafkaTaskInfoRunnable<User>{
public UserModifyNameHandler(User taskData) {
super(taskData);
}
@Override
public void run() {
User taskData = super.getTaskData();
taskData.setName(taskData.getName() + "--修改了名字");
// 睡两秒钟模仿耗时
try {
Thread.sleep(2_000);
} catch (InterruptedException ignored) {
}
log.info("用户修改名字 任务开始执行 {}", taskData);
}
}测试案例:KafkaPoolTestController.java
这个测试案例里面,我们只需要调用异常 /kafkaPoolTest/addTask 方法
会执行 10 条任务,我们再任务 UserModifyNameHandler 里面睡了两秒钟,
所以我们先设置的线程池参数(核心线程数:1,最大线程数:2,最大队列容量:2),只会执行 4 个任务
其他的就会被拒绝掉,然后放进 kafka 的队列里面,由 kafka 的消费者消费(KafkaConsumerService)
得到的效果就是线程池执行了 4 条任务(异步), kafka 执行了 6 条任务(同步)
java
@RestController
@Slf4j
@RequestMapping("/kafkaPoolTest")
public class KafkaPoolTestController {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("dynamicKafkaRejectThreadPool")
private DynamicKafkaRejectThreadPoolConfig.ThreadPoolKafkaTaskExecutor dynamicThreadPool;
@Autowired
private DynamicThreadPoolConfig dynamicThreadPoolConfig;
/**
* 记录生成了多少用户
*/
private static final AtomicLong userCount = new AtomicLong(0);
/**
* 添加任务 测试 就让他等着 看拒绝情况
*/
@GetMapping("/addTask")
public Results<String> addTask() {
// 一次性生成十个数据
List<User> users = mockUsers();
// 线程池参数 核心线程:1 最大线程:2 队列容量:2
// 那么一次调用只能有 4 个任务执行,其他的都会被拒绝
// 那么拒绝的任务都进入了 kafka 的队列,由 KafkaConsumerService 处理
users.forEach(user -> {
Future<?> submit = dynamicThreadPool.submit(new UserModifyNameHandler(user));
});
return Results.success();
}
/**
* 获取参数
*/
@GetMapping("/getParameter")
public Results<DynamicThreadPoolConfig.ThreadPoolStatus> getParameter() {
DynamicThreadPoolConfig.ThreadPoolStatus threadPoolStatus = dynamicThreadPoolConfig.getThreadPoolStatus();
return Results.success(threadPoolStatus);
}
/**
* 模拟生成用户
*/
public synchronized static List<User> mockUsers() {
List<@Nullable User> list = Lists.newArrayList();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
long count = userCount.incrementAndGet();
User user = new User().setName("用户:" + count).setAge(18);
list.add(user);
}
return list;
}
}测试结果:
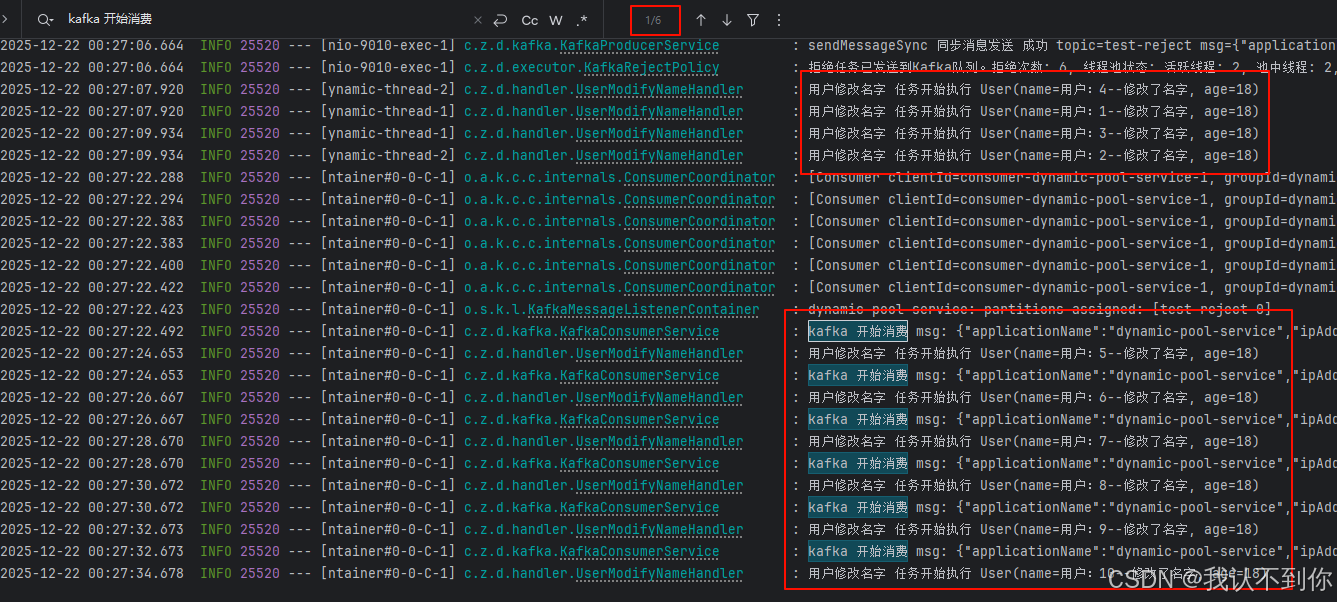
由于打印的消息有点多,所以我就截取一部分进行展示
分别是
线程池异步进行了 4 条任务,用户 4、1、3、2
kafka 同步执行了 6 条任务,用户 5、6、7、8、9、10(这里有可能也不是这个顺序执行的,这要看 kafka 入队顺序了,因为本来线程池就是异步的执行任务,kafka 为什么我要写成同步呢?因为本来进入 kafka 队列就是因为服务器资源紧张,线程池不够用了,再异步执行的话,跟线程池设置超多的最大线程数或者最大队列数有什么区别呢,这样会导致 OOM 的,所以这里使用同步,只让一个线程执行任务,就会减少服务器的压力,从而做到消峰+任务不丢失)