简介
Cache(缓存),已经是项目中不可缺失的存在,登录时,存储用户信息、操作权限、Token 等,高并发场景,存储热点信息、实时信息等。按照类型分类,可分为本地缓存和分布式缓存,前者重启服务失效,后者可以持久化,按照设置的过期时间或策略失效。
一旦项目中需要使用到缓存,就需要考虑到数据一致性问题,即缓存数据与数据库数据的一致性问题,本文介绍在 Spring Boot 项目中,如何使用 Spring 自带的注解来进行数据一致性的维护。
整合
Spring 自带了缓存维护的注解,如果你的项目就是 Spring/Spring Boot 项目,不需要额外引入依赖
但如果你需要缓存不会因项目重启而失效,可以引入 Redis,把 Redis 当作缓存容器,需引入 Redis 依赖。基本所有的项目都会用到 Redis,当然引入了就需要保证系统与 Redis 的连通。
xml
<!-- 引入 Redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>在项目中创建一个 Redis 缓存配置类,里面对缓存进行统一的配置,如过期时间等。
java
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.cache.RedisCacheManager;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializationContext;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.StringRedisSerializer;
import java.time.Duration;
/**
* Redis 缓存配置
*/
@Configuration
@EnableCaching
public class RedisCacheConfig {
@Bean
public RedisCacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30))
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new StringRedisSerializer()))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(new GenericJackson2JsonRedisSerializer()));
return RedisCacheManager.builder(connectionFactory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
}
}配置文件中,添加 Redis 配置。
yml
spring:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379使用
配合下面几个注解使用,可以加在接口上,如下,cacheNames 是设置缓存名称,key 设置缓存的 key 值,可以用 # 与方法入参关联,如 #id 表示 key 值取自方法入参 id 的值。
-
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "缓存名", key = "#id"):添加缓存;
-
@CachePut(cacheNames = "缓存名", key = "#id"):执行方法后,添加缓存;
-
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "缓存名", key = "#id"):使缓存失效;
需要注意的是,这套缓存作用的机制是,关联方法入参与返回,当方法入参相同时,返回缓存中的结果,不再执行代码。所以只有相同的入参才能用得上缓存。
验证
创建下面这四个接口,查询方法添加缓存,新增方法执行后添加缓存,删除和更新方法删除缓存。
java
import org.example.service.CacheService;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/cache")
public class CacheController {
@Resource
private CacheService cacheService;
@GetMapping("/getOne")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cacheName", key = "#id")
public String getOne(@RequestParam String id) {
return cacheService.getOne();
}
@PostMapping("/createOne")
@CachePut(cacheNames = "cacheName", key = "#id")
public String createOne(@RequestParam String id) {
return cacheService.createOne();
}
@PostMapping("/deleteOne")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "cacheName", key = "#id")
public String deleteOne(@RequestParam String id) {
return cacheService.deleteOne();
}
@PostMapping("/updateOne")
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "cacheName", key = "#id", allEntries = true)
public String updateOne(@RequestParam String id) {
return cacheService.updateOne();
}
}对应的实现类代码。
java
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class CacheServiceImpl implements CacheService {
@Override
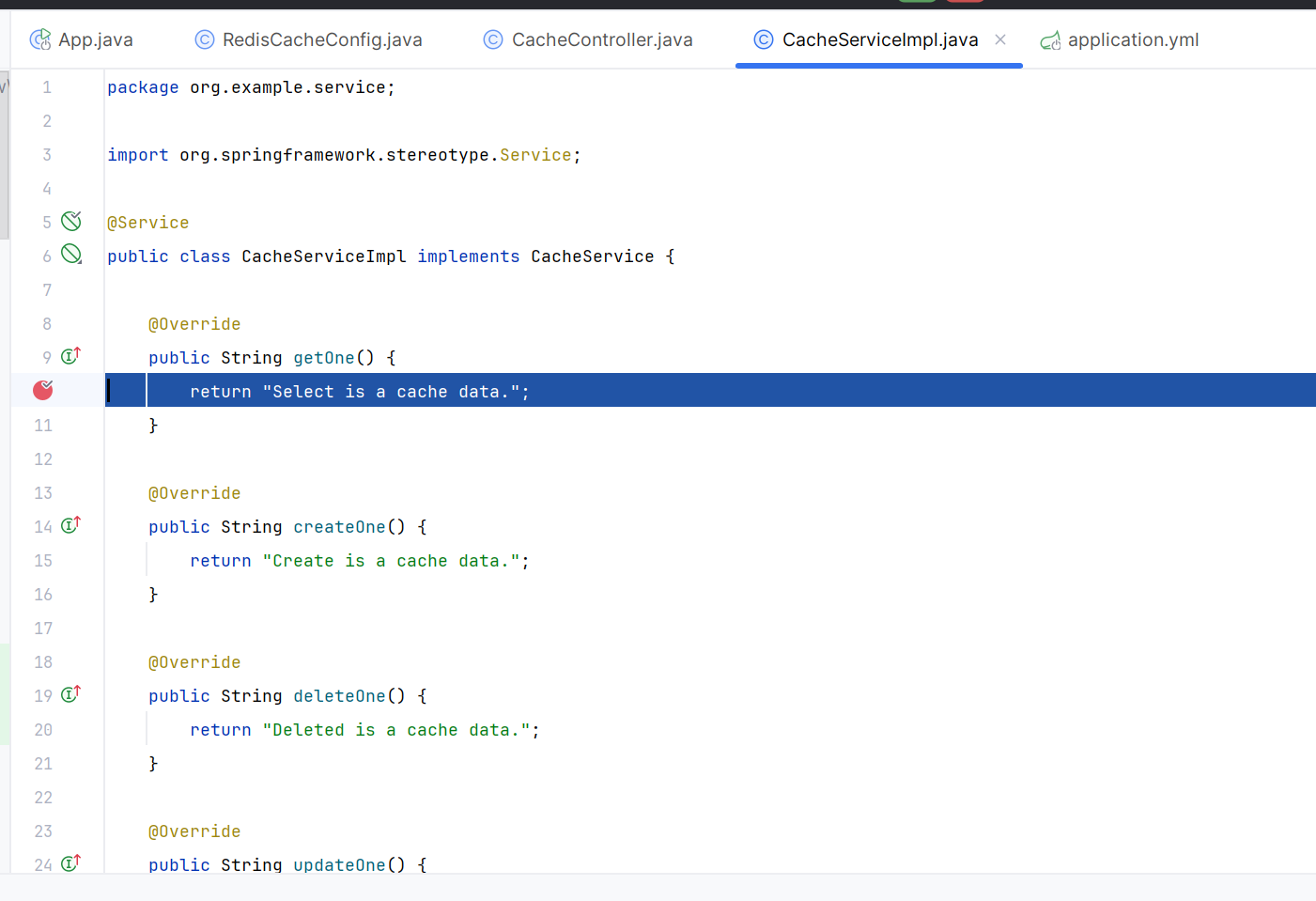
public String getOne() {
return "Select is a cache data.";
}
@Override
public String createOne() {
return "Create is a cache data.";
}
@Override
public String deleteOne() {
return "Deleted is a cache data.";
}
@Override
public String updateOne() {
return "Updated is a cache data.";
}
}启动项目,测试一下。
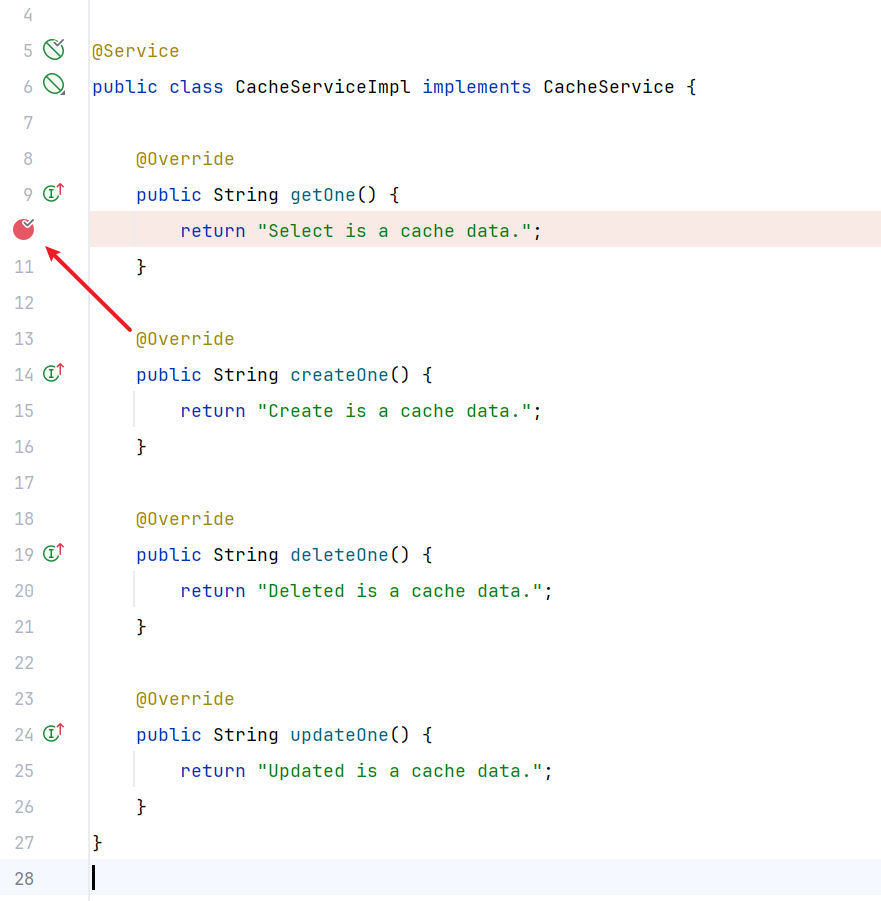
首次查询,断点卡在查询方法实现类这里,执行了实现类方法。
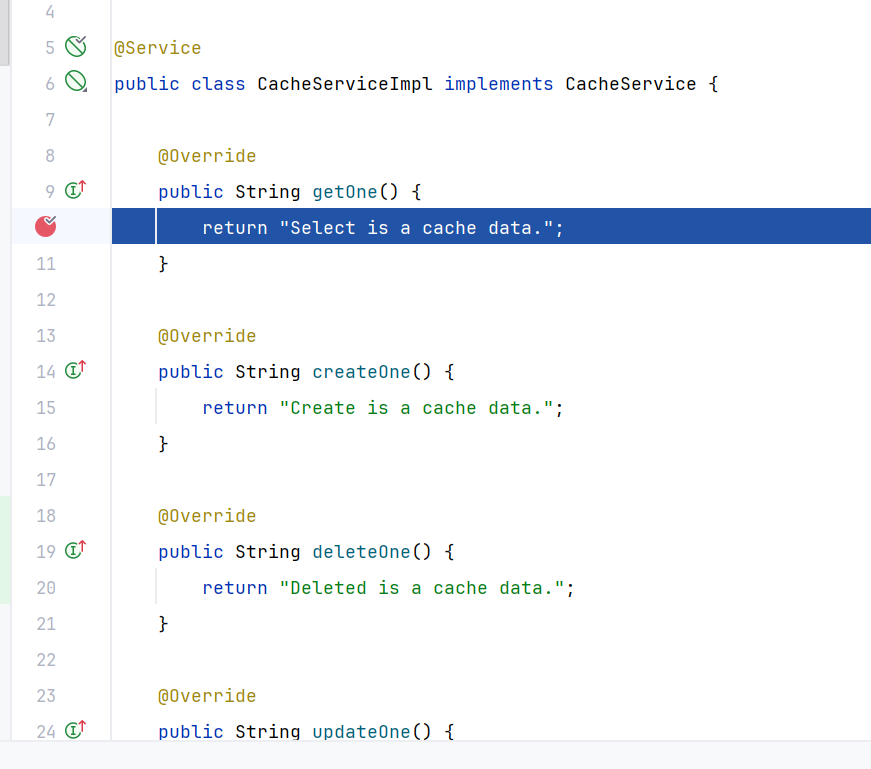
再次查询,直接返回了结果。
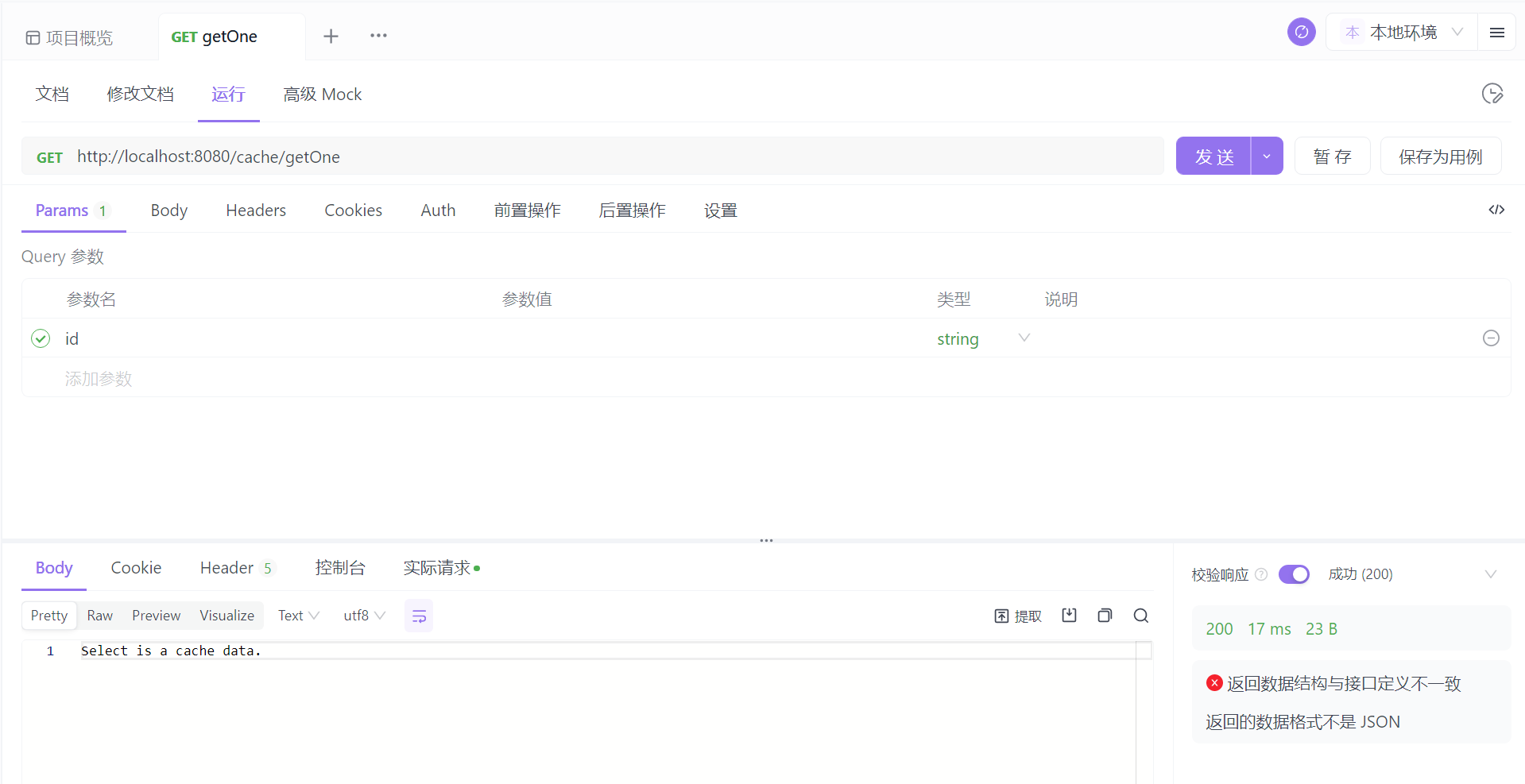
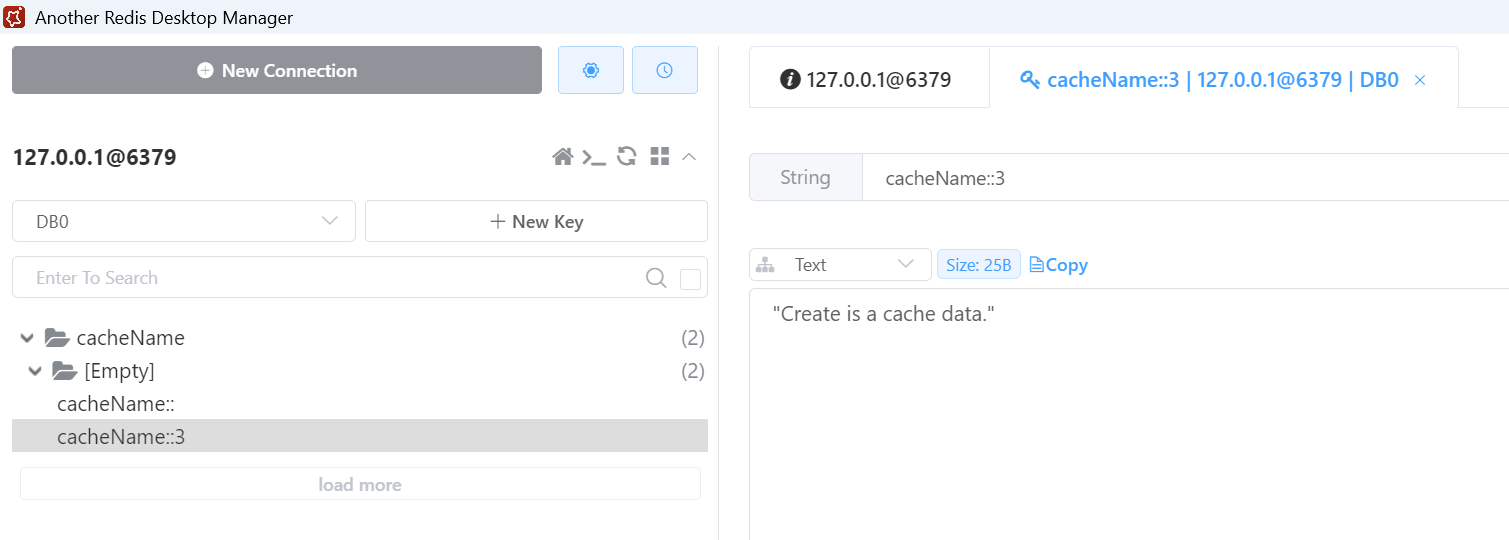
Redis 中增加了一个缓存。
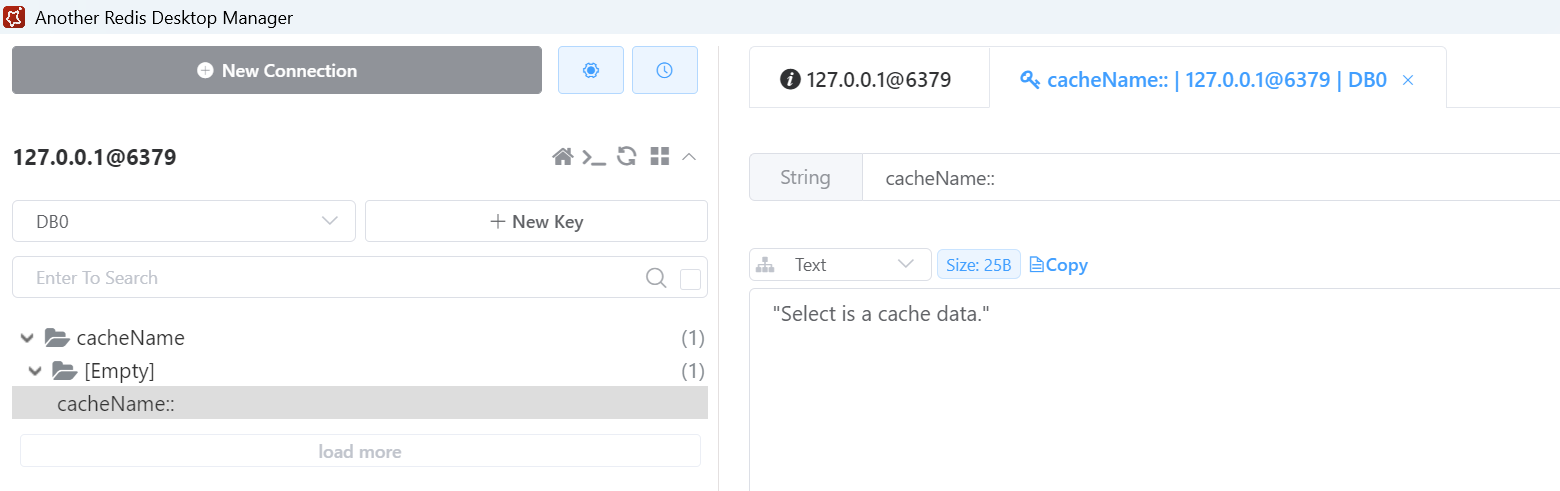
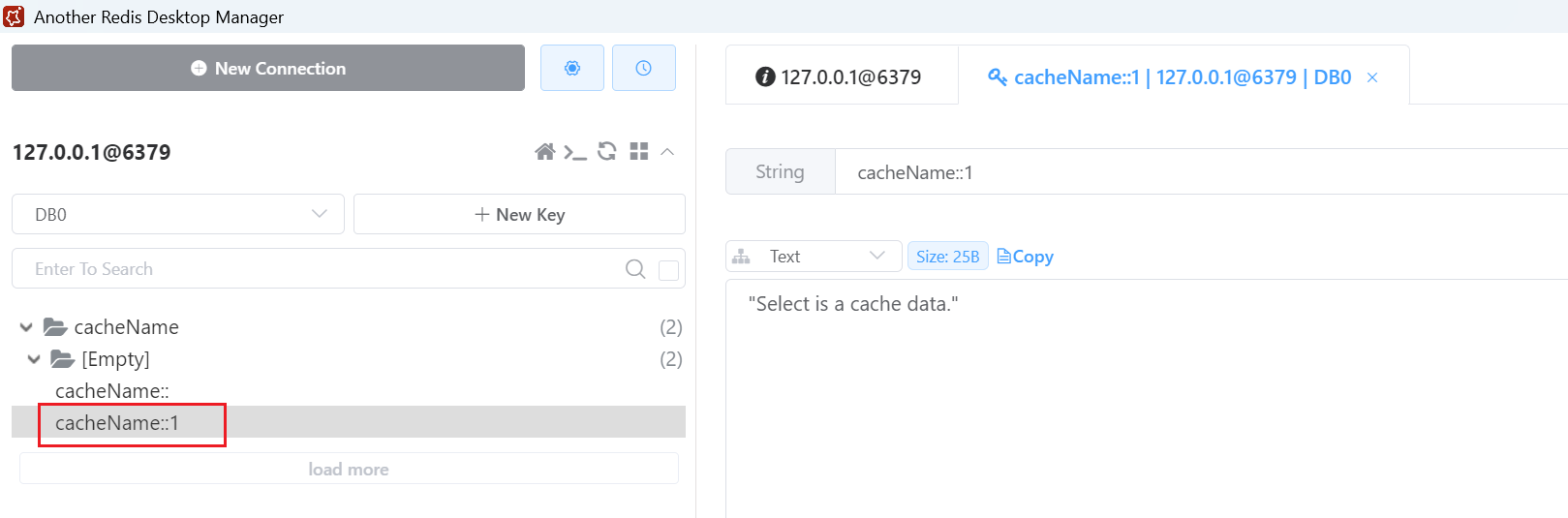
参数换一下,传入 id=1。
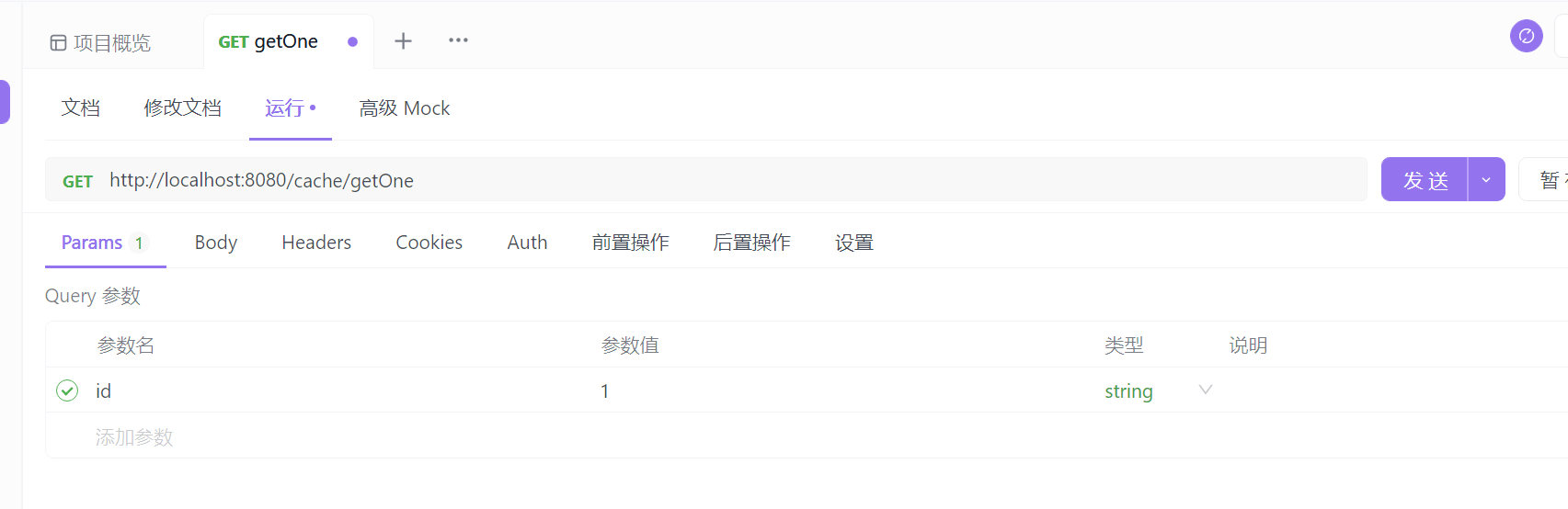
发送请求,断点卡住了,说明没走缓存。
新增了一个 id=1 的缓存。
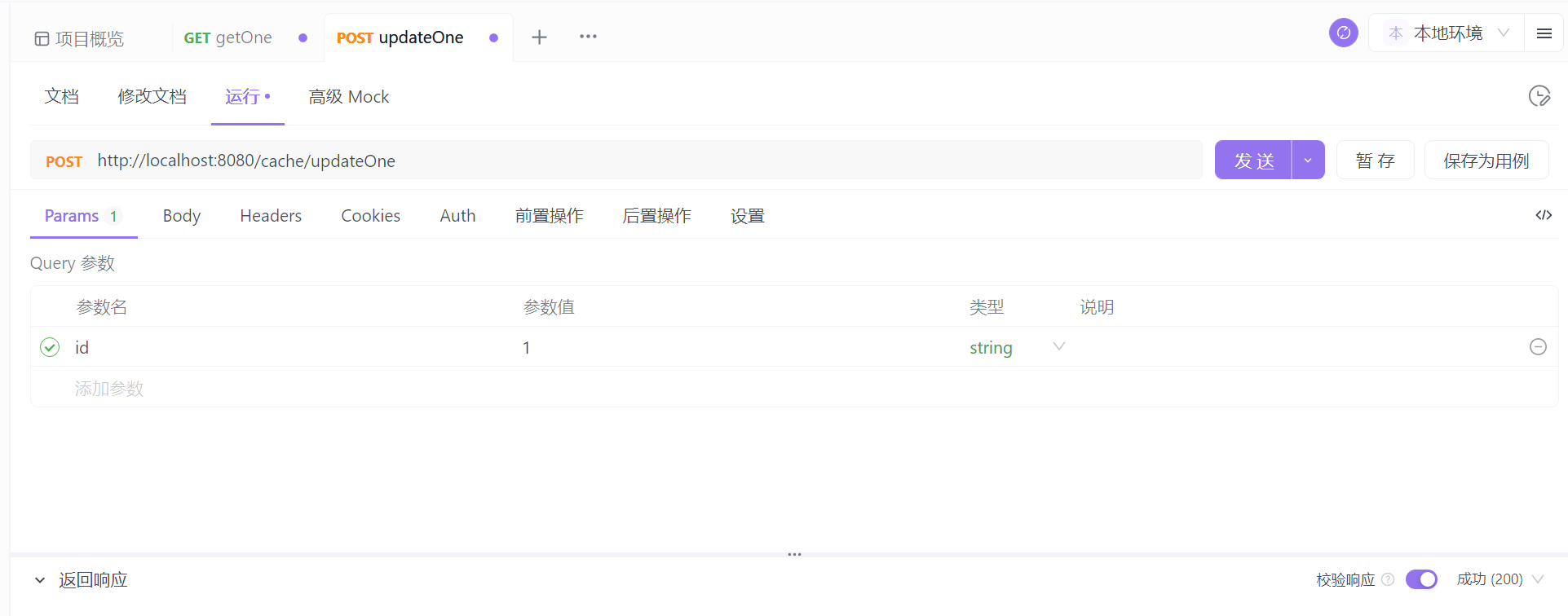
再试下更新方法,更新 id=1 的记录。
发送请求,查看 Redis,缓存都没了。
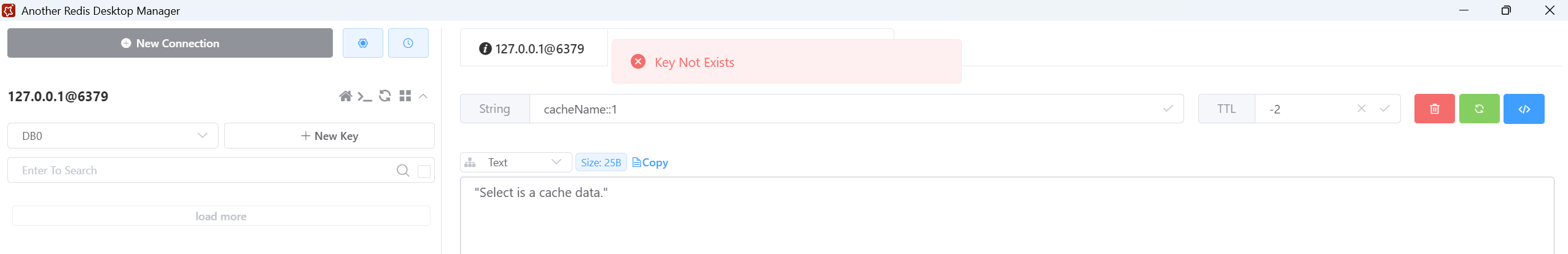
本来可以只让符合条件的,即 id=1 的缓存失效,上面都失效了,是因为我在更新方法的注解上额外加了一个属性。
allEntries = true,名称相同的所有缓存都失效,默认 false。
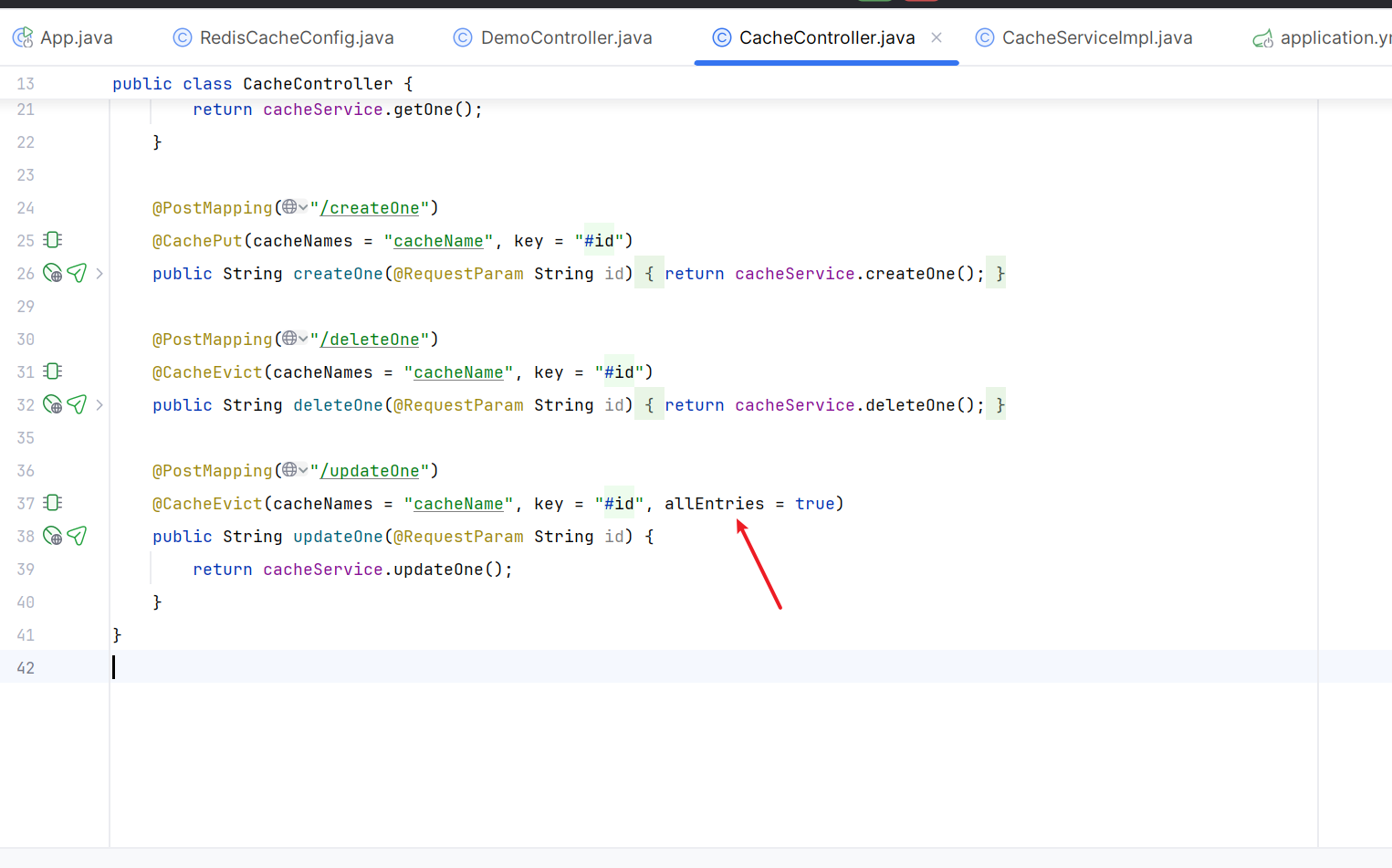
再试下,删除方法我没加这个属性。
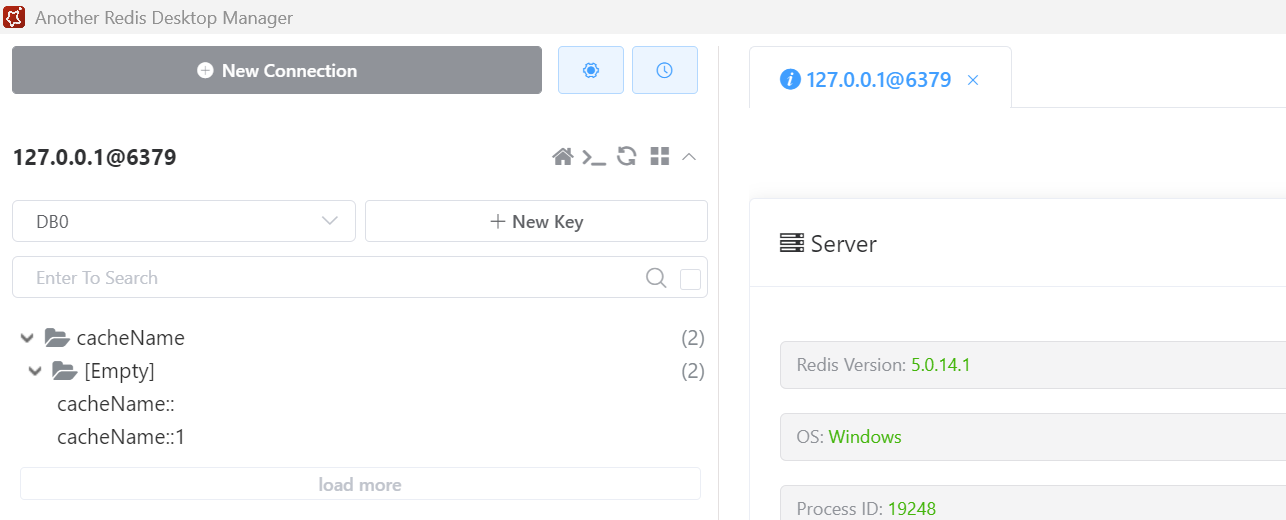
调用删除方法,删除 id=1 的记录。
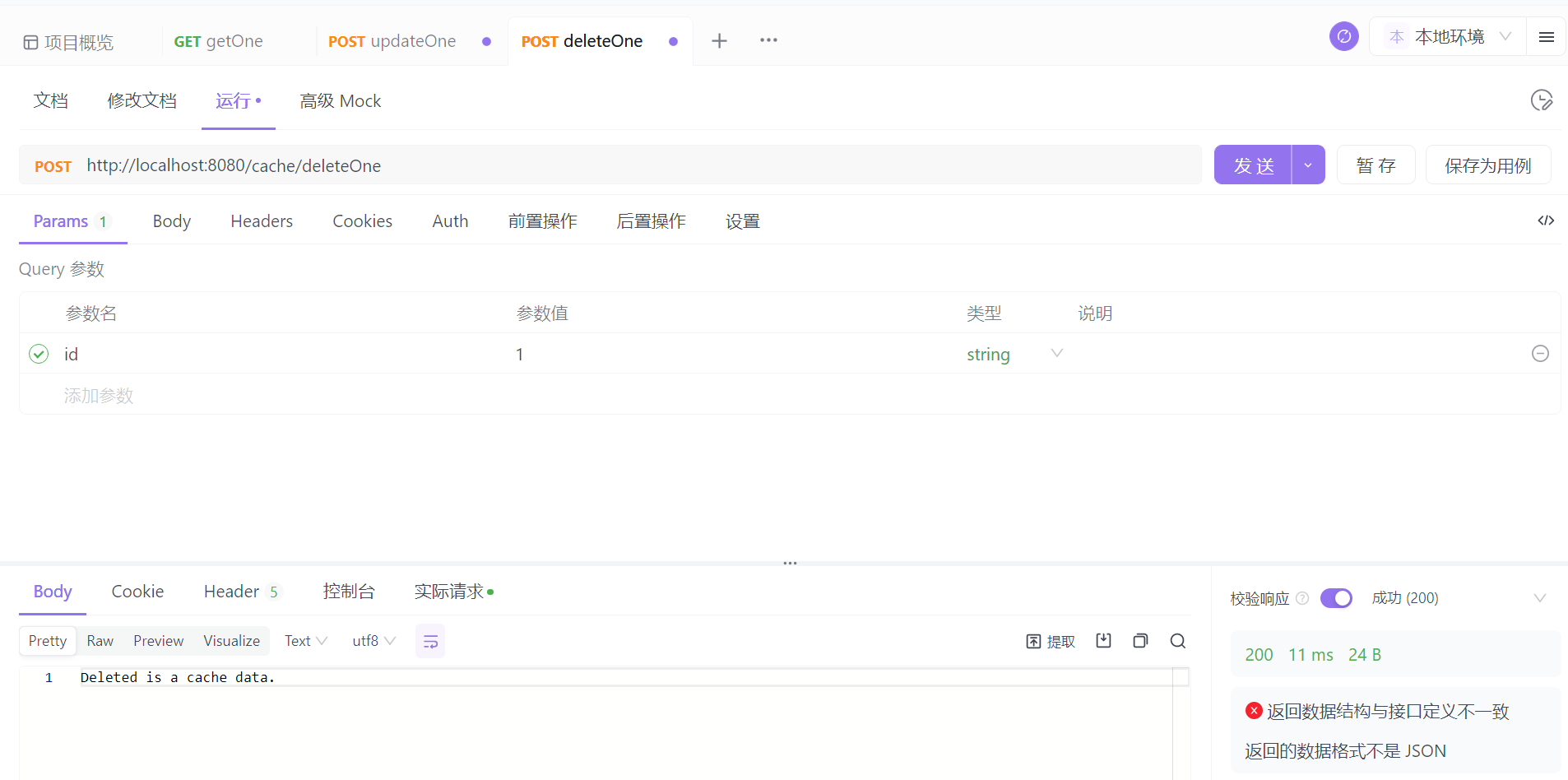
这回只有 id=1 的缓存被删除。
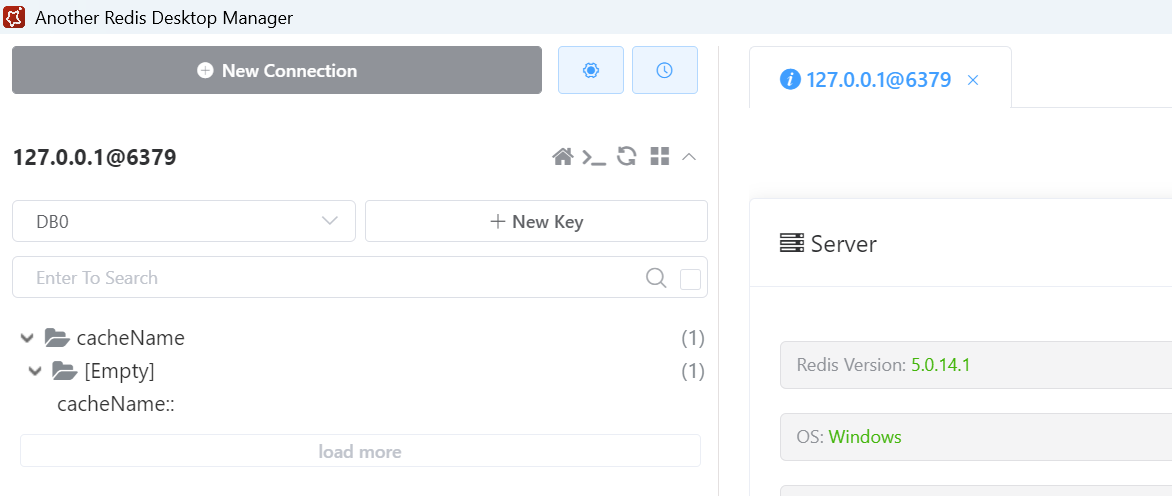
另外再试下创建方法,创建方法会再执行完创建方法后,主动将返回值添加到缓存中。
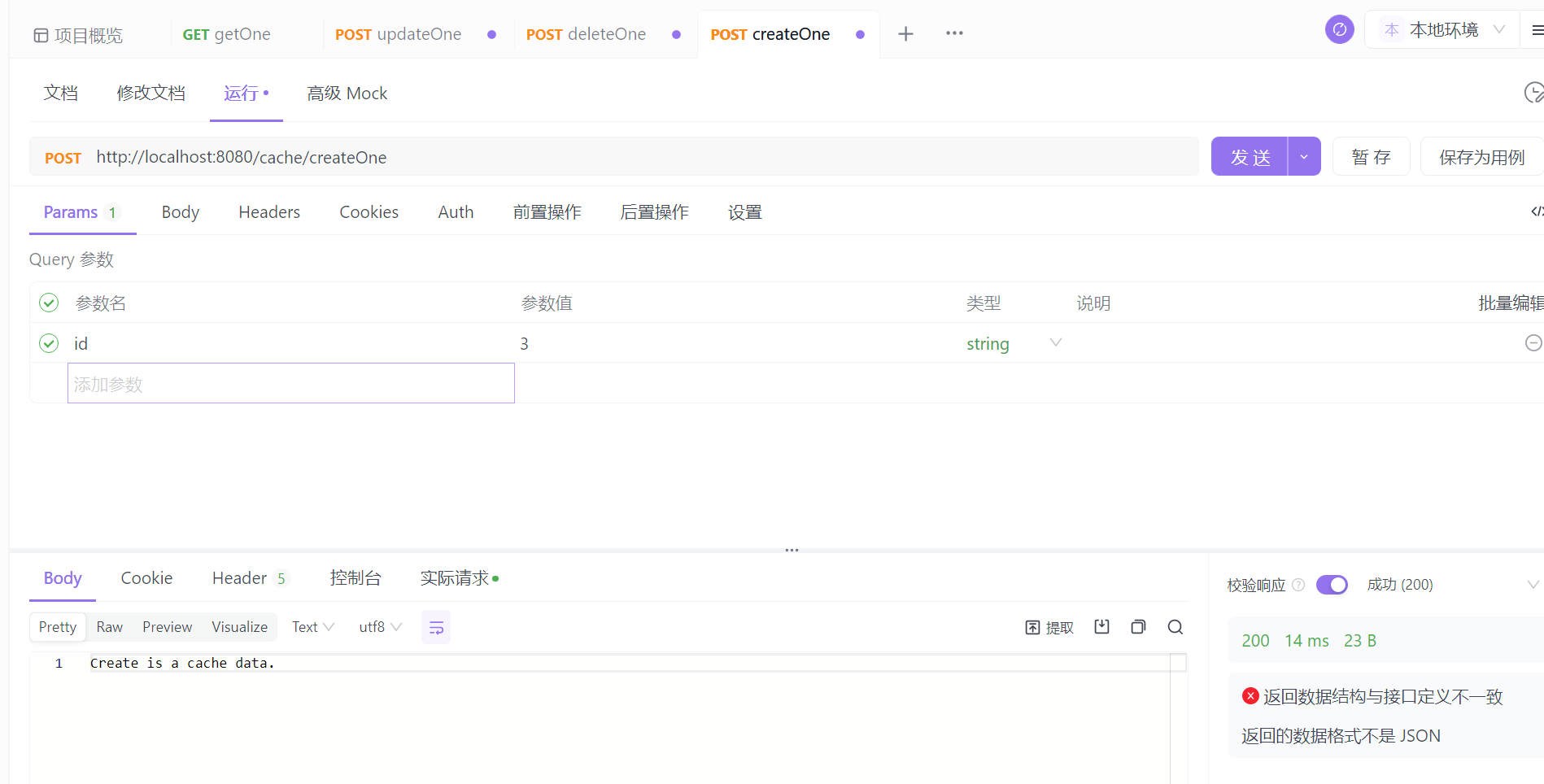
实际开发中,可以在某个创建接口完成后,将完整的对象数据返回,无缝衔接,就不用首次查询还要走一遍实现层。