目录
[unordered_set 用法详解](#unordered_set 用法详解)
[1. Key(键类型)](#1. Key(键类型))
[2. Hash(哈希函数类型,默认:std::hash )](#2. Hash(哈希函数类型,默认:std::hash ))
[3. KeyEqual(键相等比较函数,默认:std::equal_to )](#3. KeyEqual(键相等比较函数,默认:std::equal_to ))
[4. Allocator(分配器类型,默认:std::allocator >)](#4. Allocator(分配器类型,默认:std::allocator >))
[1. 容量相关](#1. 容量相关)
[2. 迭代器](#2. 迭代器)
[3. 查找操作](#3. 查找操作)
[4. 修改操作](#4. 修改操作)
[5. 桶操作](#5. 桶操作)
[6. 哈希策略](#6. 哈希策略)
[unordered_map 用法详解](#unordered_map 用法详解)
[1. Key(键类型)](#1. Key(键类型))
[2. T(值类型)](#2. T(值类型))
[3. Hash(哈希函数类型,默认:std::hash )](#3. Hash(哈希函数类型,默认:std::hash ))
[4. KeyEqual(键相等比较函数,默认:std::equal_to )](#4. KeyEqual(键相等比较函数,默认:std::equal_to ))
[5. Allocator(分配器类型,默认:std::allocator >)](#5. Allocator(分配器类型,默认:std::allocator >))
[1. 元素访问](#1. 元素访问)
[2. 查找操作](#2. 查找操作)
[3. 修改操作](#3. 修改操作)
[4. 遍历操作](#4. 遍历操作)
[5. 桶操作和哈希策略](#5. 桶操作和哈希策略)
[6. 哈希策略](#6. 哈希策略)
unordered_multimap和unordered_multiset
概述
在C++标准模板库(STL)中,unordered_set和 unordered_map是基于哈希表实现的容器,提供了平均O(1)时间复杂度的查找、插入和删除操作。与有序容器(set、map)不同,它们不维护元素的任何特定顺序。
头文件
cpp
#include <unordered_set>
#include <unordered_map>unordered_set 用法详解
模板参数介绍
cpp
template < class Key, // unordered_set::key_type/value_type
class Hash = hash<Key>, // unordered_set::hasher
class Pred = equal_to<Key>, // unordered_set::key_equal
class Alloc = allocator<Key> // unordered_set::allocator_type
> class unordered_set;1. Key(键类型)
作用:定义键的数据类型,必须是可哈希和可比较的
2. Hash(哈希函数类型,默认:std::hash<Key>)
作用 :将键转换为size_t类型的哈希值
内置数据类型和string类,可以使用stl内置的哈希函数,该参数可缺省,如果用unordered_set存储自定义数据类型,则需要自己设计哈希函数。
3. KeyEqual(键相等比较函数,默认:std::equal_to<Key>)
作用:判断两个键是否相等
内置数据类型和string类,可以使用stl内置的键相等比较函数,该参数可缺省,如果用unordered_set存储自定义数据类型,则需要自己设计键相等比较函数,该函数是实现键值去重和查找必不可少的。
4. Allocator(分配器类型,默认:std::allocator<pair<const Key, T>>)
作用:管理内存的分配和释放
绝大多数情况使用默认分配器,特殊场景(如嵌入式系统、实时系统)可能需要自定义分配器
初始化相关操作
cpp
unordered_set<int> s1; // 空set
unordered_set<int> s2 = {1, 2, 3, 4}; // 初始化列表
unordered_set<int> s3(s2.begin(), s2.end()); // 范围构造成员函数介绍
1. 容量相关
cpp
unordered_set<int> uset = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
cout << "size: " << uset.size() << endl; // 元素个数: 5
cout << "empty: " << uset.empty() << endl; // 是否为空: 0(false)
cout << "max_size: " << uset.max_size() << endl; // 可存储的最大数量
2. 迭代器
cpp
unordered_set<int> uset = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
// 遍历(无序,但通常按哈希桶顺序)
for(auto it = uset.begin(); it != uset.end(); ++it) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout<<endl;
// 使用范围for循环
for(const auto& val : uset) {
cout << val << " ";
}
3. 查找操作
cpp
unordered_set<string> uset = {"apple", "banana", "orange"};
// find - 返回迭代器,未找到则返回end()
auto it = uset.find("banana");
if(it != uset.end()) {
cout << "Found: " << *it << endl;
}
// count - 返回元素个数(0或1)
if(uset.count("apple") > 0) {
cout << "apple exists" << endl;
}
4. 修改操作
cpp
unordered_set<int> uset;
// insert - 插入元素
auto result = uset.insert(10); // 返回pair<iterator, bool>
if(result.second) {
cout << "Insert successful" << endl;
}
uset.insert({20, 30, 40}); // 插入多个元素
// emplace - 原地构造
uset.emplace(50);
// erase - 删除元素
uset.erase(20); // 通过值删除
auto it = uset.find(30);
if(it != uset.end()) {
uset.erase(it); // 通过迭代器删除
}
uset.erase(uset.begin(), uset.end()); // 范围删除
// clear - 清空所有元素
uset.clear();
注意:使用insert和emplace插入单个元素时,返回值为pair<iterator,bool>,result.first表示插入元素位置的迭代器,result.second表示插入是否成功。
auto result = uset.insert(10); result的数据类型是 std::pair<std::unordered_set<int>::iterator,bool>
5. 桶操作
STL实现哈希表示意图,对于哈希值相同的元素,STL选择将其用链表链接起来,挂到同一个桶上面去。
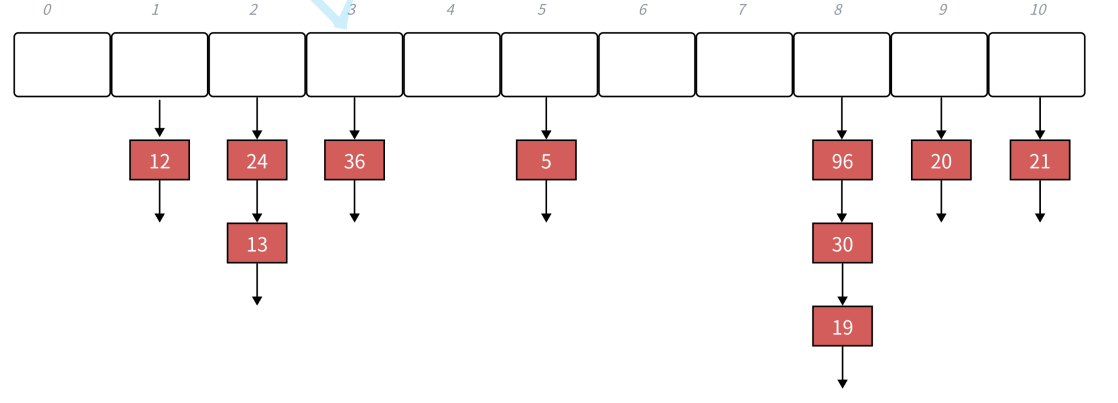
在C++ STL中,unordered_set和 unordered_map的默认最大负载因子是 1.0
(负载因子 = 插入元素数量 / 桶数量)
这意味着当容器中的元素数量超过桶的数量时(即负载因子 > 1.0),就会触发扩容。
cpp
unordered_set<int> uset = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10};
cout << "bucket_count: " << uset.bucket_count() << endl; // 桶的数量
cout << "max_bucket_count: " << uset.max_bucket_count() << endl;
cout << "load_factor: " << uset.load_factor() << endl; // 负载因子
cout << "max_load_factor: " << uset.max_load_factor() << endl; // 最大负载因子
// 遍历桶
for(size_t i = 0; i < uset.bucket_count(); ++i) {
cout << "Bucket " << i << " has " << uset.bucket_size(i) << " elements" << endl;
}
// 查找元素所在的桶
int val = 5;
cout << val << " is in bucket " << uset.bucket(val) << endl;6. 哈希策略
cpp
unordered_set<int> uset;
// 设置最大负载因子
uset.max_load_factor(0.7f);
// 预分配桶的数量
uset.reserve(100); // 预留至少100个元素的空间
// 重新哈希
uset.rehash(50); // 设置桶的数量至少为50unordered_map 用法详解
模板参数介绍:
cpp
template < class Key, // unordered_map::key_type
class T, // unordered_map::mapped_type
class Hash = hash<Key>, // unordered_map::hasher
class Pred = equal_to<Key>, // unordered_map::key_equal
class Alloc = allocator< pair<const Key,T> > // unordered_map::allocator_type
> class unordered_map;1. Key(键类型)
作用:定义键的数据类型,必须是可哈希和可比较的
2. T(值类型)
作用:定义与键关联的值的类型
3. Hash(哈希函数类型,默认:std::hash<Key>)
作用 :将键转换为size_t类型的哈希值
内置数据类型和string类,可以使用stl内置的哈希函数,该参数可缺省,如果用unordered_set存储自定义数据类型,则需要自己设计哈希函数。
4. KeyEqual(键相等比较函数,默认:std::equal_to<Key>)
作用:判断两个键是否相等
内置数据类型和string类,可以使用stl内置的键相等比较函数,该参数可缺省,如果用unordered_set存储自定义数据类型,则需要自己设计键相等比较函数,该函数是实现键值去重和查找必不可少的。
5. Allocator(分配器类型,默认:std::allocator<pair<const Key, T>>)
作用:管理内存的分配和释放
绝大多数情况使用默认分配器,特殊场景(如嵌入式系统、实时系统)可能需要自定义分配器
初始化相关操作
cpp
// 定义unordered_map
unordered_map<string, int> m1; // 空map
unordered_map<string, int> m2 = {
{"apple", 1},
{"banana", 2},
{"orange", 3}
};成员函数介绍
1. 元素访问
cpp
unordered_map<string, int> umap = {{"apple", 5}, {"banana", 3}};
// operator[] - 访问或插入元素
umap["apple"] = 10; // 修改现有元素
umap["orange"] = 7; // 插入新元素
int val = umap["apple"]; // 访问元素
// at - 访问元素,越界时抛出异常
try {
int value = umap.at("banana");
} catch(const out_of_range& e) {
cout << "Key not found" << endl;
}2. 查找操作
cpp
unordered_map<string, int> umap = {{"apple", 1}, {"banana", 2}};
// find
auto it = umap.find("apple");
if(it != umap.end()) {
cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << endl;
}
// count
if(umap.count("banana") > 0) {
cout << "banana exists" << endl;
}
// contains (C++20)
if(umap.contains("apple")) {
cout << "apple exists" << endl;
}3. 修改操作
cpp
unordered_map<string, int> umap;
// insert - 插入键值对
auto result = umap.insert({"apple", 5});
if(result.second) {
cout << "Insert successful" << endl;
}
umap.insert({{"banana", 3}, {"orange", 2}});
// emplace - 原地构造
umap.emplace("grape", 4);
// emplace_hint - 带提示的插入
auto hint = umap.begin();
umap.emplace_hint(hint, "pear", 6);
// try_emplace (C++17) - 如果键不存在则插入
umap.try_emplace("apple", 10); // 不会替换现有的"apple"
umap.try_emplace("mango", 8); // 插入新的"mango"
// insert_or_assign (C++17) - 插入或赋值
umap.insert_or_assign("apple", 15); // 替换现有值
umap.insert_or_assign("kiwi", 9); // 插入新键值对
// erase
umap.erase("banana"); // 通过键删除
auto it = umap.find("orange");
if(it != umap.end()) {
umap.erase(it); // 通过迭代器删除
}4. 遍历操作
cpp
unordered_map<string, int> umap = {
{"apple", 3},
{"banana", 5},
{"orange", 2}
};
// 使用迭代器
for(auto it = umap.begin(); it != umap.end(); ++it) {
cout << it->first << ": " << it->second << endl;
}
// 结构化绑定 (C++17)
for(const auto& [key, value] : umap) {
cout << key << ": " << value << endl;
}5. 桶操作和哈希策略
cpp
unordered_map<string, int> umap = {
{"apple", 1}, {"banana", 2}, {"orange", 3},
{"grape", 4}, {"pear", 5}, {"kiwi", 6}
};
// 桶信息
cout << "Bucket count: " << umap.bucket_count() << endl;
cout << "Load factor: " << umap.load_factor() << endl;
cout << "Max load factor: " << umap.max_load_factor() << endl;6. 哈希策略
cpp
// 设置哈希策略
umap.max_load_factor(0.75f);
umap.reserve(50); // 预留空间
umap.rehash(30); // 重新哈希unordered_multimap和unordered_multiset
unordered_map 键唯一,每个键对应一个值;unordered_multimap 允许键重复,一个键可对应多个值。
unordered_set 键唯一;unordered_multiset 允许键重复。
那么本期的内容就到这里了,觉得有收获的同学们可以给个点赞、评论、关注、收藏哦,谢谢大家。