拒绝采样是一种从复杂分布中生成样本的蒙特卡洛方法,是目前LLM微调优化的关键技术。
这里尝试基于python模拟和对比多种拒绝采样的实现方法。
所用样例参考和优化自网络资料。
1 什么是拒绝采样
拒绝采样(Rejection Sampling)是一种从复杂分布中生成样本的蒙特卡洛方法。
下面将展示多种拒绝采样算法。
1.1 基础拒绝采样
-
核心原理:从提议分布生成样本,以一定概率接受
-
关键参数:常数M,需要满足
target_pdf(x) ≤ M * proposal_pdf(x) -
优化方向:选择合适的提议分布和尽可能小的M值
1.2 自适应拒绝采样优化
-
动态调整提议分布:根据已接受的样本调整提议分布的参数
-
自动优化M值:在采样过程中重新计算最优M值
-
分批更新:每接受一定数量样本后更新提议分布
1.3 分层拒绝采样优化
-
定义域分层:将目标分布的定义域分成多个子区域
-
各层独立优化:为每个子区域选择最合适的提议分布
-
平衡采样:在各层之间合理分配采样数量
1.4 混合提议分布优化
-
多个提议分布混合:使用多个提议分布的加权和
-
自适应权重调整:根据接受率动态调整各分布的权重
-
多峰分布匹配:特别适合多峰目标分布
2 python模拟拒绝采样
2.1 拒绝采样优化模拟示例
下面将展示一个完整的Python实现,包括基础版本和多个优化版本。
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from scipy import stats
import time
from functools import wraps
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings('ignore')
# ==================== 基础拒绝采样算法 ====================
def basic_rejection_sampling(target_pdf, proposal_pdf, proposal_rv, M, n_samples=1000, max_iter=10000):
"""
基础拒绝采样算法
参数:
target_pdf: 目标分布的概率密度函数
proposal_pdf: 提议分布的概率密度函数
proposal_rv: 提议分布的随机变量生成函数
M: 常数M,使得 target_pdf(x) ≤ M * proposal_pdf(x) 对所有x成立
n_samples: 需要生成的样本数量
max_iter: 最大迭代次数(防止无限循环)
返回:
samples: 从目标分布中采样的样本
acceptance_rate: 接受率
"""
samples = []
attempts = 0
while len(samples) < n_samples and attempts < max_iter:
attempts += 1
# 1. 从提议分布生成样本
x = proposal_rv()
# 2. 从均匀分布U(0,1)生成样本
u = np.random.uniform(0, 1)
# 3. 接受/拒绝决策
if u < target_pdf(x) / (M * proposal_pdf(x)):
samples.append(x)
acceptance_rate = len(samples) / attempts if attempts > 0 else 0
return np.array(samples), acceptance_rate
# ==================== 自适应拒绝采样优化版本 ====================
class AdaptiveRejectionSampler:
"""
自适应拒绝采样器 - 优化版本1: 动态调整提议分布
"""
def __init__(self, target_pdf, initial_proposal, domain=(-10, 10)):
"""
初始化自适应拒绝采样器
参数:
target_pdf: 目标分布的概率密度函数
initial_proposal: 初始提议分布 (dict with 'pdf' and 'rv' functions)
domain: 采样域
"""
self.target_pdf = target_pdf
self.proposal_pdf = initial_proposal['pdf']
self.proposal_rv = initial_proposal['rv']
self.domain = domain
self.samples = []
self.rejections = []
self.M_history = []
def find_optimal_M(self, n_test=1000):
"""
通过测试点找到最优的M值
参数:
n_test: 测试点数量
返回:
optimal_M: 最优M值
"""
test_points = np.linspace(self.domain[0], self.domain[1], n_test)
ratios = []
for x in test_points:
target_val = self.target_pdf(x)
proposal_val = self.proposal_pdf(x)
if proposal_val > 0:
ratio = target_val / proposal_val
ratios.append(ratio)
# 使用最大比值的1.1倍作为M,确保覆盖
optimal_M = np.max(ratios) * 1.1 if ratios else 2.0
return optimal_M
def adaptive_sampling(self, n_samples=1000, adapt_every=100, verbose=False):
"""
自适应采样过程
参数:
n_samples: 需要生成的样本数量
adapt_every: 每多少个样本调整一次提议分布
verbose: 是否显示详细信息
返回:
samples: 采样结果
acceptance_rate: 平均接受率
"""
samples = []
self.M_history = []
total_attempts = 0
# 初始M值
M = self.find_optimal_M()
self.M_history.append(M)
for batch in range(0, n_samples, adapt_every):
batch_size = min(adapt_every, n_samples - len(samples))
batch_samples, batch_attempts = self._sample_batch(batch_size, M)
samples.extend(batch_samples)
total_attempts += batch_attempts
# 更新提议分布(基于已接受的样本)
if len(samples) > 10:
self._update_proposal(samples)
M = self.find_optimal_M()
self.M_history.append(M)
if verbose:
acceptance = len(batch_samples) / batch_attempts if batch_attempts > 0 else 0
print(f"Batch {batch//adapt_every}: Acceptance rate = {acceptance:.4f}, M = {M:.4f}")
acceptance_rate = len(samples) / total_attempts if total_attempts > 0 else 0
return np.array(samples), acceptance_rate
def _sample_batch(self, batch_size, M):
"""采样一个批次"""
samples = []
attempts = 0
while len(samples) < batch_size and attempts < batch_size * 100: # 防止无限循环
attempts += 1
x = self.proposal_rv()
u = np.random.uniform(0, 1)
if u < self.target_pdf(x) / (M * self.proposal_pdf(x)):
samples.append(x)
else:
self.rejections.append(x)
return samples, attempts
def _update_proposal(self, accepted_samples):
"""基于接受的样本更新提议分布参数"""
# 这里使用简单的高斯分布作为提议分布
# 在实际应用中可以使用更复杂的分布
mean = np.mean(accepted_samples)
std = np.std(accepted_samples) + 0.1 # 加一个小值防止方差为0
# 更新提议分布为新的正态分布
self.proposal_pdf = lambda x: stats.norm.pdf(x, mean, std)
self.proposal_rv = lambda: np.random.normal(mean, std)
# ==================== 分层拒绝采样优化版本 ====================
def stratified_rejection_sampling(target_pdf, domains, proposal_funcs, n_samples=1000):
"""
分层拒绝采样 - 优化版本2: 将定义域分层
参数:
target_pdf: 目标分布的概率密度函数
domains: 每个层的定义域列表 [(a1, b1), (a2, b2), ...]
proposal_funcs: 每个层的提议分布函数列表 [{'pdf': pdf1, 'rv': rv1}, ...]
n_samples: 需要生成的样本数量
返回:
samples: 采样结果
acceptance_rates: 各层的接受率
"""
samples = []
acceptance_rates = []
n_layers = len(domains)
# 分配每层的采样数量(可以根据层的权重分配)
samples_per_layer = n_samples // n_layers
remainder = n_samples % n_layers
for i in range(n_layers):
# 当前层的采样数量
layer_samples = samples_per_layer + (1 if i < remainder else 0)
# 为当前层定义截断的提议分布
a, b = domains[i]
layer_proposal_pdf = proposal_funcs[i]['pdf']
layer_proposal_rv = proposal_funcs[i]['rv']
# 在当前层中找到M值
test_points = np.linspace(a, b, 1000)
max_ratio = 0
for x in test_points:
ratio = target_pdf(x) / layer_proposal_pdf(x)
if ratio > max_ratio:
max_ratio = ratio
M = max_ratio * 1.1
# 在当前层进行拒绝采样
layer_samples_list = []
attempts = 0
while len(layer_samples_list) < layer_samples and attempts < layer_samples * 100:
attempts += 1
x = layer_proposal_rv()
# 确保x在当前层内
if a <= x <= b:
u = np.random.uniform(0, 1)
if u < target_pdf(x) / (M * layer_proposal_pdf(x)):
layer_samples_list.append(x)
samples.extend(layer_samples_list)
acceptance_rate = len(layer_samples_list) / attempts if attempts > 0 else 0
acceptance_rates.append(acceptance_rate)
return np.array(samples), acceptance_rates
# ==================== 混合提议分布优化版本 ====================
class MixtureProposalSampler:
"""
混合提议分布拒绝采样 - 优化版本3: 使用多个提议分布的混合
"""
def __init__(self, target_pdf, proposal_components):
"""
初始化混合提议分布采样器
参数:
target_pdf: 目标分布的概率密度函数
proposal_components: 提议分布组件列表
[{'pdf': pdf1, 'rv': rv1, 'weight': w1}, ...]
"""
self.target_pdf = target_pdf
self.components = proposal_components
self.n_components = len(proposal_components)
self.weights = np.array([comp['weight'] for comp in proposal_components])
self.weights = self.weights / np.sum(self.weights) # 归一化
def sample(self, n_samples=1000):
"""执行采样"""
samples = []
attempts = 0
while len(samples) < n_samples and attempts < n_samples * 100:
attempts += 1
# 1. 选择提议分布组件
comp_idx = np.random.choice(self.n_components, p=self.weights)
component = self.components[comp_idx]
# 2. 从选定的组件生成样本
x = component['rv']()
# 3. 计算混合提议分布的概率密度
mixture_pdf = 0
for i, comp in enumerate(self.components):
mixture_pdf += self.weights[i] * comp['pdf'](x)
# 4. 计算M值(对于混合分布,需要找到全局M)
# 这里简化处理,使用当前点的比值
if mixture_pdf > 0:
ratio = self.target_pdf(x) / mixture_pdf
M = 2.0 # 简化:使用固定的M,实际应用中需要计算合适的M
# 5. 接受/拒绝决策
u = np.random.uniform(0, 1)
if u < ratio / M:
samples.append(x)
acceptance_rate = len(samples) / attempts if attempts > 0 else 0
return np.array(samples), acceptance_rate
# ==================== 性能比较和可视化 ====================
def compare_sampling_methods(target_pdf, true_samples=None):
"""比较不同采样方法的性能"""
# 定义目标分布(混合高斯分布)
print("目标分布: 混合高斯分布")
print("=" * 60)
# 基础拒绝采样参数
# 使用高斯分布作为提议分布
proposal_mean = 0
proposal_std = 2
proposal_pdf = lambda x: stats.norm.pdf(x, proposal_mean, proposal_std)
proposal_rv = lambda: np.random.normal(proposal_mean, proposal_std)
# 找到合适的M值
test_points = np.linspace(-10, 10, 1000)
max_ratio = 0
for x in test_points:
ratio = target_pdf(x) / proposal_pdf(x)
if ratio > max_ratio:
max_ratio = ratio
M = max_ratio * 1.1
print(f"基础拒绝采样 - 使用的M值: {M:.4f}")
# 方法1: 基础拒绝采样
start_time = time.time()
basic_samples, basic_acceptance = basic_rejection_sampling(
target_pdf, proposal_pdf, proposal_rv, M, n_samples=2000
)
basic_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"基础拒绝采样 - 接受率: {basic_acceptance:.4f}, 时间: {basic_time:.4f}s")
# 方法2: 自适应拒绝采样
initial_proposal = {
'pdf': proposal_pdf,
'rv': proposal_rv
}
adaptive_sampler = AdaptiveRejectionSampler(target_pdf, initial_proposal, domain=(-10, 10))
start_time = time.time()
adaptive_samples, adaptive_acceptance = adaptive_sampler.adaptive_sampling(
n_samples=2000, adapt_every=200, verbose=False
)
adaptive_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"自适应拒绝采样 - 接受率: {adaptive_acceptance:.4f}, 时间: {adaptive_time:.4f}s")
# 方法3: 分层拒绝采样
# 定义三个层和对应的提议分布
domains = [(-10, -2), (-2, 2), (2, 10)]
proposal_funcs = []
for a, b in domains:
mean = (a + b) / 2
std = (b - a) / 4
proposal_funcs.append({
'pdf': lambda x, mean=mean, std=std: stats.norm.pdf(x, mean, std),
'rv': lambda mean=mean, std=std: np.random.normal(mean, std)
})
start_time = time.time()
stratified_samples, layer_acceptance = stratified_rejection_sampling(
target_pdf, domains, proposal_funcs, n_samples=2000
)
stratified_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"分层拒绝采样 - 平均接受率: {np.mean(layer_acceptance):.4f}, 时间: {stratified_time:.4f}s")
print(f" 各层接受率: {layer_acceptance}")
# 方法4: 混合提议分布拒绝采样
proposal_components = [
{'pdf': lambda x: stats.norm.pdf(x, -3, 1), 'rv': lambda: np.random.normal(-3, 1), 'weight': 0.3},
{'pdf': lambda x: stats.norm.pdf(x, 0, 1.5), 'rv': lambda: np.random.normal(0, 1.5), 'weight': 0.4},
{'pdf': lambda x: stats.norm.pdf(x, 3, 1), 'rv': lambda: np.random.normal(3, 1), 'weight': 0.3},
]
mixture_sampler = MixtureProposalSampler(target_pdf, proposal_components)
start_time = time.time()
mixture_samples, mixture_acceptance = mixture_sampler.sample(n_samples=2000)
mixture_time = time.time() - start_time
print(f"混合提议分布 - 接受率: {mixture_acceptance:.4f}, 时间: {mixture_time:.4f}s")
# 可视化结果
fig, axes = plt.subplots(2, 3, figsize=(15, 10))
# 绘制目标分布
x_vals = np.linspace(-10, 10, 1000)
target_vals = target_pdf(x_vals)
# 子图1: 基础拒绝采样
axes[0, 0].hist(basic_samples, bins=50, density=True, alpha=0.6, color='blue', label='采样分布')
axes[0, 0].plot(x_vals, target_vals, 'r-', linewidth=2, label='目标分布')
axes[0, 0].set_title(f'基础拒绝采样\n接受率: {basic_acceptance:.4f}')
axes[0, 0].legend()
axes[0, 0].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 子图2: 自适应拒绝采样
axes[0, 1].hist(adaptive_samples, bins=50, density=True, alpha=0.6, color='green', label='采样分布')
axes[0, 1].plot(x_vals, target_vals, 'r-', linewidth=2, label='目标分布')
axes[0, 1].set_title(f'自适应拒绝采样\n接受率: {adaptive_acceptance:.4f}')
axes[0, 1].legend()
axes[0, 1].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 子图3: 分层拒绝采样
axes[0, 2].hist(stratified_samples, bins=50, density=True, alpha=0.6, color='orange', label='采样分布')
axes[0, 2].plot(x_vals, target_vals, 'r-', linewidth=2, label='目标分布')
axes[0, 2].set_title(f'分层拒绝采样\n平均接受率: {np.mean(layer_acceptance):.4f}')
axes[0, 2].legend()
axes[0, 2].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 子图4: 混合提议分布
axes[1, 0].hist(mixture_samples, bins=50, density=True, alpha=0.6, color='purple', label='采样分布')
axes[1, 0].plot(x_vals, target_vals, 'r-', linewidth=2, label='目标分布')
axes[1, 0].set_title(f'混合提议分布\n接受率: {mixture_acceptance:.4f}')
axes[1, 0].legend()
axes[1, 0].grid(True, alpha=0.3)
# 子图5: 接受率比较
methods = ['基础', '自适应', '分层', '混合']
acceptances = [basic_acceptance, adaptive_acceptance, np.mean(layer_acceptance), mixture_acceptance]
times = [basic_time, adaptive_time, stratified_time, mixture_time]
x_pos = np.arange(len(methods))
axes[1, 1].bar(x_pos, acceptances, color=['blue', 'green', 'orange', 'purple'])
axes[1, 1].set_xticks(x_pos)
axes[1, 1].set_xticklabels(methods)
axes[1, 1].set_ylabel('接受率')
axes[1, 1].set_title('各方法接受率比较')
axes[1, 1].grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
# 在柱状图上显示数值
for i, v in enumerate(acceptances):
axes[1, 1].text(i, v + 0.01, f'{v:.4f}', ha='center')
# 子图6: 时间比较
axes[1, 2].bar(x_pos, times, color=['blue', 'green', 'orange', 'purple'])
axes[1, 2].set_xticks(x_pos)
axes[1, 2].set_xticklabels(methods)
axes[1, 2].set_ylabel('时间 (秒)')
axes[1, 2].set_title('各方法时间消耗比较')
axes[1, 2].grid(True, alpha=0.3, axis='y')
# 在柱状图上显示数值
for i, v in enumerate(times):
axes[1, 2].text(i, v + 0.01, f'{v:.4f}', ha='center')
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
# 返回结果供进一步分析
results = {
'basic': {'samples': basic_samples, 'acceptance': basic_acceptance, 'time': basic_time},
'adaptive': {'samples': adaptive_samples, 'acceptance': adaptive_acceptance, 'time': adaptive_time},
'stratified': {'samples': stratified_samples, 'acceptance': np.mean(layer_acceptance), 'time': stratified_time},
'mixture': {'samples': mixture_samples, 'acceptance': mixture_acceptance, 'time': mixture_time}
}
return results
# ==================== 测试和演示 ====================
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("拒绝采样算法优化与微调模拟")
print("=" * 60)
# 定义目标分布:混合高斯分布
def target_pdf(x):
# 两个高斯分布的混合
return 0.7 * stats.norm.pdf(x, -2, 1) + 0.3 * stats.norm.pdf(x, 3, 1.5)
# 比较不同采样方法
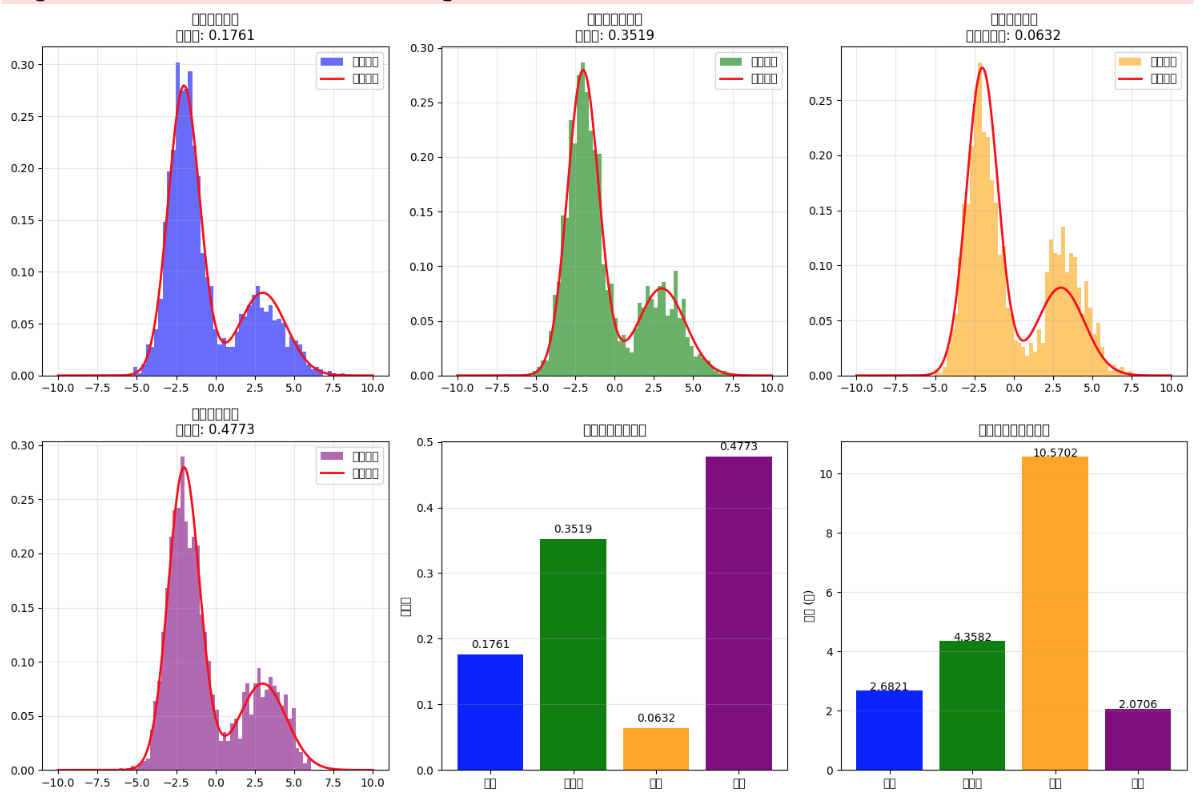
results = compare_sampling_methods(target_pdf)python模拟输出如下所示
虽然,由于中文字体原因,图例不是很清晰,但依然能看出代码较好的拟合了双峰高斯分布。
拒绝采样算法优化与微调模拟
============================================================
目标分布: 混合高斯分布
============================================================
基础拒绝采样 - 使用的M值: 5.7572
基础拒绝采样 - 接受率: 0.1761, 时间: 2.6821s
自适应拒绝采样 - 接受率: 0.3519, 时间: 4.3582s
分层拒绝采样 - 平均接受率: 0.0632, 时间: 10.5702s
各层接受率: [0.030725999631472267, 0.07261049423035053, 0.0863925282137761]
混合提议分布 - 接受率: 0.4773, 时间: 2.0706s
2.2 拒绝采样优化模拟总结
对于简单分布,基础拒绝采样通常足够;对于复杂多峰分布,自适应或分层方法更有效;混合提议分布可以更好地匹配目标分布的形状。
对于优化和模拟拒绝采样,需要注意以下几点:
-
选择合适的提议分布以匹配目标分布
-
找到尽可能小的M值以提高接受率
-
对于不同区域使用不同的提议分布(分层/混合)