
🔥个人主页:星轨初途
❄专栏传送门:C语言,数据结构,C++学习(竞赛类) 算法及编程题分享
文章目录
- 前言
- 一、string概念
- 二、string的常见操作和功能
- 结束语
前言
嗨,大家好呀!我已经很久没有更新了,今天是元旦,祝大家元旦快乐呀。◕ᴗ◕。!
我们上一篇讲解了C++的条件判断与循环及数组(算法竞赛类),了解了数组的相关知识,我们感觉其中字符串数组还是没那么好用,为了更加简单⽅便,在C++中,⼜增加了
string来处理字符串。今天我们来一起了解string的神奇之处吧!
一、string概念
string字符串其实是一种更加高级的封装,string字符串中包含大量的方法,这些方法使得字符串的操作变得更加简单。string使用的好,慢慢你就不想使用字符数组来存放字符串了。
而C++中将字符串直接作为一种类型,也就是string类型,使用string类型创建的对象就是C++的字符串。
string也就是存储字符串的另一种方式,就是和字符数组差不多,只不过封装了一些好用的功能而已,十分简单易懂
二、string的常见操作和功能
常见操作文档:常见操作
1、头文件
cpp
#include<string>2、创建字符串
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;//空字符串
string s2 = "hello world";
cout << "s1:" << s1 << endl; //s1:
cout << "s2:" << s2 << endl; //s2: hello world
return 0;
}这里就不用多说了,和字符串的初始化一样
string也可以下标进行访问
除了以上创建字符串的写法外,C++中还有一些其他的创建字符串方式。如:
当然C++中的string创建的字符串和char类型的数组所表示的字符串还有一个区别,string类型的字符串对象可以直接赋值,比如:
方式1:其他字符串创建写法
cpp
string s("hello world"); //等同于string s1 = "hello world";
string s1 = s; //用一个现成的字符串s,初始化另外一个字符串s1方式2:string对象直接赋值示例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1("hello world");
string s2("hehe");
s2 = s1;
cout << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}3、string字符串的输入
(1)正常输入(cin)
和scanf功能一样,string可以用cin输入,但是只能输入不带空格的字符串
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
//输入
cin >> s;
//输出
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}(2)getline(带空格输入)
- getline是C++标准库中的一个函数,用于从输入流中读取一行文本,并将其存储为字符串。
- getline函数有两种不同的形式,分别对应着字符串的结束方式。
cpp
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str);
istream& getline (istream& is, string& str, char delim);✅提示:
- istream是输入流类型,cin是istream类型的标准输入流对象。
- ostream是输出流类型,cout是ostream类型的标准输出流对象。
- getline函数是从输入流中读取一行文本信息,所以如果是在标准输入流(键盘)中读取数据,就可以传cin给第一个参数。
第一种(默认以'\n'为结束标志)
第一种 getline 函数以换行符('\n')作为字符串的结束标志,它的一般格式是:
cpp
getline(cin, string str)
//cin -- 表示从输入流中读取信息
//str 是存放读取到的信息的字符串这种形式的 getline 函数从输入流(例如cin)中读取文本,直到遇到换行符('\n')为止 ,然后将读取到的文本(不包括换行符)存储到指定的string类型的变量str中。
实例:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
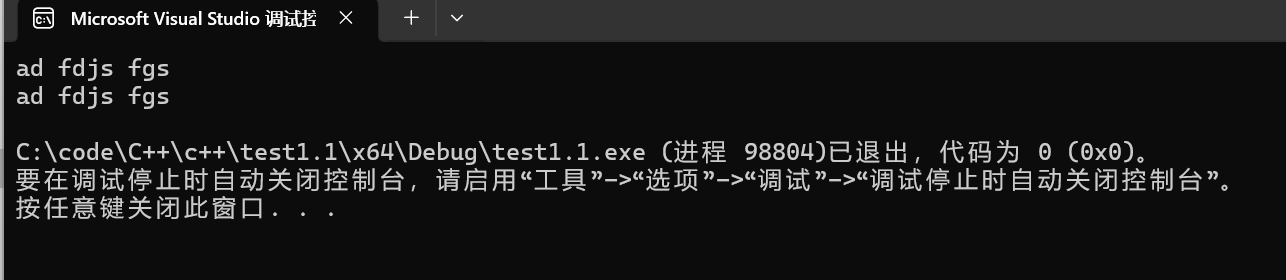
string name;
getline (cin, name);
cout << name << endl;
return 0;
}效果:
第二种(自定义结束标志)
第二种 getline 函数允许用户自定义结束标志,它的一般格式是:
cpp
getline(cin, string str, char delim)
//cin -- 表示从输入流中读取信息
//str 是存放读取到的信息的字符串
//delim 是自定义的结束标志这种形式的 getline 函数从输入流中读取文本,直到遇到用户指定的结束标志字符(delim)为止,然后将读取到的文本(不包括结束标志字符)存储到指定的string类型的变量str中。
实例:
cpp
#include<iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
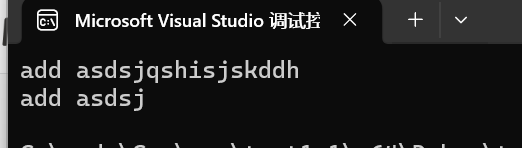
string name;
getline (cin, name, 'q');
cout << name << endl;
return 0;
}效果
4、size()------字符串长度
string中提供了size()函数用于获取字符串长度。
在C++中关于字符串的操作函数都是包含在string中的,所以需要调用这些函数时,通常用.点运算符。
使用示例:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
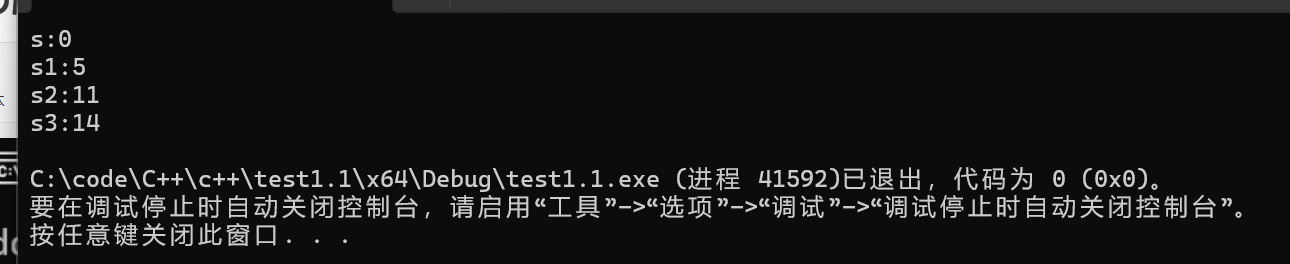
string s;
string s1 = "hello";
string s2 = "hello world";
string s3 = "12ab!~ ";
cout << "s:" << s.size() << endl;
cout << "s1:" << s1.size() << endl;
cout << "s2:" << s2.size() << endl;
cout << "s3:" << s3.size() << endl;
return 0;
}效果
5、迭代器(iterator)
迭代器是⼀种对象,它可以用来遍历容器(比如我们现在学习的 string )中的元素,迭代器的作用类似于指针,或者数组下标。
❗ 不过访问迭代器指向的值,需要解引用(*)。
C++ 中的 string 提供了多种迭代器,用于遍历和操作字符串中的内容。这里给大家介绍⼀种最常用的迭代器。
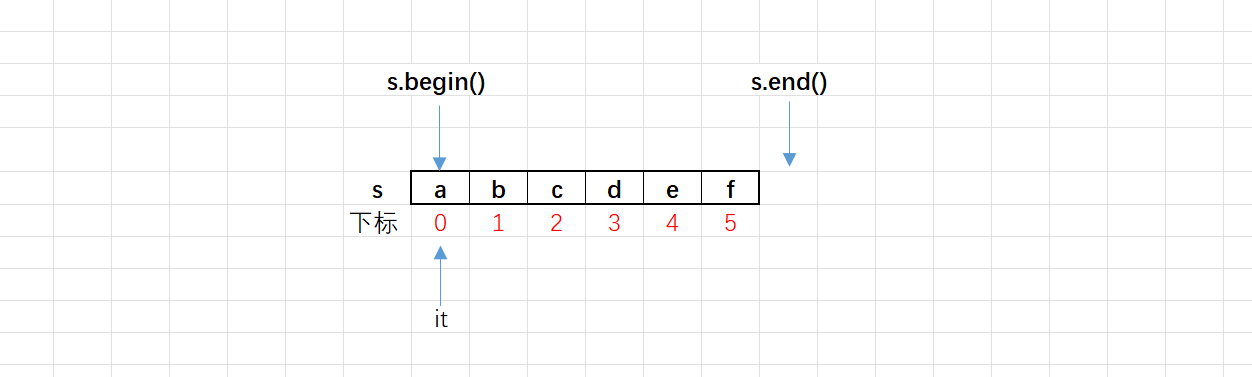
begin()和end()
- begin():返回指向字符串第一个字符的迭代器,需要一个迭代器的变量来接收。
- end():返回指向字符串最后一个字符的下一个位置的迭代器(该位置不属于字符串)。
- string中begin()和end()返回的迭代器的类型是string::iterator(也可以用auto来接收)。
(1)比较
✅注意
- 迭代器是可以进行大小比较,也可以进行+或者-整数运算的。
比如:i++,就是让迭代器前进一步,i--就是让迭代器退后一步。- 同一个容器的两个迭代器也可以相减,相减结果的绝对值,是两个迭代器中间元素的个数。
代码:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdef";
string::iterator it1 = s.begin();
string::iterator it2 = s.end();
cout << (it1 < it2) << endl;
cout << it1 - it2 << endl;
return 0;
}结果

(2)遍历
迭代器通常用于遍历字符串的,可以正序遍历,也可以逆序遍历
正序遍历如下
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdef";
//auto it 是让编译器自动推到it的类型
for (auto it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << ' ';
}
//string::iterator 是正向迭代器类型
//string::iterator it, 是直接创建迭代器,it是针对字符串的迭代器
for (string::iterator it = s.begin(); it != s.end(); ++it)
{
cout << *it << ' ';
}
return 0;
}改变指定字符
通过迭代器找到元素后,改变迭代器指向的元素,是可以直接改变字符串内容的。
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string str = "abcdef";
cout << str << endl;
for (string::iterator it = str.begin(); it != str.end(); ++it)
{
*it = 'x';
}
cout << str << endl;
return 0;
}效果如下
6、字符串的插入和删除
(1)插入
push_back()------尾插
push_back()用于在字符串尾部插一个字符。
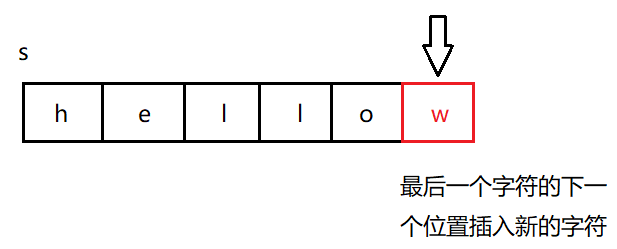
具体实现如下
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include<string> //添加string头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//向空字符串中尾插字符
string s;
s.push_back('h');
s.push_back('e');
s.push_back('l');
s.push_back('l');
s.push_back('o');
cout << s << endl;
//向非空字符串中尾插字符
string s1 = "hello ";
s1.push_back('w');
s1.push_back('o');
s1.push_back('r');
s1.push_back('l');
s1.push_back('d');
cout << s1 << endl;
//批量插入字符
string s2;
for (char c = 'a'; c <= 'f'; c++)
{
s2.push_back(c);
}
cout << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}效果
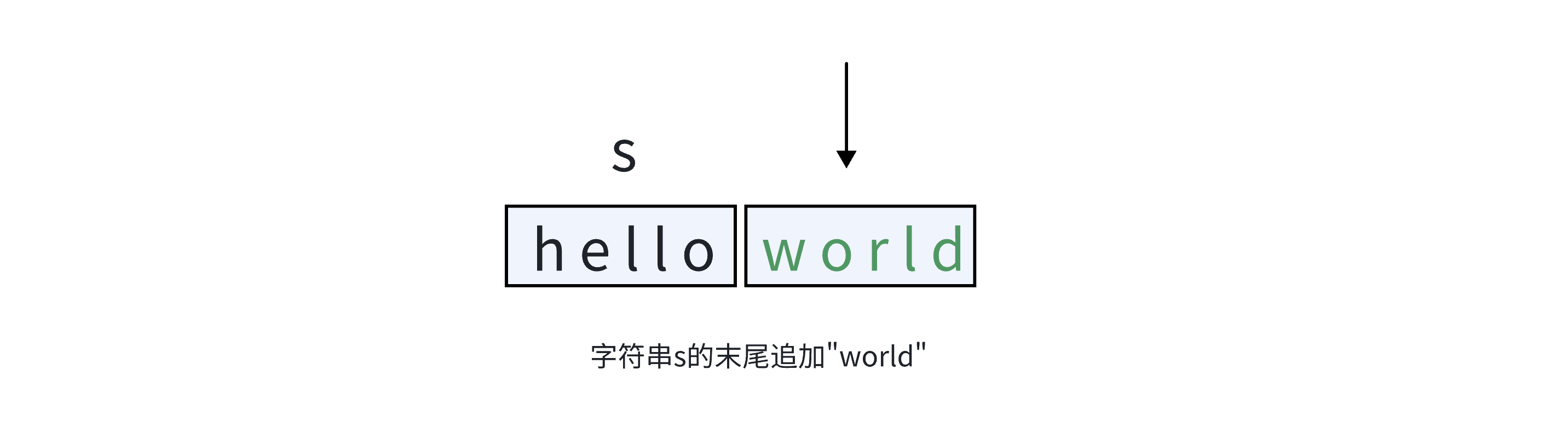
字符串的+=和+运算
push_back()用于在字符串后添加单个字符 ,若需向字符串后追加字符串 ,string类型支持+和+=运算,本质是string中重载了operator+=操作符。
效果图片展示
代码举例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello";
s += " world"; //字符串用双引号,等价于 s = s + " world"
cout << s << endl;
//除了+=操作,也可以使用'+'灵活进行字符串拼接
//头部拼接
string s2 = "hello";
s2 = "world " + s2 ;
cout << s2 << endl; //s2为: "world hello"
return 0;
}效果如下
insert------指定位置进行插入
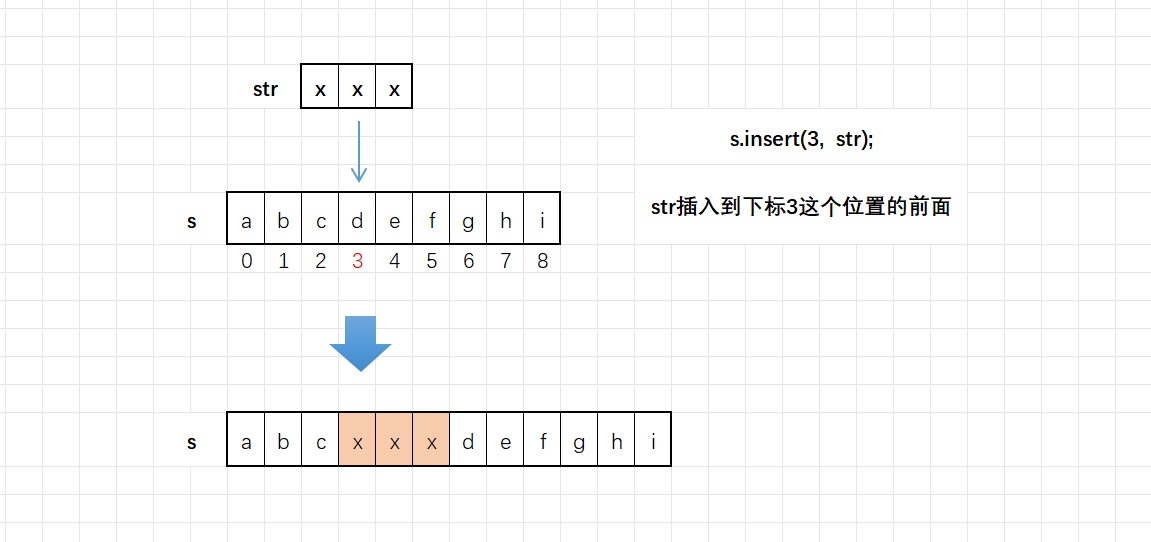
如果我们需要在字符串中间的某个位置插入一个字符串,怎么办呢?这时候我们得掌握一个函数就是insert
cpp
string& insert (size_t pos, const string& str); //pos位置前面插入一个string字符串
string& insert (size_t pos, const char* s); //pos位置前面插入一个C风格的字符串
string& insert (size_t pos, size_t n, char c); //pos位置前面插入n个字符cpos就是字符串下标
流程如下
代码功能实现:
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdefghi";
string base = s; // 保存原始字符串,用于还原
// 方式1:插入string类型字符串
cout << "原始字符串:" << s << endl;
string str = "xxx";
s.insert(3, str);
cout << "方式1-插入string字符串:" << s << endl;
s = base; // 还原原始字符串
// 方式2:插入C风格字符串
s.insert(3, "xxx");
cout << "方式2-插入C风格字符串:" << s << endl;
s = base; // 还原原始字符串
// 方式3:插入n个指定字符
s.insert(3, 3, 'x');
cout << "方式3-插入3个字符x:" << s << endl;
return 0;
}(2)删除------pop_back()
pop_back() 用于删除字符串中尾部的一个字符。
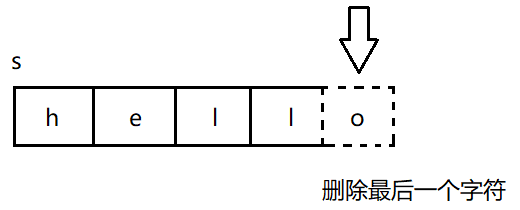
实现
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello";
cout << "s:" << s << endl;
//尾删
s.pop_back();
cout << "s:" << s << endl;
//尾删
s.pop_back();
cout << "s:" << s << endl;
return 0;
}效果
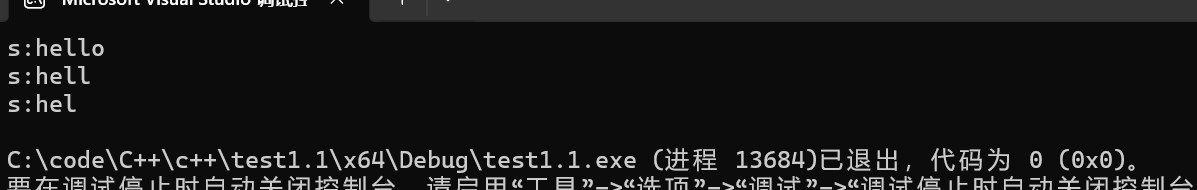
注意:不可对空字符串继续进⾏pop_back()操作,否则程序出现异常
7、字符串的查找和截取
(1)查找------find()
find()函数用于查找字符串中指定子串/字符,并返回子串/字符在字符串中第一次出现的位置。
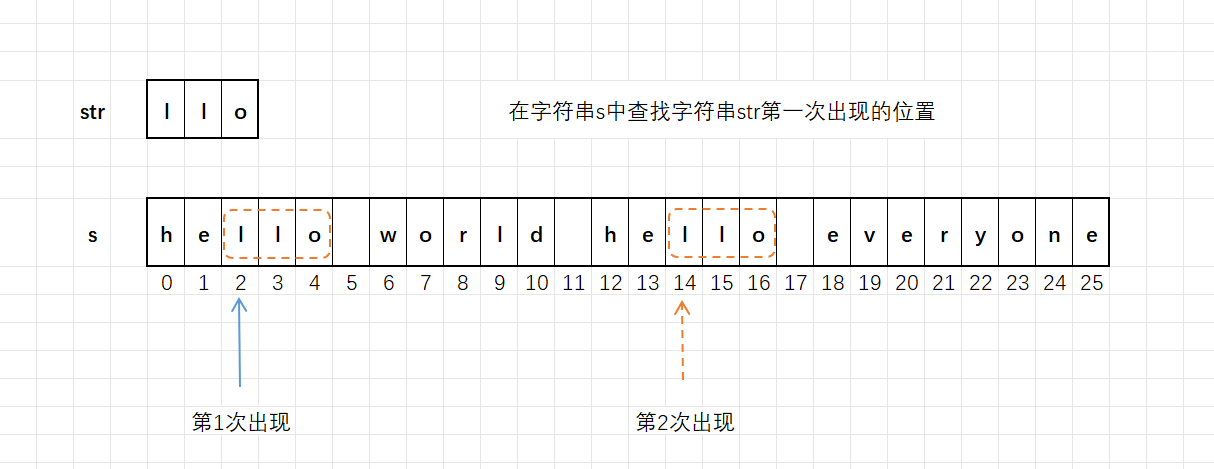
find类型
cpp
// 查找string类型的字符串str,默认是从头开始查找,pos可以指定位置开始
size_t find (const string& str, size_t pos = 0) const;
// 查找C风格的字符串s,默认是从头开始查找,pos可以指定位置开始
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
// 在字符串的pos这个位置开始查找C风格的字符串s中的前n个字符
size_t find (const char* s, size_t pos, size_t n) const;
// 查找字符c,默认是从头开始,pos可以指定位置开始
size_t find (char c, size_t pos = 0) const;返回值
- 若找到,返回子串/字符在字符串中第一次出现的起始下标位置。
- 若未找到,返回一个整数值
npos(针对npos的介绍会在下面给出)。通常判断find()函数的返回值是否等于npos就能知道是否查找到子串或者字符。
不同类型find例子
代码例子
代码1------查找【字符串 / 子串】
cpp
//代码1
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
string str = "llo";
//查找string类型的字符串
size_t n = s.find(str);
cout << n << endl;
n = s.find(str, n + 1); //从n+1这个指定位置开始查找
cout << n << endl;
//查找C风格的字符串
n = s.find("llo");
cout << n << endl;
n = s.find("llo", n + 1); //从n+1这个指定位置开始查找
cout << n << endl;
return 0;
}代码2------精准查找【C 风格字符串的前 N 个字符】
cpp
//代码2
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
//在s中,0这个指定位置开始查找"word"中的前3个字符
size_t n = s.find("word", 0, 3);
cout << n << endl;
n = s.find("everyday", n+1, 5);
cout << n << endl;
return 0;
}代码3------查找【单个字符】
cpp
//代码3
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
size_t n = s.find('o');
cout << n << endl;
n = s.find('o', n + 1);
cout << n << endl;
return 0;
}查找不到的情况
在字符串中查找字符或者字符串时,若查找不到,find函数会返回npos这个值;该值并非随机数字,而是string中定义的一个静态常量。我们通常会通过判断find函数的返回值是否等于npos,来确定查找是否成功。
cpp
//查找不到的情况
#include <iostream>
#include <string> //添加string头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
string str = "bit";
size_t n = s.find(str);
cout << n << endl;
if(n != string::npos)
cout << "找到了,位置是:" << n << endl;
else
cout << "没有找到" << endl;
return 0;
}(2)截取------substr()
函数参数
substr()函数用于截取字符串中指定位置指定长度的子串。函数原型如下:
cpp
string substr (size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos) const;
//pos 的默认值是0,也就是从下标为0的位置开始截取
//len 的默认值是npos,意思是一直截取到字符串的末尾substr()的用法:
- substr():如果函数不传参数,就是从下标为0的位置开始截取,直到结尾,得到的是整个字符串;
- substr(pos):从指定下标pos位置开始截取子串,直到结尾;
- substr(pos, len):从指定下标pos位置开始截取长度为len的子串。
两种方式效果
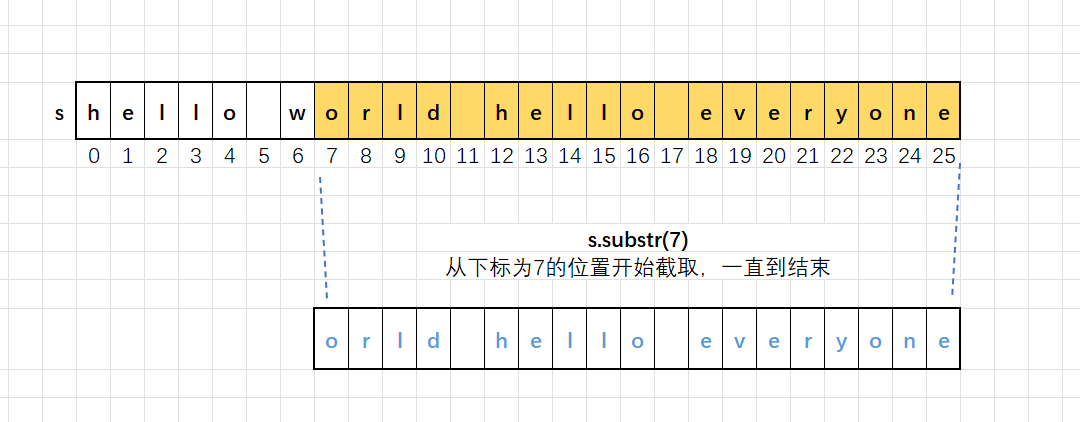
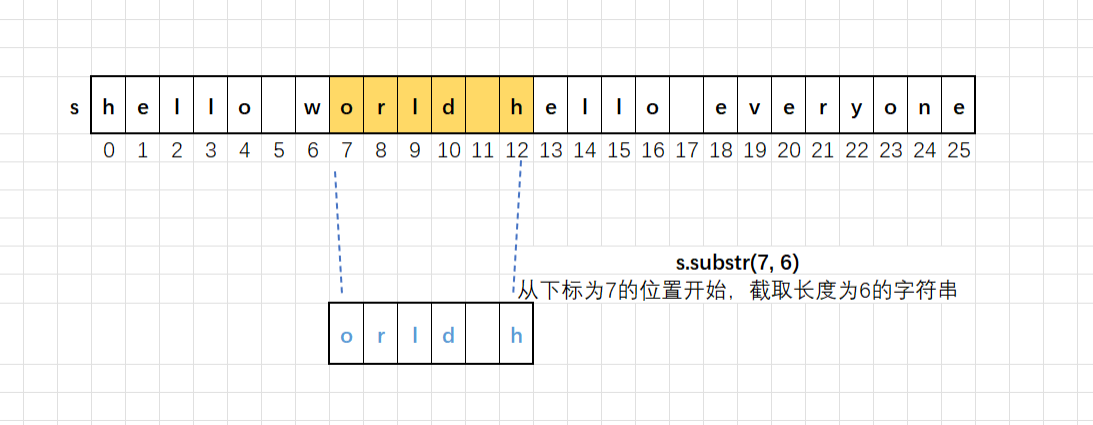
返回值
返回值类型:string,返回的是截取到的字符串,可以使用string类型的字符串接收。
代码举例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include<string> //添加string头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
string s1 = s.substr(7);
cout << s1 << endl;
string s2 = s.substr(7, 6);
cout << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}效果
(3)find()和substr()结合
substr()和find()经常是配合使用的,find负责找到位置,substr从这个位置向后获得字符串。
代码举例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include<string> //添加string头文件
using namespace std;
int main()
{
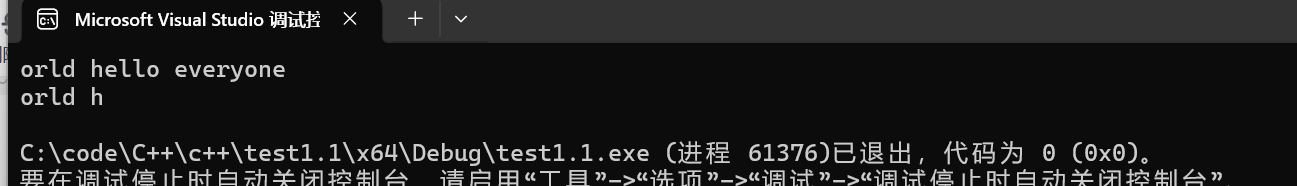
string s = "hello world hello everyone";
size_t n = s.find("world");
string s2 = s.substr(n, 10);
cout << s2 << endl;
return 0;
}效果
8、string的关系运算
string支持字符串比较,和strcmp比较规则一致,可以直接进行字符串比较,比如>,=,<等等,只不过返回类型为bool类型
这里仅简单展示
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
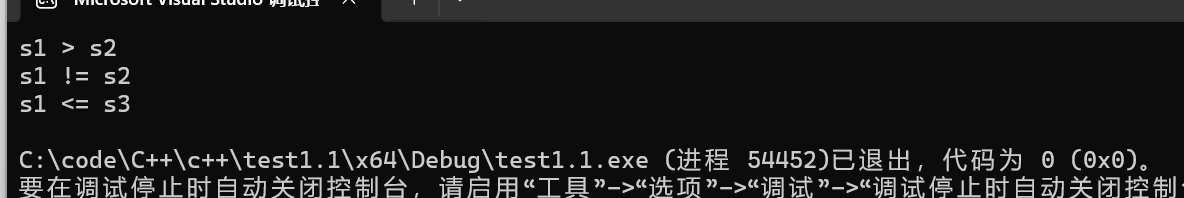
{
string s1 = "abcd";
string s2 = "abbcdef";
char s3[] = "bbc";
if (s1 > s2)
cout << "s1 > s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1 <= s2" << endl;
if (s1 == s2)
cout << "s1 == s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1 != s2" << endl;
if (s1 <= s3)
cout << "s1 <= s3" << endl;
else
cout << "s1> s3" << endl;
return 0;
}效果
9、string中字符串与基本数值类型的转换工具函数
(1)stoi/stol
- stoi :将字符串转换为
int类型的值 - stol :将字符串转换为
long int类型的值
两者用法类似,以stoi为例讲解:stoi可将string类型的字符串转化为整型,函数原型如下:
函数参数
cpp
int stoi (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10);
long stol (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10);- str :被转换的
string类型字符串 - idx :输出型参数(指针类型)。需在外创建
size_t类型变量,传递其地址给idx;该参数会带回str中无法匹配数字的第一个字符的位置。 - base :被解析字符串的进制值(支持2、8、10、16、0):
- 默认值为10,表示解析10进制数字;
- 传2:解析2进制数字,最终转为10进制;
- 传8:解析8进制数字,最终转为10进制;
- 传16:解析16进制数字,最终转为10进制;
- 传0:自动推导进制(含
0x则为16进制,0开头则为8进制),最终转为10进制。
代码举例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
size_t pos = 0;
string s1 = "11x34";
int ret1 = stoi(s1, &pos, 16);
cout << ret1 << endl;
cout << "pos:" << pos << endl;
string s2 = "11x34";
int ret2 = stoi(s2, &pos, 2);
cout << ret2 << endl;
cout << "pos:" << pos << endl;
string s3 = "0x11x34";
int ret3 = stoi(s3, &pos, 0);
cout << ret3 << endl;
cout << "pos:" << pos << endl;
return 0;
}效果如下:

(2)stod/stof
stod是将字符串转换成double类型的值,就是参数少了进制的描述
参数
cpp
double stod (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0);
float stof (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0);代码示例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "3.14x456";
double ret = stod(s, NULL);
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}(3)to_string
就是将数字转换为字符串
cpp
string to_string(数字类型 val);代码举例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string pi = "pi is " + to_string(3.14159);
cout << pi << endl;
return 0;
}结束语
嗨!本篇到这里就结束啦!今天我们了解了string的使用,在日常字符串处理中string十分常用,比如gline,字符串的+=和+运算,关系运算等等都是十分1常用且重要的,而今天还是2026的第一天,祝大家新年快乐!元旦快乐!٩(๑❛ᴗ❛๑)۶
我们下一篇讲解函数和递归,感谢大家的支持啦!让我们下篇再见!


