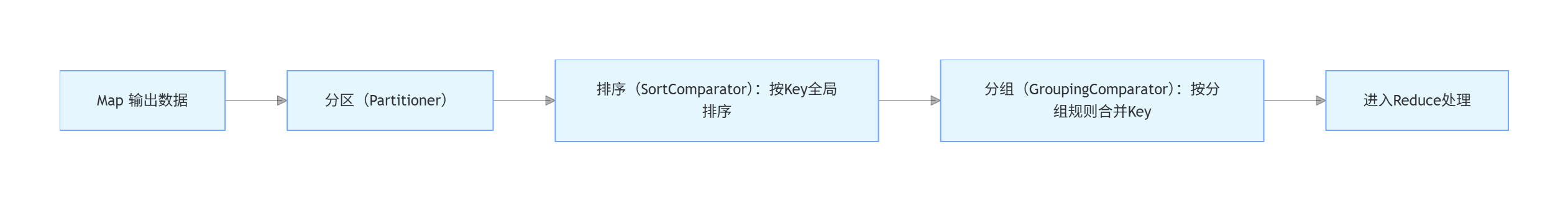
本文将通过一个案例来了解Hadoop中Partitioner,SortComparator,GroupingComparator。
需求
找出每个月温度最高的两天
数据集
2019-10-01 14:21:02 37c
2019-10-01 19:21:02 38c
2019-10-02 14:01:02 36c
2019-10-03 14:01:02 35c
2020-01-01 11:21:02 32c
2020-10-01 12:21:02 37c
2018-12-01 12:21:02 23c
2020-10-02 12:21:02 41c
2020-10-03 12:21:02 27c
2018-07-01 12:21:02 45c
2018-07-02 12:21:02 46c
2018-07-03 12:21:03 47c
案例分析
在MR中,原语是"相同"key的键值对为一组,调用一次reduce方法,方法内迭代这组数据计算。需要自定义分组比较器。(相同的年月分为一组)
找出每个月温度最高的两天(自定义排序比较器:年月相同时按照温度从高到低排序)
二次排序,分组比较器和排序比较器不一样
map:key ->LongWritable (偏移量)
value-> Text (文本中的一行内容)
日期+气温 将value中的指标拿出来组成一个新的key:自定义Weather类
分组的时候,需要将新的key拆开来比较
自定义key的类:Weather(还需要实现序列化和反序列化)
代码实现
自定义数据类型Weather
包含时间:年 月 日
包含温度
定义内部类,实现自定义排序比较规则
自定义分组比较
年月相同被视为相同的key
那么reduce迭代时,相同年月的记录有可能是同一天的,reduce中需要判断是否同一天
数据量很大:
全量数据可以切分成最少按一个月份的数据量进行判断
这种业务场景可以设置多个reduce
通过实现partition
项目准备
创建项目
配置resource资源文件和pom.xml,具体配置参数参考:实战:单词数量统计案例-CSDN博客

key类Weather的设计
java
package com.wusen.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
import java.io.DataInput;
import java.io.DataOutput;
import java.io.IOException;
public class Weather implements WritableComparable<Weather> {
private Integer year;
private Integer month;
private Integer day;
private Double temperature;
public Integer getYear() {
return year;
}
public void setYear(Integer year) {
this.year = year;
}
public Integer getMonth() {
return month;
}
public void setMonth(Integer month) {
this.month = month;
}
public Integer getDay() {
return day;
}
public void setDay(Integer day) {
this.day = day;
}
public Double getTemperature() {
return temperature;
}
public void setTemperature(Double temperature) {
this.temperature = temperature;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Weather{" +
"year=" + year +
", month=" + month +
", day=" + day +
", temperature=" + temperature +
'}';
}
//该方法可以在排序比较器中调用,也可以在分组比价器中调用
//但是两个比较器逻辑不一致,只能满足其中一方调用。想被谁调用,就按照对应的逻辑编写
@Override
public int compareTo(Weather that) {
//逻辑比较器实现
int result = this.year.compareTo(that.getYear());
if (result == 0){//年相同
result = this.month.compareTo(that.getMonth());
if (result == 0){
result =this.temperature.compareTo(that.getTemperature());
}
}
return result;
}
//通过内部类注册key自带比较器
public static class Comparator extends WritableComparator {
//向 Hadoop 底层的 WritableComparator 父类 "声明" 这个自定义比较器是专门用于 Weather 类型的
public Comparator() {
//修改为Weather.class
super(Weather.class);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
Weather wa = (Weather) a;
Weather wb = (Weather) b;
//如果Weather类中的compareTo方法的比较逻辑符合此处的逻辑,可以直接调用
return wa.compareTo(wb);
}
}
static {
//注册比较器
WritableComparator.define(Weather.class, new Weather.Comparator());
}
//序列化
@Override
public void write(DataOutput out) throws IOException {
out.writeInt(year);
out.writeInt(month);
out.writeInt(day);
out.writeDouble(temperature);
}
//反序列化
@Override
public void readFields(DataInput in) throws IOException {
this.year = in.readInt();
this.month = in.readInt();
this.day = in.readInt();
this.temperature = in.readDouble();
}
}WeatherMapper类编写
java
package com.wusen.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.LongWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
/**泛型的类型:
* 输入的key、value的类型
* LongWritable:偏移量
* Text:当前行文本的内容
* 输出的key、value的类型
* Weather:将当前行的数据拆分后封装到Weather类的对象中
* Text:当前行文本的内容
*/
public class WeatherMapper extends Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Weather, Text> {
//定义输出的key的对象
private Weather weather = new Weather();
//在map方法外定义对象的好处是一个MapTask只需要实例化一次。
private SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
private Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
//覆写父类中的map方法
@Override
protected void map(LongWritable key, Text value, Mapper<LongWritable, Text, Weather, Text>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
//2020-10-01 12:21:02 37c
//将接收到数据转换字符串,并去掉两端的空格
String line = value.toString().trim();
//首先将日期和文档拆分开
String[] datas = line.split("\t");
//将温度处理(将温度后面的c去掉)
String temperatureStr = datas[1].substring(0, datas.length - 1);
//类型转换
Double temperatureDouble = Double.parseDouble(temperatureStr);
//将温度封装到weather对象中
weather.setTemperature(temperatureDouble);
//处理日期
try {
Date date = simpleDateFormat.parse(datas[0]);
//从date对象获取出年月日,并分别封装到weather对象中
calendar.setTime(date);
weather.setYear(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));
weather.setMonth(calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH));
weather.setDay(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
//将处理后数据写入到圆形缓存区中
context.write(weather,value);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}分区类编写
(这里分区只是保证同一月的数据到同一个 Reduce, Reduce 内部后续还需要「分组比较器」确保同一年月的数据被归为一组)
如何分区?
-
要保证同一组数据(年和月都相同的)在一个分区下
-
每个区中的数据尽可能比较均衡,也就是每个分区中的数据量相差不多,避免数据倾斜(数据被分配到不同计算节点(或分区、Reduce Task)时,出现了严重的不均衡------ 有的节点要处理海量数据,有的节点却几乎没数据,导致整个任务的执行时间被最慢的那个节点拖垮)情况的出现。
可以按照月份进行分区
1,2,3 4,5,6 7,8,9 10,11,12 不太合理
1,5,9 2,6,10 3,7,11 4,8,12比较合理的分法
java
package com.wusen.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Partitioner;
//泛型中的类型分别 Mapper输出的key和value的类型
public class WeatherPartitioner extends Partitioner<Weather, Text> {
@Override
public int getPartition(Weather weather, Text text, int numPartitions) {
return weather.getMonth()%numPartitions;
}
}排序比较器类编写
这个类的作用是对全局进行排序,方便接下来的分组比较器进行分组。主要需要实现一个构造方法和重写Compare方法。构造方法是为了让其父类为我们创建key对应类对象。而Compare主要是用于告诉框架比较的逻辑。接下来的全局排序将会有Hadoop根据你的比较逻辑自动实现。
java
package com.wusen.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
public class WeatherSortComparator extends WritableComparator {
public WeatherSortComparator() {
//让当前类的父类为我们创建key对应类Weather类的对象
super(Weather.class,true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
//进行强制类型转换
Weather wa = (Weather)a;
Weather wb = (Weather)b;
//如果Weather类中的compareTo方法的比较逻辑符合排序的逻辑可以直接调用
//return wa.compareTo(wb);
//如果Weather类中的compareTo方法的比较逻辑不符合排序的逻辑需要重新编写比较的逻辑
int result = wa.getYear().compareTo(wb.getYear());
if(result==0){//年相同再比较月份
result = wa.getMonth().compareTo(wb.getMonth());
if(result==0){//月相同再比较温度,温度从高到低
result = wb.getTemperature().compareTo(wa.getTemperature());
}
}
//先比较年
return result;
}
}分组比较器
分组比较器实现原理
Reduce 阶段的「分组」逻辑由 GroupingComparator 决定,它的底层规则是:
遍历 Shuffle 后排序好的 Key 列表,用分组比较器依次比较相邻的两个 Key:
- 如果
compare(a, b) == 0→ 判定 a 和 b 属于「同一组」,合并到同一个Iterable<Value>中;- 如果
compare(a, b) != 0→ 判定 a 和 b 属于「不同组」,结束当前组,开始新组。
简单说:分组比较器的 compare 方法返回 0 = 同一组,返回非 0 = 不同组
例子:
假设 Shuffle 后排序好的 Weather Key 列表是:
| Key(Weather 对象) | 年 | 月 | 日 | 温度 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| w1 | 2023 | 1 | 1 | 10.5 |
| w2 | 2023 | 1 | 2 | 15.2 |
| w3 | 2023 | 1 | 3 | 8.8 |
| w4 | 2023 | 2 | 1 | 9.9 |
| w5 | 2024 | 1 | 1 | 12.1 |
分组比较器的执行过程:
- 比较 w1 和 w2 → 年 = 2023、月 = 1 → 返回 0 → 归为同一组;
- 比较 w2 和 w3 → 年 = 2023、月 = 1 → 返回 0 → 归到同一组(此时组内有 w1、w2、w3);
- 比较 w3 和 w4 → 年相同,但月 = 1 vs 月 = 2 → 返回 -1 → 结束当前组,开始新组;
- 比较 w4 和 w5 → 年 = 2023 vs 2024 → 返回 -1 → 结束当前组,开始新组。
最终分组结果:
- 组 1:2023 年 1 月(包含 w1、w2、w3 的所有 Value);
- 组 2:2023 年 2 月(包含 w4 的 Value);
- 组 3:2024 年 1 月(包含 w5 的 Value)。
分组比较器类编写
java
package com.wusen.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.WritableComparator;
public class WeatherGroupingComparator extends WritableComparator {
public WeatherGroupingComparator() {
//让当前类的父类WritableComparator创建指定类型Weather类的对象,否则会出现空指针异常
super(Weather.class,true);
}
@Override
public int compare(WritableComparable a, WritableComparable b) {
//强制类型转换
Weather wa = (Weather) a;
Weather wb = (Weather) b;
//如果Weather类中的compareTo比较的逻辑适合分组比较器的逻辑的话,可以直接调用
//return wa.compareTo(wb);
//如果Weather类中的compareTo比较的逻辑不适合分组比较器的逻辑的话,需要重新编写比较的逻辑
int result = wa.getYear().compareTo(wb.getYear());
if(result==0){//年份相同,在比较月份
result = wa.getMonth().compareTo(wb.getMonth());
}
return result;
}
}WeatherReducer类编写
java
package com.wusen.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer;
import java.io.IOException;
/**泛型的类型:
* 输入的key、value的类型
* Weather,:Mapper输出的Weather类对象
* Text:Mapper输出的文本内容,如:2020-10-01 12:21:02 37c
* 输出的key、value的类型
* Text:Mapper输出的文本内容,如:2020-10-01 12:21:02 37c
* NullWritable:Null
*/
public class WeatherReducer extends Reducer<Weather, Text, Text, NullWritable> {
@Override
protected void reduce(Weather key, Iterable<Text> values, Reducer<Weather, Text, Text, NullWritable>.Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
/**2019-10-01 19:21:02 38c
* 2019-10-01 14:21:02 37c
2019-10-02 14:01:02 36c
2019-10-03 14:01:02 35c
*/
//定义一个变量
int day = -1;
//遍历values
for(Text value:values){
if(day==-1){
//说明这是当前年月下的温度最高的第一条数据,将之直接输出
context.write(value,NullWritable.get());
//将当前条数据的天获取出来赋值给day变量
day = key.getDay();
}else{
if(day!=key.getDay()){//当前条数据的天不等于上一次输出的天时,才会输出。
context.write(value,NullWritable.get());
//已经输出了当前年月下温度最高的两天数据,该组数据结束。
break;
}
}
}
}
}WeatherDriver类编写
java
package com.wusen.hadoop;
import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable;
import org.apache.hadoop.io.Text;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Job;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.FileInputFormat;
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat;
public class WeatherDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.判断输入输出路径是否合法
if(args==null||args.length!=2){
System.out.println("Usage:yarn jar myweather.jar com.wusen.hadoop.WeatherDriver <inputPath> <outputPath>");
System.exit(1);
}
//2.创建配置文件对象,并加载默认的配置
Configuration configuration = new Configuration(true);
//3.设置本地运行
configuration.set("mapreduce.framework.name","local");
//4.创建Job对象
Job job = Job.getInstance(configuration);
//5.设置job对象的相关参数
//5.1设置入口类
job.setJarByClass(WeatherDriver.class);
//5.2设置Mapper类以及Mapper输出的key和value的类型
job.setMapperClass(WeatherMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(Weather.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
//5.3设置Reduce类以及Reducer输出的key和value的类型
job.setReducerClass(WeatherReducer.class);
job.setOutputKeyClass(Text.class);
job.setOutputValueClass(NullWritable.class);
//6.设置输入路径
FileInputFormat.addInputPath(job,new Path(args[0]));
//7.设置输出路径
Path outputPath = new Path(args[1]);
FileSystem fileSystem = FileSystem.get(configuration);
//Hadoop 不允许输出目录预先存在,初衷是防止数据误覆盖以及保证结果唯一性
if(fileSystem.exists(outputPath)){
//如果存在,则将之前的目录删除掉
fileSystem.delete(outputPath,true);
}
FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(job,outputPath);
//8.设置Reduce任务数量和分区类
job.setNumReduceTasks(4);
job.setPartitionerClass(WeatherPartitioner.class);
//MapReduce 的 Shuffle 阶段,排序和分组的执行顺序是先排序、后分组,这是框架的固定流程,和 Driver 中设置的代码顺序无关
//9.设置排序比较器
job.setSortComparatorClass(WeatherSortComparator.class);
//10.设置分组比较器
job.setGroupingComparatorClass(WeatherGroupingComparator.class);
//11.提交作业
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
}运行测试
-
启动hadoop集群,在node1上执行:startha.sh(脚本参考Yarn资源调度器-CSDN博客),查看四个节点上java进程是否正常
-
浏览器器中测试
- 创建输入路径
bash
[root@node1 ~]# hdfs dfs -mkdir -p /weather/input/- 创建数据文件,并将数据源中的数据拷贝到该文件中
bash
[root@node1 ~]# vim data.txt
2019-10-01 14:21:02 37c
2019-10-01 19:21:02 38c
2019-10-02 14:01:02 36c
2019-10-03 14:01:02 35c
2020-01-01 11:21:02 32c
2020-10-01 12:21:02 37c
2018-12-01 12:21:02 23c
2020-10-02 12:21:02 41c
2020-10-03 12:21:02 27c
2018-07-01 12:21:02 45c
2018-07-02 12:21:02 46c
2018-07-03 12:21:03 47c- 将data.txt文件提交hdfs文件系统的/weather/input目录
bash
[root@node1 ~]# hdfs dfs -put data.txt /weather/input
[root@node1 ~]# hdfs dfs -ls /weather/input- 在IDEA中运行WeatherDriver类
Usage:yarn jar myweather.jar com.wusen.hadoop.WeatherDriver <inputPath> <outputPath>
说明没有指定输入和输出路径,所以接下来设置输入输出路径。
- 在IDEA中设置输入输出路径
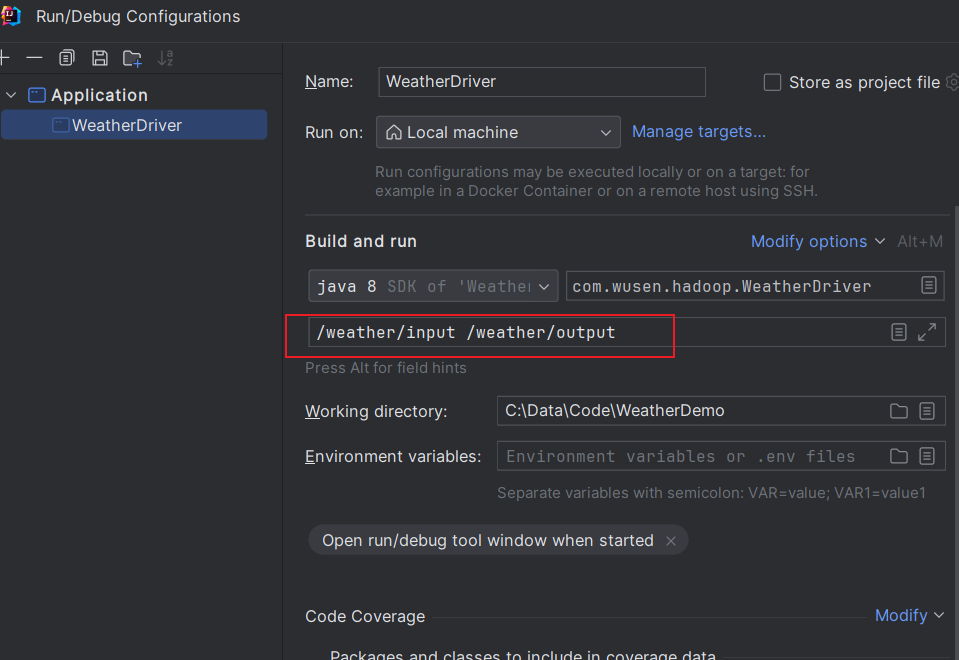 点击Appliy,然后点击OK
点击Appliy,然后点击OK
-
再次在IDEA运行程序
-
检查执行后的结果文件是否生成(我的是node2为active)
http://node2:9870/explorer.html#/weather/output
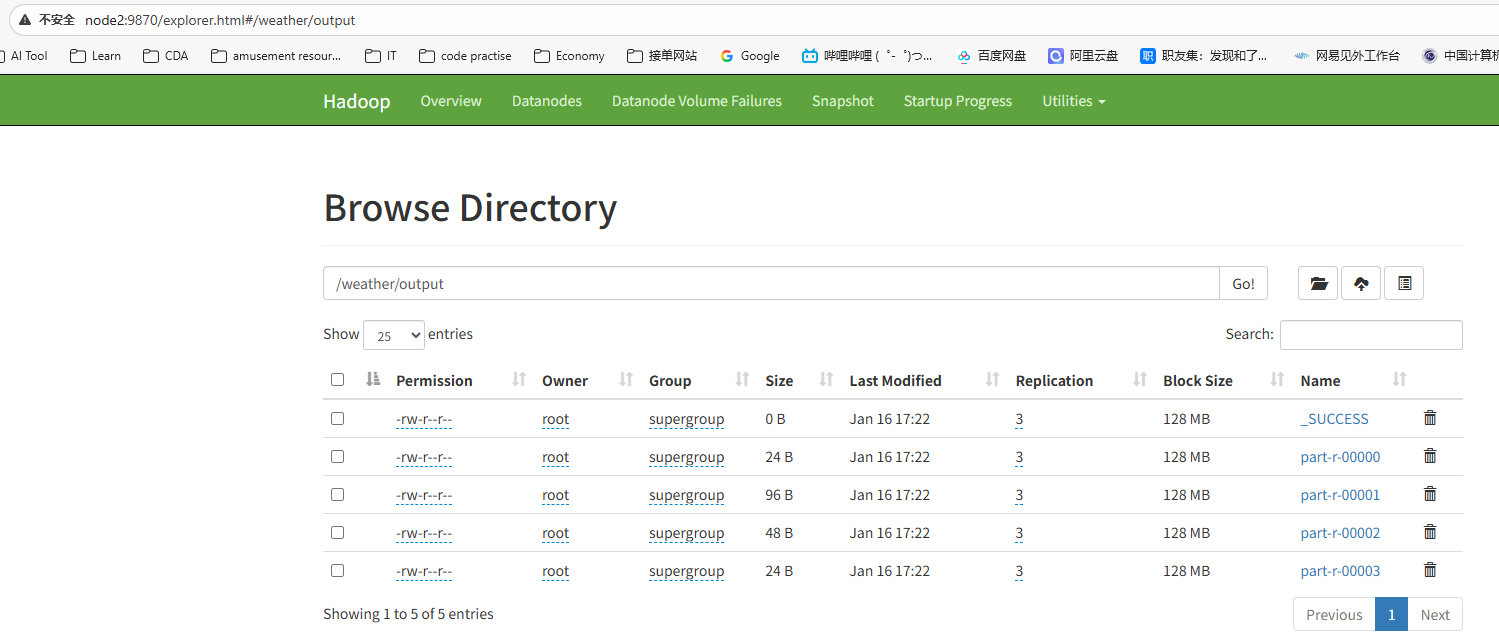
- 通过命令查看这四个文件中的内容:
bash
[root@node1 ~]# hdfs dfs -cat /weather/output/part-r-00001
2026-01-16 17:27:49,072 INFO sasl.SaslDataTransferClient: SASL encryption trust check: localHostTrusted = false, remoteHostTrusted = false
2019-10-03 14:01:02 35c
2019-10-02 14:01:02 36c
2020-10-02 12:21:02 41c
2020-10-01 12:21:02 37c