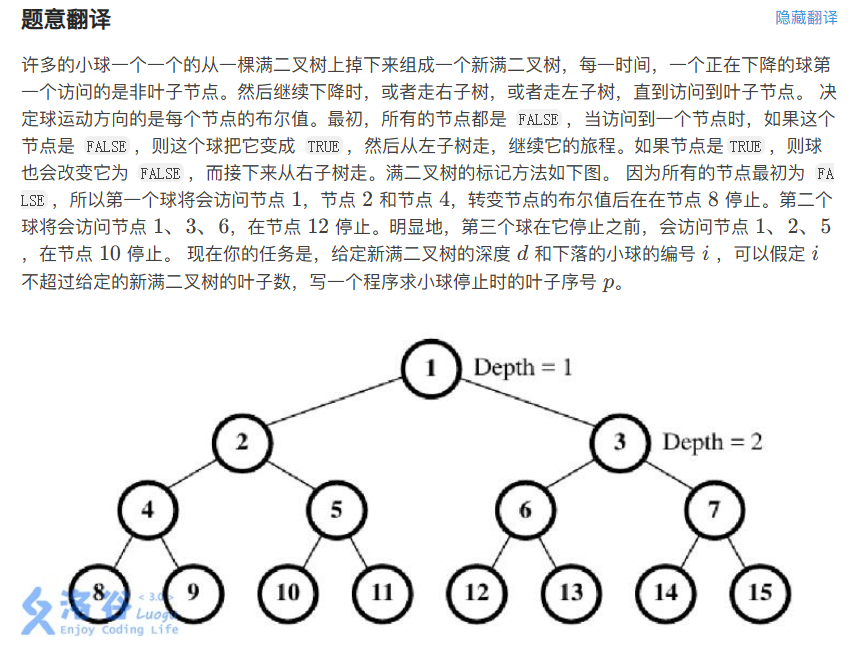
小球下落 Dropping Balls
-
每个节点有一个布尔开关
false或true,初始全为false。 -
小球从根节点(节点 1)开始下落。
-
经过一个节点时:
-
若当前节点为
false→ 小球把它变成true,然后走向左子树。 -
若当前节点为
true→ 小球把它变成false,然后走向右子树。
-
-
小球一直下落到叶子节点时停止。
输入:
给多组测试数据,每组给 dd 和 ii(小球编号)。
输出:小球最终停下的叶子节点的编号。
思路:我们需要求第 I 个小球最终停在哪一个叶子节点。我发现根节点的选择完全由小球编号 I 决定:I 为奇数时 → 走左的是第(I+1)/2个小球;I 为偶数时 → 走右的是第I/2个小球。因此我用cur表示当前所在的节点编号,i 表示当前节点看到的小球"局部编号"(到达当前节点的第几个小球)。
用for循环从深度 1 迭代到深度 d − 1 中的每一层:
如果 i 是奇数:小球走左:cur = cur * 2,更新局部编号:i = (i+1)/2
如果 i 是偶数:小球走右:cur = cur * 2 + 1,更新局部编号:i = i/2
循环结束后返回叶子节点编号
cpp
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int ball_stop(int d, int i) {
int cur = 1;
for (int k = 1; k < d; k++) {
if (i % 2 == 1) {
cur = cur * 2;
i = (i + 1) / 2;
} else {
cur = cur * 2 + 1;
i = i / 2;
}
}
return cur;
}
int main() {
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T--){
int d, i;
cin >> d;
if(d==-1) break;
cin >> i;
cout << ball_stop(d, i) << endl;
}
return 0;
}树的层次遍历 Trees on the level
Shuchong 给您一个二叉树,您的任务是写一个程序来输出依「阶层(level-order)」遍历的结果。在本问题中,二叉树的每个节点含有一个正整数,并且节点的数目在 [1,256] 的范围内。在「阶层」遍历中,依阶层从低到高,同阶层从左到右的次序来列印。
Shuchong:例如下面这个二叉树的阶层遍历结果就为: 5,4,8,11,13,4,7,2,1 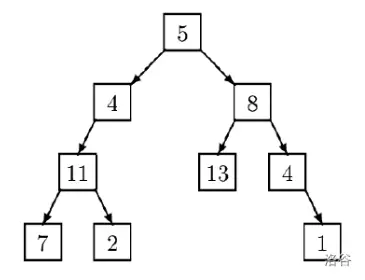
在本问题中,二叉树以节点来表示。每个节点以一个有序数对 (n,s) 来表示:
- n 代表此节点的值
- s 代表一个字符串,代表从根节点到达此节点的路径,其中
L代表左,R代表右
Shuchong:比如说上面那个值为 13 的节点用 (n,s) 的表示法就为 (13,RL),值为 2 的节点用 (n,s) 的表示法就为 (2,LLR),根节点 5 用 (n,s) 的表示法就为 (5,)。

看代码:
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main(){
string s;
while(cin >> s){
if(s == "()") continue;
vector<bool> has_value(1000,false);
vector<int> value;
map<int,int> nodes;//以图的方式存二叉树,nodes[1]为根
bool valid = true;
do{//存储每组数据
if(s == "()") break;
s = s.substr(1,s.length()-2);//去掉括号
int comma = s.find(',');
int val = stoi(s.substr(0,comma));//节点值
string path = s.substr(comma+1);//路径
int pos = 1;//计算此节点在满二叉树中的位置
for(char c:path){
if(c == 'L') pos = 2*pos;
else if(c == 'R') pos = 2*pos+1;
}
if(has_value[pos]) valid = false;//已经存过值
else {
has_value[pos] = true;
value.push_back(pos);
nodes[pos] = val;//位置为pos的结点值为val
}
}while(cin >> s);
if(!has_value[1]) valid = false;//没有根节点
for(auto & p : nodes){//遍历树
int pos = p.first;
if(pos > 1 && !has_value[pos/2]){
valid = false;//父节点不存在
break;
}
}
if(!valid) cout << "not complete" << endl;
else{//层次遍历
sort(value.begin(),value.end());//升序排序,确保按层输出
for(size_t i=0;i<value.size();i++){
if(i>0) cout << " ";
cout << nodes[value[i]];
}
cout << endl;
}
}
return 0;
} Spreadsheet Calculator 电子表格计算器
使用 DFS 标记 in_stack 来检测环。检测是否存在环,如果存在环,标记所有环中的单元格。后递归计算依赖项
cpp
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
struct Cell {
int val;
string expr;
bool is_num;
bool visited, in_stack, in_cycle;
vector<pair<int, int>> deps;
};
Cell sheet[20][20];
int n, m;
pair<int, int> parse(string s) {
int c = 0, i = 0;
while (isalpha(s[i])) {
c = c * 26 + (s[i] - 'A' + 1);
i++;
}
int r = stoi(s.substr(i));
return {r, c - 1};
}
bool dfs(int r, int c, bool mark) {
if (sheet[r][c].visited) return false;
if (sheet[r][c].in_stack) {
if (mark) sheet[r][c].in_cycle = true;
return true;
}
sheet[r][c].in_stack = true;
if (!sheet[r][c].is_num) {
for (auto& d : sheet[r][c].deps) {
if (dfs(d.first, d.second, mark)) {
if (mark) sheet[r][c].in_cycle = true;
sheet[r][c].in_stack = false;
return true;
}
}
}
sheet[r][c].in_stack = false;
sheet[r][c].visited = true;
return false;
}
int calc(int r, int c) {
if (sheet[r][c].is_num) return sheet[r][c].val;
stringstream ss(sheet[r][c].expr);
int res = 0, sign = 1;
string token;
while (ss >> token) {
if (token == "+") sign = 1;
else if (token == "-") sign = -1;
else {
int num;
if (isalpha(token[0])) {
auto p = parse(token);
num = calc(p.first, p.second);
} else {
num = stoi(token);
}
res += sign * num;
}
}
sheet[r][c].val = res;
sheet[r][c].is_num = true;
return res;
}
int main() {
bool first = true;
while (cin >> n >> m && n) {
if (!first) cout << endl;
first = false;
// 读取
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
string s;
cin >> s;
sheet[i][j].expr = s;
sheet[i][j].deps.clear();
sheet[i][j].visited = sheet[i][j].in_stack = sheet[i][j].in_cycle = false;
if (isdigit(s[0]) || (s[0] == '-' && isdigit(s[1]))) {
sheet[i][j].is_num = true;
sheet[i][j].val = stoi(s);
} else {
sheet[i][j].is_num = false;
// 解析依赖
for (int k = 0; k < s.length(); k++) {
if (isalpha(s[k])) {
int start = k;
while (k < s.length() && (isalpha(s[k]) || isdigit(s[k]))) k++;
auto p = parse(s.substr(start, k - start));
sheet[i][j].deps.push_back(p);
k--;
}
}
}
}
}
// 检测环
bool cycle = false;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!sheet[i][j].visited) {
if (dfs(i, j, false)) cycle = true;
}
}
}
if (cycle) {
// 重置并标记环中节点
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
sheet[i][j].visited = sheet[i][j].in_stack = sheet[i][j].in_cycle = false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!sheet[i][j].visited) {
dfs(i, j, true);
}
}
}
// 输出环中单元格
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (sheet[i][j].in_cycle) {
cout << char('A' + j) << i << ": " << sheet[i][j].expr << endl;
}
}
}
} else {
// 计算并输出
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
if (!sheet[i][j].is_num) {
calc(i, j);
}
}
}
// 输出表格
cout << " ";
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) cout << " " << j;
cout << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%5d:", i);
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
printf("%5d", sheet[i][j].val);
}
cout << endl;
}
}
}
return 0;
}