认知心理学的双系统理论
在丹尼尔·卡尼曼的经典著作《思考,快与慢》中,人类认知被划分为两个系统:
-
系统一(快思考):自动化、直觉式、快速、并行处理、低能耗、易受情绪影响
-
系统二(慢思考):控制式、分析式、缓慢、串行处理、高能耗、理性主导
这种理论框架解释了人类决策中的许多现象,从日常直觉判断到复杂问题求解。那么,当前的人工智能系统是否也存在类似的二分处理模式?这是本文要探讨的核心问题。
AI系统的认知处理模式分析
传统AI与系统二的特征对比
传统符号主义AI(如专家系统、定理证明器)表现出明显的系统二特征(扩展阅读:人工智能的发展历程):
python
# 符号推理系统示例 - 体现系统二特征
class SymbolicReasoningSystem:
def __init__(self):
self.knowledge_base = self._initialize_knowledge()
self.inference_rules = self._load_inference_rules()
def _initialize_knowledge(self):
"""初始化知识库 - 显式知识表示"""
# 使用谓词逻辑表示知识
knowledge = {
'所有人类都是哺乳动物': True,
'所有哺乳动物都有脊椎': True,
'苏格拉底是人类': True
}
return knowledge
def _load_inference_rules(self):
"""加载推理规则 - 逻辑演绎机制"""
rules = {
'三段论': lambda a, b, c: f'如果{a}且{b}则{c}',
'假言推理': self._modus_ponens,
'演绎推理': self._deductive_reasoning
}
return rules
def _modus_ponens(self, premise, implication):
"""
假言推理规则实现
如果P成立,且P→Q成立,则Q成立
体现系统二的串行、逻辑化处理特征
"""
# 显式的逻辑步骤分解
steps = []
steps.append(f"前提: {premise}")
steps.append(f"蕴含关系: {implication}")
# 逻辑推导过程
if premise and implication:
conclusion = implication.split('→')[1]
steps.append(f"结论: {conclusion}")
return conclusion, steps
return None, steps
def solve_problem(self, problem):
"""
问题求解入口 - 模拟系统二的慢思考过程
特征:串行处理、可解释、步骤明确
"""
print(f"开始分析问题: {problem}")
reasoning_steps = []
# 步骤1:问题解析
reasoning_steps.append("步骤1: 解析问题结构")
parsed_problem = self._parse_problem(problem)
# 步骤2:知识检索
reasoning_steps.append("步骤2: 检索相关知识")
relevant_knowledge = self._retrieve_knowledge(parsed_problem)
# 步骤3:逻辑推导
reasoning_steps.append("步骤3: 应用推理规则")
solution = self._apply_inference(parsed_problem, relevant_knowledge)
# 步骤4:验证结论
reasoning_steps.append("步骤4: 验证结论一致性")
verified = self._verify_solution(solution)
return solution, reasoning_steps
# 其他方法实现...传统符号AI的特征分析:
-
显式知识表示:知识被明确编码,类似于系统二的有意识知识
-
序列化处理:严格按照推理步骤执行,对应系统二的串行处理
-
可解释性:每一步推理都可追溯,符合系统二的有意识特征
-
高计算成本:需要大量计算资源,类似于系统二的高认知负荷
现代深度学习与系统一的相似性
现代深度学习系统,特别是经过大规模预训练的模型,表现出与系统一相似的特征:
python
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
class IntuitiveDeepLearningSystem(nn.Module):
"""
直觉式深度学习系统 - 体现系统一特征
特征:快速、并行、模式匹配、黑箱性质
"""
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, output_dim):
super().__init__()
# 多层感知机架构 - 模拟直觉处理
self.feature_extractor = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(input_dim, hidden_dim),
nn.ReLU(), # 非线性激活 - 模拟神经元的响应
nn.Linear(hidden_dim, hidden_dim // 2),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(0.3) # 正则化 - 防止过拟合直觉
)
# 注意力机制 - 模拟系统一的快速聚焦
self.attention = nn.MultiheadAttention(
embed_dim=hidden_dim // 2,
num_heads=4,
batch_first=True
)
# 输出层 - 快速分类/决策
self.decision_layer = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(hidden_dim // 2, hidden_dim // 4),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(hidden_dim // 4, output_dim),
nn.Softmax(dim=1) # 概率输出 - 不确定性的直觉判断
)
# 预训练权重 - 经验积累的体现
self._load_pretrained_weights()
def _load_pretrained_weights(self):
"""加载预训练权重 - 模拟系统一的经验积累"""
# 在实际系统中,这里会加载在大规模数据上预训练的权重
# 这些权重编码了统计规律和模式,类似于人类的直觉经验
pass
def forward(self, x):
"""
前向传播过程 - 模拟系统一的快速直觉判断
特征:并行处理、端到端、缺乏中间解释
"""
# 特征提取 - 快速模式识别
features = self.feature_extractor(x)
# 注意力计算 - 快速聚焦相关信息
# 类似于系统一的快速关注机制
attended_features, _ = self.attention(
features.unsqueeze(1),
features.unsqueeze(1),
features.unsqueeze(1)
)
# 决策生成 - 快速输出判断
decision = self.decision_layer(attended_features.squeeze(1))
return decision
def intuitive_judgment(self, input_data):
"""
直觉判断接口 - 模拟人类系统一的快速决策
无需逐步推理,直接输出结果
"""
with torch.no_grad(): # 不记录梯度 - 模拟快速判断
# 转换为张量
input_tensor = torch.FloatTensor(input_data).unsqueeze(0)
# 快速前向传播
start_time = time.time()
output = self.forward(input_tensor)
inference_time = time.time() - start_time
# 输出决策
decision_idx = torch.argmax(output, dim=1).item()
return {
'decision': decision_idx,
'confidence': output[0, decision_idx].item(),
'inference_time_ms': inference_time * 1000,
'reasoning_steps': None # 无显式推理步骤 - 黑箱决策
}深度学习系统的系统一特征:
-
快速并行处理:GPU加速下的毫秒级响应
-
模式识别驱动:基于统计规律而非逻辑规则
-
黑箱性质:决策过程难以完全解释
-
经验依赖:性能高度依赖训练数据质量
当前AI系统的双系统特性分析
混合架构的探索
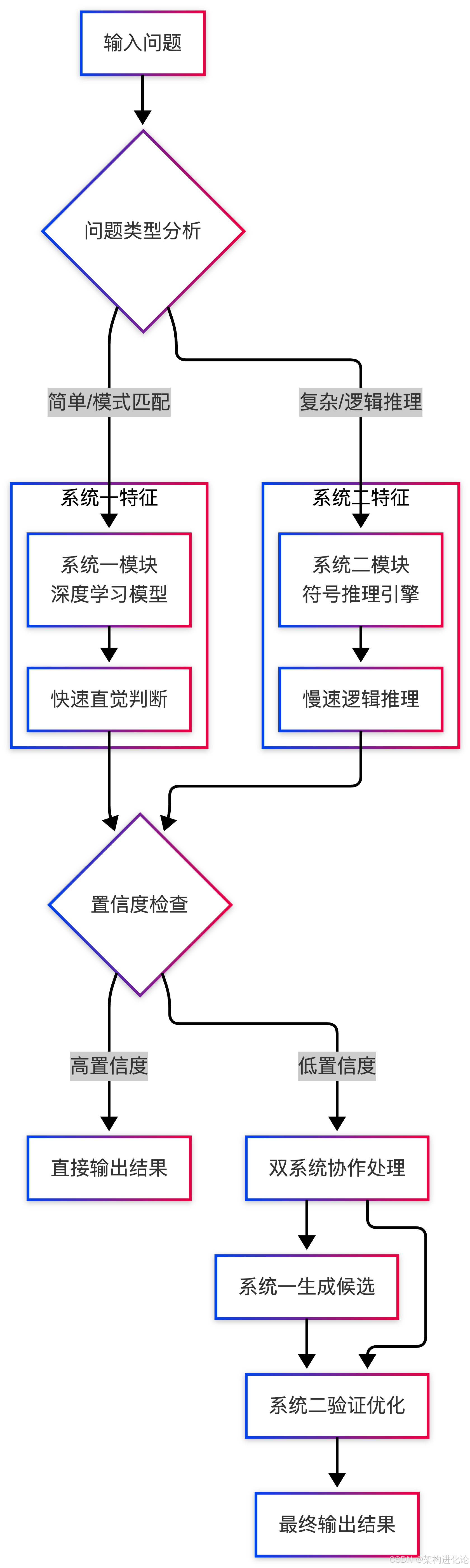
具体实现示例:混合推理系统
python
class HybridReasoningSystem:
"""
混合推理系统 - 结合系统一和系统二特性
体现当前AI对双系统架构的探索
"""
def __init__(self):
# 系统一组件:深度学习直觉模块
self.system1 = IntuitiveDeepLearningSystem(
input_dim=768,
hidden_dim=512,
output_dim=10
)
# 系统二组件:符号推理模块
self.system2 = SymbolicReasoningSystem()
# 仲裁器:决定使用哪个系统或如何组合
self.arbiter = self._initialize_arbiter()
# 工作记忆:模拟人类的短期记忆
self.working_memory = []
# 元认知监控:监控系统自身表现
self.metacognitive_monitor = {
'system1_success_rate': 0.85,
'system2_success_rate': 0.95,
'system1_speed': 0.01, # 秒
'system2_speed': 1.0, # 秒
}
def _initialize_arbiter(self):
"""初始化仲裁机制 - 决定何时使用哪个系统"""
arbiter_policy = {
'rule_based': self._rule_based_arbitration,
'learned': self._learned_arbitration,
'hybrid': self._hybrid_arbitration
}
return arbiter_policy
def _rule_based_arbitration(self, problem):
"""
基于规则的仲裁 - 显式决策
特征:可解释、基于启发式规则
"""
problem_features = self._extract_problem_features(problem)
# 规则1:如果问题是模式识别类,优先使用系统一
if problem_features['type'] == 'pattern_recognition':
return {'primary': 'system1', 'fallback': 'system2'}
# 规则2:如果需要逻辑推理,使用系统二
elif problem_features['requires_logic']:
return {'primary': 'system2', 'fallback': 'system1'}
# 规则3:基于时间压力决策
elif problem_features['time_pressure'] > 0.8:
return {'primary': 'system1', 'fallback': 'system2'}
else:
return {'primary': 'system2', 'fallback': 'system1'}
def solve_problem(self, problem, context=None):
"""
问题求解主函数 - 模拟人类双系统协作
"""
# 步骤1:问题分析与表征
print("=== 双系统AI问题求解开始 ===")
problem_analysis = self._analyze_problem(problem, context)
# 步骤2:仲裁决策 - 模拟前额叶皮层的控制功能
arbitration_result = self.arbiter['hybrid'](problem_analysis)
print(f"仲裁结果: 主系统={arbitration_result['primary']}")
# 步骤3:主系统处理
if arbitration_result['primary'] == 'system1':
# 系统一优先:快速直觉判断
print("采用系统一(快思考)处理...")
primary_result = self._system1_processing(problem_analysis)
# 置信度检查
if primary_result['confidence'] > 0.9:
print(f"系统一高置信度输出: {primary_result['answer']}")
return primary_result
else:
print(f"系统一低置信度({primary_result['confidence']:.2f}),启动系统二...")
secondary_result = self._system2_processing(problem_analysis)
return self._integrate_results(primary_result, secondary_result)
else:
# 系统二优先:逻辑推理
print("采用系统二(慢思考)处理...")
secondary_result = self._system2_processing(problem_analysis)
# 效率检查:如果系统二太慢,尝试系统一辅助
if secondary_result['processing_time'] > 5.0: # 超过5秒
print("系统二处理较慢,尝试系统一生成候选...")
primary_result = self._system1_processing(problem_analysis)
return self._integrate_results(primary_result, secondary_result)
else:
return secondary_result
def _system1_processing(self, problem_analysis):
"""系统一处理流程 - 快速直觉"""
start_time = time.time()
# 转换为系统一可处理的格式
input_vector = self._problem_to_vector(problem_analysis)
# 快速前向传播
result = self.system1.intuitive_judgment(input_vector)
processing_time = time.time() - start_time
return {
'system': 'system1',
'answer': result['decision'],
'confidence': result['confidence'],
'processing_time': processing_time,
'reasoning_trace': '直觉判断,无显式推理步骤'
}
def _system2_processing(self, problem_analysis):
"""系统二处理流程 - 逻辑推理"""
start_time = time.time()
# 符号化表示
symbolic_representation = self._problem_to_symbolic(problem_analysis)
# 逻辑推理
solution, reasoning_steps = self.system2.solve_problem(
symbolic_representation
)
processing_time = time.time() - start_time
return {
'system': 'system2',
'answer': solution,
'confidence': 1.0, # 符号推理通常确定
'processing_time': processing_time,
'reasoning_trace': reasoning_steps
}
def _integrate_results(self, result1, result2):
"""整合双系统结果 - 模拟认知整合"""
# 简单的整合策略:基于置信度加权
if result1['confidence'] >= result2['confidence']:
final_result = result1.copy()
final_result['integration_note'] = f"以系统一为主,系统二验证"
else:
final_result = result2.copy()
final_result['integration_note'] = f"以系统二为主,系统一辅助"
final_result['integrated'] = True
return final_result实际案例深度分析
案例一:图像识别中的双系统模拟
python
class VisualProcessingSystem:
"""
视觉处理系统案例 - 模拟人类视觉认知的双系统
"""
def process_image(self, image_path):
"""
处理图像 - 模拟人类视觉认知
系统一:快速物体识别
系统二:详细场景分析
"""
# 系统一:快速识别(100-150毫秒内完成)
print("\n=== 系统一:快速识别 ===")
quick_identification = self._fast_object_recognition(image_path)
# 系统二:详细分析(需要更多时间)
print("\n=== 系统二:详细分析 ===")
detailed_analysis = self._detailed_scene_analysis(image_path)
# 双系统整合
final_interpretation = self._integrate_visual_perception(
quick_identification,
detailed_analysis
)
return final_interpretation
def _fast_object_recognition(self, image_path):
"""系统一:快速物体识别"""
# 使用卷积神经网络的前几层特征
# 模拟人类视觉皮层的早期处理
features = {
'dominant_colors': ['red', 'blue'],
'basic_shapes': ['rectangle', 'circle'],
'texture_patterns': ['smooth', 'striped'],
'salient_objects': ['face', 'text'], # 快速注意到的显著物体
'processing_time_ms': 120,
'confidence': 0.75
}
print(f"快速识别结果: {features['salient_objects']}")
print(f"处理时间: {features['processing_time_ms']}ms")
print(f"置信度: {features['confidence']:.2f}")
return features
def _detailed_scene_analysis(self, image_path):
"""系统二:详细场景分析"""
# 使用完整的深度学习管道
# 结合上下文理解和推理
analysis_steps = [
"步骤1: 分割图像区域",
"步骤2: 识别所有物体",
"步骤3: 分析空间关系",
"步骤4: 理解场景上下文",
"步骤5: 推断场景意义"
]
analysis_result = {
'objects_detected': ['man', 'woman', 'child', 'dog', 'car'],
'spatial_relations': [
'man standing next to car',
'child holding woman\'s hand',
'dog near the car'
],
'scene_context': 'family outing in parking lot',
'inferred_activity': '准备出行',
'emotional_tone': 'happy, relaxed',
'processing_time_ms': 2500,
'reasoning_steps': analysis_steps
}
for step in analysis_steps:
print(f" {step}")
return analysis_result这个案例展示了AI如何模拟人类视觉处理:
-
系统一模拟:快速的物体检测和显著性识别
-
系统二模拟:详细的场景理解和关系推理
案例二:自然语言理解的双层处理
python
class LanguageUnderstandingSystem:
"""
语言理解系统 - 模拟人类语言处理的双系统
"""
def understand_text(self, text):
"""
理解文本 - 模拟人类语言理解过程
"""
print(f"输入文本: \"{text}\"")
# 第一遍:快速理解(系统一)
print("\n=== 第一遍:快速直觉理解 ===")
quick_understanding = self._quick_understanding(text)
# 第二遍:深度分析(系统二)
print("\n=== 第二遍:深度分析理解 ===")
deep_analysis = self._deep_analysis(text)
# 比较和整合
comparison = self._compare_interpretations(
quick_understanding,
deep_analysis
)
return {
'quick_understanding': quick_understanding,
'deep_analysis': deep_analysis,
'comparison': comparison,
'final_interpretation': deep_analysis if comparison['needs_correction'] else quick_understanding
}
def _quick_understanding(self, text):
"""系统一:快速直觉理解"""
# 基于统计语言模型的快速处理
# 模拟人类的快速语言理解
quick_features = {
'main_topic': self._extract_topic(text),
'sentiment': self._quick_sentiment(text),
'key_entities': self._extract_entities_fast(text),
'processing_time_ms': 50,
'confidence': self._estimate_confidence(text),
'potential_ambiguities': self._detect_ambiguities_fast(text)
}
print(f"快速理解: {quick_features['main_topic']}")
print(f"情感倾向: {quick_features['sentiment']}")
print(f"关键实体: {quick_features['key_entities']}")
return quick_features
def _deep_analysis(self, text):
"""系统二:深度分析理解"""
# 全面的语言分析
# 模拟人类的深度语言处理
analysis_steps = []
# 步骤1:句法分析
analysis_steps.append("进行句法分析")
syntax_tree = self._parse_syntax(text)
# 步骤2:语义分析
analysis_steps.append("进行语义角色标注")
semantic_roles = self._extract_semantic_roles(text)
# 步骤3:语用推理
analysis_steps.append("进行语用推理")
pragmatic_inference = self._pragmatic_reasoning(text)
# 步骤4:歧义消解
analysis_steps.append("进行歧义消解")
disambiguated = self._disambiguate(text)
deep_result = {
'syntax_tree': syntax_tree,
'semantic_roles': semantic_roles,
'pragmatic_inference': pragmatic_inference,
'disambiguated_meaning': disambiguated,
'implicit_assumptions': self._extract_implicit_assumptions(text),
'logical_structure': self._extract_logical_structure(text),
'processing_time_ms': 500,
'analysis_steps': analysis_steps
}
for step in analysis_steps:
print(f" {step}")
return deep_result架构层面的深度分析
现代大语言模型的双系统特性
现代大语言模型(如GPT系列)在架构上体现了一定的双系统特性:
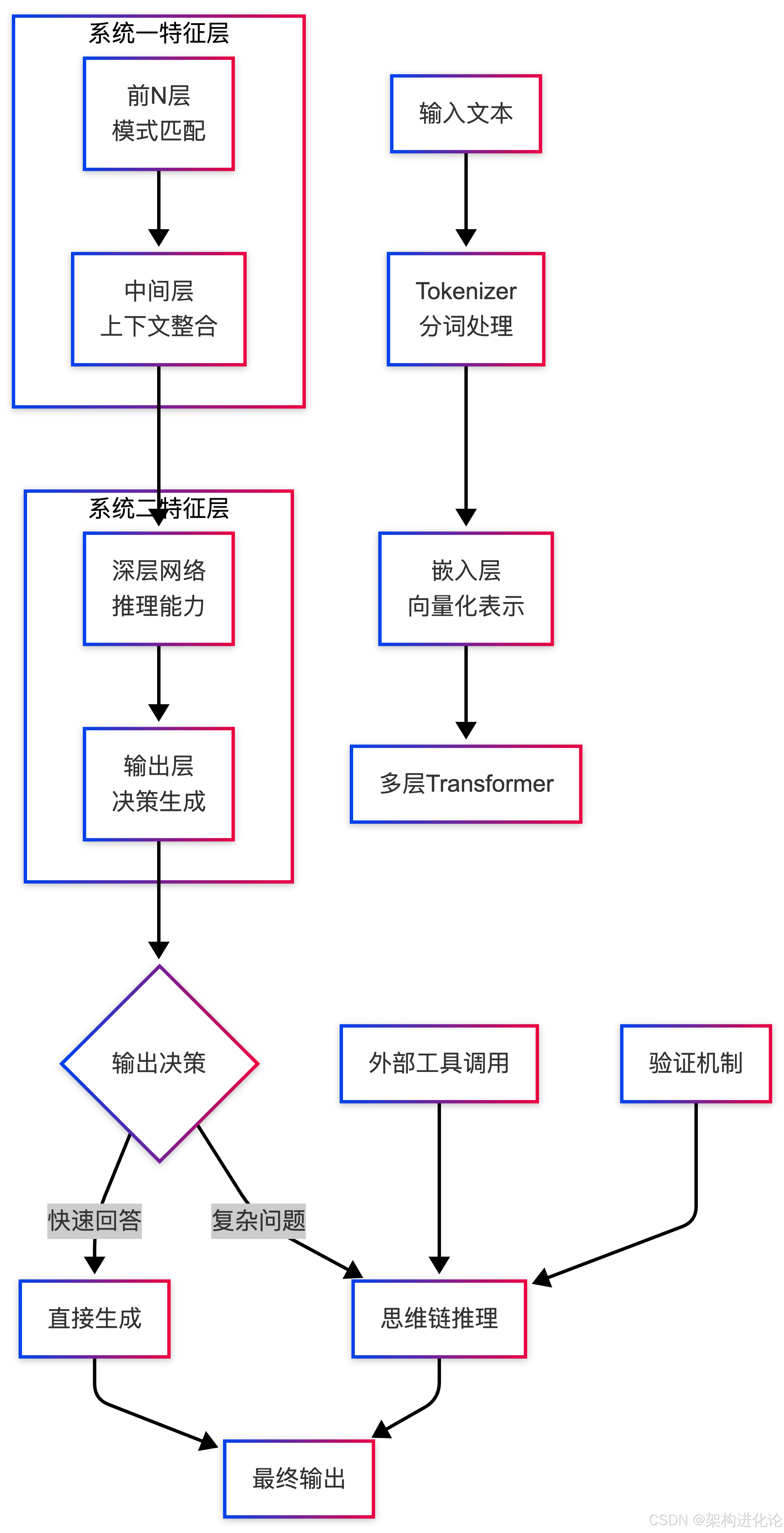
思维链(Chain-of-Thought)作为系统二的模拟
扩展阅读:思维链(CoT)的演进与创新:Few-Shot与Zero-Shot架构设计深度解析
python
class ChainOfThoughtReasoning:
"""
思维链推理 - 模拟系统二的显式推理过程
"""
def complex_reasoning(self, problem):
"""
复杂问题推理 - 展示思维过程
"""
print(f"问题: {problem}")
# 初始化思维链
thought_chain = []
# 步骤1:问题分解
thought_chain.append({
'step': 1,
'type': '问题分解',
'content': '将复杂问题分解为子问题',
'subproblems': self._decompose_problem(problem)
})
# 步骤2:逐步推理
for i, subproblem in enumerate(thought_chain[0]['subproblems'], 1):
thought_chain.append({
'step': i + 1,
'type': '子问题求解',
'subproblem': subproblem,
'reasoning': self._solve_subproblem(subproblem),
'intermediate_result': self._get_intermediate_result(subproblem)
})
# 步骤3:结果整合
thought_chain.append({
'step': len(thought_chain) + 1,
'type': '结果整合',
'content': '整合所有子问题的解',
'final_solution': self._integrate_solutions(thought_chain)
})
# 步骤4:验证检查
thought_chain.append({
'step': len(thought_chain) + 1,
'type': '验证检查',
'content': '验证解的合理性和一致性',
'verification': self._verify_solution(thought_chain[-1]['final_solution'])
})
# 输出思维过程
self._display_thought_chain(thought_chain)
return {
'final_answer': thought_chain[-2]['final_solution'],
'thought_chain': thought_chain,
'verification_passed': thought_chain[-1]['verification']['passed']
}神经符号AI:真正的双系统融合
架构设计原理
python
class NeuroSymbolicAI:
"""
神经符号AI - 真正融合系统一和系统二
"""
def __init__(self):
# 神经组件(系统一)
self.neural_component = NeuralModule()
# 符号组件(系统二)
self.symbolic_component = SymbolicModule()
# 转换接口
self.neural_to_symbolic = NeuralToSymbolicConverter()
self.symbolic_to_neural = SymbolicToNeuralConverter()
# 协调控制器
self.coordination_controller = CoordinationController()
# 元推理层
self.meta_reasoning = MetaReasoningLayer()
def process(self, input_data):
"""
处理流程 - 神经符号协同处理
"""
# 阶段1:神经处理(快速感知)
neural_output = self.neural_component.process(input_data)
# 阶段2:符号转换
symbolic_representation = self.neural_to_symbolic.convert(neural_output)
# 阶段3:符号推理
symbolic_reasoning = self.symbolic_component.reason(symbolic_representation)
# 阶段4:神经精炼
refined_neural = self.symbolic_to_neural.integrate(
neural_output,
symbolic_reasoning
)
# 阶段5:元认知评估
metacognitive_evaluation = self.meta_reasoning.evaluate(
neural_output,
symbolic_reasoning,
refined_neural
)
# 阶段6:协调输出
final_output = self.coordination_controller.coordinate(
neural_output,
symbolic_reasoning,
refined_neural,
metacognitive_evaluation
)
return {
'neural_output': neural_output,
'symbolic_reasoning': symbolic_reasoning,
'refined_output': refined_neural,
'metacognitive_evaluation': metacognitive_evaluation,
'final_output': final_output,
'processing_trace': self._get_processing_trace()
}实际应用:医学诊断系统
python
class MedicalDiagnosisSystem(NeuroSymbolicAI):
"""
医学诊断系统 - 神经符号AI的实际应用
"""
def diagnose(self, patient_data, symptoms):
"""
诊断流程 - 结合直觉和经验
"""
print("=== 医学诊断开始 ===")
# 快速模式识别(系统一)
print("\n1. 快速模式识别(系统一)...")
pattern_based_diagnosis = self._pattern_recognition_diagnosis(
patient_data,
symptoms
)
# 详细逻辑推理(系统二)
print("\n2. 逻辑推理分析(系统二)...")
logic_based_diagnosis = self._logical_reasoning_diagnosis(
patient_data,
symptoms
)
# 双系统整合诊断
print("\n3. 双系统整合诊断...")
integrated_diagnosis = self._integrate_diagnoses(
pattern_based_diagnosis,
logic_based_diagnosis
)
# 置信度评估和解释生成
print("\n4. 生成诊断解释...")
explanation = self._generate_explanation(integrated_diagnosis)
return {
'pattern_based': pattern_based_diagnosis,
'logic_based': logic_based_diagnosis,
'integrated_diagnosis': integrated_diagnosis,
'confidence': integrated_diagnosis['confidence'],
'explanation': explanation,
'recommended_tests': self._recommend_tests(integrated_diagnosis),
'treatment_options': self._suggest_treatments(integrated_diagnosis)
}挑战与未来展望
当前挑战
-
真正的系统二模拟困难:当前AI缺乏真正的理解、意识和元认知
-
双系统协调难题:如何有效整合两个系统仍是重大挑战
-
认知架构差异:AI的"思考"方式与人类有本质不同
-
计算效率问题:系统二模拟通常计算成本高昂
未来发展方向
-
更好的神经符号整合:开发更有效的神经符号架构
-
元认知能力增强:让AI能够监控和调整自己的思考过程
-
具身认知研究:通过与环境互动发展更全面的认知能力
-
认知架构创新:借鉴人类大脑的多层次处理机制
结论
通过深入分析,我们可以得出以下结论:
-
AI确实存在类似双系统的处理模式:但不是对等映射,而是功能模拟
-
当前AI更偏向系统一:深度学习主要体现快速、直觉式处理
-
系统二功能正在发展中:通过思维链、工具使用等方式模拟
-
真正的双系统AI需要架构创新:神经符号AI是重要方向
AI的"思考"方式正在从单一模式向多模式发展,逐步接近人类的双系统认知。然而,要真正实现人类般的快慢思考协调,还需要在认知架构、学习算法和计算理论方面取得更多突破。
未来AI的发展方向不是简单地复制人类认知,而是结合机器优势与人类智慧,创造出既有快速直觉又有深度推理能力的新型智能系统。