练习一:

package Day16_thread;
public class Ticket extends Thread {
static int ticket=0;
@Override
public void run() {
//写循环
//同步代码块
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,到了末尾会怎么样
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,如果没有到末尾会怎么样
while(true){
synchronized(Ticket.class){
if(ticket>=1000){
break;
}else {
try {
Thread.sleep(300);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
ticket++;
System.out.println(this.getName()+"正在卖第"+ticket+"张票");
}
}
}
}
}package Day16_thread;
public class ThreadQuestion1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//
Ticket ticket1 = new Ticket();
Ticket ticket2 = new Ticket();
Ticket ticket3 = new Ticket();
ticket1.setName("窗口1");
ticket2.setName("窗口2");
ticket3.setName("窗口3");
ticket1.start();
ticket2.start();
ticket3.start();
}
}练习二:

package Day16_thread;
public class gift extends Thread{
static int giftNumber=100;
@Override
public void run() {
//写循环
//同步代码块
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,到了末尾会怎么样
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,没有到末尾会怎么样
while(true){
synchronized (gift.class){
if(giftNumber<10){
break;
}else {
giftNumber--;
System.out.println(this.getName()+"正在发放礼物,剩余礼物数量"+giftNumber);
}
}
}
}
}package Day16_thread;
public class ThreadQuestion2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建线程对象
gift g1 = new gift();
gift g2 = new gift();
g1.setName("线程1");
g2.setName("线程2");
g1.start();
g2.start();
}
}
练习三:

package Day16_thread;
public class OddNumber extends Thread {
static int i = 1;
@Override
public void run() {
//写循环
//同步代码块
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,到了末尾会怎么样
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,如果没有到末尾会怎么样
while (true) {
synchronized (OddNumber.class) {
if(i<100){
if(i%2==0){
i++;
}else {
System.out.println(this.getName()+"奇数为:"+i);
i++;
}
}else {
break;
}
}
}
}
}package Day16_thread;
public class ThreadQuestion3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建线程对象
OddNumber n1 = new OddNumber();
OddNumber n2 = new OddNumber();
n1.setName("线程1");
n2.setName("线程2");
n1.start();
n2.start();
}
}练习四:

package Day16_thread;
import java.util.Random;
public class RedEnvelope extends Thread {
static double money=100;
static int count=3;
//最小红包金额
static final double MIN=0.01;
@Override
public void run() {
//同步代码块
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,已经到末尾
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,没有到末尾
synchronized (RedEnvelope.class) {
if(count==0){
//共享数据到了末尾,就没有抢到红包
System.out.println(this.getName()+"没有抢到红包");
}else {
//共享数据没有到末尾,开始抢红包
//需要注意不能直接随机,需要判断现在红包已经被抢了多少个
double price=0;//定义每次抽奖的金额
if(count==1){
//表示此时是最后一个红包,就不用随机了
price=money;//最后一次红包,就把钱全部给price
}else{
//这里就要随机一个金额
Random random=new Random();
double bounds = money - (3 - 1) * 0.01;
price=random.nextDouble(bounds);
if(price<MIN){
price=MIN;
}
//修改money的金额,需要把money减去中奖的金额
money=money-price;
}
//抽奖完成
count--;
System.out.println(this.getName()+"抢到了"+price+"元");
}
}
}
}package Day16_thread;
public class ThreadQuestion4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建线程对象
RedEnvelope r1 = new RedEnvelope();
RedEnvelope r2 = new RedEnvelope();
RedEnvelope r3 = new RedEnvelope();
RedEnvelope r4 = new RedEnvelope();
RedEnvelope r5 = new RedEnvelope();
r1.setName("线程1");
r2.setName("线程2");
r3.setName("线程3");
r4.setName("线程4");
r5.setName("线程5");
r1.start();
r2.start();
r3.start();
r4.start();
r5.start();
}
}
练习五:

package Day16_thread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class LotteryPool extends Thread{
//定义一个集合,用来存储奖池
//巧思:为啥要创建一个构造方法,因为这里可以保证每个线程
//执行的是同一个集合
ArrayList<Integer> list;
public LotteryPool(ArrayList<Integer> list){
this.list=list;
}
@Override
public void run(){
//套路:
//循环
//同步代码块
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,到了末尾
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,没有到末尾
while(true){
synchronized (LotteryPool.class){
if(list.size()==0){
break;
} else {
//生成随机数,抽奖
Random random = new Random();
int i = random.nextInt(list.size());
Integer result = list.get(i);
System.out.println(this.getName()+"产生了一个"+result+"元大奖");
//抽中奖励就把奖池中该奖项去掉
list.remove(result);
}
}
}
}
}package Day16_thread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class ThreadQuestion5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
Collections.addAll(list,10,5,20,50,100,200,500,800,
2,80,300,700);
LotteryPool L1 = new LotteryPool(list);
LotteryPool L2 = new LotteryPool(list);
L1.setName("抽奖箱1");
L2.setName("抽奖箱2");
L1.start();
L2.start();
}
}
练习六:
package Day16_thread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class LotteryPool extends Thread{
//定义一个集合,用来存储奖池
//巧思:为啥要创建一个构造方法,因为这里可以保证每个线程
//执行的是同一个集合
ArrayList<Integer> list;
public LotteryPool(ArrayList<Integer> list){
this.list=list;
}
//定义集合用来把不同的线程数据存起来
static ArrayList<Integer> list1=new ArrayList<>();
static ArrayList<Integer> list2=new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void run(){
//套路:
//循环
//同步代码块
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,到了末尾
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,没有到末尾
while(true){
synchronized (LotteryPool.class){
if(list.size()==0){
//这里表示抽奖结束了
if(this.getName().equals("抽奖箱1")){
int list1max = getMax(list1);
int list1sum = getSum(list1);
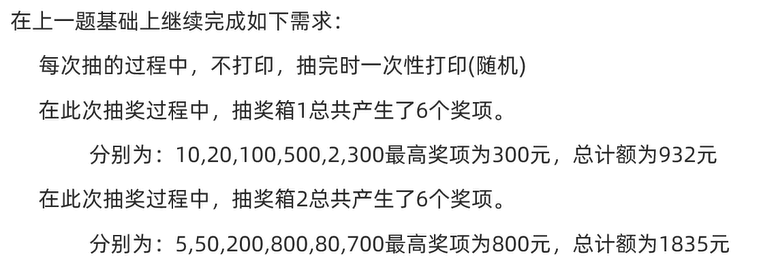
System.out.println("在本次抽奖中"+this.getName()+"总共产生了"+list1.size()+"个奖项");
System.out.println("分别为:"+list1+","+"最高奖项为"+list1max+","+"总计额为"+list1sum);
} else if (this.getName().equals("抽奖箱2")) {
int list2max = getMax(list2);
int list2sum = getSum(list2);
System.out.println("在本次抽奖中"+this.getName()+"总共产生了"+list2.size()+"个奖项");
System.out.println("分别为:"+list2+","+"最高奖项为"+list2max+","+"总计额为"+list2sum);
}
break;
} else {
//生成随机数,抽奖
Random random = new Random();
int i = random.nextInt(list.size());
Integer result = list.get(i);
if(this.getName().equals("抽奖箱1")){
list1.add(result);
} else if (this.getName().equals("抽奖箱2")) {
list2.add(result);
}
//抽中奖励就把奖池中该奖项去掉
list.remove(result);
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
//获取集合中的最大值和求和
public static int getMax(ArrayList<Integer> list){
int max=list.get(0);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if(list.get(i)>max){
max=list.get(i);
}
}
return max;
}
public static int getSum(ArrayList<Integer> list){
int sum=0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
sum+=list.get(i);
}
return sum;
}
}package Day16_thread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
public class ThreadQuestion5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<Integer>();
Collections.addAll(list,10,5,20,50,100,200,500,800,
2,80,300,700);
LotteryPool L1 = new LotteryPool(list);
LotteryPool L2 = new LotteryPool(list);
L1.setName("抽奖箱1");
L2.setName("抽奖箱2");
L1.start();
L2.start();
}
}上面的写法是有点弊端的,如果抽奖箱有很多,就需要创建多个集合,可以利用线程栈的方式来改写
package Day16_thread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
public class LotteryPool extends Thread{
//定义一个集合,用来存储奖池
//巧思:为啥要创建一个构造方法,因为这里可以保证每个线程
//执行的是同一个集合
ArrayList<Integer> list;
public LotteryPool(ArrayList<Integer> list){
this.list=list;
}
@Override
public void run(){
//套路:
//循环
//同步代码块
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,到了末尾
//判断共享数据是否到了末尾,没有到末尾
//利用线程栈来改写
ArrayList<Integer> boxList=new ArrayList<>();
while(true){
synchronized (LotteryPool.class){
if(list.size()==0){
//这里表示抽奖结束了
System.out.println("在本次抽奖中"+this.getName()+"总共产生了"+boxList.size()+"个奖项");
System.out.println("分别是:"+boxList+"最高奖金为"+getMax(boxList)+"总计额为"+getSum(boxList));
break;
} else {
//生成随机数,抽奖
Random random = new Random();
int i = random.nextInt(list.size());
Integer result = list.get(i);
boxList.add(result);
//抽中奖励就把奖池中该奖项去掉
list.remove(result);
}
}
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
//获取集合中的最大值和求和
public static int getMax(ArrayList<Integer> list){
int max=list.get(0);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if(list.get(i)>max){
max=list.get(i);
}
}
return max;
}
public static int getSum(ArrayList<Integer> list){
int sum=0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
sum+=list.get(i);
}
return sum;
}
}效果是一样的:

练习七(多线程的比较):

package Day16_thread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.Callable;
public class LotterPoolCompare implements Callable<Integer> {
//创建集合用来定义构造方法,放奖池中的奖项
ArrayList<Integer> list;
public LotterPoolCompare(ArrayList<Integer> list){
this.list=list;
}
@Override
public Integer call() throws Exception {
//创建线程栈来存储不同线程的数据
ArrayList<Integer> boxList=new ArrayList<>();
while(true){
synchronized (LotterPoolCompare.class){
if(list.size()==0){
//这里表示抽奖结束了
System.out.println("在本次抽奖中"+Thread.currentThread().getName()+"总共产生了"+boxList.size()+"个奖项");
System.out.println("分别是:"+boxList+"最高奖金为"+getMax(boxList)+"总计额为"+getSum(boxList));
break;
}else{
//随机抽奖
Random random = new Random();
int i = random.nextInt(list.size());
Integer result = list.get(i);
boxList.add(result);
//抽中奖之后,就把该奖项从集合中去掉
list.remove(result);
}
}
//为了让每个线程抽中的数据更均匀
Thread.sleep(10);
}
//循环结束之后,返回抽奖箱中的最大值
int max = getMax(boxList);
return max;
}
public static int getMax(ArrayList<Integer> list){
int max=list.get(0);
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
if(list.get(i)>max){
max=list.get(i);
}
}
return max;
}
public static int getSum(ArrayList<Integer> list){
int sum=0;
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
sum+=list.get(i);
}
return sum;
}
}package Day16_thread;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutionException;
import java.util.concurrent.FutureTask;
public class ThreadQuestion6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ExecutionException, InterruptedException {
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(list,10,5,20,50,100,200,500,800,
2,80,300,700);
LotterPoolCompare L = new LotterPoolCompare(list);
//创建多线程的管理对象
FutureTask<Integer> f1=new FutureTask<Integer>(L);
FutureTask<Integer> f2=new FutureTask<Integer>(L);
Thread t1 = new Thread(f1);
Thread t2 = new Thread(f2);
t1.setName("抽奖箱1");
t2.setName("抽奖箱2");
t1.start();
t2.start();
//利用FutureTask得到线程运行的结果
Integer f1Max = f1.get();
Integer f2Max = f2.get();
if (f1Max > f2Max) {
System.out.println("抽奖箱1中产生了最大奖项:"+f1Max);
}else {
System.out.println("抽奖箱2中产生了最大奖项:"+f2Max);
}
}
}