本期我们就来学习LRU Cache这个数据结构。
作者的个人gitee:楼田莉子/CPP代码学习
目录
[LRU Cache](#LRU Cache)
什么是Cache?
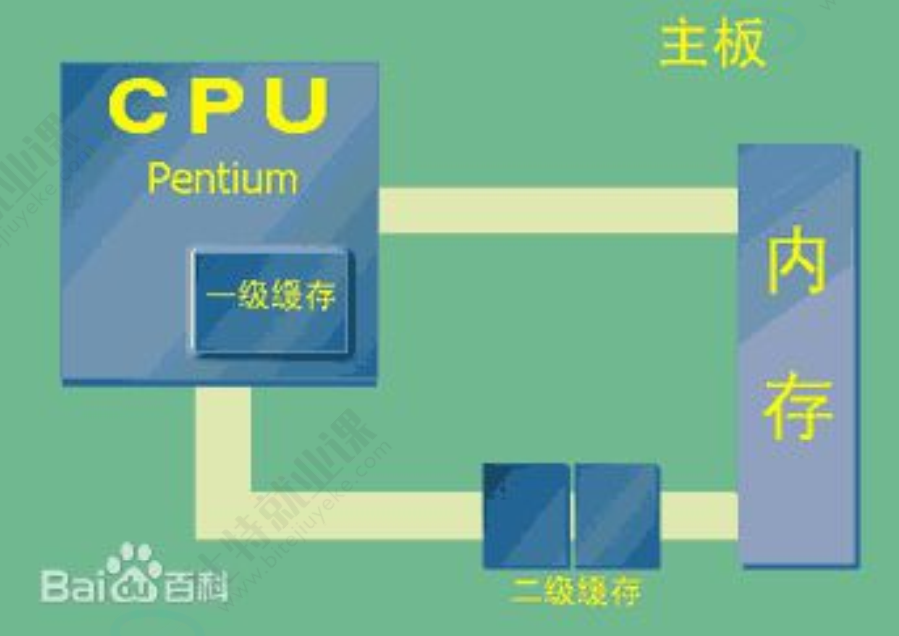
从硬件角度,Cache 是应用于速度不相同的两种存储介质之间的信息传输所应用到的硬件
狭义的Cache指的是位于CPU和主存间的快速RAM, 通常它不像系统主存那样使用DRAM技术,而使用昂贵但较快速的SRAM技术。
广义上的Cache指的是位于速度相差较大的两种硬件之间, 用于协调两者数据传输速度差异的结构。
除了CPU与主存之间有Cache, 内存与硬盘之间也有Cache,乃至在硬盘与网络之间也有某种意义上的Cache── 称为Internet临时文件夹或网络内容缓存等。
Cache基于局部性原理工作:
-
时间局部性:刚被访问的数据很可能再次被访问
-
空间局部性:一个位置被访问,其附近位置也可能被访问
在软件层面,Cache 是一种用空间换时间的策略,将计算结果或数据副本存储在快速访问的介质中。
Cache的关键特性
硬件 Cache 的典型结构(以现代 CPU 为例)
L1 Cache: 32KB 指令 + 32KB 数据,3-4 cycle 延迟
L2 Cache: 256KB-512KB,10-12 cycle 延迟
L3 Cache: 8MB-32MB,30-40 cycle 延迟
主内存: 8GB-64GB,100-200 cycle 延迟
LRU Cache
介绍
LRU是Least Recently Used的缩写,意思是最近最少使用,它是一种Cache替换算法。因此LRU Cache 是一种缓存淘汰算法,当缓存容量满时,优先淘汰最久未使用的数据。
用途
-
数据库缓存:MySQL 查询缓存
-
Web 服务器:缓存热点数据
-
操作系统:页面置换算法
-
应用层缓存:减少重复计算
特性
-
时间复杂度:O(1) 的插入、查找、删除
-
空间复杂度:O(n)
-
数据组织:维护访问顺序,最近访问的放头部,最久未访问的放尾部
实现
cpp
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <list>
#include <utility>
class LRUCache {
public:
explicit LRUCache(int capacity) : capacity_(capacity) {}
int get(int key) {
auto it = map_.find(key);
if (it == map_.end()) return -1;
// 将节点移动到链表头(最近使用)
nodes_.splice(nodes_.begin(), nodes_, it->second);
return it->second->second;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
auto it = map_.find(key);
if (it != map_.end()) {
// 已存在:更新值并移动到头部
it->second->second = value;
nodes_.splice(nodes_.begin(), nodes_, it->second);
return;
}
if (capacity_ <= 0) return; // 容量非正时不存储
if (static_cast<int>(map_.size()) == capacity_) {
// 驱逐尾部(最久未使用)
auto last = nodes_.back();
map_.erase(last.first);
nodes_.pop_back();
}
// 插入新节点到头部
nodes_.emplace_front(key, value);
map_[key] = nodes_.begin();
}
private:
int capacity_;
// 双向链表保存 (key, value),头为最近使用
std::list<std::pair<int, int>> nodes_;
// key -> 链表节点迭代器
std::unordered_map<int, std::list<std::pair<int, int>>::iterator> map_;
};测试代码:
cpp
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include"LRU_Cache.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
static int failures = 0;
// 简单测试
void esaytest()
{
LRUCache cache(2);
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
std::cout << cache.get(1) << "\n"; // 返回 1
cache.put(3, 3); // 淘汰 key 2
std::cout << cache.get(2) << "\n"; // 返回 -1 (未找到)
cache.put(4, 4); // 淘汰 key 1
std::cout << cache.get(1) << "\n"; // 返回 -1 (未找到)
std::cout << cache.get(3) << "\n"; // 返回 3
std::cout << cache.get(4) << "\n"; // 返回 4
}
bool expectEqual(int got, int want, const std::string& caseDesc) {
if (got == want) {
std::cout << "PASS: " << caseDesc << "\n";
return true;
}
else {
std::cout << "FAIL: " << caseDesc << " -> got " << got << ", expected " << want << "\n";
++failures;
return false;
}
}
void test_leetcode_example() {
std::cout << "--- test_leetcode_example ---\n";
LRUCache cache(2);
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
expectEqual(cache.get(1), 1, "get(1) == 1");
cache.put(3, 3); // evict key 2
expectEqual(cache.get(2), -1, "get(2) == -1");
cache.put(4, 4); // evict key 1
expectEqual(cache.get(1), -1, "get(1) == -1 after eviction");
expectEqual(cache.get(3), 3, "get(3) == 3");
expectEqual(cache.get(4), 4, "get(4) == 4");
}
void test_update_existing_key() {
std::cout << "--- test_update_existing_key ---\n";
LRUCache cache(2);
cache.put(1, 1);
cache.put(2, 2);
cache.put(1, 10); // update value of key 1 and move to MRU
expectEqual(cache.get(1), 10, "updated get(1) == 10");
cache.put(3, 3); // should evict key 2
expectEqual(cache.get(2), -1, "key 2 evicted after inserting key 3");
}
void test_capacity_one() {
std::cout << "--- test_capacity_one ---\n";
LRUCache cache(1);
cache.put(1, 1);
expectEqual(cache.get(1), 1, "capacity1 get(1) == 1");
cache.put(2, 2); // evict key 1
expectEqual(cache.get(1), -1, "capacity1 key1 evicted");
expectEqual(cache.get(2), 2, "capacity1 get(2) == 2");
}
void test_capacity_zero() {
std::cout << "--- test_capacity_zero ---\n";
LRUCache cache(0);
cache.put(1, 1); // should not store anything
expectEqual(cache.get(1), -1, "capacity0 get(1) == -1");
}
void test_access_ordering() {
std::cout << "--- test_access_ordering ---\n";
LRUCache cache(3);
cache.put(1, 1); // order: 1
cache.put(2, 2); // order: 2,1
cache.put(3, 3); // order: 3,2,1
expectEqual(cache.get(1), 1, "access: get(1) moves 1 to MRU");
expectEqual(cache.get(2), 2, "access: get(2) moves 2 to MRU");
cache.put(4, 4); // should evict key 3 (least recently used)
expectEqual(cache.get(3), -1, "key 3 evicted after inserting key 4");
expectEqual(cache.get(1), 1, "get(1) still present");
expectEqual(cache.get(2), 2, "get(2) still present");
expectEqual(cache.get(4), 4, "get(4) == 4");
}
int main()
{
esaytest();
test_leetcode_example();
test_update_existing_key();
test_capacity_one();
test_capacity_zero();
test_access_ordering();
if (failures == 0) {
std::cout << "\nAll tests passed.\n";
return 0;
}
else {
std::cout << "\nTests failed: " << failures << "\n";
return 1;
}
}结果为:
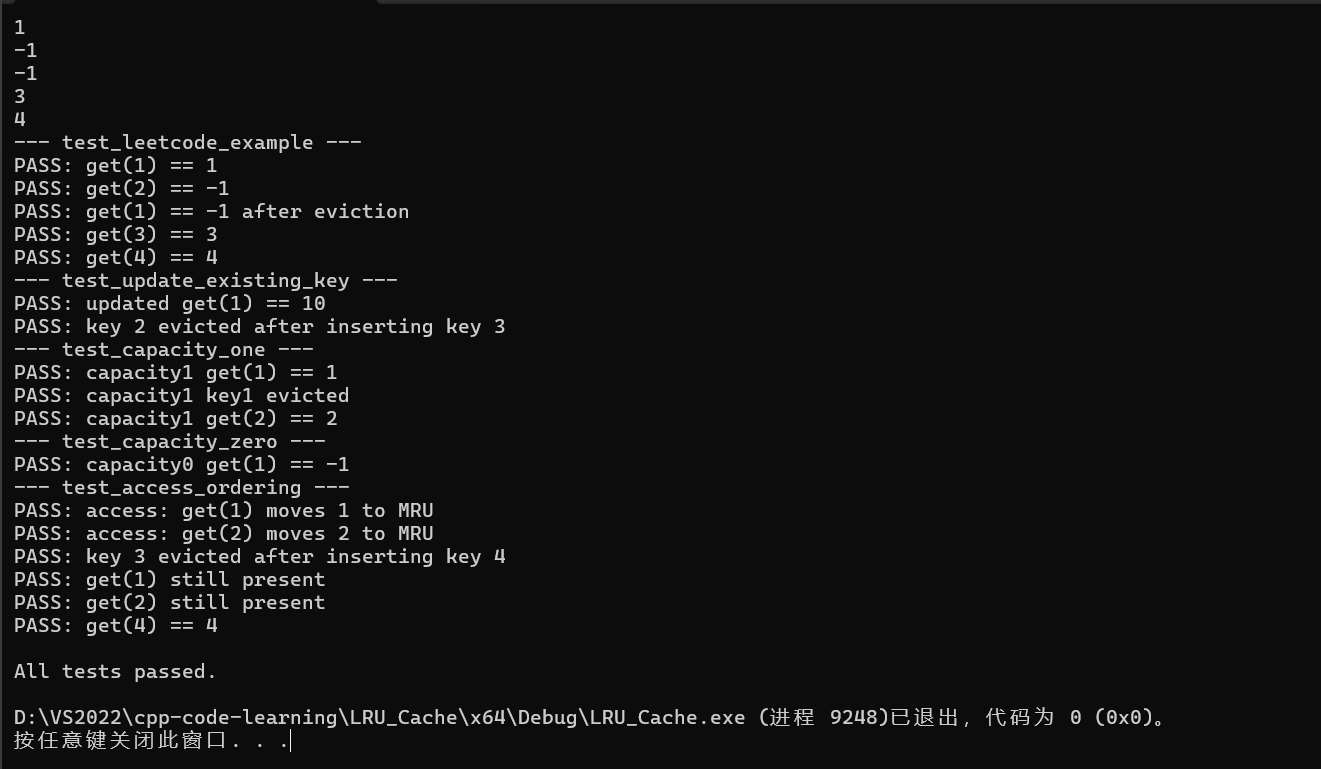
OJ测试练习
leetcode中有关于LRU cache的习题:

结果为:
cpp
#include <list>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
class LRUCache {
private:
// 类型别名定义在private区域
using NodeList = list<pair<int, int>>;
using Iterator = NodeList::iterator; // 注意:这里不需要typename,因为NodeList是具体类型
unordered_map<int, Iterator> _hashMap; // 哈希表:key -> 链表迭代器
NodeList _LRUList; // 双向链表,存储(key, value)
size_t _capacity; // 缓存容量
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) : _capacity(capacity)
{
// 构造函数初始化
}
int get(int key)
{
// 1. 在哈希表中查找
auto ret = _hashMap.find(key);
if (ret != _hashMap.end())
{
// 2. 找到节点,获取迭代器
Iterator it = ret->second;
// 3. 使用splice将节点移动到链表头部
// splice参数说明:目标位置,源链表,要移动的节点迭代器
_LRUList.splice(_LRUList.begin(), _LRUList, it);
// 4. 返回value
return it->second; // it指向的是pair<int, int>
}
else
{
return -1;
}
}
void put(int key, int value)
{
// 1. 先在哈希表中查找key是否存在
auto ret = _hashMap.find(key);
if (ret != _hashMap.end())
{
// 情况1:key已存在,更新value并移动到头部
Iterator it = ret->second;
it->second = value; // 更新value
// 移动到链表头部
_LRUList.splice(_LRUList.begin(), _LRUList, it);
} else
{
// 情况2:key不存在,需要新增
// 2.1 检查容量是否已满
if (_hashMap.size() >= _capacity)
{
// 容量已满,删除最久未使用的节点(链表尾部)
// 获取尾部节点的key
int keyToRemove = _LRUList.back().first;
// 从哈希表中删除
_hashMap.erase(keyToRemove);
// 从链表中删除
_LRUList.pop_back();
}
// 2.2 插入新节点到链表头部
_LRUList.push_front(make_pair(key, value));
// 2.3 将迭代器存入哈希表
_hashMap[key] = _LRUList.begin();
}
}
};
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/本期内容到这里就结束了,喜欢请点个赞谢谢
封面图自取:
