hello~这里是维构lbs智能定位,如果有项目需求和技术交流欢迎来私信我们~点击文章最下方可获取免费获取技术文档和解决方案
室内外融合定位的核心目标是打破"室外卫星定位精准但室内失效,室内定位技术覆盖有限但无法延伸至室外"的割裂困境,通过多技术协同与智能算法,实现"室外高精度盯防、室内精准管控、过渡区域无缝衔接"的全场景定位。在化工、矿山、港口、大型厂区等工业场景中,"北斗(含RTK增强)+ UWB"是当前最成熟、应用最广泛的融合方案,可实现厘米级到分米级的全场景精度覆盖。本文将从系统架构、核心技术原理、部署实施流程、精度保障机制、典型工业应用及实测指标等方面展开详细解析。
一、室内外融合定位的系统核心架构
室内外融合定位系统采用"终端感知-网络传输-平台管控"三层架构,各层级深度协同,确保定位数据的实时性、准确性与连续性。其中室外以北斗卫星星座为核心,室内以UWB基站网络为支撑,通过融合算法实现技术无缝衔接。
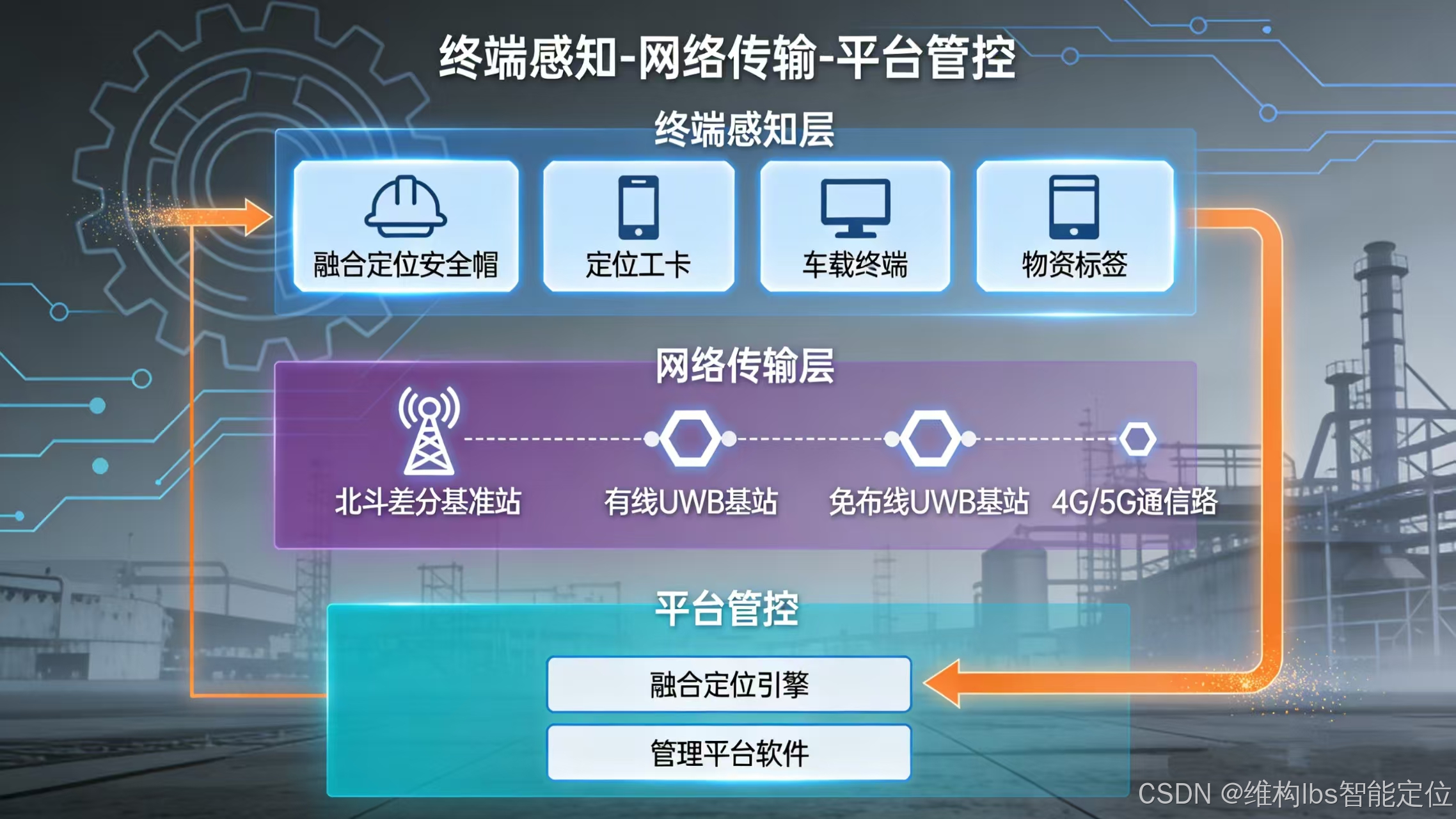
1 . 终端层:多模融合定位终端(核心感知单元)
终端是实现室内外切换的核心载体,采用模块化设计,集成北斗(单频/双频)、UWB、IMU(惯性测量单元)等多种定位模块,同时具备通信、报警、姿态感知等扩展功能,适配工业场景的复杂环境要求。常见形态包括:
(1)融合定位安全帽
一体化设计,内置北斗+UWB+IMU模块,支持SOS一键报警、跌倒检测、语音提示,符合本安防爆标准,适用于化工、矿山等高危场景。
(2)定位工卡/手环
体积小巧,便于携带,支持北斗米级定位与UWB亚米级定位,具备静止检测、门禁联动功能,适用于普通厂区人员管控。
(3)车载定位终端
带强磁吸附与防拆报警,可直接车载取电,支持北斗RTK厘米级定位与UWB室内定位,适配厂区工程车辆、危险品运输车辆跟踪。
(4)物资定位标签
低功耗设计,续航可达3-5年,支持北斗室外定位与UWB室内存在性检测/精准定位,用于设备、物料的全生命周期追踪。
终端核心功能:自动识别定位场景(通过卫星信号强度、UWB基站信号感知),实现北斗与UWB技术的毫秒级切换;内置IMU模块,在过渡区域或信号遮挡瞬间,通过惯性导航补盲,避免定位断点。
2.网络层:定位基站+通信网络(数据传输桥梁)
网络层分为室外北斗增强网络与室内UWB基站网络,搭配多元化通信链路,确保定位数据实时上传。
(1)室外北斗增强网络
核心设备为北斗差分基准站,部署于室外空旷区域(如厂区楼顶、管廊制高点),单台基准站覆盖半径可达10公里。其核心作用是:接收北斗卫星信号,计算卫星轨道误差、电离层/对流层延迟等误差数据,生成修正信息并实时播发,为室外终端提供厘米级定位支撑。基准站支持有线(光纤/网线)或无线(4G/5G)数据传输,可接入本地服务器或云平台。
(2)室内UWB基站网络
UWB基站是室内定位的核心,通过接收终端发送的纳秒级窄脉冲信号,实现测距与定位。根据部署方式分为两种类型:
有线UWB基站:支持POE供电(一根网线实现供电+通信),定位精度30-50cm,适用于大型厂房、地下管廊等固定区域,数据通过交换机、光纤传输至服务器,稳定性强。
免布线UWB基站:电池供电(续航3-5年),无需现场布线,通信距离大于100米,数据通过终端的4G/5G模块或本地通信网关上传,安装便捷,适合老旧厂区改造、临时施工区域等场景。
基站部署原则:二维定位区域至少部署3台基站,确保终端在任意位置能接收3台及以上基站信号;狭长区域(如隧道、走廊)部署2台基站即可实现一维定位;存在性检测区域仅需部署1台基站。
(3)通信网络
支持4G/5G、Wi-Fi、LoRa、光纤等多种通信方式:室外终端通过4G/5G接收基准站修正数据并上传定位信息;室内UWB基站数据可通过有线网络或网关传输;涉密场景采用本地通信网关,避免数据接入公网,保障信息安全。
3.平台层:融合定位引擎+管理平台(数据处理与管控核心)
平台层是系统的"大脑",负责定位数据的融合计算、可视化展示、智能分析与报警联动,核心包括融合定位引擎与管理平台软件。
(1)融合定位引擎
采用自主研发的场景自适应算法,接收终端上传的北斗伪距数据、UWB测距数据、IMU惯性数据,通过卡尔曼滤波、最小二乘法等算法融合解算,输出统一坐标系(如WGS-84坐标系、本地平面坐标系)下的精准位置,确保切换过程轨迹平滑无跳变。
import numpy as np
import math
from typing import Tuple, List, Dict
# 常量定义
WGS84_A = 6378137.0 # WGS84椭球长半轴
WGS84_E2 = 0.00669437999014 # WGS84第一偏心率平方
LOCAL_ORIGIN = np.array([30.0, 120.0, 50.0]) # 本地平面坐标系原点(纬度, 经度, 高度)
class MultiSensorFusion:
def __init__(self, coordinate_system: str = "WGS84"):
"""
多传感器融合定位初始化
:param coordinate_system: 输出坐标系,支持"WGS84"或"LOCAL"
"""
self.coordinate_system = coordinate_system
# 卡尔曼滤波器参数初始化
self.state = np.array([0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]) # [x, y, z, vx, vy, vz]
self.P = np.eye(6) * 10.0 # 状态协方差矩阵
self.Q = np.eye(6) * 0.1 # 过程噪声协方差
self.R = np.diag([1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 0.5, 0.5, 0.5]) # 观测噪声协方差
# 时间戳记录
self.last_timestamp = None
self.smoothed_trajectory = []
def wgs84_to_ecef(self, lat: float, lon: float, alt: float) -> np.ndarray:
"""
WGS84经纬度高度转ECEF地心地固坐标系
:param lat: 纬度(度)
:param lon: 经度(度)
:param alt: 高度(米)
:return: ECEF坐标[x, y, z]
"""
lat_rad = math.radians(lat)
lon_rad = math.radians(lon)
N = WGS84_A / math.sqrt(1 - WGS84_E2 * math.sin(lat_rad)**2)
x = (N + alt) * math.cos(lat_rad) * math.cos(lon_rad)
y = (N + alt) * math.cos(lat_rad) * math.sin(lon_rad)
z = (N * (1 - WGS84_E2) + alt) * math.sin(lat_rad)
return np.array([x, y, z])
def ecef_to_local(self, ecef: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
"""
ECEF转本地平面坐标系(东北天ENU)
:param ecef: ECEF坐标
:return: 本地平面坐标[x, y, z]
"""
# 计算原点的ECEF坐标
origin_ecef = self.wgs84_to_ecef(LOCAL_ORIGIN[0], LOCAL_ORIGIN[1], LOCAL_ORIGIN[2])
# 计算旋转矩阵
lat0_rad = math.radians(LOCAL_ORIGIN[0])
lon0_rad = math.radians(LOCAL_ORIGIN[1])
R = np.array([
[-math.sin(lon0_rad), math.cos(lon0_rad), 0],
[-math.sin(lat0_rad)*math.cos(lon0_rad), -math.sin(lat0_rad)*math.sin(lon0_rad), math.cos(lat0_rad)],
[math.cos(lat0_rad)*math.cos(lon0_rad), math.cos(lat0_rad)*math.sin(lon0_rad), math.sin(lat0_rad)]
])
# 计算本地坐标
delta_ecef = ecef - origin_ecef
local_enu = R @ delta_ecef
return local_enu
def preprocess_data(self, beidou_data: Dict, uwb_data: Dict, imu_data: Dict) -> Tuple[np.ndarray, np.ndarray, np.ndarray]:
"""
数据预处理:异常值过滤、格式标准化
:param beidou_data: 北斗伪距数据 {timestamp, lat, lon, alt, accuracy}
:param uwb_data: UWB测距数据 {timestamp, distance, anchor_positions, accuracy}
:param imu_data: IMU惯性数据 {timestamp, acc_x, acc_y, acc_z, gyro_x, gyro_y, gyro_z}
:return: 标准化后的北斗、UWB、IMU数据数组
"""
# 北斗数据标准化
beidou_pos = np.array([beidou_data['lat'], beidou_data['lon'], beidou_data['alt']])
beidou_ecef = self.wgs84_to_ecef(*beidou_pos)
# UWB数据标准化(基于锚点位置最小二乘解算)
anchor_positions = np.array(uwb_data['anchor_positions'])
distances = np.array(uwb_data['distance'])
uwb_pos = self.least_squares_uwb(anchor_positions, distances)
# IMU数据标准化
imu_acc = np.array([imu_data['acc_x'], imu_data['acc_y'], imu_data['acc_z']])
imu_gyro = np.array([imu_data['gyro_x'], imu_data['gyro_y'], imu_data['gyro_z']])
imu_data_arr = np.hstack([imu_acc, imu_gyro])
return beidou_ecef, uwb_pos, imu_data_arr
def least_squares_uwb(self, anchors: np.ndarray, distances: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
"""
最小二乘法解算UWB位置
:param anchors: 锚点位置数组 Nx3
:param distances: 到各锚点的距离数组 N
:return: 解算后的位置 [x, y, z]
"""
n = anchors.shape[0]
A = np.zeros((n-1, 3))
b = np.zeros(n-1)
for i in range(n-1):
A[i] = 2 * (anchors[i] - anchors[-1])
b[i] = distances[-1]**2 - distances[i]**2 - np.sum(anchors[-1]**2) + np.sum(anchors[i]**2)
# 最小二乘求解
pos, residuals, rank, s = np.linalg.lstsq(A, b, rcond=None)
return pos
def kalman_predict(self, dt: float, imu_acc: np.ndarray):
"""
卡尔曼滤波预测步骤(基于IMU数据)
:param dt: 时间间隔
:param imu_acc: IMU加速度 [ax, ay, az]
"""
# 状态转移矩阵
F = np.eye(6)
F[0, 3] = dt
F[1, 4] = dt
F[2, 5] = dt
# 控制矩阵
B = np.zeros((6, 3))
B[3, 0] = dt
B[4, 1] = dt
B[5, 2] = dt
# 状态预测
self.state = F @ self.state + B @ imu_acc
# 协方差预测
self.P = F @ self.P @ F.T + self.Q
def kalman_update(self, observation: np.ndarray):
"""
卡尔曼滤波更新步骤(融合北斗/UWB观测值)
:param observation: 观测值 [x, y, z, vx, vy, vz]
"""
# 观测矩阵
H = np.eye(6)
# 卡尔曼增益
S = H @ self.P @ H.T + self.R
K = self.P @ H.T @ np.linalg.inv(S)
# 状态更新
self.state = self.state + K @ (observation - H @ self.state)
# 协方差更新
I = np.eye(6)
self.P = (I - K @ H) @ self.P
def adaptive_smoothing(self, current_pos: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
"""
场景自适应平滑算法,确保轨迹无跳变
:param current_pos: 当前解算位置
:return: 平滑后的位置
"""
window_size = min(5, len(self.smoothed_trajectory))
if window_size == 0:
smoothed_pos = current_pos
else:
# 加权平均平滑,最近的点权重更高
weights = np.linspace(0.1, 1.0, window_size)
weights = weights / np.sum(weights)
recent_positions = np.array(self.smoothed_trajectory[-window_size:])
smoothed_pos = np.sum(recent_positions * weights.reshape(-1, 1), axis=0)
# 限制位置跳变幅度(自适应阈值)
max_jump = 0.5 # 最大允许跳变距离(米)
delta = np.linalg.norm(current_pos - smoothed_pos)
if delta > max_jump:
smoothed_pos = smoothed_pos + (current_pos - smoothed_pos) * max_jump / delta
self.smoothed_trajectory.append(smoothed_pos)
return smoothed_pos
def fusion_calculate(self, beidou_data: Dict, uwb_data: Dict, imu_data: Dict) -> Dict:
"""
多源数据融合解算主函数
:param beidou_data: 北斗数据 {timestamp, lat, lon, alt, accuracy}
:param uwb_data: UWB数据 {timestamp, distance, anchor_positions, accuracy}
:param imu_data: IMU数据 {timestamp, acc_x, acc_y, acc_z, gyro_x, gyro_y, gyro_z}
:return: 融合后的位置信息 {timestamp, x, y, z, coordinate_system, accuracy}
"""
# 数据预处理
beidou_ecef, uwb_pos, imu_data_arr = self.preprocess_data(beidou_data, uwb_data, imu_data)
# 计算时间间隔
current_timestamp = imu_data['timestamp']
if self.last_timestamp is None:
dt = 0.01 # 默认100Hz
else:
dt = current_timestamp - self.last_timestamp
self.last_timestamp = current_timestamp
# 卡尔曼滤波预测(IMU)
imu_acc = imu_data_arr[:3]
self.kalman_predict(dt, imu_acc)
# 构建观测值(融合北斗和UWB)
beidou_weight = 0.7 if beidou_data['accuracy'] < 5 else 0.3
uwb_weight = 0.3 if uwb_data['accuracy'] < 2 else 0.7
# 组合观测位置
obs_pos = beidou_weight * beidou_ecef + uwb_weight * uwb_pos
obs_vel = np.zeros(3) # 简化处理,实际可从IMU积分或北斗速度得到
observation = np.hstack([obs_pos, obs_vel])
# 卡尔曼滤波更新
self.kalman_update(observation)
# 获取融合后的位置
fused_pos_ecef = self.state[:3]
# 坐标转换
if self.coordinate_system == "LOCAL":
final_pos = self.ecef_to_local(fused_pos_ecef)
else: # WGS84
final_pos = self.ecef_to_wgs84(fused_pos_ecef)
# 轨迹平滑
smoothed_pos = self.adaptive_smoothing(final_pos)
# 计算融合精度
fused_accuracy = beidou_weight * beidou_data['accuracy'] + uwb_weight * uwb_data['accuracy']
return {
'timestamp': current_timestamp,
'x': smoothed_pos[0],
'y': smoothed_pos[1],
'z': smoothed_pos[2],
'coordinate_system': self.coordinate_system,
'accuracy': fused_accuracy
}
def ecef_to_wgs84(self, ecef: np.ndarray) -> np.ndarray:
"""
ECEF转WGS84经纬度高度
:param ecef: ECEF坐标[x, y, z]
:return: WGS84坐标[lat, lon, alt]
"""
x, y, z = ecef
# 计算经度
lon = math.atan2(y, x)
# 迭代计算纬度和高度
p = math.hypot(x, y)
lat = math.atan2(z, p * (1 - WGS84_E2))
for _ in range(5): # 迭代5次足够收敛
N = WGS84_A / math.sqrt(1 - WGS84_E2 * math.sin(lat)**2)
alt = p / math.cos(lat) - N
lat = math.atan2(z, p * (1 - WGS84_E2 * N / (N + alt)))
# 转换为度
lat_deg = math.degrees(lat)
lon_deg = math.degrees(lon)
return np.array([lat_deg, lon_deg, alt])
# ---------------------- 测试代码 ----------------------
def test_fusion():
# 初始化融合器
fusion = MultiSensorFusion(coordinate_system="LOCAL")
# 模拟测试数据
test_anchors = np.array([
[3252435.0, 537638.0, 5424567.0], # UWB锚点1 (ECEF)
[3252440.0, 537640.0, 5424570.0], # UWB锚点2
[3252438.0, 537635.0, 5424565.0] # UWB锚点3
])
# 模拟100帧数据
results = []
for i in range(100):
timestamp = i * 0.01 # 100Hz
# 模拟北斗数据(缓慢移动)
beidou_data = {
'timestamp': timestamp,
'lat': 30.0 + i * 0.00001,
'lon': 120.0 + i * 0.00001,
'alt': 50.0 + i * 0.001,
'accuracy': np.random.uniform(1.0, 3.0)
}
# 模拟UWB数据
uwb_data = {
'timestamp': timestamp,
'distance': [np.linalg.norm(test_anchors[j] - np.array([3252435.0+i*0.1, 537638.0+i*0.1, 5424567.0+i*0.05])) + np.random.uniform(-0.1, 0.1) for j in range(3)],
'anchor_positions': test_anchors,
'accuracy': np.random.uniform(0.5, 1.5)
}
# 模拟IMU数据
imu_data = {
'timestamp': timestamp,
'acc_x': 0.1 + np.random.uniform(-0.01, 0.01),
'acc_y': 0.1 + np.random.uniform(-0.01, 0.01),
'acc_z': 9.8 + np.random.uniform(-0.05, 0.05),
'gyro_x': np.random.uniform(-0.01, 0.01),
'gyro_y': np.random.uniform(-0.01, 0.01),
'gyro_z': np.random.uniform(-0.01, 0.01)
}
# 融合解算
result = fusion.fusion_calculate(beidou_data, uwb_data, imu_data)
results.append(result)
if i % 10 == 0:
print(f"第{i}帧 - 位置: ({result['x']:.3f}, {result['y']:.3f}, {result['z']:.3f}) 精度: {result['accuracy']:.2f}m")
if __name__ == "__main__":
test_fusion()(2)管理平台软件
具备实时定位监控、轨迹回放、电子围栏、报警管理、数据分析等功能。支持3D电子地图(分楼层、分区域展示),可与视频监控、门禁系统、气体监测系统等联动,实现"定位+安防"一体化管控。例如,当人员进入危险区域时,平台立即触发报警,同时联动现场摄像头聚焦目标区域。
希望本篇对大家有所帮助~因为篇幅有限(二)将放在下篇,感兴趣的朋友可以关注一下~
点击下方可获取免费获取技术文档和解决方案↓↓↓↓↓↓↓