文章目录
- 前言
- [一、@Cacheable 是什么?](#一、@Cacheable 是什么?)
- [二、Springboot 项目中如何使用](#二、Springboot 项目中如何使用)
-
- [2.1 基于内存实现:](#2.1 基于内存实现:)
-
- [2.1.1 Cacheable 引入并使用:](#2.1.1 Cacheable 引入并使用:)
- [2.1.2 Cacheable 配置参数](#2.1.2 Cacheable 配置参数)
- [2.2 Cacheable 基于redis 缓存](#2.2 Cacheable 基于redis 缓存)
- [2.3 @Cacheable 注解属性](#2.3 @Cacheable 注解属性)
- 总结
前言
一、@Cacheable 是什么?
@Cacheable 是 Spring 缓存抽象的核心注解,作用是将方法的返回结果缓存起来:
- 当第一次调用该方法时,执行方法体并将返回值存入缓存;
- 后续使用「相同参数」调用时,直接从缓存获取结果,无需执行方法体;
- 本质是「方法级缓存」,基于「键值对」存储(键:方法名 + 参数;值:方法返回值);
- 适用场景:查询类方法(如根据 ID 查用户、查商品详情),数据变更频率低、查询频率高。
二、Springboot 项目中如何使用
2.1 基于内存实现:
2.1.1 Cacheable 引入并使用:
(1) 引入缓存依赖
在 pom.xml(Maven)中添加 Spring 缓存启动器(Gradle 同理):
xml
<!-- Spring Cache Starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Caffeine 缓存实现 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.github.ben-manes.caffeine</groupId>
<artifactId>caffeine</artifactId>
</dependency>(2)开启缓存功能
在 SpringBoot 启动类上添加 @EnableCaching 注解,全局开启缓存支持:
java
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.EnableCaching;
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching // 核心:开启缓存
public class CacheDemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(CacheDemoApplication.class, args);
}
}(3)在查询方法上添加 @Cacheable
在 Service/Controller 的查询方法上标注 @Cacheable,指定缓存名称(必填):
java
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class UserService {
// cacheNames:缓存名称(必填,相当于缓存的"命名空间")
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache")
public User getUserById(Long id) {
// 模拟数据库查询(首次调用执行,后续从缓存获取)
System.out.println("执行数据库查询,用户ID:" + id);
return new User(id, "张三", 20);
}
// 模拟用户实体类(需有 getter/setter,Lombok 可简化)
public static class User {
private Long id;
private String name;
private Integer age;
public User(Long id, String name, Integer age) {
this.id = id;
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// getter/setter 省略(实际开发用 @Data 注解)
public Long getId() { return id; }
public String getName() { return name; }
public Integer getAge() { return age; }
}
}(4) 更新缓存:
java
// 修改用户后更新缓存(key 需与 @Cacheable 一致)
@CachePut(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#user.studentId")
public StudentDto updateUser(StudentDto user) {
System.out.println("更新用户:" + user.getStudentId());
return user;
}(5) 删除缓存:
java
// 删除用户后清理缓存
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#id")
public void deleteUser(String id) {
System.out.println("删除用户:" + id);
}
// 清空整个 userCache 缓存
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "userCache", allEntries = true)
public void clearUserCache() {
System.out.println("清空用户缓存");
}2.1.2 Cacheable 配置参数
yaml
spring:
cache:
type: caffeine # 指定缓存类型为 Caffeine(替代默认的 ConcurrentHashMap/Redis)
caffeine:
spec: initialCapacity=100,maximumSize=1000,expireAfterWrite=10s # Caffeine 核心参数- initialCapacity:缓存初始容量(100):缓存初始化时的容器大小,避免频繁扩容导致性能损耗
- maximumSize:缓存最大容量(1000):缓存条目数超过 1000 时,会按 LRU 策略淘汰旧数据
- expireAfterWrite:写入后过期时间(10s):缓存条目创建 / 更新后,10 秒未访问则自动过期
2.2 Cacheable 基于redis 缓存
SpringBoot 默认使用「内存缓存(ConcurrentHashMap)」,重启后缓存丢失,此时可以切换为 Redis:
(1) 引入依赖:
xml
<!-- redis jar-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.13.5</version>
</dependency>(2)配置项:
yaml
spring:
cache:
type: redis
redis:
# 1. 全局过期时间(核心,替代 Caffeine 的 expireAfterWrite)
time-to-live: 1000s # 所有缓存默认 10 秒过期(支持 s/m/h/d)
# 3. 是否缓存空值(防止缓存穿透)
cache-null-values: true
# 4. 缓存 key 前缀(避免不同业务 key 冲突)
key-prefix: "cache:"
# 5. 是否使用前缀(建议开启)
use-key-prefix: true
data:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6379
timeout: 120000
database: 1
lettuce:
pool:
max-active: 50
max-idle: 8
max-wait: -1
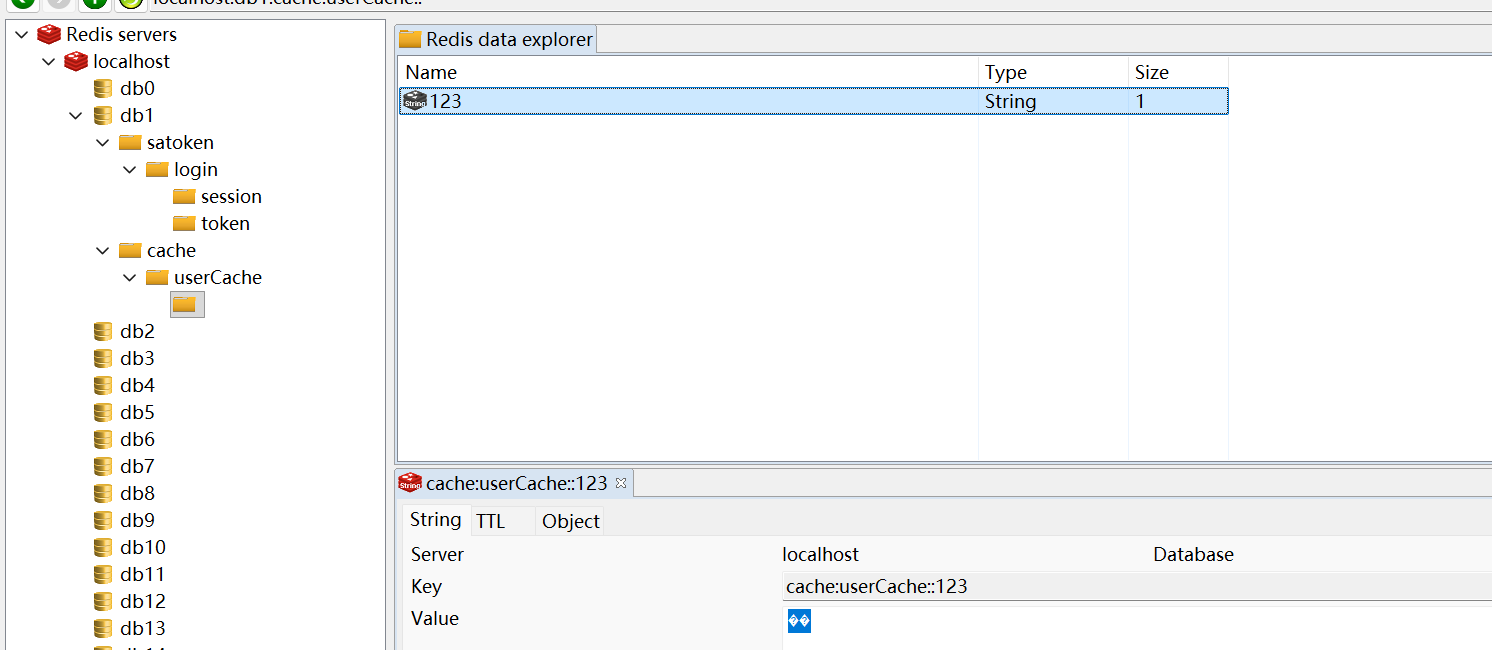
min-idle: 1(3) 测试结果:
java
@Override
// 使用缓存
@Cacheable(cacheNames ="userCache", key = "#root.args[0]")
public StudentDto getStudentById(String studentId) {
log.info("getStudentById:{}", studentId);
StudentDto dto = StudentDto.builder().studentId(studentId).studentAge(12)
.studentName("test").studentSex("man").build();
return dto;
}redids 缓存结果
2.3 @Cacheable 注解属性
(1) 注解属性:
java
@Target({ElementType.METHOD, ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Inherited
@Documented
public @interface Cacheable {
// 核心属性(按使用频率排序)
String[] value() default {}; // 等价于 cacheNames,缓存名称(必填)
String[] cacheNames() default {}; // 缓存名称(必填,和 value 二选一,推荐用这个)
String key() default ""; // 自定义缓存键(SpEL 表达式)
String keyGenerator() default ""; // 自定义键生成器(与 key 互斥)
String cacheManager() default ""; // 指定缓存管理器(多缓存源时用)
String cacheResolver() default ""; // 自定义缓存解析器(比 cacheManager 更灵活)
String condition() default ""; // 缓存条件(满足则缓存,SpEL)
String unless() default ""; // 排除条件(满足则不缓存,SpEL)
boolean sync() default false; // 是否同步缓存(解决缓存击穿)
}- cacheNames: 定义缓存的「命名空间」,区分不同业务的缓存(如用户缓存、订单缓存),必填属性;每个 cacheNames 对应一个独立的缓存容器(如 Caffeine 中的一个 Cache 实例、Redis 中的一个 key 前缀);不能省略,否则 Spring 会抛出「cacheNames/value 不能为空」异常。
- key(自定义缓存键,SpEL 表达式)自定义缓存的 key,替代默认的「方法名 + 所有参数组合」,灵活控制缓存粒度;默认规则:若不指定 key,Spring 会用 KeyGenerator 生成默认 key(格式:方法全限定名::参数1=值1,参数2=值2);可以使用SpEL 灵活定义缓存的key值
(2) redis key 生成策略:
| SpEL 表达式 | 含义 | 示例 |
|---|---|---|
| #参数名 | 引用方法参数 | key = "#id" |
| #参数.属性 | 引用参数对象的属性 | key = "#user.id" |
| #result | 引用方法返回值(仅 condition/unless 生效) | key = "#result.id"(不推荐) |
| #root | 根对象,包含方法 / 参数等信息 | key = "#root.methodName + #id" |
代码示例:
java
// 仅以 id 为键(忽略其他参数)
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#id")
public User getUserById(Long id, String unusedParam) { ... }
// 以参数对象的属性为键
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#user.id + '_' + #user.name")
public User getUserByUser(User user) { ... }
// 结合根对象:方法名 + 参数(避免不同方法的相同参数冲突)
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#root.methodName + '_' + #id")
public User getUserById(Long id) { ... }(3) 条件控制属性
condition(缓存条件,SpEL 表达式) 作用:仅当表达式结果为 true 时,才将方法结果存入缓存; 执行时机:方法执行后、存入缓存前
java
// 仅当 id > 0 时缓存(参数条件)
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#id", condition = "#id > 0")
public User getUserById(Long id) { ... }
// 仅当返回值 age > 18 时缓存(返回值条件)
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#id", condition = "#result.age > 18")
public User getUserById(Long id) { ... }
// 多条件组合(参数 id > 0 且返回值不为 null)
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#id", condition = "#id > 0 and #result != null")
public User getUserById(Long id) { ... }unless(排除缓存条件,SpEL 表达式)作用:与 condition 相反,当表达式结果为 true 时,不 缓存结果;执行时机:方法执行后、存入缓存前;核心场景:排除 null 值(避免缓存穿透)、排除异常结果等;
java
// 不缓存 null 值(解决缓存穿透)
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#id", unless = "#result == null")
public User getUserById(Long id) {
if (id == 999L) return null; // 不缓存
return new User(id, "张三", 20); // 缓存
}
// 不缓存 age <= 18 的用户
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#id", unless = "#result.age <= 18")
public User getUserById(Long id) { ... }(4)sync(同步缓存,解决缓存击穿)
作用:开启同步模式,当缓存未命中时,多个并发请求只会有一个请求执行方法体,其余请求等待缓存生成(解决热点 key 缓存击穿);默认值:false(非同步,多个请求同时执行方法体);
java
// 开启同步缓存,解决缓存击穿
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "userCache", key = "#id", sync = true)
public User getUserById(Long id) { ... }注意:
① sync=true 时,unless 属性失效(无法基于返回值排除缓存);
② 仅适用于本地缓存(Caffeine),分布式缓存(Redis)需结合分布式锁使用
总结
本文记录Springboot 缓存@Cacheable 的引入和使用。