在机器人学领域,逆运动学(Inverse Kinematics, IK)是一个经典而又挑战性的问题。想象一下,你告诉机械臂末端要到达某个特定位置和姿态,机械臂如何知道每个关节应该转动多少角度?这就是逆运动学要解决的问题。
与正运动学(已知关节角求末端位姿)相比,逆运动学更像是解一道复杂的几何代数方程。今天,我将深入探讨六轴机械臂的逆运动学实现,并提供完整的Python代码。
一、为什么逆运动学如此重要?
1.1 实际应用场景
-
路径规划:机械臂需要从A点移动到B点
-
目标抓取:末端执行器需要以特定姿态抓取物体
-
轨迹跟踪:沿预定轨迹移动
-
避障规划:绕过障碍物到达目标位置
1.2 技术挑战
-
多解性:同一末端位姿可能对应多个关节角组合
-
奇异位置:某些位置会导致自由度丢失
-
计算复杂性:需要高效稳定的算法
-
实时性要求:工业应用需要毫秒级响应
二、我的六轴机械臂模型

2.1 D-H参数定义
| 连杆 i | 关节角 qᵢ(°) | 连杆偏移 dᵢ(mm) | 连杆长度 aᵢ(mm) | 连杆扭转角 αᵢ(°) | 关节角偏移 offset(°) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | q₁(变量) | 540 | 0 | 90 | 90 |
| 2 | q₂(变量) | 0 | -900 | 0 | -90 |
| 3 | q₃(变量) | 0 | -900 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | q₄(变量) | 500 | 0 | 90 | -90 |
| 5 | q₅(变量) | 345 | 0 | -90 | 0 |
| 6 | q₆(变量) | 175 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
2.2 机械臂特点
-
结构:典型的6自由度串联机械臂
-
工作空间:半径约2000mm的球形区域
-
关节类型:前三个关节确定位置,后三个关节确定姿态
三、逆运动学求解原理
3.1 整体思路:分而治之
我将逆运动学问题分解为两个子问题:
-
位置求解(关节1-3):确定腕部中心位置
-
姿态求解(关节4-6):确定末端姿态
3.2 腕部分离技术
关键洞察:最后三个关节轴相交于一点(腕部中心)。这意味着:
-
腕部中心位置仅取决于前三个关节
-
末端姿态由后三个关节调整
python
# 腕部中心计算
wrist_center = 末端位置 - d[6] * 末端Z轴方向四、逐步求解算法
4.1 第一步:求解关节1 (θ₁)
关节1决定机械臂在水平面上的旋转:
python
# 几何关系求解
wx, wy, wz = wrist_center
q1_1 = atan2(wy, wx) - atan2(d[3], sqrt(wx² + wy² - d[3]²))
q1_2 = atan2(wy, wx) - atan2(d[3], -sqrt(wx² + wy² - d[3]²))物理意义:第一个关节有两个可能方向,对应机械臂的"左手"和"右手"构型。
4.2 第二步:求解关节3 (θ₃)
使用余弦定理求解肘关节:
python
# 余弦定理
A = -2*a₁*a₂
B = 2*a₂*d₃
D = (距离公式)/2
cos_θ₃ = (D - a₁*d₃) / (a₁² + d₃² + 2*a₁*d₃*cos(θ₁))肘部配置:θ₃有两个解,对应"肘部向上"和"肘部向下"。
4.3 第三步:求解关节2 (θ₂)
基于已知的θ₁和θ₃:
python
k₁ = a₁ + a₂*cos(θ₃) + d₃*sin(θ₃)
k₂ = a₂*sin(θ₃) - d₃*cos(θ₃)
θ₂ = atan2(s, r) - atan2(k₂, k₁)4.4 第四步:求解关节4-6 (θ₄, θ₅, θ₆)
前三个关节确定后,我们计算剩余旋转:
python
# 计算前三个关节的变换
T₀₃ = T₁ @ T₂ @ T₃
# 计算需要由后三个关节完成的旋转
R₃₆ = R₀₃⁻¹ @ R_target
# 从R₃₆提取ZYZ欧拉角(对应关节4-6)
# 注意:这里假设关节4、5、6的旋转轴分别为Z、Y、Z欧拉角提取:
python
if |R₃₆[2,2]| < 1: # 非奇异情况
θ₅ = acos(R₃₆[2,2])
θ₄ = atan2(R₃₆[1,2]/sin(θ₅), R₃₆[0,2]/sin(θ₅))
θ₆ = atan2(R₃₆[2,1]/sin(θ₅), -R₃₆[2,0]/sin(θ₅))
else: # 奇异位置(θ₅ = 0 或 π)
# 此时θ₄和θ₆不能唯一确定
θ₅ = 0 if R₃₆[2,2] > 0 else π
θ₄ = 0 # 选择任意值
θ₆ = atan2(-R₃₆[0,1], R₃₆[0,0])五、代码实现详解
5.1 核心逆运动学函数
python
def your_arm_inverse_kinematics(T_target, q_initial=None):
"""
六轴机械臂逆运动学求解(解析法)
参数:
T_target: 4x4齐次变换矩阵,目标末端位姿
q_initial: 初始关节角(弧度),用于选择最接近的解
返回:
solutions: 所有可能的关节角解列表
"""
# 完整的求解流程
# 1. 提取目标位姿
# 2. 计算腕部中心
# 3. 求解θ₁(两个解)
# 4. 对每个θ₁,求解θ₃(两个解)
# 5. 对每个(θ₁,θ₃),求解θ₂
# 6. 求解θ₄,θ₅,θ₆
# 7. 处理奇异位置
# 8. 返回所有有效解5.2 多解处理策略
对于六轴机械臂,最多可能有8个数学解:
-
关节1:2个解(左/右)
-
关节3:2个解(肘上/肘下)
-
关节5:2个解(腕部翻转)
python
# 实际实现中需要考虑:
# 1. 关节限位:排除超出物理限制的解
# 2. 奇异位置:特殊处理
# 3. 连续性:选择最接近当前姿态的解5.3 验证机制
python
def inverse_kinematics_verification(T_target, q_initial=None):
"""
逆运动学求解并验证
验证步骤:
1. 求解逆运动学得到关节角
2. 使用正运动学计算实际位姿
3. 比较目标位姿和实际位姿
4. 计算位置误差和姿态误差
5. 选择误差最小的解
"""六、算法性能优化
6.1 数值稳定性处理
python
# 1. 避免除零
if abs(denominator) < 1e-10:
# 处理奇异情况
# 2. 浮点数精度处理
if abs(value) < 1e-10:
value = 0
# 3. 角度归一化
angle = (angle + π) % (2*π) - π6.2 实时性考虑
python
# 缓存常用计算结果
cos_cache = {}
sin_cache = {}
def fast_cos(theta):
if theta not in cos_cache:
cos_cache[theta] = math.cos(theta)
return cos_cache[theta]七、完整演示程序
我的程序提供三种模式:
7.1 模式一:正运动学演示
输入:关节角度
输出:机械臂位姿 + 3D可视化7.2 模式二:逆运动学演示
输入:目标位姿(位置+欧拉角)
输出:关节角度 + 验证误差7.3 模式三:完整验证
输入:一组关节角度
过程:
1. 正运动学计算目标位姿
2. 逆运动学求解关节角度
3. 比较原始解和求解结果
输出:验证误差 + 可视化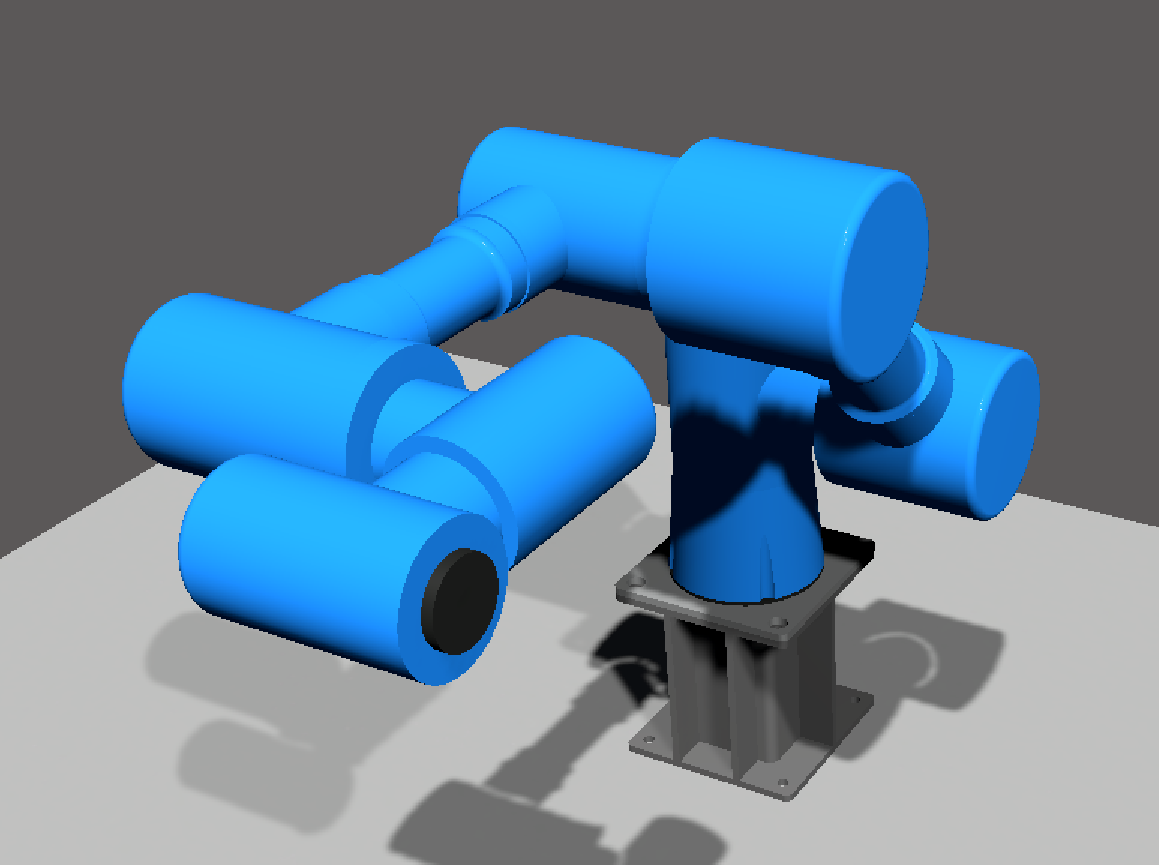
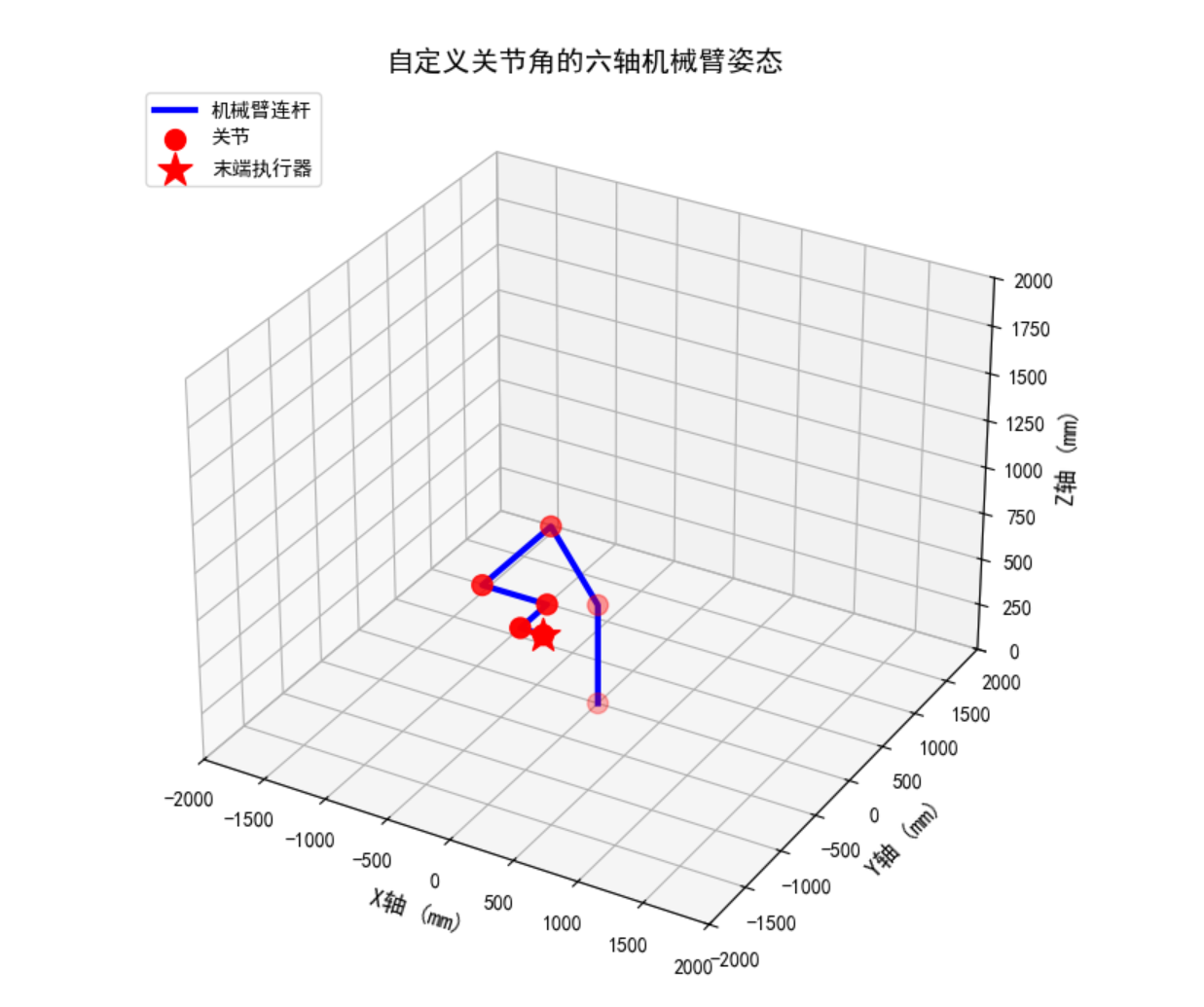
附件(完整代码):
python
"""
六轴机械臂逆运动学
基于标准D-H模型,单位:mm(长度)、度(角度)
核心功能:输入末端位姿(齐次变换矩阵),输出所有可行且符合限位的关节角解
"""
import math
import numpy as np
# ========================== 机械臂D-H参数配置 ==========================
# 连杆参数(mm)
d1 = 540.0 # 关节1的连杆偏移
a2 = -900.0 # 关节2的连杆长度
a3 = -900.0 # 关节3的连杆长度
d4 = 500.0 # 关节4的连杆偏移
d5 = 345.0 # 关节5的连杆偏移
d6 = 175.0 # 关节6的连杆偏移
# 关节角偏移(度):补偿机械臂实际安装的角度偏差
theta_offset = [90.0, -90.0, 0.0, -90.0, 0.0, 0.0]
# ========================== 关节角度限位配置(度)==========================
# 格式:[q1_min, q1_max, q2_min, q2_max, ..., q6_min, q6_max]
JOINT_LIMITS_DEG = [
-180.0, 180.0, # q1:基座旋转
-90.0, 90.0, # q2:肩部俯仰
-150.0, 150.0, # q3:肘部俯仰
-180.0, 180.0, # q4:腕部旋转
-120.0, 120.0, # q5:腕部俯仰
-180.0, 360.0 # q6:末端旋转
]
# 常量定义
PI = math.pi
DEG_TO_RAD = PI / 180.0 # 角度转弧度
RAD_TO_DEG = 180.0 / PI # 弧度转角度
ZERO_THRESH = 1e-10 # 数值计算容差(避免除以0或根号负数)
# ========================== 逆运动学核心类 ==========================
class SixAxisIK:
def __init__(self):
"""初始化:存储逆解结果"""
self.solutions_rad = [] # 关节角解(弧度)
self.solutions_deg = [] # 关节角解(度)
self.valid_solutions_deg = [] # 符合限位的关节角解(度)
self.valid_solutions_normalized = [] # 归一化后的有效解(度)
# 解析关节限位为字典,便于调用
self.joint_limits = {
i: (JOINT_LIMITS_DEG[2 * i], JOINT_LIMITS_DEG[2 * i + 1])
for i in range(6)
}
@staticmethod
def sign(x):
"""符号函数:处理数值正负"""
return 1 if x > 0 else (-1 if x < 0 else 0)
@staticmethod
def clamp_angle_rad(theta):
"""将弧度角限制在[-2π, 2π]范围"""
while theta < -2 * PI or theta > 2 * PI:
theta -= SixAxisIK.sign(theta) * 2 * PI
return theta
@staticmethod
def clamp_angle_deg(theta):
"""将角度制角限制在[-360°, 360°]范围"""
while theta < -360.0 or theta > 360.0:
theta -= SixAxisIK.sign(theta) * 360.0
return theta
@staticmethod
def normalize_angle_deg(theta):
"""
将角度归一化到[-180°, 180°]范围(机械臂关节旋转的等效角度)
:param theta: 原始角度(度)
:return: 归一化后的角度(度)
"""
theta = theta % 360.0
if theta > 180.0:
theta -= 360.0
return theta
def check_joint_limit(self, joint_angle_deg, joint_idx):
"""
检查单个关节角是否符合限位(考虑角度循环特性)
:param joint_angle_deg: 关节角(度)
:param joint_idx: 关节索引(0-5对应q1-q6)
:return: (是否符合限位, 归一化后的角度)
"""
min_deg, max_deg = self.joint_limits[joint_idx]
# 归一化到[-180°, 180°],体现关节的实际旋转角度
norm_angle = self.normalize_angle_deg(joint_angle_deg)
# 特殊处理q6的限位(-180°~360°),不做归一化
if joint_idx == 5:
return min_deg <= joint_angle_deg <= max_deg, joint_angle_deg
else:
return min_deg <= norm_angle <= max_deg, norm_angle
def filter_solutions_by_limit(self):
"""筛选符合关节限位的解,并保存归一化后的角度"""
self.valid_solutions_deg = []
self.valid_solutions_normalized = []
for sol in self.solutions_deg:
is_valid = True
norm_sol = []
for idx, angle in enumerate(sol):
valid, norm_angle = self.check_joint_limit(angle, idx)
norm_sol.append(norm_angle)
if not valid:
is_valid = False
break
if is_valid:
self.valid_solutions_deg.append(sol)
self.valid_solutions_normalized.append(norm_sol)
return self.valid_solutions_deg, self.valid_solutions_normalized
@staticmethod
def euler_to_trans(position, euler_zyx):
"""
由末端位置和欧拉角生成齐次变换矩阵
:param position: 末端位置 [x, y, z] (mm)
:param euler_zyx: 欧拉角 [α, β, γ](Z-Y-X顺序,度)
:return: 4x4齐次变换矩阵
"""
x, y, z = position
alpha, beta, gamma = [ang * DEG_TO_RAD for ang in euler_zyx]
# 绕Z轴旋转矩阵
Rz = np.array([
[math.cos(alpha), -math.sin(alpha), 0],
[math.sin(alpha), math.cos(alpha), 0],
[0, 0, 1]
])
# 绕Y轴旋转矩阵
Ry = np.array([
[math.cos(beta), 0, math.sin(beta)],
[0, 1, 0],
[-math.sin(beta), 0, math.cos(beta)]
])
# 绕X轴旋转矩阵
Rx = np.array([
[1, 0, 0],
[0, math.cos(gamma), -math.sin(gamma)],
[0, math.sin(gamma), math.cos(gamma)]
])
# 组合旋转矩阵:R = Rz * Ry * Rx
R = np.dot(Rz, np.dot(Ry, Rx))
# 构造齐次变换矩阵
T = np.eye(4)
T[:3, :3] = R
T[:3, 3] = [x, y, z]
return T
def solve(self, T):
"""
逆运动学核心求解:输入末端齐次矩阵,计算所有可行关节角
:param T: 4x4末端齐次变换矩阵
:return: 所有解(度),符合限位的解(度),归一化后的有效解(度)
"""
# 清空历史解
self.solutions_rad = []
self.solutions_deg = []
self.valid_solutions_deg = []
self.valid_solutions_normalized = []
# 提取齐次矩阵的旋转轴和位置向量
n = T[:, 0] # x轴单位向量
o = T[:, 1] # y轴单位向量
a = T[:, 2] # z轴单位向量
p = T[:, 3] # 位置向量
# ========================== 步骤1:求解关节1(θ1) ==========================
m = d6 * a[1] - p[1]
n_val = d6 * a[0] - p[0]
r = m ** 2 + n_val ** 2 - d4 ** 2
theta1_candidates = []
if r >= -ZERO_THRESH:
r = max(r, 0)
sqrt_r = math.sqrt(r)
theta1_1 = math.atan2(m, n_val) - math.atan2(d4, sqrt_r)
theta1_2 = math.atan2(m, n_val) - math.atan2(d4, -sqrt_r)
theta1_candidates = [theta1_1, theta1_2]
else:
theta1 = math.atan2(m, n_val)
theta1_candidates = [theta1]
# ========================== 步骤2:求解关节5(θ5) ==========================
theta5_candidates = []
for theta1 in theta1_candidates:
temp = a[0] * math.sin(theta1) - a[1] * math.cos(theta1)
temp = np.clip(temp, -1, 1)
theta5_1 = math.acos(temp)
theta5_2 = -math.acos(temp)
theta5_candidates.append([theta1, theta5_1])
theta5_candidates.append([theta1, theta5_2])
# ========================== 步骤3:求解关节6(θ6) ==========================
theta6_candidates = []
for theta1, theta5 in theta5_candidates:
m = n[0] * math.sin(theta1) - n[1] * math.cos(theta1)
n_val = o[0] * math.sin(theta1) - o[1] * math.cos(theta1)
theta6 = math.atan2(m, n_val) - math.atan2(math.sin(theta5), 0)
theta6_candidates.append([theta1, theta5, theta6])
# ========================== 步骤4:求解关节3(θ3) ==========================
theta3_candidates = []
for theta1, theta5, theta6 in theta6_candidates:
c1 = math.cos(theta1)
s1 = math.sin(theta1)
c6 = math.cos(theta6)
s6 = math.sin(theta6)
m = d5 * (s6 * (n[0] * c1 + n[1] * s1) + c6 * (o[0] * c1 + o[1] * s1)) - d6 * (a[0] * c1 + a[1] * s1) + p[
0] * c1 + p[1] * s1
n_val = p[2] - d1 - a[2] * d6 + d5 * (o[2] * c6 + n[2] * s6)
m2_n2 = m ** 2 + n_val ** 2
denominator = 2 * a2 * a3
if abs(denominator) < ZERO_THRESH:
continue
cos_theta3 = (m2_n2 - a2 ** 2 - a3 ** 2) / denominator
cos_theta3 = np.clip(cos_theta3, -1, 1)
theta3_1 = math.acos(cos_theta3)
theta3_2 = -math.acos(cos_theta3)
theta3_candidates.append([theta1, theta5, theta6, theta3_1])
theta3_candidates.append([theta1, theta5, theta6, theta3_2])
# ========================== 步骤5:求解关节2(θ2) ==========================
theta2_candidates = []
for theta1, theta5, theta6, theta3 in theta3_candidates:
c1 = math.cos(theta1)
s1 = math.sin(theta1)
c6 = math.cos(theta6)
s6 = math.sin(theta6)
c3 = math.cos(theta3)
s3 = math.sin(theta3)
m = d5 * (s6 * (n[0] * c1 + n[1] * s1) + c6 * (o[0] * c1 + o[1] * s1)) - d6 * (a[0] * c1 + a[1] * s1) + p[
0] * c1 + p[1] * s1
n_val = p[2] - d1 - a[2] * d6 + d5 * (o[2] * c6 + n[2] * s6)
denominator = a2 ** 2 + a3 ** 2 + 2 * a2 * a3 * c3
if abs(denominator) < ZERO_THRESH:
continue
s2 = ((a3 * c3 + a2) * n_val - a3 * s3 * m) / denominator
c2 = (m + a3 * s3 * s2) / (a3 * c3 + a2)
theta2 = math.atan2(s2, c2)
theta2_candidates.append([theta1, theta2, theta3, theta5, theta6])
# ========================== 步骤6:求解关节4(θ4) ==========================
for theta1, theta2, theta3, theta5, theta6 in theta2_candidates:
c1 = math.cos(theta1)
s1 = math.sin(theta1)
c6 = math.cos(theta6)
s6 = math.sin(theta6)
numerator = -s6 * (n[0] * c1 + n[1] * s1) - c6 * (o[0] * c1 + o[1] * s1)
denominator = o[2] * c6 + n[2] * s6
if abs(denominator) < ZERO_THRESH:
continue
theta4 = math.atan2(numerator, denominator) - theta2 - theta3
self.solutions_rad.append([theta1, theta2, theta3, theta4, theta5, theta6])
# ========================== 结果处理 ==========================
for sol_rad in self.solutions_rad:
sol_deg = []
for i in range(6):
theta_rad = sol_rad[i] - theta_offset[i] * DEG_TO_RAD
theta_deg = self.clamp_angle_deg(theta_rad * RAD_TO_DEG)
sol_deg.append(theta_deg)
self.solutions_deg.append(sol_deg)
# ========================== 筛选符合限位的解 ==========================
self.filter_solutions_by_limit()
return self.solutions_deg, self.valid_solutions_deg, self.valid_solutions_normalized
# ========================== 测试代码 ==========================
if __name__ == "__main__":
ik_solver = SixAxisIK()
# 定义末端位姿
target_pos = [675.0, -1800.0, 1100.0]
target_euler = [0.0, 90.0, 0.0]
# 生成齐次变换矩阵
T_target = ik_solver.euler_to_trans(target_pos, target_euler)
print("=" * 60)
print("目标末端齐次变换矩阵:")
print(np.round(T_target, 3))
# 求解逆运动学
all_solutions, valid_solutions, valid_normalized = ik_solver.solve(T_target)
# 输出所有解
print("=" * 60)
print(f"逆运动学总解数:{len(all_solutions)} 组")
if len(all_solutions) > 0:
print("所有解(单位:度):")
for i, sol in enumerate(all_solutions):
print(
f"解{i + 1}: q1={sol[0]:6.2f}° q2={sol[1]:6.2f}° q3={sol[2]:6.2f}° q4={sol[3]:6.2f}° q5={sol[4]:6.2f}° q6={sol[5]:6.2f}°")
# 输出有效解(含归一化角度)
print("=" * 60)
print(f"符合关节限位的解数:{len(valid_solutions)} 组")
if len(valid_solutions) > 0:
print("有效解(原始角度/归一化角度,单位:度):")
for i, (sol, norm_sol) in enumerate(zip(valid_solutions, valid_normalized)):
print(f"解{i + 1}:")
print(
f" 原始:q1={sol[0]:6.2f}° q2={sol[1]:6.2f}° q3={sol[2]:6.2f}° q4={sol[3]:6.2f}° q5={sol[4]:6.2f}° q6={sol[5]:6.2f}°")
print(
f" 归一:q1={norm_sol[0]:6.2f}° q2={norm_sol[1]:6.2f}° q3={norm_sol[2]:6.2f}° q4={norm_sol[3]:6.2f}° q5={norm_sol[4]:6.2f}° q6={norm_sol[5]:6.2f}°")
else:
print("警告:无符合关节限位的解!")
python
# 测试末端位姿
target_pos = [675.0, -1800.0, 1100.0]
target_euler = [0.0, 90.0, 0.0]运行实例: