206.反转链表
这题想起来很简单,但写起来稍微难。
1.双链表思想
可以让cur=head,pre=null,让cur指向pre,之后再往后挪,但cur指向pre后就没法找到之前的第二个位置,所以要再设置一个tmp指向cur的下一个,之后再让cur的下一个指向pre。代码如下
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if(head==null||head.next==null)
return head;
ListNode cur=head;
ListNode pre=null;
while(cur!=null){
ListNode tmp=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
pre=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}2.使用递归
按照上面的思想,在cur为null时停止递归,并返回最终结果pre,其余就按上面的写,让tmp=cur.next,cur.next=pre,之后进入递归,因为递归函数为reverse(cur,pre),所以我们要写下一次递归的,下一次会让pre=cur,cur=tmp,所以写为reverse(tmp,cur)。代码如下
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
return reverse(head,null);
}
public ListNode reverse(ListNode cur,ListNode pre){
if(cur==null)
return pre;
ListNode tmp=cur.next;
cur.next=pre;
return reverse(tmp,cur);
}
}24.两两交换链表中的节点
这题细节很多,有一定难度。
例如有4个数字,我们要想交换1,2,就必须知道它们前面的那个节点,这样才好交换,因此,设计一个虚拟节点head1,让cur=head1,cur即为每个交换数字前的一个节点。
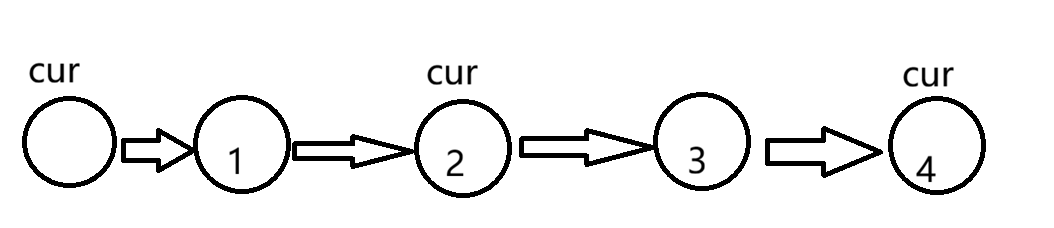
在循环时要注意cur.next!=null,但如果是奇数个格数,则cur.next.next!=null。
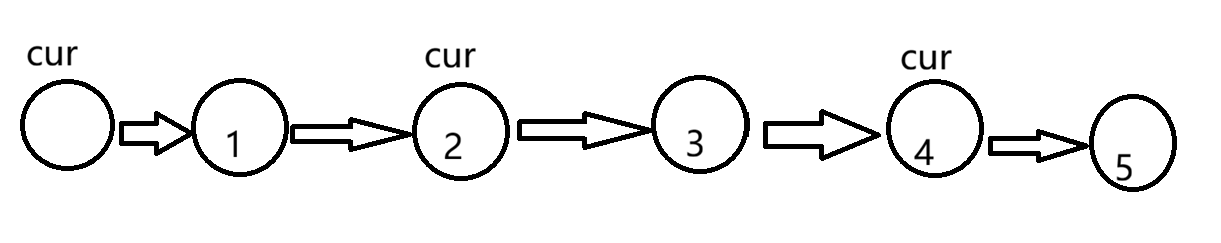
我们要让cur.next=cur.next.next
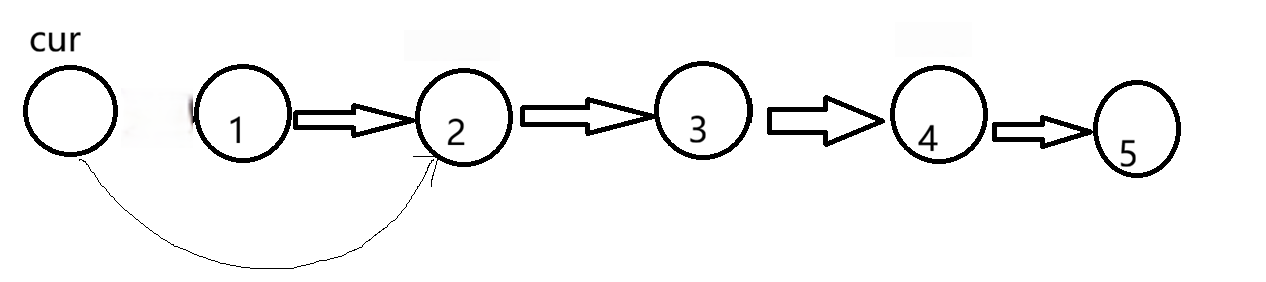
接着让2指向1,但此时无法获得1,因此在开始是就要设计一个tmp=cur.next,之后让cur.next=cur.next.next,这样我们就可以让cur.next.next=tmp
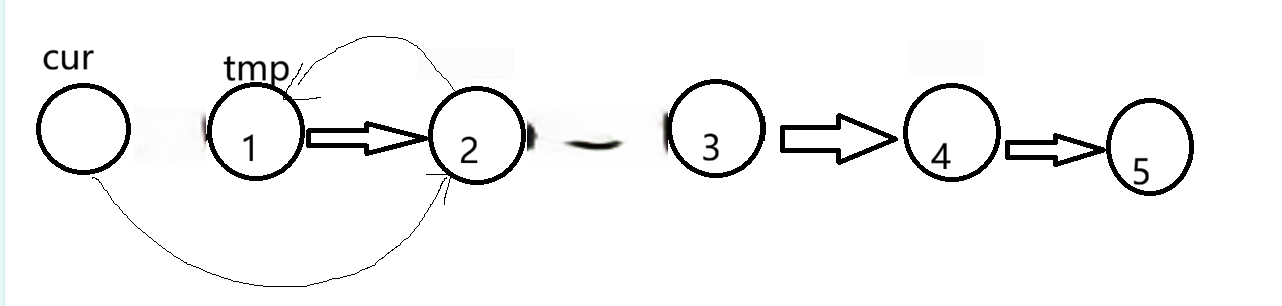
最后我们让1指向3就行,但此时我们又无法获得3的位置了,所以在一开始时要设计一个tmp1=cur.next.next.next,这样tmp1就指向3了,我们可以写tmp.next=tmp1。
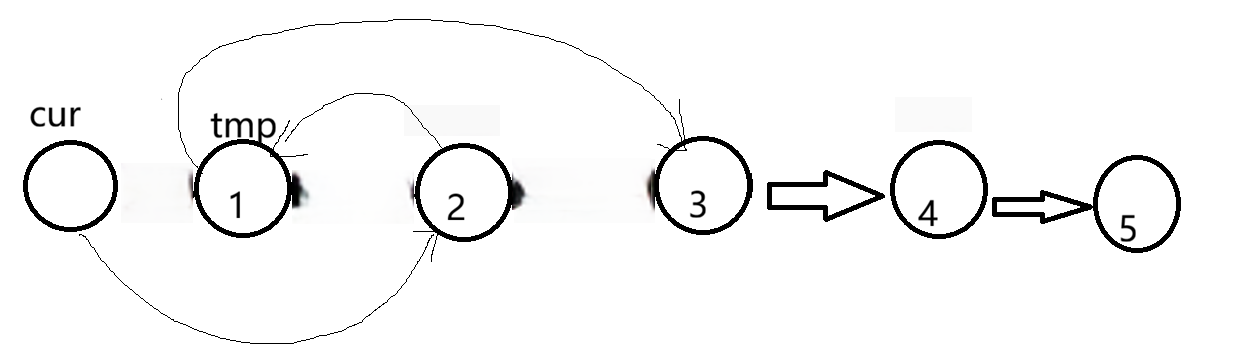
以后也如此,代码如下。
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode swapPairs(ListNode head) {
ListNode head1=new ListNode();
head1.next=head;
ListNode cur=head1;
while(cur.next!=null&&cur.next.next!=null){
ListNode tmp=cur.next;
ListNode tmp1=cur.next.next.next;
cur.next=cur.next.next;
cur.next.next=tmp;
tmp.next=tmp1;
cur=cur.next.next;
}
return head1.next;
}
}19. 删除链表的倒数第 N 个结点
通过前面的学习,这题很容易就能想到用双指针的做法,先让fast走n个,之后slow再走,但由于我们要删除第n个,所以要知道前面的那个节点,因此让slow少走一个即fast多走一个,这样slow最终停留的位置就是第n-1个。代码如下。
java
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode() {}
* ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; }
* ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode head1=new ListNode();
head1.next=head;
ListNode fast=head1;
ListNode slow=head1;
n++;
while(n!=0&&fast!=null){
fast=fast.next;
n--;
}
while(fast!=null){
fast=fast.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
slow.next=slow.next.next;
return head1.next;
}
}