摘要:随机森林是一种集成学习算法,通过构建多个决策树并综合其预测结果来提高准确性。该算法具有抗过拟合、处理缺失数据、识别特征重要性等优势。本文详细介绍了其工作原理,包括随机抽样、构建决策树、投票预测等步骤,并提供了Python实现示例(使用Iris数据集)。虽然随机森林准确率高、适用性强,但也存在计算复杂度高、预测速度慢等缺点。实验结果显示该算法在测试集上达到98.1%的准确率,验证了其有效性。
目录
[步骤1 − 导入库](#步骤1 − 导入库)
[步骤2 − 加载数据](#步骤2 − 加载数据)
[步骤3 − 数据预处理](#步骤3 − 数据预处理)
[步骤4 − 训练模型](#步骤4 − 训练模型)
[步骤5 − 做出预测](#步骤5 − 做出预测)
[步骤6 − 模型评估](#步骤6 − 模型评估)
随机森林是一种机器学习算法,利用一组决策树进行预测。该算法最早由Leo Breiman于2001年提出。该算法的核心思想是创建大量决策树,每个决策树训练于不同的数据子集。这些单独树的预测随后被合并,生成最终预测。
随机森林算法的工作原理
我们可以通过以下步骤理解随机森林算法的工作原理------
-
步骤1 − 首先,从给定数据集中随机抽取样本开始。
-
步骤2 − 接下来,该算法将为每个样本构建决策树。然后它会从每个决策树中获得预测结果。
-
步骤3 − 在此阶段,将对每个预测结果进行投票。
-
步骤4 − 最后,选择投票最多的预测结果作为最终预测结果。
下图展示了随机森林算法的工作原理------
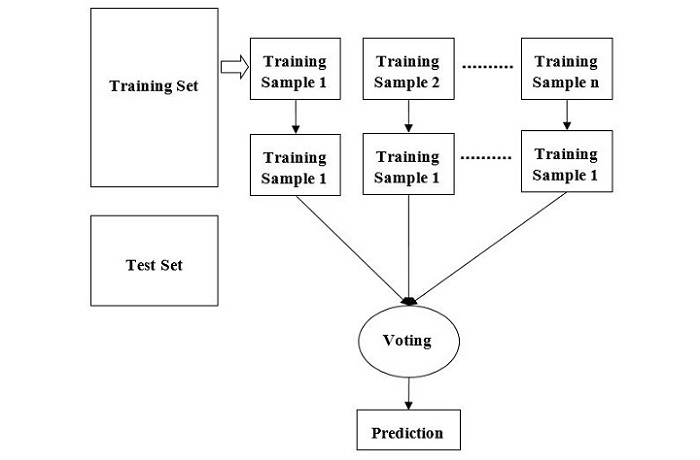
随机森林是一种灵活的算法,既可用于分类任务,也可用于回归任务。在分类任务中,算法利用单个树的预测模式来做出最终预测。在回归任务中,算法使用单个树预测的平均值。
随机森林算法的优势
随机森林算法相比其他机器学习算法有多个优势。其中一些主要优势包括 −
-
对过拟合的鲁棒性 − 随机森林算法以其对过拟合的鲁棒性著称。这是因为该算法使用决策树的集合,有助于减少数据中离群值和噪声的影响。
-
高精度 − 随机森林算法以其高准确率著称。这是因为该算法结合了多个决策树的预测,有助于减少单个决策树可能存在偏见或不准确的影响。
-
处理缺失数据 − 随机森林算法可以处理缺失数据而无需补全。这是因为算法只考虑每个数据点可用的特征,并不要求所有数据点都具备所有特征。
-
非线性关系 − 随机森林算法可以处理特征与目标变量之间的非线性关系。这是因为该算法使用决策树,可以模拟非线性关系。
-
特征重要性 − 随机森林算法可以提供模型中每个特征的重要性信息。这些信息可用于识别数据中最重要的特征,并可用于特征选择和特征工程。
Python中随机森林算法的实现
让我们看看Python中随机森林算法的实现。我们将使用 scikit-learn 库来实现该算法。scikit-learn库是一个流行的机器学习库,提供广泛的机器学习算法和工具。
步骤1 − 导入库
我们将先导入必要的库。我们将使用pandas库进行数据作,scikit-learn库用于实现随机森林算法。
python
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier步骤2 − 加载数据
接下来,我们将数据加载到pandas数据帧中。在本教程中,我们将使用著名的Iris数据集,这是分类任务的经典数据集。
python
# Loading the iris dataset
iris = pd.read_csv('https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learningdatabases/iris/iris.data', header=None)
iris.columns = ['sepal_length', 'sepal_width', 'petal_length','petal_width', 'species']步骤3 − 数据预处理
在我们用数据训练模型之前,需要先进行预处理。这包括将特征和目标变量分离,并将数据拆分为训练集和测试集。
python
# Separating the features and target variable
X = iris.iloc[:, :-1]
y = iris.iloc[:, -1]
# Splitting the data into training and testing sets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.35, random_state=42)步骤4 − 训练模型
接下来,我们将基于训练数据训练随机森林分类器。
python
# Creating the Random Forest classifier object
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)
# Training the model on the training data
rfc.fit(X_train, y_train)步骤5 − 做出预测
一旦我们训练好模型,就可以用它对测试数据做预测。
python
# Making predictions on the test data
y_pred = rfc.predict(X_test)步骤6 − 模型评估
最后,我们将利用准确性、精度、召回率和F1分数等多种指标评估模型的性能。
python
# Importing the metrics library
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score,
recall_score, f1_score
# Calculating the accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
precision = precision_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted')
recall = recall_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted')
f1 = f1_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted')
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)
print("Precision:", precision)
print("Recall:", recall)
print("F1-score:", f1)完整实现示例
以下是使用 iris 数据集 − 的完整示例 Python 中随机森林算法的实现示例
python
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
# Loading the iris dataset
iris = pd.read_csv('https://archive.ics.uci.edu/ml/machine-learningdatabases/iris/iris.data', header=None)
iris.columns = ['sepal_length', 'sepal_width', 'petal_length', 'petal_width', 'species']
# Separating the features and target variable
X = iris.iloc[:, :-1]
y = iris.iloc[:, -1]
# Splitting the data into training and testing sets
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y,
test_size=0.35, random_state=42)
# Creating the Random Forest classifier object
rfc = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100)
# Training the model on the training data
rfc.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Making predictions on the test data
y_pred = rfc.predict(X_test)
# Importing the metrics library
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, precision_score,
recall_score, f1_score
# Calculating the accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score
accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
precision = precision_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted')
recall = recall_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted')
f1 = f1_score(y_test, y_pred, average='weighted')
print("Accuracy:", accuracy)
print("Precision:", precision)
print("Recall:", recall)
print("F1-score:", f1)输出
这将给出随机森林分类器的性能指标如下 −
Accuracy: 0.9811320754716981
Precision: 0.9821802935010483
Recall: 0.9811320754716981
F1-score: 0.9811157396063056随机森林的优缺点
优点
以下是随机森林算法的优势------
它通过平均或组合不同决策树的结果来克服过拟合的问题。
随机森林对大量数据项的处理效果比单一决策树更有效。
随机森林的方差比单一决策树更小。
随机森林非常灵活,准确率很高。
随机森林算法不需要数据的缩放。即使提供数据且未进行扩展,它依然保持良好的准确性。
随机森林算法不需要数据的缩放。即使提供数据且未进行扩展,它依然保持良好的准确性。
缺点
以下是随机森林算法的缺点 −
复杂性是随机森林算法的主要缺点。
构建随机森林比决策树更为困难且耗时。
实现随机森林算法需要更多的计算资源。
当我们有大量决策树时,这种方式就不那么直观了。
使用随机森林进行预测过程相比其他算法非常耗时。