set
set的使用
set的插入
cpp
int main()
{
//去重+升序排序
set<int>s;
s.insert(5);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(7);
s.insert(5);
}set在插入的时候会默认升序,并且不会插入的值不会重复
set的遍历
cpp
int main()
{
set<int>s = { 4,2,7,2,8,5,9 };
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}set的遍历就是使用迭代器去遍历
set的find接口
cpp
#include<set>
void test_set()
{
set<int> s;
s.insert(4);
s.insert(2);
s.insert(3);
s.insert(6);
s.insert(1);
s.insert(8);
set<int>::iterator ret = s.find(4);// O(logN)
//这两个有效率的区别
auto ret = find(s.begin(),s.end(),4);//这个是暴力查找,在一段迭代器区间里进行查找 O(N)
}find我们可以用算法里面的find接口,也可以用set提供的find接口
cpp
set<int>::iterator ret = s.find(4);//O(logN)
//这两个有效率的区别
auto ret = find(s.begin(),s.end(),4);//这个是暴力查找,在一段迭代器区间里进行查找 O(N)但是这两个的区别是效率的问题,set的底层是二叉搜索树的性质,时间复杂度为O(logN),而算法当中的find是在一段迭代器区间暴力查询,在一段迭代器区间里进行查找,时间复杂度O(N)
set的erase接口
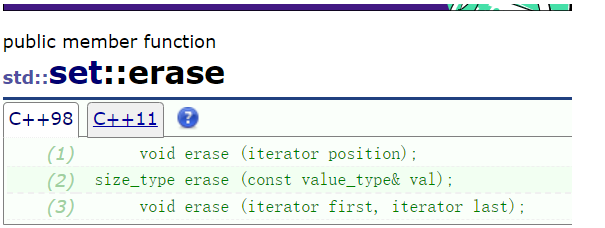
删除接口可以传迭代器,也可以传val,也可以传迭代器区间
cpp
int main()
{
set<int>s = { 4,2,7,2,8,5,9 };
for (auto e : s)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
//1、直接删除x
int x;
cin >> x;
int num = s.erase(x);
if (num == 0)
{
cout << x << "不存在" << endl;
}
else
cout << "删除成功!" << endl;
//2、使用迭代器删除
cin >> x;
auto pos = s.find(x);
if (pos != s.end()) {
// 删除成功
cout << "找到 " << *pos << ",正在删除..." << endl;
s.erase(pos); // 删除
cout << x << "删除成功!" << endl;
}
else {
cout << x << "不存在!" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
cpp
int main()
{
std::set<int> myset;
for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++)
myset.insert(i * 10);
//3、实现查找到的[itlow, itup)包含[30, 60]区间
// 返回>= 30
auto itlow = myset.lower_bound(30);
// 返回> 60
auto itup = myset.upper_bound(60);
// 删除这段区间的值
myset.erase(itlow, itup);
for (auto e : myset)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}map介绍
map是关联容器,它按照特定的次序(按照key来比较)存储由键值key和值value组合而成的元素
1、在map中,键值key通常用于排序和唯一地标识元素,而值value中存储与此键值key关联的内容。键值key和值value的类型可能不同,并且在map的内部,key与value通过成员类型value_type绑定在一起,为其取名为pair:typedef pair value_type;
2、在内部,map中的元素总是按照键值key进行排序的
3、map中通过键值访问单个元素的速度通常比unordered_map容器慢,但map允许根据顺序对元素进行直接迭代(即对map中的元素进行迭代时,可以得到一个有序的序列)。
4、map支持下标访问符,即在[]中放入key,就可以找到与key对应的value。
5、map通常被实现为二叉搜索树(更准确的说:平衡二叉搜索树(红黑树))。
键值对
用来表示具有一一对应关系的一种结构,该结构中一般只包含两个成员变量key和value,key代表键值,value表示与key对应的信息。例如:建立一个英汉互典的字典,那该字典中必然有英文字母单词与对应的中文含义
cpp
template <class T1, class T2>
struct pair
{
typedef T1 first_type;
typedef T2 second_type;
T1 first;
T2 second;
pair(): first(T1()), second(T2())
{}
pair(const T1& a, const T2& b): first(a), second(b)
{}
};map
map的使用
map的模板参数
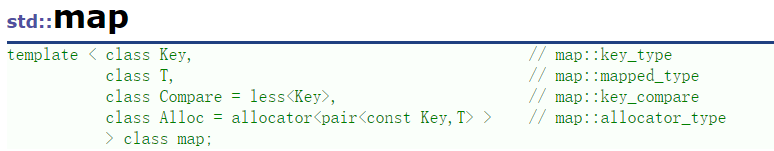
key: 键值对中key的类型
T: 键值对中value的类型
Compare: 比较器的类型,map中的元素是按照key来比较的,缺省情况下按照小于来比较,一般情况下(内置类型元素)该参数不需要传递,如果无法比较时(自定义类型),需要用户自己显式传递比较规则(一般情况下按照函数指针或者仿函数来传递)
Alloc:通过空间配置器来申请底层空间,不需要用户传递,除非用户不想使用标准库提供的空间配置器
注意:在使用map时,需要包含头文件。
map的插入
cpp
#include <map>
int main()
{
map<string, string> dict;
//C++98
pair<string, string>kvl("left", "排序");
dict.insert(kvl);
dict.insert(pair<string, string>("left", "左边"));
dict.insert(make_pair("pair", "左边"));
//C++11
dict.insert({ "right", "左边" });
dict.insert({{ "string", "字符串" }, { "map","地图、映射" }});
return 0;
}因为C++98的写法太麻烦,并且效率低
但是下面的C++11的写法,效率高不麻烦
所以建议去使用C++11的写法
那么我们应该怎么去读取呢?
cpp
map<int,int>::iterator it = m.begin();
while(it != m.end())
{
cout<<*it<<" ";//这里编译不过,这里如果这样的话需要返回两个值key和value,而C++不支持返回两个值,要返回两个值就需要构成一个结构来返回
++it;
}*cout<<it<<endl;这里编译不过,这里如果这样的话需要返回两个值key和value,而C++不支持返回两个值,要返回两个值就需要构成一个结构来返回
cpp
int main()
{
map<string, string> dict;
//C++98
pair<string, string>kvl("left", "排序");
dict.insert(kvl);
dict.insert(pair<string, string>("left", "左边"));
dict.insert(make_pair("pair", "左边"));
//C++11
dict.insert({ "right", "左边" });
dict.insert({{ "string", "字符串" }, { "map","地图、映射" }});
auto e = dict.begin();
while (e != dict.end())
{
//cout<<(*it).first << ":" << (*it).second << endl;
//operator* 返回的是节点中值的引用
cout << e->first << ":" << e->second << endl;//这里为了可读性省略了一个箭头
//operator-> 返回的是节点中值的指针,也就是pair<k,v>*
++e;
}
return 0;
}
也支持我们的for循环遍历
cpp
for (auto e : dict)
{
cout << e.first << ":" << e.second << endl;
}统计字符串的个数
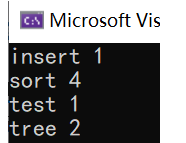
cpp
void test_map3()
{
string str[] = {"sort","sort","tree","insert","sort","tree","sort","test"};
map<string,int> countMap;//统计字符串个数
for(auto& e:str)
{
auto ret = countMap.fin1d(e);//返回一个迭代器
if(ret == countMap.end())
{
//如果不存在,则插入
countMap.insert(make_pair(e,1));
//countMap.insert(pair<>(e,1));
}
else
{
//如果存在,则次数++
//(*ret).second++;
ret->second++;
}
}
for(auto& kv:countMap)
{
cout<<kv.first<<" "<<kv.second<<endl;
}
}
统计次数的方式二:
正常来说如果insert插入成功了返回true,已经存在此时插入失败了返回false,但是我们可以看到insert的返回值是一个pair:
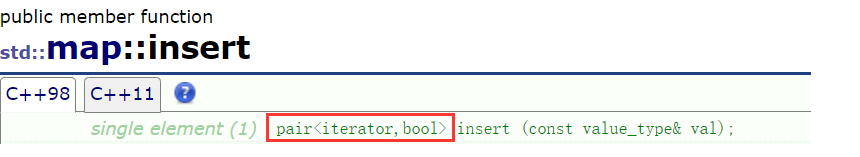
返回值是pair,其成员pair::first被设为一个迭代器,指向新插入的元素否则指向map中具有相等key的元素,如果插入了新元素,则将该对中的第二个元素pair::second设置为true;否则如果已经存在相等的key,则将其设置为false。
cpp
void test_map4()
{
string str[] = { "sort","sort","tree","insert","sort","tree","sort","test" };
map<string, int> countMap;
for (const auto& e : str)
{
//先插入,如果str在map中,insert会返回str所在的节点的迭代器,++次数即可
pair<map<string, int>::iterator, bool> ret = countMap.insert(make_pair(e, 1));
//auto ret = countMap.insert(make_pair(e, 1));
if (ret.second == false)
{
//说明插入失败了,之前已经插入过了
ret.first->second++;//ret.first是指向相同key的那个元素的迭代器,ret是insert返回的pair
}
}
map<string, int>::iterator it = countMap.begin();
while (it != countMap.end())
{
cout << it->first << " " << it->second << endl;
++it;
}
}
operator[]的使用
统计次数方式3

operator[]的实现;
cpp
mapped_type& operator[](const key_type& k)
{
return (*((this->insert(make_pair(k,mapped_type()))).first)).second;//插入时的匿名对象默认值为0
}operator[]的实现进行简化,也可以这样实现:
cpp
mapped_type& operator[](const key_type& k)
{
pair<iterator,bool> ret = insert(make_pair(k,mapped_type()));//插入时的匿名对象默认值为0
return ret.first->second;
}这里也分两种情况:
k在map中,insert插入失败,因为k已经有了,insert返回的pair会带出k在map中存储节点的迭代器,通过这个迭代器,我们可以拿到k对应的value值,进行返回。
k不在map中,insert进行插入,插入的值是pair<k,value()>,insert返回新插入值节点的迭代器,通过这个迭代器,我们可以拿到k对应的value值,进行返回。
总结map的operator[]特征:
k不存在时,插入默认构造函数生成缺省值的value的pair<k,v()>
k存在时,返回k对应的value值
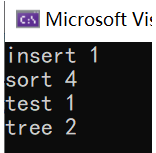
cpp
void test_map5()
{
string str[] = { "sort","sort","tree","insert","sort","tree","sort","test" };
map<string,int> countMap;
//[]的用法
for(const auto& e:str)
{
countMap[e]++;//countMap[]返回的是value
}
for(const auto& kv:countMap)
{
cout<<kv.first<<" "<<kv.second<<endl;
}
}
1、如果k不在map中,先插入<k,V()>,返回新插入节点中V对象的引用
2、如果k已经在map中,返回k所在节点中对应V对象的引用
cpp
void test_map6()
{
map<string,string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("sort","排序"));
dict["left"] = "左边";//插入+修改
dict["insert"];//插入
dict["insert"] = "插入";//已经存在所以只是修改
dict["left"] = "左边、剩余";//已经存在所以只是修改
}第一个是插入+修改,因为刚开始没有则插入,[]返回的是value,所以赋值相当于将他修改了,第二个只是插入,第三个只是修改,因为insert已经存在了就没有再插入只是修改,第四个也已经存在,所以只是修改
map和multimap的对比
关于map和multimap的区别:
- 允许键值冗余与否,map不允许键值冗余,multimap允许键值冗余
- multimap不支持[]
在multiset中查找一个值的实现:比如4,找到4以后,不能停止,要查找中序的第一个4,即找到4以后,要继续看4的左孩子是不是4,不是,就返回当前这个4,如果是,继续取左边的4,继续刚才的判断不断往后走
cpp
auto pos = s.find(4);//返回中序的第一个4
while(pos!=s.end() && *pos == 4)
{
//找出所有的4
cout<<*pos<<" ";
++pos;
}如果想看4有几个,有对应的接口
cpp
cout<<s.count(4)<<endl;
cout<<s.count(8 )<<endl;下面我们看一下map和multmap的区别:
cpp
void test_map8()
{
map<string,string> dict;
dict.insert(make_pair("left","左边"));
multimap<string,string> mdict;
mdict.insert(make_pair("left","左边"));
mdict.insert(make_pair("left","剩余"));
mdict.insert(make_pair("left","左边"));
}
multimap在value相同时也会插入