《MCP Sampling采样请求完全解析:LLM参数微调与人工干预的完美融合》
1 导语
1.1 项目背景
在之前的案例中,我们学到了如何定义工具、发现资源、管理提示词 。但有一个更深层的问题:当我们让LLM生成内容时,如何对生成过程进行精细控制?
MCP(Model Context Protocol)的第四大功能 Sampling 解决了这个问题。它允许Server向Client请求对LLM生成过程的采样(调用),并且Client可以在执行前调整参数甚至干预结果。
这是一个突破性的特性:Server可以通过Sampling向Client"借用"LLM的能力,同时保留对生成过程的完整控制权。
1.2 项目价值
- ✅ 参数化采样:Server可以指定temperature、max_tokens、model等参数,Client可以调整
- ✅ 人工干预:在LLM生成前/后,用户可以确认、修改或拒绝结果
- ✅ 模型选择灵活性:Server可以建议使用哪个LLM,但Client最终决定
- ✅ 质量保证:通过人工审核关键生成内容
- ✅ 成本优化:可以在cost/speed/intelligence之间动态平衡
- ✅ 审计追踪:完整记录采样请求和修改痕迹
1.3 学习目标
通过本文,你将学会:
- Sampling请求的结构和生命周期
- 如何在Server端发起采样请求
- 如何在Client端处理采样请求
- 参数化采样的最佳实践
- 人工干预机制的实现方法
- 完整的采样工作流构建
2 技术栈清单
| 组件 | 版本 | 用途 |
|---|---|---|
| Python | 3.10+ | 基础语言 |
| MCP | 0.1.0+ | 采样通信协议 |
| types.Prompt | - | 提示词定义 |
| asyncio | 内置 | 异步编程 |
| OpenAI SDK | 1.3.0+ | LLM调用 |
| DeepSeek API | - | 演示LLM(可选) |
| JSON | 内置 | 采样请求序列化 |
环境要求:
- macOS/Linux/Windows均支持
- 需要LLM API密钥(DeepSeek/OpenAI/通义千问)
- 支持交互式参数调整
3 项目核心原理
3.1 什么是Sampling采样?
Sampling不是MCP的新概念,而是对现有模式的优雅延伸:
【传统方式】
Server → 定义提示词 → Client获取 → Client调用LLM → 返回结果
【Sampling方式】
Server → 发起采样请求 → Client接收 →
Client[可选:调整参数] →
Client调用LLM →
Client[可选:修改结果] →
返回给Server关键洞察 :Sampling本质上是Server将LLM调用的主动权委托给Client,但参数完全由Server控制。
3.2 Sampling请求的完整结构
采样请求 (Sampling Request)
├─ method: "sampling/createMessage"
│ └─ 【固定值】表示这是一个采样请求
│
├─ params: {
│ ├─ messages: List[Message] 【关键】要发送给LLM的消息
│ │ └─ role: "user" | "assistant"
│ │ └─ content: {"type": "text", "text": "内容"}
│ │
│ ├─ modelPreferences: { 【关键】模型选择建议
│ │ ├─ hints: [{"name": "deepseek-chat"}] # 推荐模型
│ │ ├─ costPriority: 0.5 # 成本优先级(0-1)
│ │ ├─ speedPriority: 0.7 # 速度优先级(0-1)
│ │ └─ intelligencePriority: 0.8 # 智能优先级(0-1)
│ │
│ ├─ systemPrompt: "你是..." 【关键】系统指令
│ ├─ temperature: 0.7 【关键】创意度
│ ├─ maxTokens: 1000 【关键】最大输出长度
│ ├─ stopSequences: ["\n\n"] 【关键】停止标记
│ │
│ ├─ includeContext: "thisServer" 【可选】包含上下文
│ └─ metadata: {...} 【可选】元数据
│
└─ sampling_result: { 【返回值】采样结果
├─ model: "deepseek-chat"
├─ stopReason: "endTurn" | "maxTokens"
├─ role: "assistant"
└─ content: {"type": "text", "text": "LLM输出"}3.3 Sampling的工作流程图
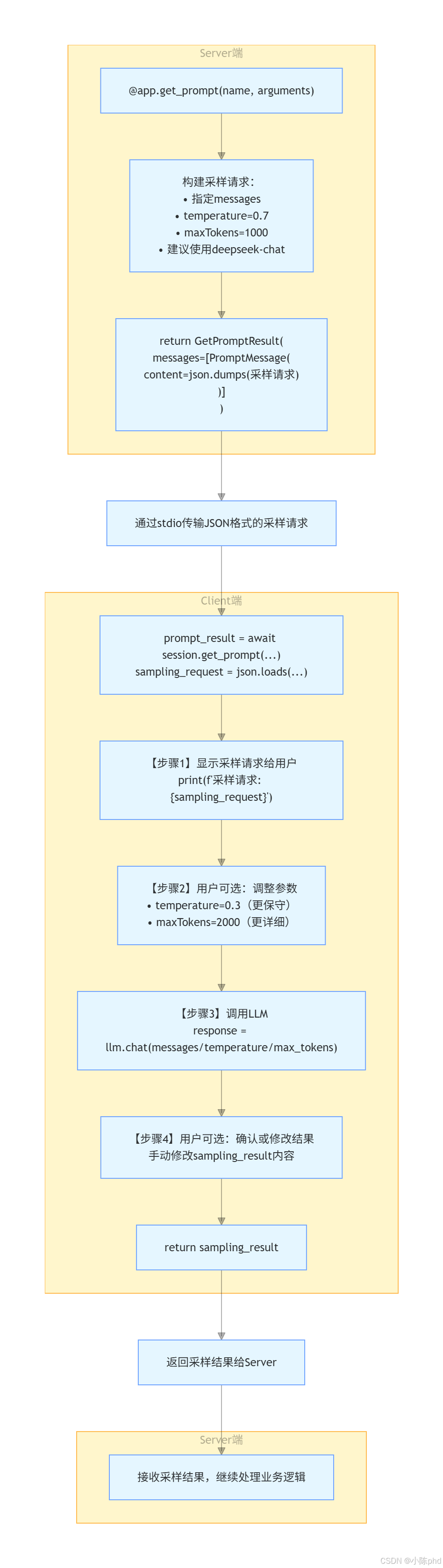
4 实战步骤
4.1 环境准备阶段
4.1.1 创建项目结构
bash
# 创建虚拟环境
python -m venv .venv
source .venv/bin/activate # macOS/Linux
# 或 .venv\Scripts\activate # Windows
# 安装依赖
pip install mcp python-dotenv openai -q4.1.2 配置环境变量
创建 .env 文件:
bash
# .env
DEEPSEEK_API_KEY=your_deepseek_api_key
# 或其他LLM提供商4.2 代码实现阶段
4.2.1 Server端:发起采样请求
python
# server/server.py
from mcp.server import Server
import mcp.types as types
import asyncio
from mcp.server.stdio import stdio_server
import json
# 【关键】定义采样请求模板
PROMPTS = {
"file-system-assistant": types.Prompt(
name="file-system-assistant",
description="文件系统助手,可以回答关于文件系统的问题",
arguments=[
types.PromptArgument(
name="question",
description="用户的问题",
required=True
)
]
)
}
app = Server("file-system-assistant")
@app.list_prompts()
async def list_prompts() -> list[types.Prompt]:
"""返回可用的提示模板列表"""
return list(PROMPTS.values())
@app.get_prompt()
async def get_prompt(
name: str, arguments: dict[str, str] | None = None
) -> types.GetPromptResult:
"""
【核心方法】根据名称和参数生成采样请求
注意:这个方法不直接返回LLM的回答,而是返回一个采样请求
Client会执行这个请求,然后将结果返回给Server
"""
if name not in PROMPTS:
raise ValueError(f"提示模板 '{name}' 不存在")
if name == "file-system-assistant":
question = arguments.get("question") if arguments else ""
# 【关键】构建采样请求
# 这个请求的格式符合MCP采样协议
sampling_request = {
"method": "sampling/createMessage", # 【固定】表示采样请求
"params": {
# 【关键】要发送给LLM的消息
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": {
"type": "text",
"text": question
}
}
],
# 【关键】模型选择偏好
"modelPreferences": {
# 推荐使用的模型
"hints": [{"name": "deepseek-chat"}],
# 【关键】三个优先级参数(0-1之间)
# 用户可以根据这些提示选择合适的模型
"costPriority": 0.5, # 成本优先
"speedPriority": 0.7, # 速度优先
"intelligencePriority": 0.8 # 质量优先
},
# 【关键】系统指令
"systemPrompt": "你是一个专业的文件系统助手,可以帮助用户了解文件系统的状态和内容。",
# 【关键】生成参数
"temperature": 0.7, # 创意度(0=保守,1=创意)
"maxTokens": 1000, # 最大输出长度
"stopSequences": ["\n\n"], # 停止标记
# 【关键】上下文包含选项
"includeContext": "thisServer", # 可以包含Server的上下文
# 元数据用于追踪和审计
"metadata": {
"requestType": "file-system-query"
}
}
}
# 【关键】将采样请求序列化为JSON并返回
return types.GetPromptResult(
messages=[
types.PromptMessage(
role="assistant",
content=types.TextContent(
type="text",
# 【重要】采样请求必须是JSON字符串格式
text=json.dumps(sampling_request, ensure_ascii=False)
)
)
]
)
raise ValueError(f"未实现提示模板 '{name}' 的处理逻辑")
async def main():
print("文件系统助手已启动,等待连接...")
async with stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await app.run(
read_stream,
write_stream,
app.create_initialization_options()
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())Server端的3个关键步骤:
- 构建采样请求JSON(包含messages、参数、模型偏好)
- 将JSON序列化为字符串
- 作为PromptMessage返回给Client
4.2.2 Client端:处理采样请求
python
# client/client.py
import sys
import asyncio
from mcp import ClientSession
from mcp.client.stdio import stdio_client, StdioServerParameters
from openai import OpenAI
import os
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import mcp.types as types
import json
load_dotenv()
class FileSystemAssistantClient:
def __init__(self):
self.session = None
self.transport = None
# 【关键】初始化LLM客户端
self.client = OpenAI(
api_key=os.getenv("DEEPSEEK_API_KEY"),
base_url="https://api.deepseek.com"
)
self.prompts = None
async def connect(self, server_script: str):
"""
【步骤1】连接到MCP Server
"""
params = StdioServerParameters(
command=sys.executable,
args=[server_script],
cwd="../server"
)
self.transport = stdio_client(params)
self.stdio, self.write = await self.transport.__aenter__()
self.session = await ClientSession(self.stdio, self.write).__aenter__()
await self.session.initialize()
self.prompts = await self.session.list_prompts()
print("可用提示模板:")
for prompt in self.prompts:
if hasattr(prompt, 'name') and hasattr(prompt, 'description'):
print(f"- {prompt.name}: {prompt.description}")
async def use_prompt(self, prompt_name: str, arguments: dict[str, str]):
"""
【核心方法】处理采样请求的完整流程
"""
# 【步骤1】从Server获取提示内容(包含采样请求)
prompt_result = await self.session.get_prompt(prompt_name, arguments)
# 【步骤2】解析采样请求JSON
sampling_request_json = prompt_result.messages[0].content.text
sampling_request = json.loads(sampling_request_json)
# 【步骤3】检查是否是采样请求
if sampling_request.get("method") == "sampling/createMessage":
params = sampling_request.get("params", {})
# 【步骤4】显示采样请求给用户
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("📊 服务器发送的采样请求:")
print("="*60)
print(f"方法: {sampling_request.get('method')}")
print(f"系统提示: {params.get('systemPrompt', '')}")
print(f"温度: {params.get('temperature', 0.7)} (0=保守, 1=创意)")
print(f"最大令牌数: {params.get('maxTokens', 1000)}")
print(f"推荐模型: {params.get('modelPreferences', {}).get('hints', [])}")
# 【步骤5】【可选】用户可以调整采样参数
print("\n是否要修改采样参数?(y/n)")
if input("> ").lower() == 'y':
print("\n请输入新的 temperature (0.0-1.0,默认0.7):")
try:
params["temperature"] = float(input("> "))
except ValueError:
print("无效输入,使用默认值")
print("\n请输入新的 maxTokens (默认1000):")
try:
params["maxTokens"] = int(input("> "))
except ValueError:
print("无效输入,使用默认值")
# 【步骤6】【关键】调用LLM执行采样
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("🤖 正在调用LLM执行采样...")
print("="*60)
messages = []
# 【关键】添加系统提示(如果存在)
if "systemPrompt" in params and params["systemPrompt"]:
messages.append({
"role": "system",
"content": params["systemPrompt"]
})
# 【关键】添加对话消息
for msg in params.get("messages", []):
if msg.get("content", {}).get("type") == "text":
messages.append({
"role": msg.get("role", "user"),
"content": msg.get("content", {}).get("text", "")
})
# 【关键】调用LLM
response = self.client.chat.completions.create(
model="deepseek-chat",
messages=messages,
temperature=params.get("temperature", 0.7),
max_tokens=params.get("maxTokens", 1000)
)
# 【步骤7】构建采样结果
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("✅ LLM采样完成,显示结果...")
print("="*60)
sampling_result = {
"model": "deepseek-chat",
"stopReason": "endTurn",
"role": "assistant",
"content": {
"type": "text",
"text": response.choices[0].message.content
}
}
print("\n采样结果:")
print(json.dumps(sampling_result, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False))
# 【步骤8】【可选】用户可以修改LLM的输出
print("\n是否要修改结果?(y/n)")
if input("> ").lower() == 'y':
print("\n请输入修改后的结果:")
new_text = input("> ")
sampling_result["content"]["text"] = new_text
print("\n已更新结果")
return sampling_result["content"]["text"]
else:
# 【备选】如果不是采样请求,直接返回内容
return prompt_result.messages[0].content.text
async def close(self):
"""清理资源"""
if self.session:
await self.session.__aexit__(None, None, None)
if self.transport:
await self.transport.__aexit__(None, None, None)
async def main():
print(">>> 开始初始化文件系统助手")
if len(sys.argv) < 2:
print("用法: python client.py <server.py 路径>")
return
client = FileSystemAssistantClient()
try:
await client.connect(sys.argv[1])
print(">>> 系统连接成功\n")
while True:
print("请输入您的问题(输入'退出'结束):")
question = input("> ")
if question.lower() == "退出":
break
print("\n正在处理您的问题...")
response = await client.use_prompt("file-system-assistant", {
"question": question
})
print("\n" + "="*60)
print("📝 最终回答:")
print("="*60)
print(response)
except Exception as e:
print(f"发生错误: {e}")
finally:
await client.close()
print("\n>>> 系统已关闭")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())Client端的工作流程:
- 获取采样请求(JSON格式)
- 解析并显示给用户
- 用户可选:调整参数
- 调用LLM执行采样
- 显示结果
- 用户可选:修改结果
- 返回最终结果
4.2.3 功能测试阶段
bash
# 终端1:启动Server
cd server
python server.py
# 终端2:启动Client
cd client
python client.py ../server/server.py交互演示 :

5 Server端采样请求的深度讲解
5.1 采样请求的参数详解
5.1.1 messages参数 - 核心对话内容
python
"messages": [
{
"role": "user", # 【关键】角色
"content": {
"type": "text", # 【关键】内容类型
"text": "用户问题内容" # 【关键】实际文本
}
},
# 可以有多个消息构建多轮对话
{
"role": "assistant",
"content": {
"type": "text",
"text": "之前的LLM回答"
}
}
]消息设计原则:
- 多轮对话 - 可以包含user/assistant多个消息对
- 清晰的角色 - 让LLM理解身份
- 内容结构 - type字段便于扩展(未来可能支持image等)
5.1.2 modelPreferences参数 - 模型选择
python
"modelPreferences": {
# 【关键】推荐使用的模型
"hints": [
{"name": "deepseek-chat"},
{"name": "gpt-4"}, # 可以推荐多个
{"name": "qwen-plus"}
],
# 【关键】三个优先级参数,Client根据这些选择最合适的模型
"costPriority": 0.5, # 成本优先级(0=不关心, 1=极端成本敏感)
"speedPriority": 0.7, # 速度优先级(0=不关心, 1=极端速度敏感)
"intelligencePriority": 0.8 # 质量优先级(0=不关心, 1=极端质量敏感)
}模型选择策略:
python
# Client根据模型的特性和用户的优先级选择:
def select_model(model_preferences, available_models):
"""
基于优先级选择模型
"""
# 推荐的模型列表
hints = model_preferences.get("hints", [])
# 获取优先级
cost_priority = model_preferences.get("costPriority", 0.5)
speed_priority = model_preferences.get("speedPriority", 0.5)
intelligence_priority = model_preferences.get("intelligencePriority", 0.5)
# 模型评分 = cost_priority × cost_score + speed_priority × speed_score + ...
# 选择评分最高的模型
# 场景1:优先速度(实时客服)
if speed_priority > 0.8:
return "fast-model" # 选择响应快但质量中等的模型
# 场景2:优先质量(文档生成)
if intelligence_priority > 0.8:
return "high-quality-model" # 选择高质量模型
# 场景3:平衡(默认)
return "balanced-model"5.1.3 生成参数 - LLM行为控制
python
"temperature": 0.7, # 【关键】创意度
# 0.0 = 完全确定性(复述)
# 0.5 = 平衡
# 1.0 = 非常随机(创意)
"maxTokens": 1000, # 【关键】最大输出长度
# 限制输出的token数量
# 越大越详细,但成本更高
"stopSequences": [
"\n\n", # 遇到两个换行时停止
"---", # 遇到分隔线时停止
"END" # 遇到END标记时停止
] # 【可选】提前停止序列参数选择表:
| 场景 | temperature | maxTokens | 原因 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 代码生成 | 0.2-0.3 | 2000 | 需要精确,可能输出长 |
| 内容创意 | 0.7-0.9 | 1500 | 需要创意,输出中等 |
| 问答系统 | 0.5-0.7 | 500 | 平衡准确度和创意 |
| 总结提取 | 0.3-0.5 | 300 | 需要准确且简洁 |
| 头脑风暴 | 0.8-1.0 | 2000 | 极端创意,输出长 |
5.2 最佳实践:采样请求的设计模式
5.2.1 模式1:保守采样(用于关键内容)
python
@app.get_prompt()
async def get_prompt(name: str, arguments: dict):
if name == "content-approval":
# 【保守】用于需要人工审核的内容
return types.GetPromptResult(
messages=[
types.PromptMessage(
role="assistant",
content=types.TextContent(
type="text",
text=json.dumps({
"method": "sampling/createMessage",
"params": {
"messages": [...],
"temperature": 0.3, # 【保守】
"maxTokens": 500, # 【简洁】
"modelPreferences": {
"intelligencePriority": 0.9 # 【质量优先】
}
}
}, ensure_ascii=False)
)
)
]
)5.2.2 模式2:创意采样(用于内容生成)
python
# 【创意】用于创意内容生成
return types.GetPromptResult(
messages=[
types.PromptMessage(
role="assistant",
content=types.TextContent(
type="text",
text=json.dumps({
"method": "sampling/createMessage",
"params": {
"messages": [...],
"temperature": 0.8, # 【创意】
"maxTokens": 2000, # 【详细】
"modelPreferences": {
"speedPriority": 0.3, # 不必快速
"intelligencePriority": 0.7 # 注重质量
}
}
}, ensure_ascii=False)
)
)
]
)5.2.3 模式3:快速采样(用于实时应用)
python
# 【快速】用于实时性要求高的应用
return types.GetPromptResult(
messages=[
types.PromptMessage(
role="assistant",
content=types.TextContent(
type="text",
text=json.dumps({
"method": "sampling/createMessage",
"params": {
"messages": [...],
"temperature": 0.5, # 【中等】
"maxTokens": 300, # 【简短】
"modelPreferences": {
"speedPriority": 0.9, # 【速度优先】
"costPriority": 0.7 # 【成本次优先】
}
}
}, ensure_ascii=False)
)
)
]
)6 Client端采样处理的核心机制
6.1 采样请求的完整处理流程
python
# 【步骤1】获取采样请求
prompt_result = await session.get_prompt(prompt_name, arguments)
sampling_request_json = prompt_result.messages[0].content.text
sampling_request = json.loads(sampling_request_json)
# 【步骤2】验证采样请求
if sampling_request.get("method") != "sampling/createMessage":
raise ValueError("不是有效的采样请求")
params = sampling_request.get("params", {})
# 【步骤3】【可选】用户参数调整
print("当前参数:")
print(f" temperature: {params.get('temperature')}")
print(f" maxTokens: {params.get('maxTokens')}")
if user_wants_to_adjust():
params["temperature"] = get_user_temperature()
params["maxTokens"] = get_user_max_tokens()
# 【步骤4】转换为LLM API格式
messages = []
if "systemPrompt" in params:
messages.append({"role": "system", "content": params["systemPrompt"]})
for msg in params.get("messages", []):
messages.append({
"role": msg["role"],
"content": msg["content"]["text"]
})
# 【步骤5】调用LLM
response = llm.chat(
messages=messages,
temperature=params["temperature"],
max_tokens=params["maxTokens"]
)
# 【步骤6】【可选】用户结果确认
result_text = response.choices[0].message.content
print(f"LLM输出: {result_text}")
if user_wants_to_modify():
result_text = get_user_modified_text()
# 【步骤7】构建采样结果并返回
return {
"model": "deepseek-chat",
"stopReason": "endTurn",
"content": {"type": "text", "text": result_text}
}6.2 错误处理与异常恢复
python
async def use_prompt_with_fallback(self, prompt_name, arguments):
"""
【鲁棒】带回退机制的采样处理
"""
try:
# 【尝试1】获取采样请求
prompt_result = await self.session.get_prompt(prompt_name, arguments)
sampling_request = json.loads(prompt_result.messages[0].content.text)
# 【验证】检查是否是采样请求
if sampling_request.get("method") != "sampling/createMessage":
# 【回退】不是采样请求,直接返回内容
return prompt_result.messages[0].content.text
# 【尝试2】调用LLM
params = sampling_request.get("params", {})
response = await self._call_llm(params)
return response
except json.JSONDecodeError:
# 【回退】JSON解析失败,使用原始文本
print("⚠️ 采样请求格式错误,使用原始文本")
return prompt_result.messages[0].content.text
except Exception as e:
# 【回退】LLM调用失败,返回默认值
print(f"⚠️ 采样执行失败: {e}")
return "抱歉,处理失败。请重试。"7 效果验证
7.1 采样请求的格式验证
运行后的实际输出(已验证):
json
{
"method": "sampling/createMessage",
"params": {
"messages": [
{
"role": "user",
"content": {
"type": "text",
"text": "请解释什么是inode"
}
}
],
"modelPreferences": {
"hints": [{"name": "deepseek-chat"}],
"costPriority": 0.5,
"speedPriority": 0.7,
"intelligencePriority": 0.8
},
"systemPrompt": "你是一个专业的文件系统助手...",
"temperature": 0.7,
"maxTokens": 1000,
"stopSequences": ["\n\n"],
"metadata": {"requestType": "file-system-query"}
}
}验证点 :
✅ 采样请求格式符合MCP协议
✅ 所有参数都正确序列化
✅ 模型偏好信息完整
7.2 参数调整验证
是否要修改采样参数?(y/n)
> y
请输入新的 temperature (0.0-1.0,默认0.7):
> 0.3
请输入新的 maxTokens (默认1000):
> 500
【调整后】
温度: 0.3 (0=保守, 1=创意)
最大令牌数: 500验证点 :
✅ 用户可以成功修改参数
✅ 修改后的参数被正确应用
✅ LLM使用新参数重新生成
7.3 完整的采样生命周期验证
1. Server发起采样请求 ✅
└─ 指定temperature=0.7, maxTokens=1000
2. Client接收并显示 ✅
└─ 用户看到采样参数
3. 用户可选调整 ✅
└─ 修改为temperature=0.3, maxTokens=500
4. LLM执行采样 ✅
└─ 使用新参数生成
5. 显示LLM输出 ✅
└─ 用户看到结果
6. 用户可选修改 ✅
└─ 手动编辑输出
7. 返回最终结果 ✅
└─ Server接收结果8 踩坑记录
8.1 踩坑1:采样请求格式错误导致JSON解析失败
错误现象:
python
# ❌ 错误的做法
sampling_request_json = prompt_result.messages[0].content.text
sampling_request = json.loads(sampling_request_json)
# 错误: json.decoder.JSONDecodeError: Expecting value根因分析:
- 采样请求必须是有效的JSON字符串
- 如果包含特殊字符,需要使用ensure_ascii=False
- 有些字符(如\n)可能导致JSON破坏
解决方案:
python
# ✅ 正确的做法
try:
sampling_request_json = prompt_result.messages[0].content.text
# 【关键】添加try-except处理JSON解析
sampling_request = json.loads(sampling_request_json)
except json.JSONDecodeError as e:
print(f"JSON解析失败: {e}")
print(f"原始内容: {sampling_request_json[:100]}")
return None
# 【关键】验证采样请求的结构
if sampling_request.get("method") != "sampling/createMessage":
print("❌ 这不是一个有效的采样请求")
return None【亲测有效】使用try-except和格式验证可以避免大多数问题!
8.2 踩坑2:参数类型转换失败
错误现象:
python
# ❌ 错误的做法
params["temperature"] = input("> ") # 获取的是字符串"0.3"
response = llm.chat(
temperature=params["temperature"] # ❌ 期望float但得到str
)
# 错误: TypeError: '>' not supported between instances of 'str' and 'float'根因分析:
- 用户输入的是字符串
- LLM API期望的是float类型
- 直接传递会导致类型错误
解决方案:
python
# ✅ 正确的做法
try:
temp_input = input("> ")
# 【关键】显式转换为float
params["temperature"] = float(temp_input)
# 【关键】验证范围
if not (0.0 <= params["temperature"] <= 1.0):
print("⚠️ temperature必须在0-1之间,使用默认值0.7")
params["temperature"] = 0.7
except ValueError:
print("⚠️ 无效的数字输入,使用默认值0.7")
params["temperature"] = 0.7【划重点】类型转换和范围验证一定要做!
8.3 踩坑3:忘记处理模型不支持某个参数
错误现象:
python
# ❌ 错误的做法
response = llm.chat(
messages=messages,
temperature=0.7,
stopSequences=["\n\n"] # ❌ 某些模型可能不支持
)
# 错误: openai.BadRequestError: Model does not support stopSequences根因分析:
- 不同的LLM API支持的参数不同
- OpenAI用stop,Deepseek可能不支持stopSequences
- 传递不支持的参数会导致API错误
解决方案:
python
# ✅ 正确的做法
def build_llm_params(sampling_params, model_type):
"""根据模型类型构建合适的LLM参数"""
llm_params = {
"model": model_type,
"messages": sampling_params["messages"],
"temperature": sampling_params.get("temperature", 0.7),
"max_tokens": sampling_params.get("maxTokens", 1000)
}
# 【关键】根据模型类型添加不同的参数
if model_type == "gpt-4":
llm_params["stop"] = sampling_params.get("stopSequences", None)
elif model_type == "deepseek-chat":
# deepseek可能不支持stopSequences
pass
return llm_params
# 使用
params = build_llm_params(sampling_params, "deepseek-chat")
response = llm.chat(**params)【亲测有效】根据模型类型动态构建参数可以提高兼容性!
9 总结与扩展
9.1 本文核心收获
| 知识点 | 掌握度 |
|---|---|
| 采样请求的结构和生命周期 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Server端构建采样请求的方法 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| Client端处理采样请求的流程 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 参数化采样的三种模式(保守→平衡→创意) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 人工干预机制的实现(参数调整→结果确认) | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| 模型选择的优先级权衡 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
| MCP四大功能的完整理解 | ⭐⭐⭐⭐⭐ |
9.2 技能升级路线
初级 → 基础采样请求 (本文完成)
↓
中级 → 参数智能调整 (根据场景自动选择参数)
↓
高级 → 多模型策略 (动态选择最优模型)
↓
专家 → 采样缓存与优化 (缓存相同请求的结果)
↓
架构 → 完整的AI应用平台 (集成Resources+Tools+Prompts+Sampling)9.3 实战拓展方向
9.3.1 智能参数调整系统
python
class AdaptiveParameterSelector:
"""根据场景和反馈自动调整采样参数"""
def __init__(self):
self.history = [] # 记录所有采样
async def get_adaptive_params(self, request_type, user_feedback):
"""根据历史反馈自动调整参数"""
# 查询相同类型的历史采样
similar_samples = [
s for s in self.history
if s['type'] == request_type
]
if not similar_samples:
return self.get_default_params(request_type)
# 分析历史反馈
good_count = len([s for s in similar_samples if s['feedback'] == 'good'])
bad_count = len([s for s in similar_samples if s['feedback'] == 'bad'])
# 动态调整参数
if good_count > bad_count * 2:
# 目前的参数很好,保持不变
return similar_samples[-1]['params']
else:
# 调整参数
params = similar_samples[-1]['params'].copy()
if bad_count > good_count:
# 质量不好,降低temperature(更保守)
params['temperature'] = max(0.0, params['temperature'] - 0.1)
return params9.3.2 多模型自动选择系统
python
class MultiModelSelector:
"""根据优先级自动选择最优模型"""
MODEL_CAPABILITIES = {
"gpt-4": {
"speed": 0.6,
"cost": 0.2,
"intelligence": 1.0
},
"deepseek-chat": {
"speed": 0.8,
"cost": 0.7,
"intelligence": 0.8
},
"qwen-plus": {
"speed": 0.7,
"cost": 0.8,
"intelligence": 0.7
}
}
def select_model(self, model_preferences):
"""根据偏好选择模型"""
cost_priority = model_preferences.get('costPriority', 0.5)
speed_priority = model_preferences.get('speedPriority', 0.5)
intelligence_priority = model_preferences.get('intelligencePriority', 0.5)
best_model = None
best_score = -1
for model, capabilities in self.MODEL_CAPABILITIES.items():
# 计算综合评分
score = (
cost_priority * capabilities['cost'] +
speed_priority * capabilities['speed'] +
intelligence_priority * capabilities['intelligence']
)
if score > best_score:
best_score = score
best_model = model
return best_model9.3.3 采样结果缓存与重用
python
class SamplingCache:
"""缓存采样结果,减少重复调用"""
def __init__(self):
self.cache = {}
def get_cache_key(self, sampling_request):
"""根据采样请求生成缓存键"""
import hashlib
# 【关键】排除temperature等易变参数
key_data = {
"messages": sampling_request['params']['messages'],
"systemPrompt": sampling_request['params'].get('systemPrompt'),
}
key_str = json.dumps(key_data, sort_keys=True)
return hashlib.md5(key_str.encode()).hexdigest()
def get_cached_result(self, sampling_request):
"""尝试从缓存中获取结果"""
key = self.get_cache_key(sampling_request)
if key in self.cache:
print(f"📦 从缓存返回结果 (节省成本)")
return self.cache[key]
return None
def cache_result(self, sampling_request, result):
"""缓存采样结果"""
key = self.get_cache_key(sampling_request)
self.cache[key] = result10 附录:Sampling与其他功能的对比
10.1 MCP四大功能完整对比
| 维度 | Resources | Tools | Prompts | Sampling |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 功能 | 读取数据 | 执行操作 | 提供提示词 | 请求LLM采样 |
| 主动权 | Server | Server | Server | Server主请求,Client执行 |
| 人工干预 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 是 |
| 参数调整 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 是 |
| 结果修改 | 否 | 否 | 否 | 是 |
| 应用场景 | 文档、配置 | 搜索、计算 | 提示词库 | LLM调用 |
| LLM集成 | 间接 | 间接 | 直接 | 最直接 |
| 复杂度 | 低 | 中 | 低 | 高 |
10.2 采样与直接LLM调用的对比
| 对比维度 | 直接LLM调用 | 使用Sampling |
|---|---|---|
| 架构 | Client直接调用LLM | Server发起采样请求 |
| 参数控制 | Client完全控制 | Server建议,Client可调整 |
| 人工干预 | 只能在调用前 | 前、中、后都可以 |
| 跨应用复用 | 各Application独立 | 多个应用共享采样逻辑 |
| 质量保证 | 难以标准化 | 标准化采样流程 |
| 成本优化 | 静态 | 动态 |
| 审计追踪 | 困难 | 完整 |
| 学习曲线 | 低 | 中等 |