[一、U-Boot 图形化配置体验](#一、U-Boot 图形化配置体验)
[二、menuconfig 图形化配置原理](#二、menuconfig 图形化配置原理)
[2.1、make menuconfig 过程分析](#2.1、make menuconfig 过程分析)
[2.2、Kconfig 语法简介](#2.2、Kconfig 语法简介)
[2、调用其他目录下的 Kconfig 文件](#2、调用其他目录下的 Kconfig 文件)
[3、menu/endmenu 条目](#3、menu/endmenu 条目)
[4、config 条目](#4、config 条目)
[5、depends on 和 select](#5、depends on 和 select)
前言
在前几期uboot移植博客中我们可以uboot 可以通过 mx6ull_alientek_emmc_defconfig 来配置,或者通过文件 mx6ull_alientek_emmc.h 来配置 uboot,还有另外一种配置 uboot 的方法,就是图形化配置,所以这期来学习一下如何通过图形化配置 uboot。
一、U-Boot 图形化配置体验
uboot 或 Linux 内核可以通过输入"make menuconfig"来打开图形化配置界面,menuconfig是一套图形化的配置工具,需要 ncurses 库支持。ncurses 库提供了一系列的 API 函数供调用者生成基于文本的图形界面,因此需要先在 Ubuntu 中安装 ncurses 库,命令如下:
sudo apt-get install build-essential
sudo apt-get install libncurses5-devmenuconfig 重点会用到两个文件:.config 和 Kconfig,.config 文件保存着 uboot 的配置项,使用 menuconfig 配置完 uboot 以后肯定要更新.config 文件。Kconfig文件是图形界面的描述文件,也就是描述界面应该有什么内容,很多目录下都会有 Kconfig 文件。
在打开图形化配置界面之前,要先使用"make xxx_defconfig"对 uboot 进行一次默认配置, 只需要一次即可。如果使用"make clean"清理了工程的话就那就需要重新使用"makexxx_defconfig"再对 uboot 进行一次配置。进入 uboot 根目录,输入如下命令:
make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- mx6ull_alientek_emmc_defconfig
make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- menuconfig再用以下命令打开图形化界面:
make menuconfig以下就是图形化界面
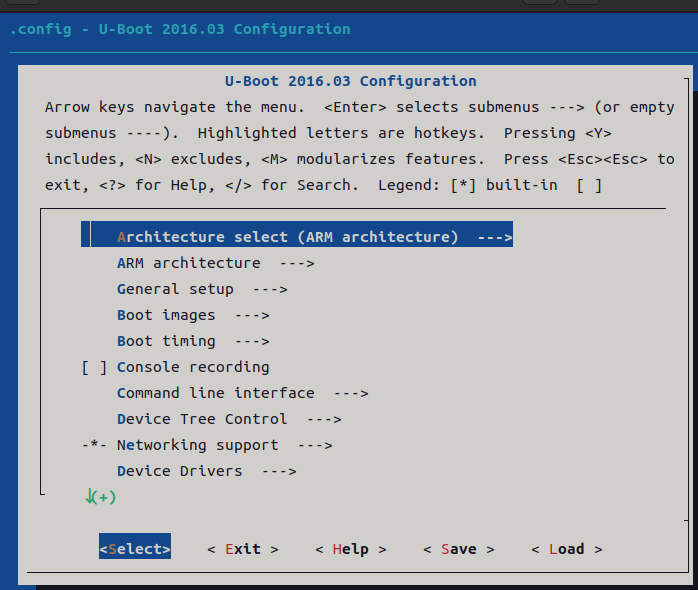
主界面上方的英文就是简单的操作说明,操作方法如下:
通过键盘上的 "↑" 和 "↓" 键来选择要配置的菜单,按下 "Enter" 键进入子菜单。菜单中高亮的字母就是此菜单的热键,在键盘上按下此高亮字母对应的键可以快速选中对应的菜单。
选中子菜单以后按下 "Y" 键就会将相应的代码编译进 Uboot 中,菜单前面变为 "<*>"。按下 "N" 键不编译相应的代码,按下 "M" 键就会将相应的代码编译为模块,菜单前面变为 "<M>"。
按两下 "Esc" 键退出,也就是返回到上一级,按下 "?" 键查看此菜单的帮助信息,按下 "/" 键打开搜索框,可以在搜索框输入要搜索的内容。
在配置界面下方会有五个按钮,这五个按钮的功能如下:
<Select>:选中按钮,和 "Enter" 键的功能相同,负责选中并进入某个菜单。<Exit>:退出按钮,和按两下 "Esc" 键功能相同,退出当前菜单,返回到上一级。<Help>:帮助按钮,查看选中菜单的帮助信息。<Save>:保存按钮,保存修改后的配置文件。<Load>:加载按钮,加载指定的配置文件。
图中共有13 个配置主配置项,通过键盘上的上下键调节配置项。后面跟着"--->"表示此配置项是有子配置项的,按下回车键就可以进入子配置项。
我们就以如何使能 dns 命令为例,讲解一下如何通过图形化界面来配置 uboot。进入"Command line interface --->"这个配置项,此配置项用于配置 uboot 的命令,进入以后如图:
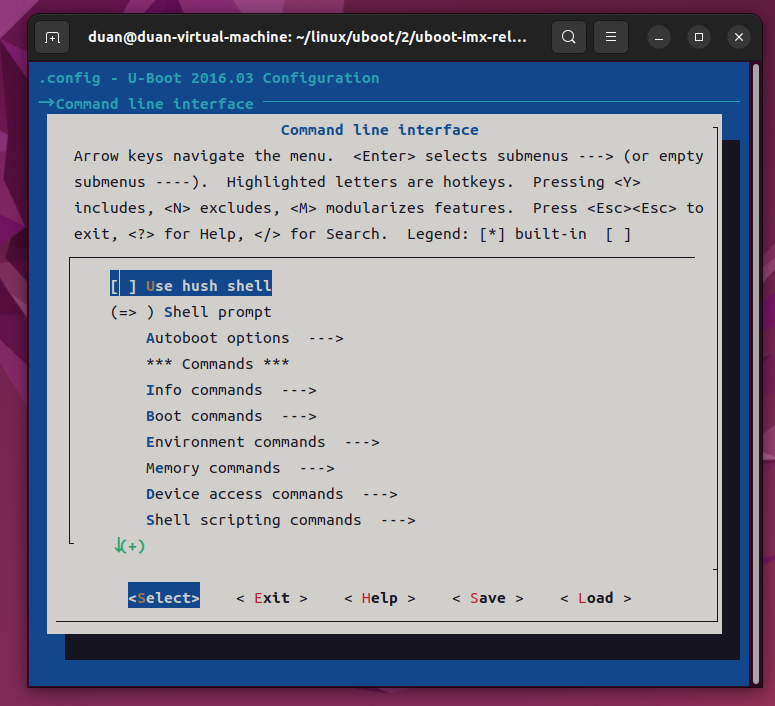
上图中可以看出,有很多配置项,这些配置项也有子配置项,选择"Network commands --->",进入网络相关命令配置项,如下图所示:
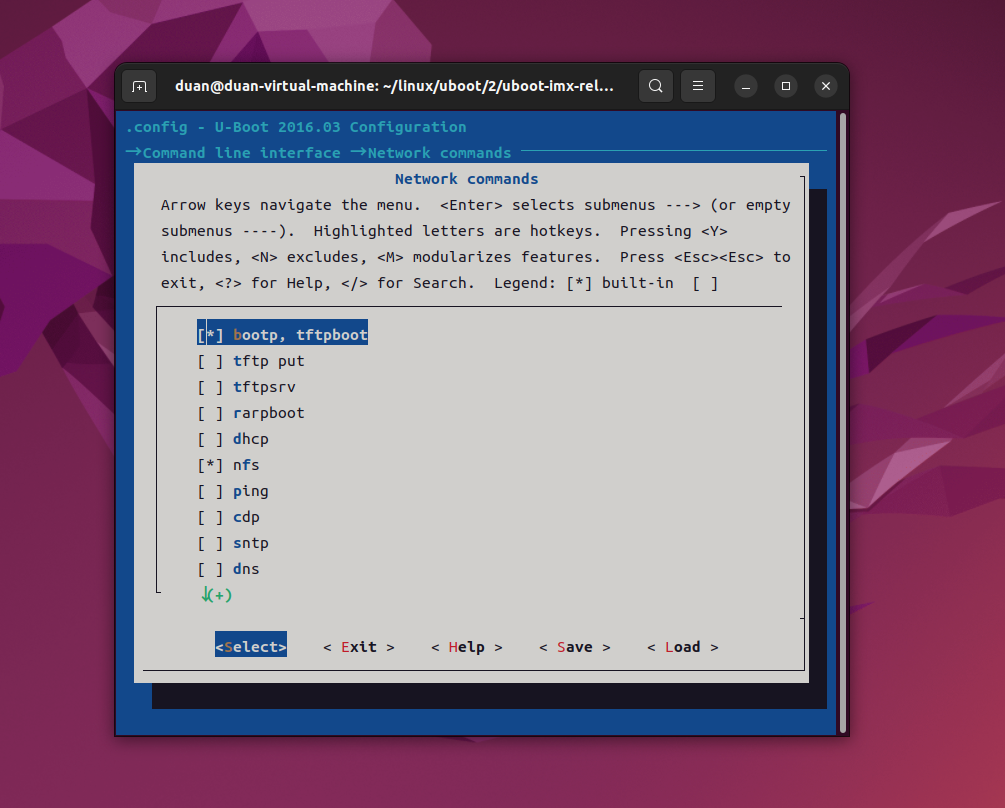
从上图中可以看出,uboot 中有很多和网络有关的命令,比如 bootp、tftpboot、dhcp 等等。选中 dns,然后按下键盘上的"Y"键,此时 dns 前面的"[ ]"变成了"[ * ]",如下图所示:
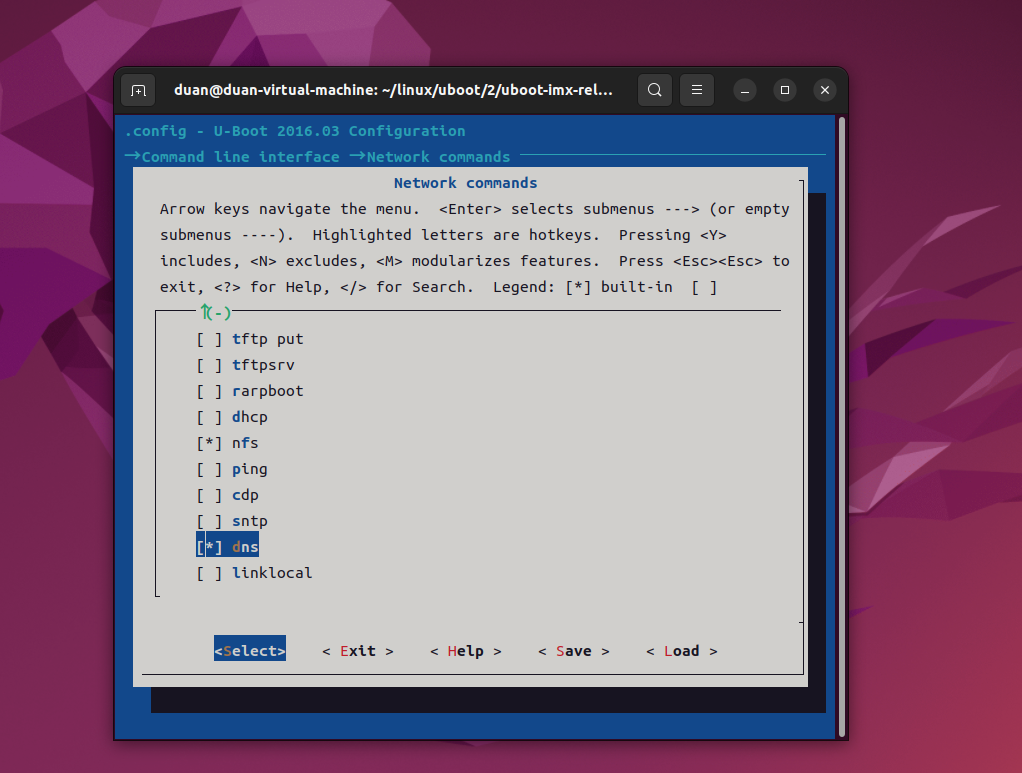
图形化配置界面对于一个功能的编译,或者叫做选择有3中模式:
Y:对应的功能编译uboot里面。
N:对应的功能不编译进uboot里面
M:将对应的功能编译位模块,.ko,Linux内核里面常用。
注意:在 mx6ull_alientek_emmc.h 里面我们配置使能了 dhcp 和 ping 命令,但是在上图中 dhcp 和 ping 前面的"[ ]"并不是"[ * ]",也就是说不编译 dhcp 和 ping 命令,这不是冲突了吗?实际情况是 dhcp 和 ping 命令是会编译的。
原因:因为我们是直接在 mx6ull_alientek_emmc.h 中定义的宏 CONFIG_CMD_PING 和CONFIG_CMD_DHCP,而 menuconfig 是通过读取.config 文件来判断使能了哪些功能,.config 里面并没有宏CONFIG_CMD_PING和CONFIG_CMD_DHCP,所以menuconfig就会识别出错。
选中 dns,然后按下"H"或者"?"键可以打开 dns 命令的提示信息:
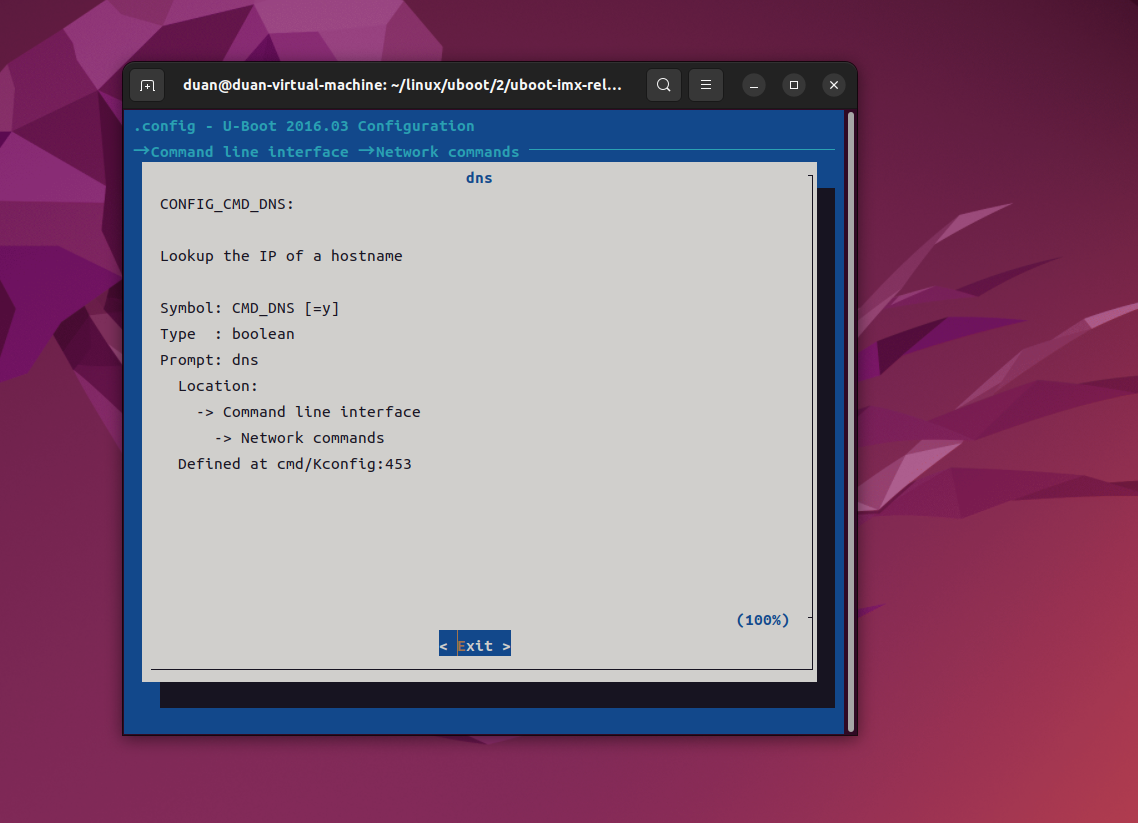
按两下 ESC 键即可退出提示界面,相当于返回上一层。选择 dns 命令以后,按两下 ESC 键(按两下 ESC 键相当于返回上一层),退出当前配置项,进入到上一层配置项。如果没有要修改的就按两下 ESC 键,退出到主配界面,如果也没有其他要修改的,那就再次按两下 ESC 键退出 menuconfig 配置界面。如果修改过配置的话,在退出主界面的时候会有如图:
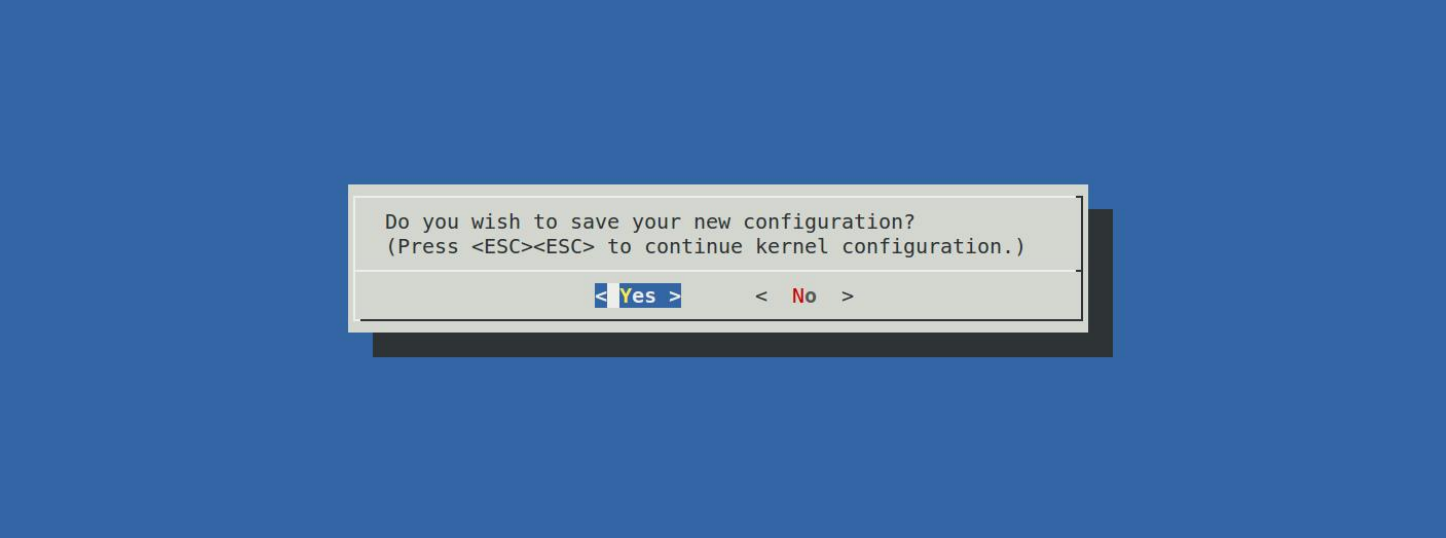
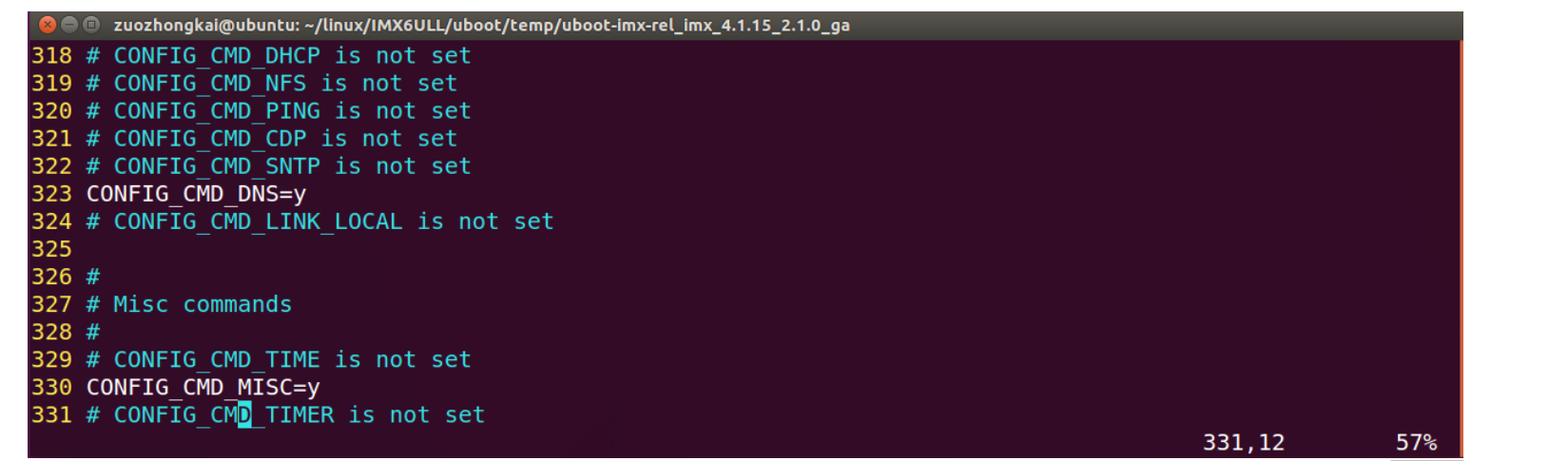
上图询问是否保存新的配置文件,通过键盘的←或→键来选择"Yes"项,然后按下键盘上的回车键确认保存。至此,我们就完成了通过图形界面使能了 uboot 的 dns 命令,打开.config文件,会发现多了"CONFIG_CMD_DNS=y"这一行,如下图所示:
使用如下命令编译 uboot:
make ARCH=arm CROSS_COMPILE=arm-linux-gnueabihf- -j16注意:不能用以下命令:
./mx6ull_alientek_emmc.sh因为 mx6ull_alientek_emmc.sh 在编译之前会清理工程,会删除掉.config 文件!通过图形化界面配置所有配置项都会被删除,这样相当于刚才做的图形化设置白做了!!!!
编译完成以后烧写到 SD 卡中,重启开发板进入 uboot 命令模式,输入"?"查看是否有"dns"
命令。
这个就是通过图形化命令来配置 uboot,一般用来使能一些命令还是很方便的,这样就不需
要到处找命令的配置宏是什么,然后在到配置文件里面去定义。
二、menuconfig 图形化配置原理
2.1、make menuconfig 过程分析
当输入 make menuconfig 以后会匹配到顶层 Makefile 的如下代码:
%config: scripts_basic outputmakefile FORCE
$(Q)$(MAKE) $(build)=scripts/kconfig $@其中 build=-f ./scripts/Makefile.build obj,将第二行的规则展开就是:
@make -f ./scripts/Makefile.build obj=scripts/kconfig menuconfigMakefile.build 会读取 scripts/kconfig/Makefile 中的内容,在 scripts/kconfig/Makefile 中可以找到如下代码:
menuconfig: $(obj)/mconf
$< $(silent) $(Kconfig)其中obj= scripts/kconfig,silent是设置静默编译的,在这里可以忽略不计,Kconfig=Kconfig,因此扩展以后就是:
menuconfig: scripts/kconfig/mconf
scripts/kconfig/mconf Kconfig目标 menuconfig 依赖 scripts/kconfig/mconf,因此 scripts/kconfig/mconf.c 这个文件会被编译,生成 mconf 这个可执行文件。目标 menuconfig 对应的规则为 scripts/kconfig/mconf Kconfig,也就是说 mconf 会调用 uboot 根目录下的 Kconfig 文件开始构建图形配置界面。
2.2、Kconfig 语法简介
上一小节我们已经知道了 scripts/kconfig/mconf 会调用 uboot 根目录下的 Kconfig 文件开始
构建图形化配置界面,接下来简单学习一下 Kconfig 的语法。对于 Kconfig 语法我们不需要太深入的去研究。大概了解其原理即可。打开 uboot 根目录下的Kconfig,这个Kconfig文件就是顶层Kconfig,我们就以这个文件为例来简单学习一下 Kconfig语法。
1 、 mainmenu
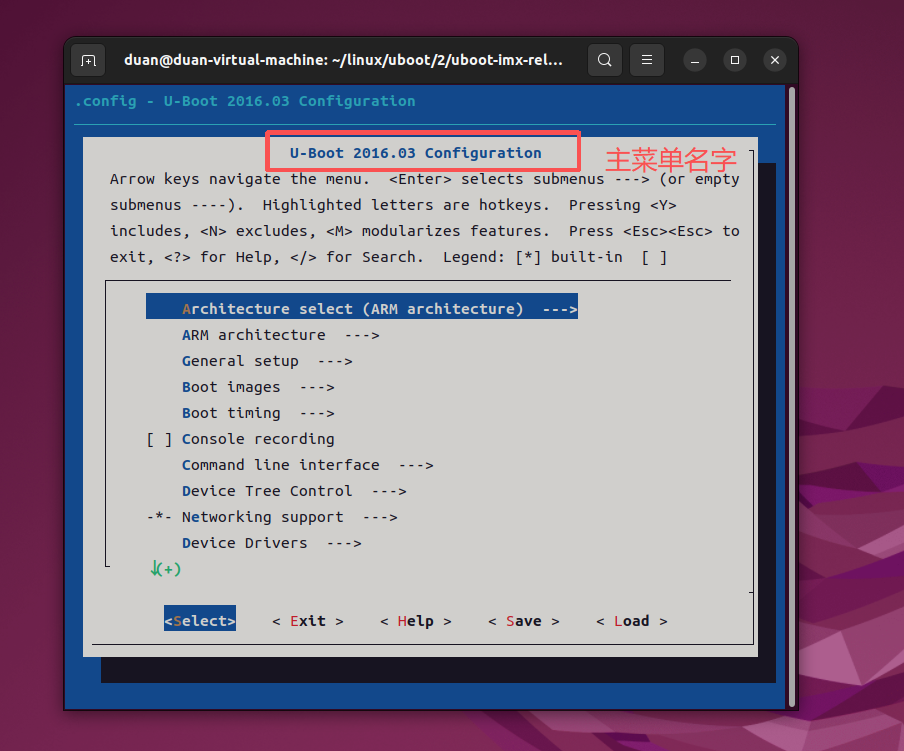
顾名思义 mainmenu 就是主菜单,也就是输入"make menuconfig"以后打开的默认界面,在顶层 Kconfig 中有如下代码:
mainmenu "U-Boot $UBOOTVERSION Configuration"上述代码就是定义了一个名为"U-Boot $UBOOTVERSION Configuration"的主菜单,其中
UBOOTVERSION=2016.03,因此主菜单名为"U-Boot 2016.03 Configuration",如下图所示:
2 、调用其他目录下的 Kconfig 文件
和 makefile 一样,Kconfig 也可以调用其他子目录中的 Kconfig 文件,调用方法如下:
source "xxx/Kconfig" // xxx为具体的目录名,相对路径在顶层 Kconfig 中有如下代码:
source "arch/Kconfig"
source "common/Kconfig"
source "cmd/Kconfig"
source "dts/Kconfig"
source "net/Kconfig"
source "drivers/Kconfig"
source "fs/Kconfig"
source "lib/Kconfig"
source "test/Kconfig"从上述代码中可以看出,顶层 Kconfig 文件调用了很多其他子目录下的 Kcofig 文件,这些子目录下的 Kconfig 文件在主菜单中生成各自的菜单项。
3、menu/endmenu 条目
menu 用于生成菜单,endmenu 就是菜单结束标志,这两个一般是成对出现的。在顶层Kconfig 中有如下代码:
102 menu "Boot images"
103
104 config SUPPORT_SPL
105 bool
106
......
224 endmenu # Boot images上述代码为一个menu/endmenu 代码块,表示子菜单"Boot images",体现在主菜单界面中就如下图所示:
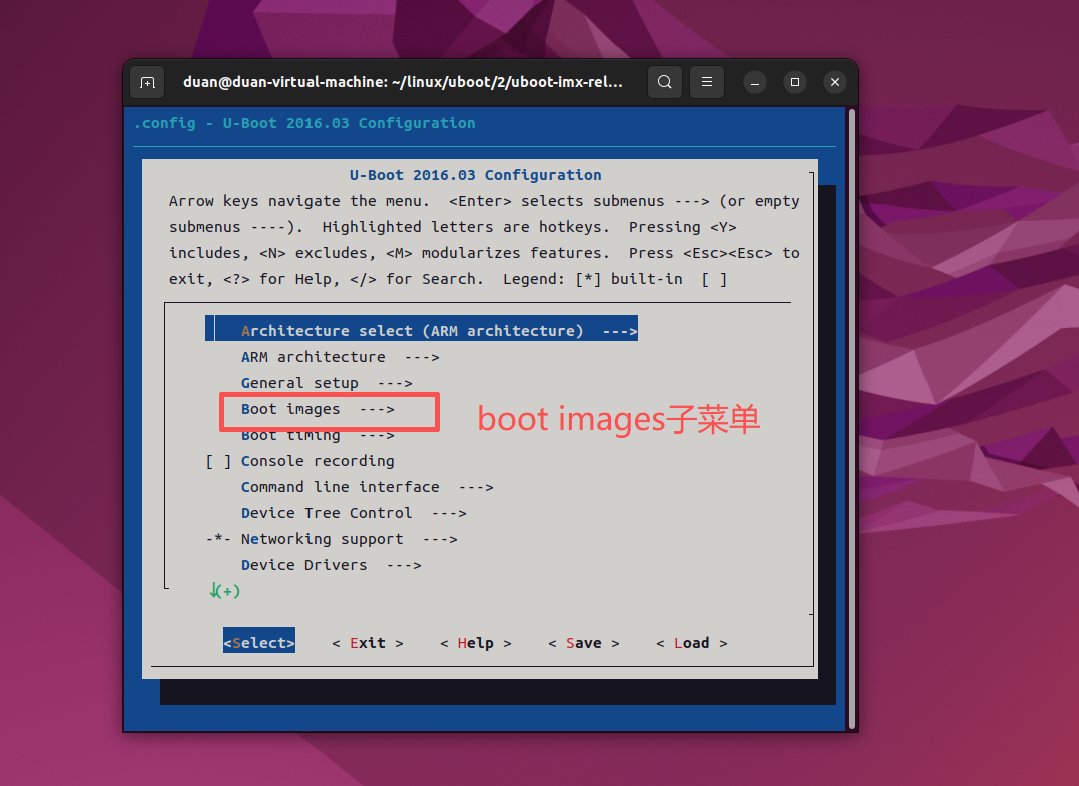
注意:还有一些子菜单并没有使用menu/endmenu 代码块,主界面中的"Boot timing"、"Console recording"等等这些子菜单,都是分别由顶层Kconfig 所调用的 common/Kconfig、cmd/Kconfig 等这些子 Kconfig 文件来创建的。
4、 config 条目
顶层 Kconfig 中的"General setup"子菜单内容如下:
menu "General setup"
config LOCALVERSION
string "Local version - append to U-Boot release"
help
Append an extra string to the end of your U-Boot version.
This will show up on your boot log, for example.
The string you set here will be appended after the contents of
any files with a filename matching localversion* in your
object and source tree, in that order. Your total string can
be a maximum of 64 characters.
config LOCALVERSION_AUTO
bool "Automatically append version information to the version string"
default y
help
This will try to automatically determine if the current tree is a
release tree by looking for git tags that belong to the current
top of tree revision.
A string of the format -gxxxxxxxx will be added to the localversion
if a git-based tree is found. The string generated by this will be
appended after any matching localversion* files, and after the value
set in CONFIG_LOCALVERSION.
(The actual string used here is the first eight characters produced
by running the command:
$ git rev-parse --verify HEAD
which is done within the script "scripts/setlocalversion".)
config CC_OPTIMIZE_FOR_SIZE
bool "Optimize for size"
default y
help
Enabling this option will pass "-Os" instead of "-O2" to gcc
resulting in a smaller U-Boot image.
This option is enabled by default for U-Boot.
config SYS_MALLOC_F
bool "Enable malloc() pool before relocation"
default y if DM
help
Before relocation memory is very limited on many platforms. Still,
we can provide a small malloc() pool if needed. Driver model in
particular needs this to operate, so that it can allocate the
initial serial device and any others that are needed.
config SYS_MALLOC_F_LEN
hex "Size of malloc() pool before relocation"
depends on SYS_MALLOC_F
default 0x400
help
Before relocation memory is very limited on many platforms. Still,
we can provide a small malloc() pool if needed. Driver model in
particular needs this to operate, so that it can allocate the
initial serial device and any others that are needed.
menuconfig EXPERT
bool "Configure standard U-Boot features (expert users)"
default y
help
This option allows certain base U-Boot options and settings
to be disabled or tweaked. This is for specialized
environments which can tolerate a "non-standard" U-Boot.
Only use this if you really know what you are doing.
if EXPERT
config SYS_MALLOC_CLEAR_ON_INIT
bool "Init with zeros the memory reserved for malloc (slow)"
default y
help
This setting is enabled by default. The reserved malloc
memory is initialized with zeros, so first malloc calls
will return the pointer to the zeroed memory. But this
slows the boot time.
It is recommended to disable it, when CONFIG_SYS_MALLOC_LEN
value, has more than few MiB, e.g. when uses bzip2 or bmp logo.
Then the boot time can be significantly reduced.
Warning:
When disabling this, please check if malloc calls, maybe
should be replaced by calloc - if expects zeroed memory.
endif
endmenu # General setup可以看出,在 menu/endmenu 代码块中有大量的"config xxxx"的代码块,也就是 config 条目,config 条目就是"General setup"菜单的具体配置项,如下图所示:
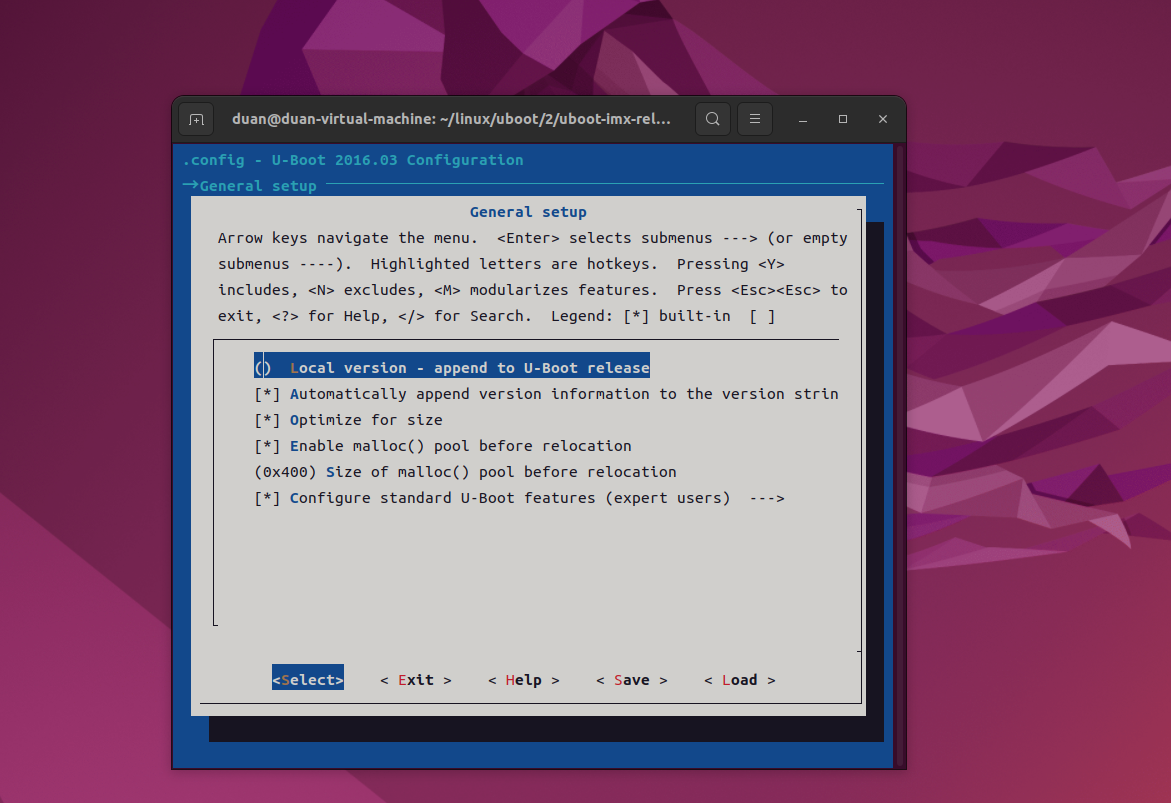
"config LOCALVERSION"对应着第一个配置项,"config LOCALVERSION_AUTO"对应
着 第 二 个 配 置 项 , 以 此 类 推 。
5、depends on 和 select
打开 arch/Kconfig 文件,在里面有这如下代码:
7 config SYS_GENERIC_BOARD
8 bool
9 depends on HAVE_GENERIC_BOARD
10
11 choice
12 prompt "Architecture select"
13 default SANDBOX
14
15 config ARC
16 bool "ARC architecture"
17 select HAVE_PRIVATE_LIBGCC
18 select HAVE_GENERIC_BOARD
19 select SYS_GENERIC_BOARD
20 select SUPPORT_OF_CONTROL第 9 行,"depends on"说明"SYS_GENERIC_BOARD"项依赖于"HAVE_GENERIC_BOARD", 也就是说"HAVE_GENERIC_BOARD"被选中以后"SYS_GENERIC_BOARD"才能被选中。
第 17~20 行,"select"表示方向依赖,当选中"ARC"以后,"HAVE_PRIVATE_LIBGCC""HAVE_GENERIC_BOARD"、"SYS_GENERIC_BOARD"和"SUPPORT_OF_CONTROL"这四个也会被选中。
6、 choice/endchoice
在 arch/Kconfig 文件中有如下代码:
choice
prompt "Architecture select"
default SANDBOX
config ARC
bool "ARC architecture"
......
config ARM
bool "ARM architecture"
......
config AVR32
bool "AVR32 architecture"
......
config BLACKFIN
bool "Blackfin architecture"
......
config M68K
bool "M68000 architecture"
......
endchoicechoice/endchoice 代码段定义了一组可选择项,将多个类似的配置项组合在一起,供用户单选或者多选。示例代码 34.2.2.7 就是选择处理器架构,可以从 ARC、ARM、AVR32 等这些架构中选择,这里是单选。在 uboot 图形配置界面上选择"Architecture select",进入以后如图所示:
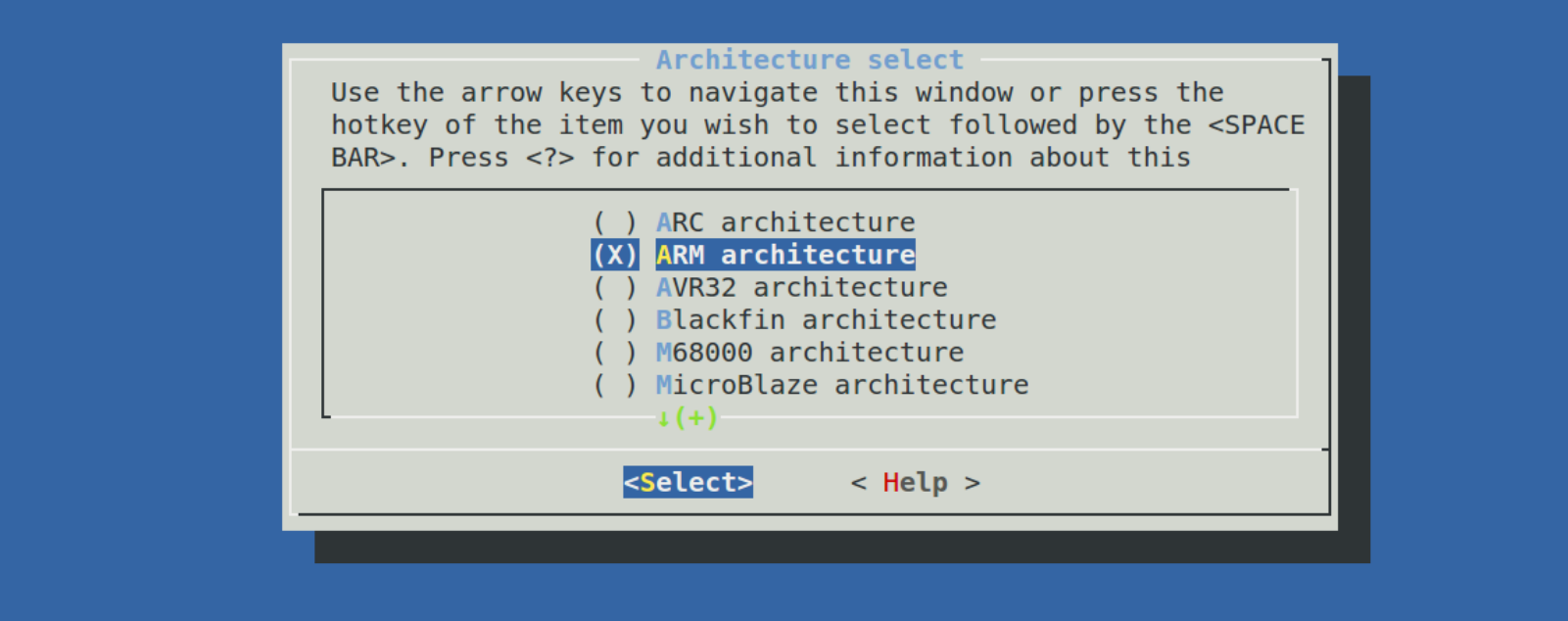
可以在上图中通过移动光标来选择所使用的 CPU 架构。第 12 行的 prompt 给出这个choice/endchoice 段的提示信息为"Architecture select"。
7、menuconfig
menuconfig 和 menu 很类似,但是 menuconfig 是个带选项的菜单,其一般用法为:
1 menuconfig MODULES
2 bool "菜单"
3 if MODULES
4 ...
5 endif # MODULES第 1 行,定义了一个可选的菜单 MODULES,只有选中了 MODULES 第 3~5 行 if 到 endif之间的内容才会显示。在顶层 Kconfig 中有如下代码:
14 menu "General setup"
......
74 menuconfig EXPERT
75 bool "Configure standard U-Boot features (expert users)"
76 default y
77 help
78 This option allows certain base U-Boot options and settings
79 to be disabled or tweaked. This is for specialized
80 environments which can tolerate a "non-standard" U-Boot.
81 Only use this if you really know what you are doing.
82
83 if EXPERT
84 config SYS_MALLOC_CLEAR_ON_INIT
85 bool "Init with zeros the memory reserved for malloc (slow)"
86 default y
87 help
88 This setting is enabled by default. The reserved malloc
89 memory is initialized with zeros, so first malloc calls
......
98 should be replaced by calloc - if expects zeroed memory.
99 endif
100 endmenu # General setup第 74~99 行使用 menuconfig 实现了一个菜单,如下图:
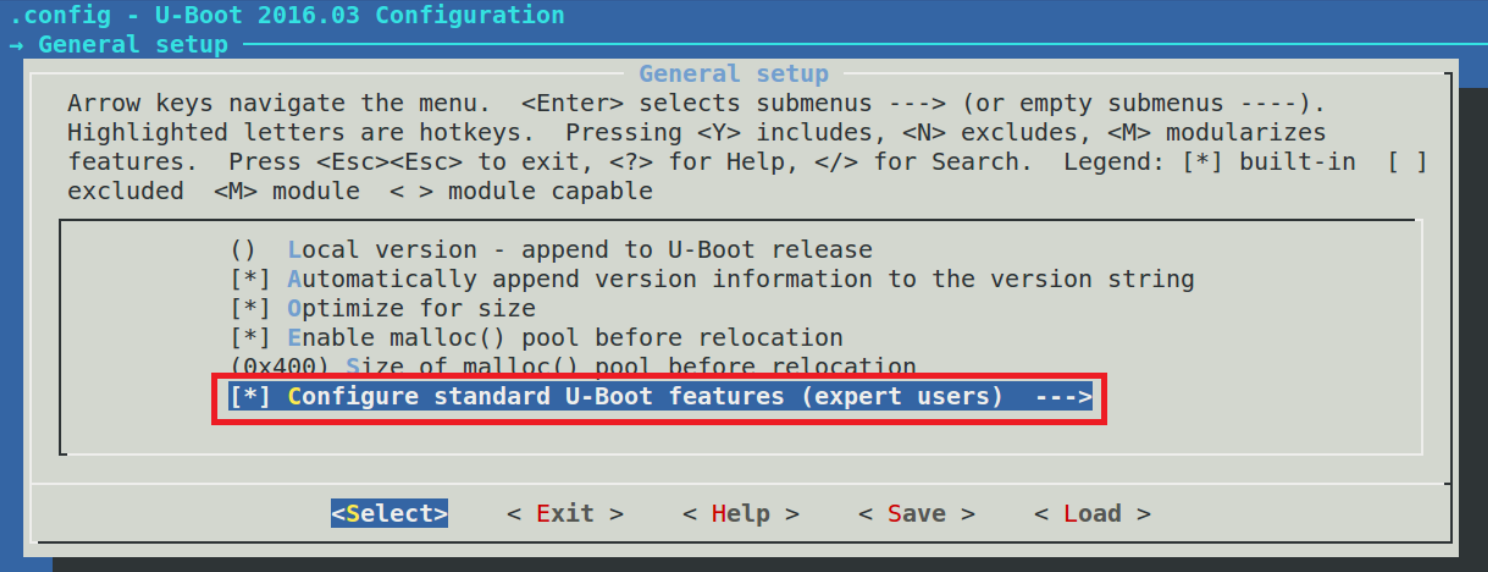
从上图可以看到,前面有"[ ]"说明这个菜单是可选的,当选中这个菜单以后就可以进入到子选项中,也就是之前代码中的第 83~99 行所描述的菜单,如下图 所示:
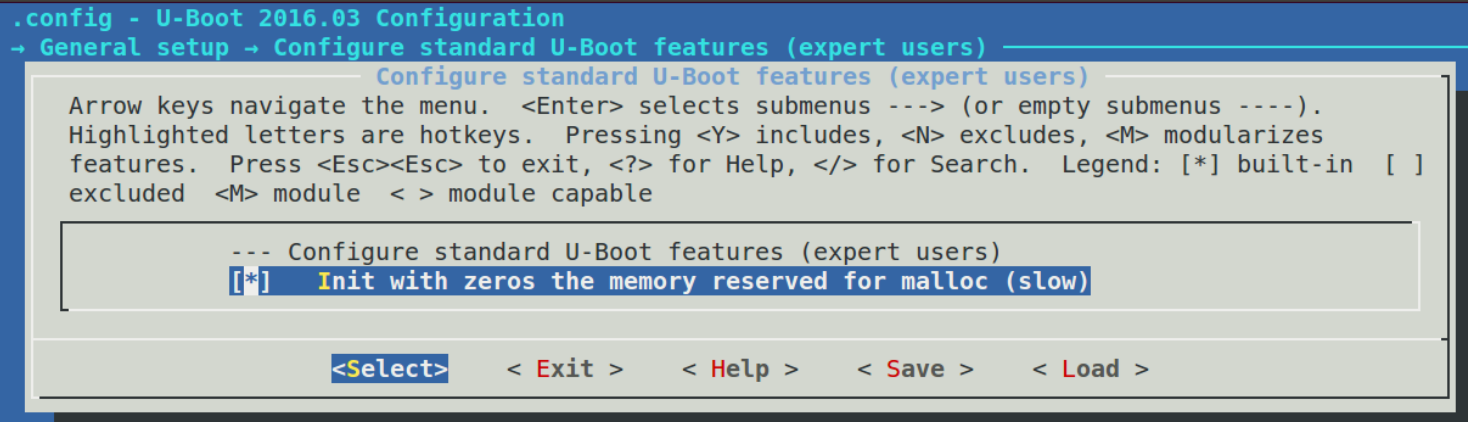
8、 comment
comment 用 于 注 释 , 也 就 是 在 图 形 化 界 面 中 显 示 一 行 注 释 , 打 开 文 件 drivers/mtd/nand/Kconfig,有如下所示代码:
74 config NAND_ARASAN
75 bool "Configure Arasan Nand"
76 help
......
80
81 comment "Generic NAND options"第 81 行使用 comment 标注了一行注释,注释内容为:"Generic NAND options",这行注释
在配置项 NAND_ARASAN 的下面。在图形化配置界面中按照如下路径打开:
-> Device Drivers
-> NAND Device Support
如下图:
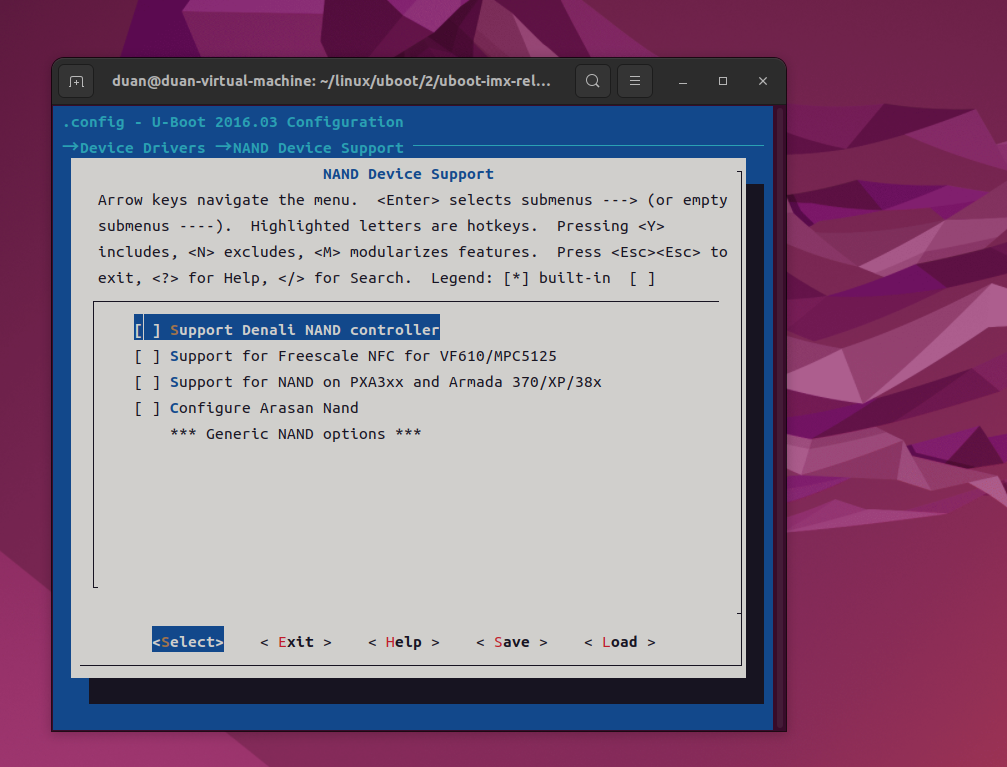
从上图可以看出,在配置项"Configure Arasan Nand"下面有一行注释,注释内容为
"*** Generic NAND options ***"。
9、 source
source 用于读取另一个 Kconfig,比如:
source "arch/Kconfig"Kconfig 语法简介到这里,基本上常用的语法就是这些,因为 uboot 相比 Linux 内核要小很多,所以配置项也要少很多,所以建议大家使用 uboot 来学习 Kconfig。一般不会修改 uboot中的 Kconfig 文件,甚至都不会使用 uboot 的图形化界面配置工具,本小节学习 Kconfig 的目的主要还是为了 Linux 内核作准备。
总结
本次博客通过uboot 的图形化界面配置工具学习 Kconfig,为了 Linux 内核作准备。