文章目录
- 1.欧拉角和旋转矩阵之间的转换
- 2.欧拉角
-
- [2.1 基本概念](#2.1 基本概念)
-
- [2.1.1 欧拉角的名称](#2.1.1 欧拉角的名称)
- [2.1.2 欧拉角方向](#2.1.2 欧拉角方向)
- [2.1.3 欧拉角范围](#2.1.3 欧拉角范围)
- [2.2 旋转顺序](#2.2 旋转顺序)
-
- [2.2.1 旋转顺序和旋转轴](#2.2.1 旋转顺序和旋转轴)
- [2.2.2 内旋和外旋](#2.2.2 内旋和外旋)
- 3.旋转矩阵
-
- [3.1 由欧拉角到旋转矩阵](#3.1 由欧拉角到旋转矩阵)
- [3.2 任意轴旋转](#3.2 任意轴旋转)
- 3.欧拉角与旋转矩阵相互转换
-
- [3.1 欧拉角和旋转矩阵之间的转换程序示例](#3.1 欧拉角和旋转矩阵之间的转换程序示例)
- 4.四元素
-
- [4.1 欧拉角转四元素](#4.1 欧拉角转四元素)
- [4.2 欧拉角转旋转矩阵](#4.2 欧拉角转旋转矩阵)
- [4.3 四元数转欧拉角](#4.3 四元数转欧拉角)
- [4.4 四元数转旋转矩阵](#4.4 四元数转旋转矩阵)
- [4.5 旋转矩阵转四元数](#4.5 旋转矩阵转四元数)
- [4.6 旋转矩阵转欧拉角](#4.6 旋转矩阵转欧拉角)
- [5. 四元数、欧拉角、旋转矩阵、旋转向量之间的转换](#5. 四元数、欧拉角、旋转矩阵、旋转向量之间的转换)
-
- [5.1 旋转向量](#5.1 旋转向量)
- [5.2 旋转矩阵](#5.2 旋转矩阵)
- [5.3 欧拉角](#5.3 欧拉角)
- [5.4 四元数](#5.4 四元数)
- 6.学习链接
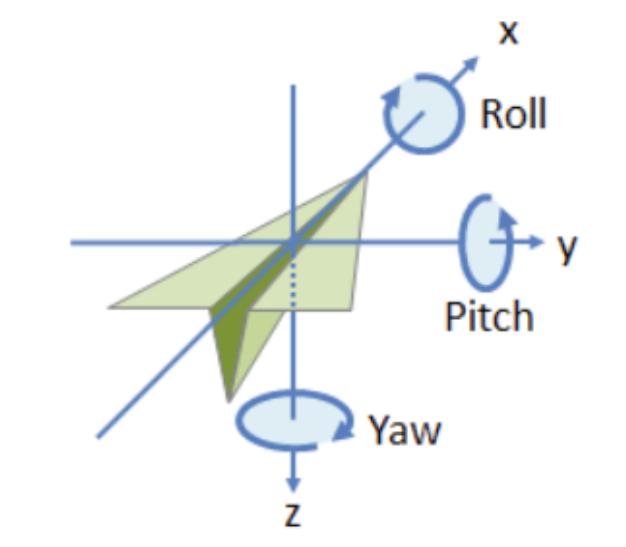
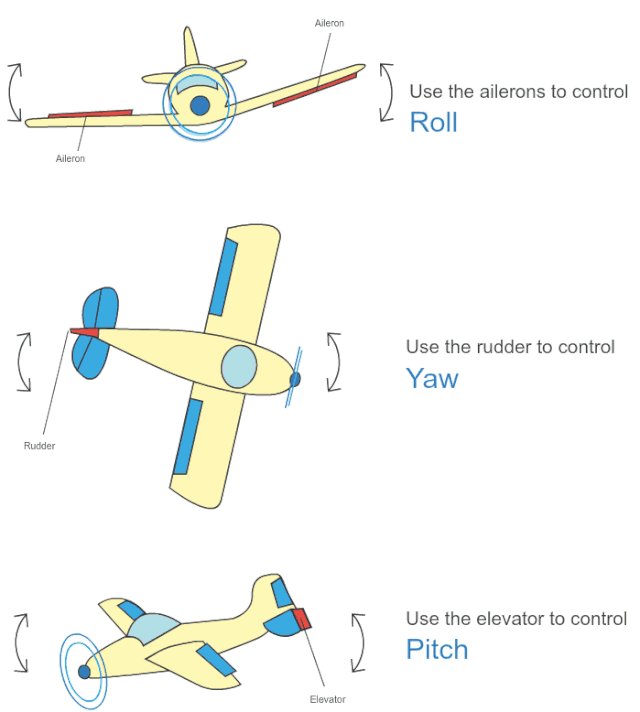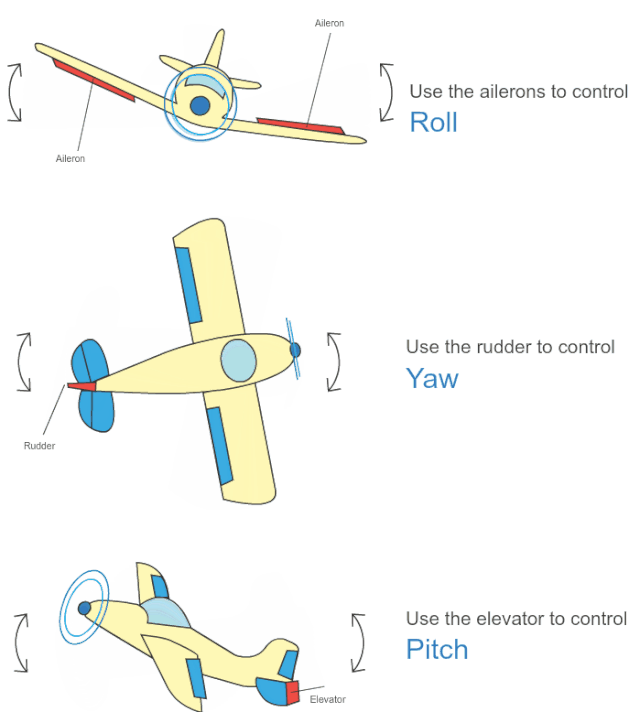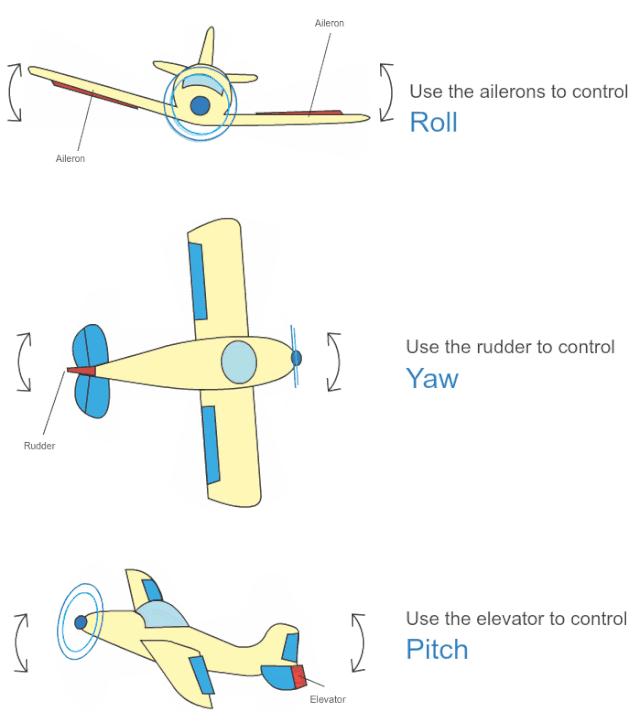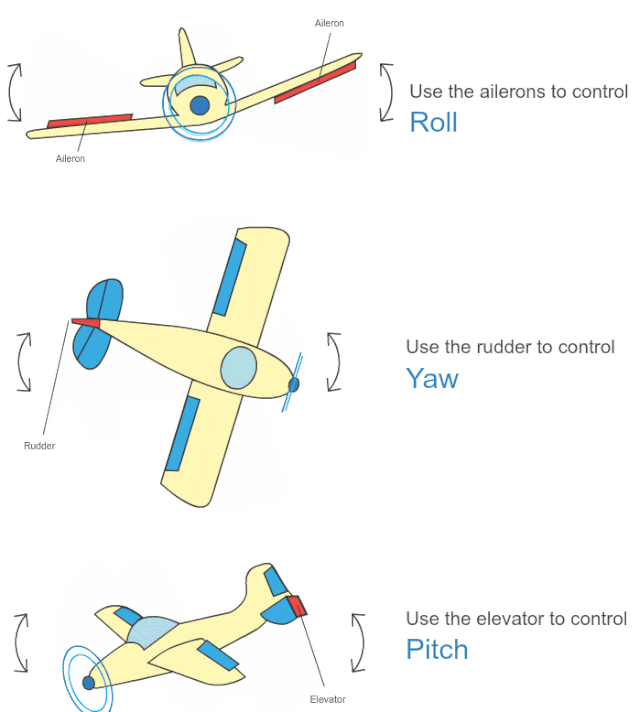
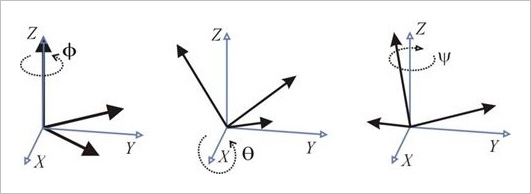
翻滚角roll是围绕x轴旋转。
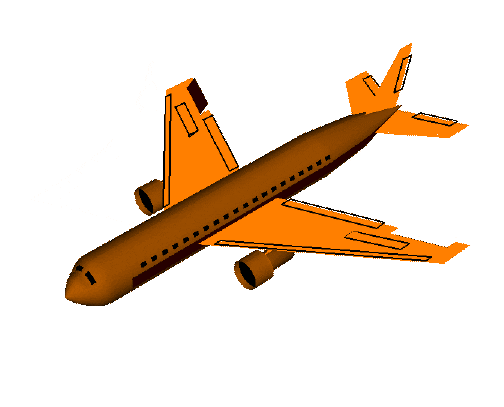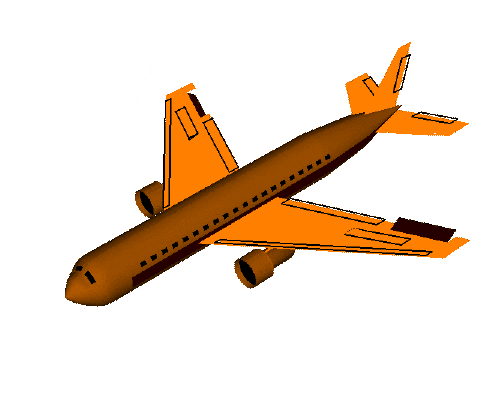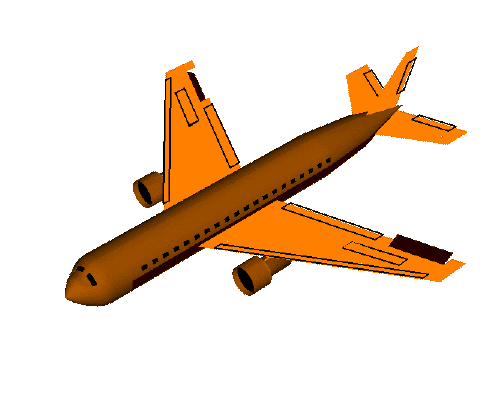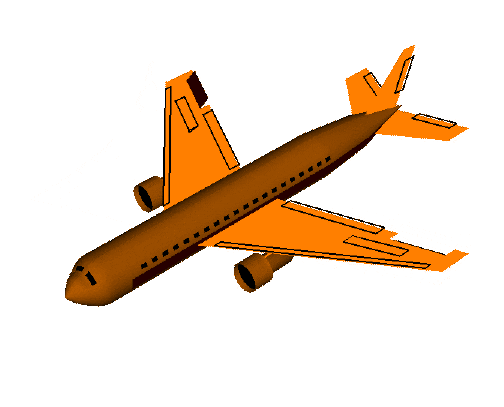
俯仰角pitch是围绕y轴的旋转,可视为飞机的上下俯仰。

偏航角yaw是围绕z轴旋转,可视为控制飞机的偏航。
1.欧拉角和旋转矩阵之间的转换
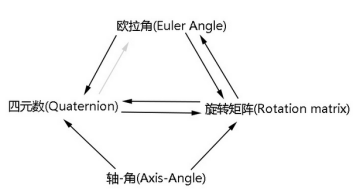
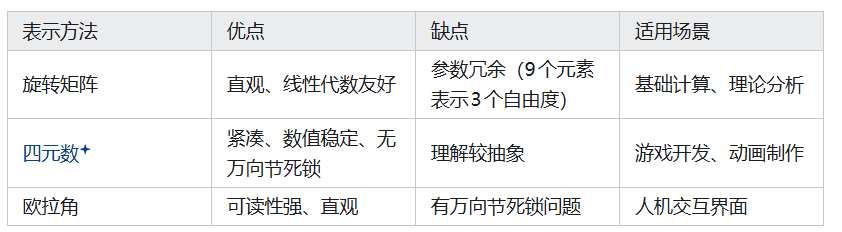
在机器人视觉应用中,经常会遇到旋转矩阵、旋转向量、四元素、欧拉角之间的相互转换。其中最容易出错的是旋转矩阵与欧拉角之间的相互转换。

2.欧拉角
2.1 基本概念
2.1.1 欧拉角的名称
1.欧拉角的叫法不固定,跟坐标轴的定义强相关。
2.在图1中,假设X是车头,Y是车左方,Z是车上方,那么绕X轴旋转得到的是roll,绕Y轴旋转得到的是pitch,绕Z轴得到的是yaw。
3.在图1中,假设Y是车头,X是车右方,Z是车上方,那么绕X轴旋转得到的是pitch,绕Y轴旋转得到的是roll,绕Z轴得到的是yaw。
2.1.2 欧拉角方向
1.如果是右手系,旋转轴正方向面对观察者时,逆时针方向的旋转是正、顺时针方向的旋转是负。
2.亦可这样描述:使用右手的大拇指指向旋转轴正方向,其他4个手指在握拳过程中的指向便是正方向。
3.如图1中的三次旋转都是正向旋转。

2.1.3 欧拉角范围
1.这个要具体问题具体对待。
2.假如是车体坐标系(x-前,y-左,z-上),那么roll和pitch应该定义在(-90°,+90°),yaw应该定义在(-180°,+180°)。
3.假如是飞机坐标系,那么roll、pitch和yaw都应该定义在(-180°,+180°)。
4.Eigen 中的默认范围roll、pitch和yaw都是(-180°,+180°)。
2.2 旋转顺序
欧拉角旋转序列(Euler Angle Rotational Sequence)一共有12种顺规,6种绕三条轴的旋转(也叫Tait-Bryan Angle,XYZ,XZY,YXZ,YZX,ZXY,ZYX),另外6种只绕两条轴的旋转(也叫Proper Euler Angle,XYX,YXY,XZX,ZXZ,YZY,ZYZ)。
2.2.1 旋转顺序和旋转轴
1.对于x,y,z三个轴的不同旋转顺序一共有(x-y-z,y-z-x,z-x-y,x-z-y,z-y-x,y-x-z)六种组合,在旋转相同的角度的情况下不同的旋转顺序得到的姿态是不一样的。
2.比如,先绕x轴旋转alpha,再绕y轴旋转beta;先绕y轴旋转beta,再绕x轴旋转alpha。这两种顺序得到的姿态是不一样的。
2.2.2 内旋和外旋
1.每次旋转是绕固定轴(一个固定参考系,比如世界坐标系)旋转,称为外旋。
2.每次旋转是绕自身旋转之后的轴旋转,称为内旋。
下图说明了内旋和外旋的区别
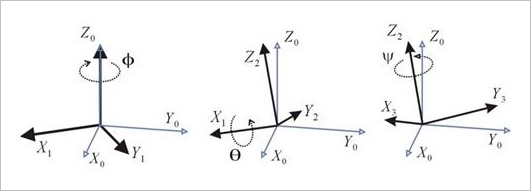
内在旋转
外在旋转

3.旋转矩阵
3.1 由欧拉角到旋转矩阵
假设绕XYZ三个轴旋转的角度分别为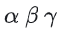 ,则三次旋转的旋转矩阵计算方法如下:
,则三次旋转的旋转矩阵计算方法如下:
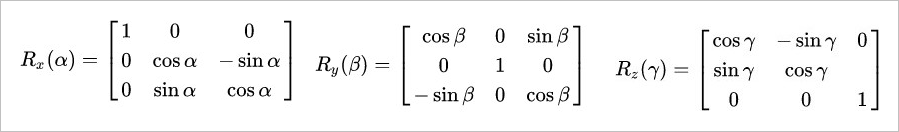
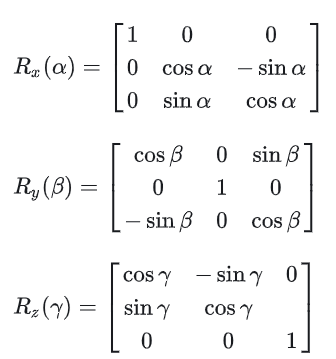
按照内旋方式,Z-Y-X旋转顺序(指先绕自身轴Z,再绕自身轴Y,最后绕自身轴X),可得旋转矩阵(内旋是右乘):
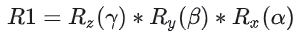
按照外旋方式,X-Y-Z旋转顺序(指先绕固定轴X,再绕固定轴Y,最后绕固定轴Z),可得旋转矩阵(外旋是左乘):
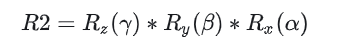
注意:这个结论说明ZYX顺序的内旋等价于XYZ顺序的外旋。
1.slam十四讲中提到的常用旋转顺序是Z-Y-X,对应rpy,指的就是内旋(绕自身轴),Z-Y-X顺序。
2.而欧拉角转成旋转矩阵(相对于世界坐标系的旋转矩阵),通常是按外旋方式(绕固定轴),即X-Y-Z顺序
3.2 任意轴旋转

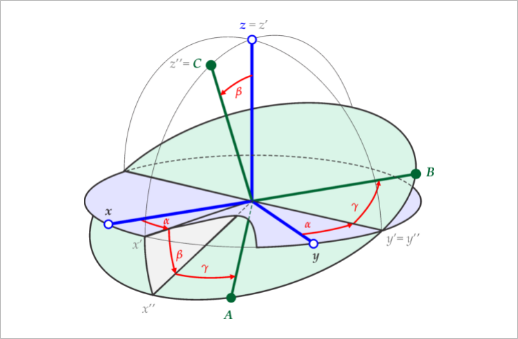
旋转角与旋转矩阵
3.欧拉角与旋转矩阵相互转换
以下代码用来实现旋转矩阵和欧拉角之间的相互变换。
C++语言:
cpp
Mat eulerAnglesToRotationMatrix(Vec3f &theta)
{
// Calculate rotation about x axis
Mat R_x = (Mat_<double>(3,3) <<
1, 0, 0,
0, cos(theta[0]), -sin(theta[0]),
0, sin(theta[0]), cos(theta[0])
);
// Calculate rotation about y axis
Mat R_y = (Mat_<double>(3,3) <<
cos(theta[1]), 0, sin(theta[1]),
0, 1, 0,
-sin(theta[1]), 0, cos(theta[1])
);
// Calculate rotation about z axis
Mat R_z = (Mat_<double>(3,3) <<
cos(theta[2]), -sin(theta[2]), 0,
sin(theta[2]), cos(theta[2]), 0,
0, 0, 1
);
// Combined rotation matrix
Mat R = R_z * R_y * R_x;
return R;
}
Vec3f rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(Mat &R)
{
float sy = sqrt(R.at<double>(0,0) * R.at<double>(0,0) + R.at<double>(1,0) * R.at<double>(1,0) );
bool singular = sy < 1e-6; // If
float x, y, z;
if (!singular)
{
x = atan2(R.at<double>(2,1) , R.at<double>(2,2));
y = atan2(-R.at<double>(2,0), sy);
z = atan2(R.at<double>(1,0), R.at<double>(0,0));
}
else
{
x = atan2(-R.at<double>(1,2), R.at<double>(1,1));
y = atan2(-R.at<double>(2,0), sy);
z = 0;
}
#if 1
x = x*180.0f/3.141592653589793f;
y = y*180.0f/3.141592653589793f;
z = z*180.0f/3.141592653589793f;
#endif
return Vec3f(x, y, z);
}Python语言实现:
python
def rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(rvecs):
R = np.zeros((3, 3), dtype=np.float64)
cv2.Rodrigues(rvecs, R)
sy = math.sqrt(R[0,0] * R[0,0] + R[1,0] * R[1,0])
singular = sy < 1e-6
if not singular:
x = math.atan2(R[2,1] , R[2,2])
y = math.atan2(-R[2,0], sy)
z = math.atan2(R[1,0], R[0,0])
else :
x = math.atan2(-R[1,2], R[1,1])
y = math.atan2(-R[2,0], sy)
z = 0
#print('dst:', R)
x = x*180.0/3.141592653589793
y = y*180.0/3.141592653589793
z = z*180.0/3.141592653589793
return x,y,z
def eulerAnglesToRotationMatrix(angles1) :
theta = np.zeros((3, 1), dtype=np.float64)
theta[0] = angles1[0]*3.141592653589793/180.0
theta[1] = angles1[1]*3.141592653589793/180.0
theta[2] = angles1[2]*3.141592653589793/180.0
R_x = np.array([[1, 0, 0 ],
[0, math.cos(theta[0]), -math.sin(theta[0]) ],
[0, math.sin(theta[0]), math.cos(theta[0]) ]
])
R_y = np.array([[math.cos(theta[1]), 0, math.sin(theta[1]) ],
[0, 1, 0 ],
[-math.sin(theta[1]), 0, math.cos(theta[1]) ]
])
R_z = np.array([[math.cos(theta[2]), -math.sin(theta[2]), 0],
[math.sin(theta[2]), math.cos(theta[2]), 0],
[0, 0, 1]
])
R = np.dot(R_z, np.dot( R_y, R_x ))
sy = math.sqrt(R[0,0] * R[0,0] + R[1,0] * R[1,0])
singular = sy < 1e-6
if not singular:
x = math.atan2(R[2,1] , R[2,2])
y = math.atan2(-R[2,0], sy)
z = math.atan2(R[1,0], R[0,0])
else :
x = math.atan2(-R[1,2], R[1,1])
y = math.atan2(-R[2,0], sy)
z = 0
#print('dst:', R)
x = x*180.0/3.141592653589793
y = y*180.0/3.141592653589793
z = z*180.0/3.141592653589793
#rvecs = np.zeros((1, 1, 3), dtype=np.float64)
#rvecs,_ = cv2.Rodrigues(R, rvecstmp)
return x,y,z3.1 欧拉角和旋转矩阵之间的转换程序示例
cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
using namespace std;
Eigen::Matrix3d eulerAnglesToRotationMatrix(Eigen::Vector3d &theta);
bool isRotationMatirx(Eigen::Matrix3d R);
Eigen::Vector3d rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(Eigen::Matrix3d &R);
const double ARC_TO_DEG = 57.29577951308238;
const double DEG_TO_ARC = 0.0174532925199433;
int main()
{
// 设定车体欧拉角(角度),绕固定轴
double roll_deg = 0.5; // 绕X轴
double pitch_deg = 0.8; // 绕Y轴
double yaw_deg = 108.5; // 绕Z轴
// 转化为弧度
double roll_arc = roll_deg * DEG_TO_ARC; // 绕X轴
double pitch_arc = pitch_deg * DEG_TO_ARC; // 绕Y轴
double yaw_arc = yaw_deg * DEG_TO_ARC; // 绕Z轴
cout << endl;
cout << "roll_arc = " << roll_arc << endl;
cout << "pitch_arc = " << pitch_arc << endl;
cout << "yaw_arc = " << yaw_arc << endl;
// 初始化欧拉角(rpy),对应绕x轴,绕y轴,绕z轴的旋转角度
Eigen::Vector3d euler_angle(roll_arc, pitch_arc, yaw_arc);
// 使用Eigen库将欧拉角转换为旋转矩阵
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix1, rotation_matrix2;
rotation_matrix1 = Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle[2], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle[1], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(euler_angle[0], Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
cout << "\nrotation matrix1 =\n" << rotation_matrix1 << endl << endl;
// 使用自定义函数将欧拉角转换为旋转矩阵
rotation_matrix2 = eulerAnglesToRotationMatrix(euler_angle);
cout << "rotation matrix2 =\n" << rotation_matrix2 << endl << endl;
// 使用Eigen将旋转矩阵转换为欧拉角
Eigen::Vector3d eulerAngle1 = rotation_matrix1.eulerAngles(2,1,0); // ZYX顺序,yaw,pitch,roll
cout << "roll_1 pitch_1 yaw_1 = " << eulerAngle1[2] << " " << eulerAngle1[1]
<< " " << eulerAngle1[0] << endl << endl;
// 使用自定义函数将旋转矩阵转换为欧拉角
Eigen::Vector3d eulerAngle2 = rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(rotation_matrix1); // roll,pitch,yaw
cout << "roll_2 pitch_2 yaw_2 = " << eulerAngle2[0] << " " << eulerAngle2[1]
<< " " << eulerAngle2[2] << endl << endl;
return 0;
}
Eigen::Matrix3d eulerAnglesToRotationMatrix(Eigen::Vector3d &theta)
{
Eigen::Matrix3d R_x; // 计算旋转矩阵的X分量
R_x <<
1, 0, 0,
0, cos(theta[0]), -sin(theta[0]),
0, sin(theta[0]), cos(theta[0]);
Eigen::Matrix3d R_y; // 计算旋转矩阵的Y分量
R_y <<
cos(theta[1]), 0, sin(theta[1]),
0, 1, 0,
-sin(theta[1]), 0, cos(theta[1]);
Eigen::Matrix3d R_z; // 计算旋转矩阵的Z分量
R_z <<
cos(theta[2]), -sin(theta[2]), 0,
sin(theta[2]), cos(theta[2]), 0,
0, 0, 1;
Eigen::Matrix3d R = R_z * R_y * R_x;
return R;
}
bool isRotationMatirx(Eigen::Matrix3d R)
{
double err=1e-6;
Eigen::Matrix3d shouldIdenity;
shouldIdenity=R*R.transpose();
Eigen::Matrix3d I=Eigen::Matrix3d::Identity();
return (shouldIdenity - I).norm() < err;
}
Eigen::Vector3d rotationMatrixToEulerAngles(Eigen::Matrix3d &R)
{
assert(isRotationMatirx(R));
double sy = sqrt(R(0,0) * R(0,0) + R(1,0) * R(1,0));
bool singular = sy < 1e-6;
double x, y, z;
if (!singular)
{
x = atan2( R(2,1), R(2,2));
y = atan2(-R(2,0), sy);
z = atan2( R(1,0), R(0,0));
}
else
{
x = atan2(-R(1,2), R(1,1));
y = atan2(-R(2,0), sy);
z = 0;
}
return {x, y, z};
}程序输出如下:
cpp
roll_arc = 0.00872665
pitch_arc = 0.0139626
yaw_arc = 1.89368
rotation matrix1 =
-0.317274 -0.948326 0.00384548
0.948231 -0.317177 0.0160091
-0.0139622 0.00872568 0.999864
rotation matrix2 =
-0.317274 -0.948326 0.00384548
0.948231 -0.317177 0.0160091
-0.0139622 0.00872568 0.999864
roll_1 pitch_1 yaw_1 = 0.00872665 0.0139626 1.89368
roll_2 pitch_2 yaw_2 = 0.00872665 0.0139626 1.893684.四元素
一个四元数的定义如下:
cpp
q=q0+q1i+q2j+q3k一个四元数拥有一个实部和三个虚部,三个虚部之间满足如下关系。
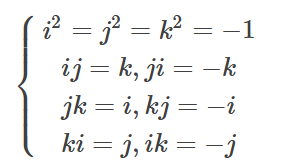
有时四元数也定义成(w,x,y,z)的形式,q0对应w,x、y、z依次对应q1、q2、q3。四元数的定义有了,那么如何用四元数表示旋转呢?如某次旋转是绕某一向量K=(Kx,Ky,Kz)进行了角度为θ的旋转,那么利用四元数就可以表示这个旋转:
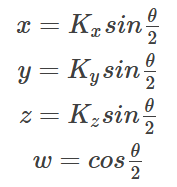
而且满足条件:
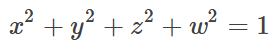
4.1 欧拉角转四元素
设ψ,θ,ϕ分别为绕Z轴、Y轴、X轴的旋转角度,对应Yaw、Pitch、Roll。
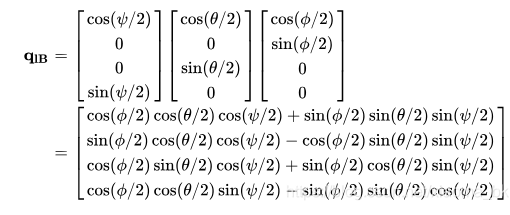
csharp
using System;
public class Quaternion
{
public double W { get; set; }
public double X { get; set; }
public double Y { get; set; }
public double Z { get; set; }
public Quaternion(double w, double x, double y, double z)
{
W = w;
X = x;
Y = y;
Z = z;
}
public override string ToString()
{
return $"Quaternion(W: {W}, X: {X}, Y: {Y}, Z: {Z})";
}
}
public class Program
{
public static Quaternion YDR2Quanterion(double roll, double pitch, double yaw)
{
// 将角度转换为弧度
double rollRad = roll * Math.PI / 180.0;
double pitchRad = pitch * Math.PI / 180.0;
double yawRad = yaw * Math.PI / 180.0;
// 计算每个轴的半角三角函数
double cy = Math.Cos(yawRad * 0.5);
double sy = Math.Sin(yawRad * 0.5);
double cp = Math.Cos(pitchRad * 0.5);
double sp = Math.Sin(pitchRad * 0.5);
double cr = Math.Cos(rollRad * 0.5);
double sr = Math.Sin(rollRad * 0.5);
// 计算四元数分量
double w = cr * cp * cy + sr * sp * sy;
double x = sr * cp * cy - cr * sp * sy;
double y = cr * sp * cy + sr * cp * sy;
double z = cr * cp * sy - sr * sp * cy;
return new Quaternion(w, x, y, z);
}
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
double roll = 30.0; // 你可以修改这里的值来测试
double pitch = 45.0;
double yaw = 60.0;
Quaternion result = YDR2Quanterion(roll, pitch, yaw);
Console.WriteLine(result);
}
}
cpp
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion;
// 依次旋转yaw, pitch, roll
// 即: R = R_z * R_y * R_x
quaternion = Eigen::AngleAxisd(yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY()) *
Eigen::AngleAxisd(roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());而C++相关接口:
cpp
Eigen::AngleAxisd yawAngle(yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ());
Eigen::AngleAxisd pitchAngle(pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY());
Eigen::AngleAxisd rollAngle(roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
Eigen::Quaternion<double> q = yawAngle * pitchAngle * rollAngle;4.2 欧拉角转旋转矩阵
将Z-Y-X欧拉角(或RPY角:绕固定坐标系的X-Y-Z依次旋转α, β, γ角)转换为矩阵:

cpp
// 先转四元数, 再转旋转矩阵
// 依次旋转yaw, pitch, roll
// 即: R = R_z * R_y * R_x
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion = Eigen::AngleAxisd(yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ())*
Eigen::AngleAxisd(pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY())*
Eigen::AngleAxisd(roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
Eigen::Matrix3d rot = quaternion.toRotationMatrix();
cpp
Eigen::AngleAxisd yawAngle(yaw, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitZ());
Eigen::AngleAxisd pitchAngle(pitch, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitY());
Eigen::AngleAxisd rollAngle(roll, Eigen::Vector3d::UnitX());
Eigen::Quaternion<double> q = yawAngle * pitchAngle * rollAngle;
Eigen::Matrix3d rotationMatrix = q.matrix();4.3 四元数转欧拉角

cpp
#define _USE_MATH_DEFINES
#include <cmath>
struct Quaternion {
double w, x, y, z;
};
struct EulerAngles {
double roll, pitch, yaw;
};
EulerAngles ToEulerAngles(Quaternion q) {
EulerAngles angles;
// roll (x-axis rotation)
double sinr_cosp = 2 * (q.w * q.x + q.y * q.z);
double cosr_cosp = 1 - 2 * (q.x * q.x + q.y * q.y);
angles.roll = std::atan2(sinr_cosp, cosr_cosp);
// pitch (y-axis rotation)
double sinp = 2 * (q.w * q.y - q.z * q.x);
if (std::abs(sinp) >= 1)
angles.pitch = std::copysign(M_PI / 2, sinp);
else
angles.pitch = std::asin(sinp);
// yaw (z-axis rotation)
double siny_cosp = 2 * (q.w * q.z + q.x * q.y);
double cosy_cosp = 1 - 2 * (q.y * q.y + q.z * q.z);
angles.yaw = std::atan2(siny_cosp, cosy_cosp);
return angles;
}方式二
cpp
Eigen::Quaterniond qua;
// 按照yaw, pitch, roll的方式进行分解。即:
// euler(0) = yaw
// euler(1) = pitch
// euler(2) = roll
Eigen::Vector3d euler = qua.toRotationMatrix().eulerAngles(2, 1, 0);
return euler;4.4 四元数转旋转矩阵

cpp
QuaternionBase<Derived>::toRotationMatrix(void) const;
Eigen::Quaterniond qua;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 3> rot = qua.toRotationMatrix();4.5 旋转矩阵转四元数

cpp
// 从旋转矩阵构造
Quaternion(const MatrixBase<Derived>& other) { *this = other; }
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 3> rot;
Eigen::Quaterniond qua(rot);4.6 旋转矩阵转欧拉角

cpp
Eigen::Vector3d R_ZYX = R.eulerAngles(2,1,0);
std::cout << yaw, pitch, roll" << R_ZYX.transpose() *180/ M_PI << std::endl;
// 或者
double yaw = atan2(R(1,0),R(0,0)) * 180/ M_PI;5. 四元数、欧拉角、旋转矩阵、旋转向量之间的转换
5.1 旋转向量
1.初始化旋转向量:旋转角为 alpha,旋转轴为 ( x , y , z ) (x,y,z)(x,y,z)
cpp
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector(alpha,Vector3d(x,y,z));2.旋转向量转旋转矩阵
cpp
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix;
rotation_matrix=rotation_vector.matrix();
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix;
rotation_matrix=rotation_vector.toRotationMatrix();3.旋转向量转欧拉角(Z-Y-X内旋,即 RPY)
cpp
//(2,1,0)表示旋转顺序ZYX,数字越小表示优先级越高
Eigen::Vector3d eulerAngle=rotation_vector.matrix().eulerAngles(2,1,0);4.旋转向量转四元数
cpp
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion(rotation_vector);5.2 旋转矩阵
初始化旋转矩阵
cpp
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix;
rotation_matrix<<x_00,x_01,x_02,x_10,x_11,x_12,x_20,x_21,x_22;2.旋转矩阵转旋转向量
cpp
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector(rotation_matrix);
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector;
rotation_vector=rotation_matrix;
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector;
rotation_vector.fromRotationMatrix(rotation_matrix);3.旋转矩阵转欧拉角(Z-Y-X内旋,即 RPY)
cpp
Eigen::Vector3d eulerAngle=rotation_matrix.eulerAngles(2,1,0);4.旋转向量转四元数
cpp
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion(rotation_matrix);
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion;
quaternion=rotation_matrix;5.3 欧拉角
1.初始化欧拉角(Z-Y-X,即RPY)
cpp
Eigen::Vector3d eulerAngle(yaw,pitch,roll);2.欧拉角转旋转向量
cpp
Eigen::AngleAxisd rollAngle(AngleAxisd(eulerAngle(2),Vector3d::UnitX()));
Eigen::AngleAxisd pitchAngle(AngleAxisd(eulerAngle(1),Vector3d::UnitY()));
Eigen::AngleAxisd yawAngle(AngleAxisd(eulerAngle(0),Vector3d::UnitZ()));
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector;
rotation_vector=yawAngle*pitchAngle*rollAngle;3.欧拉角转旋转矩阵
cpp
Eigen::AngleAxisd rollAngle(AngleAxisd(eulerAngle(2),Vector3d::UnitX()));
Eigen::AngleAxisd pitchAngle(AngleAxisd(eulerAngle(1),Vector3d::UnitY()));
Eigen::AngleAxisd yawAngle(AngleAxisd(eulerAngle(0),Vector3d::UnitZ()));
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix;4.欧拉角转四元数
cpp
Eigen::AngleAxisd rollAngle(AngleAxisd(eulerAngle(2),Vector3d::UnitX()));
Eigen::AngleAxisd pitchAngle(AngleAxisd(eulerAngle(1),Vector3d::UnitY()));
Eigen::AngleAxisd yawAngle(AngleAxisd(eulerAngle(0),Vector3d::UnitZ()));
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion;
quaternion=yawAngle*pitchAngle*rollAngle;5.4 四元数
1.初始化四元数
cpp
Eigen::Quaterniond quaternion(w,x,y,z);2.四元数转旋转向量
cpp
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector(quaternion);
Eigen::AngleAxisd rotation_vector;
rotation_vector=quaternion;3.四元数转旋转矩阵
cpp
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix;
rotation_matrix=quaternion.matrix();
Eigen::Matrix3d rotation_matrix;
rotation_matrix=quaternion.toRotationMatrix();4.四元数转欧拉角(Z-Y-X,即RPY)
cpp
// yaw pitch roll
Eigen::Vector3d eulerAngle=quaternion.matrix().eulerAngles(2,1,0);下面代码与上面接口可得到相同结果:
cpp
static Eigen::Vector3d getEulerFromQuternion(const Eigen::Quaterniond& q)
{
double roll, pitch ,yaw;
// roll (x-axis rotation)
double sinr_cosp = +2.0 * (q.w() * q.x() + q.y() * q.z());
double cosr_cosp = +1.0 - 2.0 * (q.x() * q.x() + q.y() * q.y());
roll = atan2(sinr_cosp, cosr_cosp);
// pitch (y-axis rotation)
double sinp = +2.0 * (q.w() * q.y() - q.z() * q.x());
if (fabs(sinp) >= 1)
pitch = copysign(M_PI / 2, sinp); // use 90 degrees if out of range
else
pitch = asin(sinp);
// yaw (z-axis rotation)
double siny_cosp = +2.0 * (q.w() * q.z() + q.x() * q.y());
double cosy_cosp = +1.0 - 2.0 * (q.y() * q.y() + q.z() * q.z());
yaw = atan2(siny_cosp, cosy_cosp);
Eigen::Vector3d eulers;
eulers << yaw, pitch, roll;
return eulers;
}6.学习链接
1.彻底搞懂"旋转矩阵/欧拉角/四元数",让你体会三维旋转之美
5.3D数学基础
8.四元数计算器